731:
719:
523:), the subendocardial coronary vessels (the vessels that enter the myocardium) are compressed due to the high ventricular pressures. This compression results in momentary retrograde blood flow (i.e., blood flows backward toward the aorta) which further inhibits perfusion of myocardium during systole. However, the epicardial coronary vessels (the vessels that run along the outer surface of the heart) remain open. Because of this, blood flow in the subendocardium stops during ventricular contraction. As a result, most myocardial perfusion occurs during heart relaxation (
743:
40:
365:
160:
171:
376:, which lack function, as opposed to true anastomoses like that in the palm of the hand. This is because blockage of one coronary artery generally results in death of the heart tissue due to lack of sufficient blood supply from the other branch. When two arteries or their branches join, the area of the myocardium receives dual blood supply. These junctions are called anastomoses. If one coronary artery is obstructed by an
384:
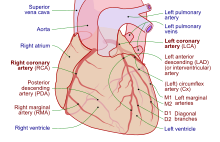
interventricular sulcus (groove). More superiorly, there is an anastomosis between the circumflex artery (a branch of the left coronary artery) and the right coronary artery in the atrioventricular groove. There is also an anastomosis between the septal branches of the two coronary arteries in the interventricular septum. The photograph shows area of heart supplied by the right and the left coronary arteries.
269:
476:) to the wall of the heart. If the papillary muscles are not functioning properly, the mitral valve may leak during contraction of the left ventricle. This causes some of the blood to travel "in reverse", from the left ventricle to the left atrium, instead of forward to the aorta and the rest of the body. This leaking of blood to the left atrium is known as
539:
or vasoconstriction of the coronary arteries based upon the oxygen requirements of the heart. This contributes to the filling difficulties of the coronary arteries. Compression remains the same. Failure of oxygen delivery caused by a decrease in blood flow in front of increased oxygen demand of the
259:
arise from the right coronary artery inferior to the right atrium. The marginal arteries supply blood to the superficial portions of the right ventricle. On the posterior surface of the heart, the right coronary artery gives rise to the posterior interventricular artery, also known as the posterior
392:
The left and right coronary arteries occasionally arise by a common trunk, or their number may be increased to three; the additional branch being the posterior coronary artery (which is smaller in size). In rare cases, a person will have the third coronary artery run around the root of the aorta.
383:
Under the most common configuration of coronary arteries, there are three areas of anastomoses. Small branches of the LAD (left anterior descending/anterior interventricular) branch of the left coronary join with branches of the posterior interventricular branch of the right coronary in the
434:
Approximately 70% of the general population are right-dominant, 20% are co-dominant, and 10% are left-dominant. A precise anatomic definition of dominance would be the artery which gives off supply to the AV node i.e. the AV nodal artery. Most of the time this is the right coronary artery.
236:. An anastomosis is an area where vessels unite to form interconnections that normally allow blood to circulate to a region even if there may be partial blockage in another branch. The anastomoses in the heart are very small. Therefore, this ability is somewhat restricted in the heart so a
122:, needs a steady supply of oxygenated blood that is free of all but the slightest interruptions, the heart is required to function continuously. Therefore its circulation is of major importance not only to its own tissues but to the entire body and even the
228:(LAD), is the second major branch arising from the left coronary artery. It follows the anterior interventricular sulcus around the pulmonary trunk. Along the way it gives rise to numerous smaller branches that interconnect with the branches of the
707:. The coronary arteries are classified as "terminal circulation", since they represent the only source of blood supply to the myocardium; there is very little redundant blood supply, that is why blockage of these vessels can be so critical.
527:) when the subendocardial coronary vessels are open and under lower pressure. Flow never comes to zero in the right coronary artery, since the right ventricular pressure is less than the diastolic blood pressure.
260:
descending artery. It runs along the posterior portion of the interventricular sulcus toward the apex of the heart, giving rise to branches that supply the interventricular septum and portions of both ventricles.
499:(insufficiency of oxygen-rich blood). On the other hand, the posteromedial papillary muscle is usually supplied only by the PDA. This makes the posteromedial papillary muscle significantly more susceptible to
380:, the second artery is still able to supply oxygenated blood to the myocardium. However, this can only occur if the atheroma progresses slowly, giving the anastomoses a chance to proliferate.
372:
There are some anastomoses between branches of the two coronary arteries. However the coronary arteries are functionally end arteries and so these meetings are referred to as potential
430:
If the posterior descending artery is supplied by both the right coronary artery and the circumflex artery, then the coronary circulation can be classified as "co-dominant."
555:
In addition to metabolism, the coronary circulation possesses unique pharmacologic characteristics. Prominent among these is its reactivity to adrenergic stimulation.
648:
642:
396:
Occasionally, a coronary artery will exist as a double structure (i.e. there are two arteries, parallel to each other, where ordinarily there would be one).
480:. Similarly, the leaking of blood from the right ventricle through the tricuspid valve and into the right atrium can also occur, and this is described as
209:, typically does not give rise to a vessel. Coronary vessel branches that remain on the surface of the heart and follow the sulci of the heart are called
181:
supply blood to the myocardium and other components of the heart. Two coronary arteries originate from the left side of the heart at the beginning (root)
919:
Voci P, Bilotta F, Caretta Q, Mercanti C, Marino B (1995). "Papillary muscle perfusion pattern. A hypothesis for ischemic papillary muscle dysfunction".
610:
604:
332:
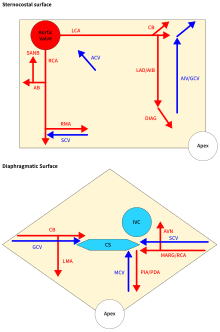
of the veins of the heart is very variable, but generally it is formed by the following veins: heart veins that go into the coronary sinus: the
256:
216:
The left coronary artery distributes blood to the left side of the heart, the left atrium and ventricle, and the interventricular septum. The
251:
The right coronary artery proceeds along the coronary sulcus and distributes blood to the right atrium, portions of both ventricles, and the
759:
688:
are healthy, they are capable of autoregulating themselves to maintain the coronary blood flow at levels appropriate to the needs of the
730:
718:
1413:
424:
217:
17:
1028:
742:
876:
837:
1089:
900:
229:
1084:
598:
349:
225:
118:
then drain away the blood after it has been deoxygenated. Because the rest of the body, and most especially the
626:
111:
1491:
1268:
1021:
806:
636:
552:. Chronic moderate ischemia causes contraction of the heart to weaken, known as myocardial hibernation.
409:
91:
224:
to the left. Eventually, it will fuse with the small branches of the right coronary artery. The larger
126:
of the brain from moment to moment. Interruptions of coronary circulation quickly cause heart attacks (
955:
427:(CX), a branch of the left artery, then the coronary circulation can be classified as "left-dominant."
1292:
189:(dilations) in the wall of the aorta just superior to the aortic semilunar valve. Two of these, the
1561:
827:
544:, a condition of oxygen deficiency. Brief ischemia is associated with intense chest pain, known as
488:
237:
58:
1272:
1185:
1153:
1141:
481:
405:
252:
202:
139:
1510:
1288:
1260:
1252:
1014:
590:
584:
578:
492:
353:
309:
305:
123:
70:
1433:
1338:
1306:
1180:
1099:
789:
704:
631:
620:
549:
504:
417:
241:
127:
563:
The following are the named branches of the coronary circulation in a right-dominant heart:
1428:
1364:
1284:
1256:
1203:
1104:
784:
572:
477:
198:
8:
1566:
1486:
1069:
337:
297:
1530:
1498:
1158:
1131:
1079:
980:
520:
341:
333:
301:
293:
1571:
1540:
1468:
1418:
1264:
1163:
1148:
1136:
1064:
1059:
985:
936:
896:
833:
681:
516:
496:
178:
163:
135:
131:
107:
352:. Heart veins that go directly to the right atrium: the anterior cardiac veins, the
47:
of the coronary circulation of the human heart viewed from the front and from behind
39:
1302:
1198:
1168:
975:
967:
928:
764:
548:. Severe ischemia can cause the heart muscle to die from hypoxia, such as during a
449:
1448:
1443:
1423:
1296:
1280:
1276:
1074:
859:
700:
696:
545:
473:
465:
221:
63:
971:
487:
The anterolateral papillary muscle more frequently receives two blood supplies:
1405:
1346:
1328:
1242:
1126:
774:
769:
461:
345:
325:
182:
103:
1555:
1438:
932:
1354:
1350:
1342:
1248:
989:
871:
665:
536:
469:
453:
420:(RCA), then the coronary circulation can be classified as "right-dominant."
321:
277:
206:
194:
190:
186:
44:
940:
27:
Circulation of blood in the blood vessels of the heart muscle (myocardium)
1478:
1460:
1395:
1387:
1334:
1238:
1228:
1175:
457:
373:
233:
807:
OpenStax
College, Anatomy & Physiology. OpenStax CNX. 30 July 2014.
1503:
1318:
1006:
779:
689:
677:
317:
76:
364:
159:
541:
524:
500:
377:
245:
143:
95:
272:
Base and diaphragmatic surface of heart showing some cardiac veins
170:
146:
from other causes like obstruction in blood flow through vessels.
890:
695:
The relatively narrow coronary arteries are commonly affected by
329:
954:
Algranati, Dotan; Kassab, Ghassan S; Lanir, Yoram (March 2010).
507:
involving the PDA is more likely to cause mitral regurgitation.
685:
669:
313:
324:. Most of the blood of the coronary veins returns through the
1360:
1038:
802:
673:
567:
285:
281:
119:
289:
99:
918:
268:
956:"Mechanisms of myocardium-coronary vessel interaction"
423:
If the posterior descending artery is supplied by the
416:
If the posterior descending artery is supplied by the
368:
Cast of coronary arteries (right = yellow, left = red)
220:
arises from the left coronary artery and follows the
953:
495:(LCX). It is therefore more frequently resistant to
404:
The artery that supplies the posterior third of the
166:
labeled in red text and other landmarks in blue text
312:. Cardiac veins carry blood with a poor level of
1553:
503:. The clinical significance of this is that a
443:
1022:
891:Fuster, V; Alexander RW; O'Rourke RA (2001).
760:Anomalous aortic origin of a coronary artery
399:
530:
134:. Such interruptions are usually caused by
130:), in which the heart muscle is damaged by
1029:
1015:
895:(10th ed.). McGraw-Hill. p. 53.
979:
821:
819:
817:
412:(PDA) determines the coronary dominance.
1036:
801:This article incorporates text from the
659:
363:
267:
169:
158:
886:
884:
14:
1554:
1289:moderator band/septomarginal trabecula
914:
912:
814:
736:Posterior view of coronary circulation
510:
1010:
825:
724:Anterior view of coronary circulation
205:, respectively. The third sinus, the
881:
710:
154:
909:
575:/ Left main coronary artery (LMCA)
248:supplied by the particular vessel.
24:
535:The heart regulates the amount of
115:
25:
1583:
748:Illustration of coronary arteries
230:posterior interventricular artery
741:
729:
717:
699:and can become blocked, causing
263:
38:
960:Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol
599:Left anterior descending artery
226:left anterior descending artery
947:
864:
853:
359:
13:
1:
795:
627:Atrioventricular nodal branch
280:that remove the deoxygenated
484:or tricuspid regurgitation.
387:
344:, the posterior vein of the
207:right posterior aortic sinus
149:
7:
1492:sternopericardial ligaments
1269:valve of inferior vena cava
972:10.1152/ajpheart.00925.2009
753:
637:Posterior descending artery
558:
444:Supply to papillary muscles
438:
410:posterior descending artery
191:left posterior aortic sinus
174:Schematic view of the heart
114:blood to the heart muscle.
10:
1588:
1090:posterior interventricular
515:During contraction of the
1523:
1504:epicardium/visceral layer
1477:
1459:
1404:
1386:
1379:
1317:
1293:crista supraventricularis
1227:
1220:
1194:
1122:
1115:
1085:anterior interventricular
1052:
1045:
826:Betts, J. Gordon (2013).
400:Coronary artery dominance
69:
57:
52:
37:
32:
18:Coronary artery dominance
933:10.1161/01.cir.91.6.1714
829:Anatomy & physiology
540:heart results in tissue
531:Changes in oxygen demand
489:left anterior descending
350:oblique vein of Marshall
255:. Normally, one or more
238:coronary artery blockage
1273:valve of coronary sinus
1186:atrioventricular septum
1154:interventricular septum
482:tricuspid insufficiency
468:(the valve between the
456:(the valve between the
406:interventricular septum
288:muscle are the cardiac
253:heart conduction system
203:right coronary arteries
140:coronary artery disease
1511:fold of left vena cava
1261:limbus of fossa ovalis
649:Posteriolateral artery
643:Posteriolateral artery
591:Obtuse marginal artery
585:Obtuse marginal artery
579:Left circumflex artery
493:left circumflex artery
369:
354:smallest cardiac veins
310:anterior cardiac veins
306:smallest cardiac veins
273:
175:
167:
128:myocardial infarctions
124:level of consciousness
71:Anatomical terminology
1307:pulmonary circulation
790:Right coronary artery
660:Clinical significance
632:Right marginal artery
621:Right coronary artery
550:myocardial infarction
505:myocardial infarction
491:(LAD) artery and the
418:right coronary artery
367:
271:
242:myocardial infarction
195:anterior aortic sinus
173:
162:
1536:Coronary circulation
1365:systemic circulation
1204:intervenous tubercle
860:www.radiopaedia.org/
832:. pp. 787–846.
785:Left coronary artery
573:Left coronary artery
478:mitral regurgitation
292:. These include the
92:circulation of blood
88:Coronary circulation
33:Coronary circulation
1487:fibrous pericardium
511:Changes in diastole
356:(Thebesian veins).
338:middle cardiac vein
298:middle cardiac vein
213:coronary arteries.
197:, give rise to the
142:, and sometimes to
1531:Circulatory system
1499:serous pericardium
1461:Pericardial cavity
1159:trabeculae carneae
1132:interatrial septum
370:
342:small cardiac vein
334:great cardiac vein
302:small cardiac vein
294:great cardiac vein
274:
246:death of the cells
185:. There are three
176:
168:
1549:
1548:
1541:Coronary arteries
1519:
1518:
1469:pericardial sinus
1429:Bachmann's bundle
1419:cardiac pacemaker
1414:Conduction system
1375:
1374:
1265:crista terminalis
1216:
1215:
1212:
1211:
1164:chordae tendineae
1137:pectinate muscles
893:Hurst's The Heart
711:Additional images
682:coronary arteries
497:coronary ischemia
450:papillary muscles
425:circumflex artery
257:marginal arteries
240:often results in
218:circumflex artery
179:Coronary arteries
164:Coronary arteries
155:Coronary arteries
136:coronary ischemia
132:oxygen starvation
108:Coronary arteries
85:
84:
80:
16:(Redirected from
1579:
1384:
1383:
1339:atrial appendage
1303:pulmonary artery
1253:atrial appendage
1225:
1224:
1199:cardiac skeleton
1169:papillary muscle
1120:
1119:
1050:
1049:
1031:
1024:
1017:
1008:
1007:
1001:
1000:
998:
996:
983:
951:
945:
944:
927:(6): 1714–1718.
916:
907:
906:
888:
879:
868:
862:
857:
851:
850:
848:
846:
823:
765:Cardiac skeleton
745:
733:
721:
102:that supply the
77:edit on Wikidata
74:
42:
30:
29:
21:
1587:
1586:
1582:
1581:
1580:
1578:
1577:
1576:
1562:Cardiac anatomy
1552:
1551:
1550:
1545:
1515:
1473:
1455:
1449:Purkinje fibers
1444:bundle branches
1400:
1371:
1329:pulmonary veins
1313:
1297:pulmonary valve
1281:right ventricle
1277:tricuspid valve
1208:
1190:
1142:terminal sulcus
1111:
1041:
1037:Anatomy of the
1035:
1005:
1004:
994:
992:
966:(3): H861–873.
952:
948:
917:
910:
903:
889:
882:
869:
865:
858:
854:
844:
842:
840:
824:
815:
798:
756:
749:
746:
737:
734:
725:
722:
713:
697:atherosclerosis
662:
611:Diagonal artery
605:Diagonal artery
561:
533:
513:
474:right ventricle
466:tricuspid valve
446:
441:
402:
390:
362:
266:
222:coronary sulcus
157:
152:
81:
48:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1585:
1575:
1574:
1569:
1564:
1547:
1546:
1544:
1543:
1538:
1533:
1527:
1525:
1521:
1520:
1517:
1516:
1514:
1513:
1508:
1507:
1506:
1496:
1495:
1494:
1483:
1481:
1475:
1474:
1472:
1471:
1465:
1463:
1457:
1456:
1454:
1453:
1452:
1451:
1446:
1441:
1436:
1431:
1426:
1421:
1410:
1408:
1402:
1401:
1399:
1398:
1392:
1390:
1381:
1377:
1376:
1373:
1372:
1370:
1369:
1347:left ventricle
1323:
1321:
1315:
1314:
1312:
1311:
1243:coronary sinus
1233:
1231:
1222:
1218:
1217:
1214:
1213:
1210:
1209:
1207:
1206:
1201:
1195:
1192:
1191:
1189:
1188:
1183:
1178:
1173:
1172:
1171:
1166:
1161:
1156:
1146:
1145:
1144:
1139:
1134:
1123:
1117:
1113:
1112:
1110:
1109:
1108:
1107:
1102:
1094:
1093:
1092:
1087:
1082:
1077:
1067:
1062:
1056:
1054:
1047:
1043:
1042:
1034:
1033:
1026:
1019:
1011:
1003:
1002:
946:
908:
901:
880:
863:
852:
839:978-1938168130
838:
812:
811:
797:
794:
793:
792:
787:
782:
777:
775:Coronary steal
772:
770:Coronary sinus
767:
762:
755:
752:
751:
750:
747:
740:
738:
735:
728:
726:
723:
716:
712:
709:
661:
658:
657:
656:
655:
654:
653:
652:
646:
640:
634:
629:
618:
617:
616:
615:
614:
608:
596:
595:
594:
588:
560:
557:
532:
529:
512:
509:
462:left ventricle
445:
442:
440:
437:
432:
431:
428:
421:
401:
398:
389:
386:
361:
358:
346:left ventricle
326:coronary sinus
265:
262:
187:aortic sinuses
183:left ventricle
156:
153:
151:
148:
106:(myocardium).
83:
82:
73:
67:
66:
61:
55:
54:
50:
49:
43:
35:
34:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1584:
1573:
1570:
1568:
1565:
1563:
1560:
1559:
1557:
1542:
1539:
1537:
1534:
1532:
1529:
1528:
1526:
1522:
1512:
1509:
1505:
1502:
1501:
1500:
1497:
1493:
1490:
1489:
1488:
1485:
1484:
1482:
1480:
1476:
1470:
1467:
1466:
1464:
1462:
1458:
1450:
1447:
1445:
1442:
1440:
1439:bundle of His
1437:
1435:
1432:
1430:
1427:
1425:
1422:
1420:
1417:
1416:
1415:
1412:
1411:
1409:
1407:
1403:
1397:
1394:
1393:
1391:
1389:
1385:
1382:
1378:
1368:
1366:
1362:
1356:
1352:
1348:
1344:
1340:
1336:
1332:
1330:
1325:
1324:
1322:
1320:
1316:
1310:
1308:
1304:
1298:
1294:
1290:
1286:
1282:
1278:
1274:
1270:
1266:
1262:
1258:
1254:
1250:
1246:
1244:
1240:
1235:
1234:
1232:
1230:
1226:
1223:
1219:
1205:
1202:
1200:
1197:
1196:
1193:
1187:
1184:
1182:
1179:
1177:
1174:
1170:
1167:
1165:
1162:
1160:
1157:
1155:
1152:
1151:
1150:
1147:
1143:
1140:
1138:
1135:
1133:
1130:
1129:
1128:
1125:
1124:
1121:
1118:
1114:
1106:
1103:
1101:
1098:
1097:
1095:
1091:
1088:
1086:
1083:
1081:
1078:
1076:
1073:
1072:
1071:
1068:
1066:
1063:
1061:
1058:
1057:
1055:
1051:
1048:
1044:
1040:
1032:
1027:
1025:
1020:
1018:
1013:
1012:
1009:
991:
987:
982:
977:
973:
969:
965:
961:
957:
950:
942:
938:
934:
930:
926:
922:
915:
913:
904:
902:0-07-135694-0
898:
894:
887:
885:
878:
874:
873:
867:
861:
856:
841:
835:
831:
830:
822:
820:
818:
813:
810:
809:
808:
804:
791:
788:
786:
783:
781:
778:
776:
773:
771:
768:
766:
763:
761:
758:
757:
744:
739:
732:
727:
720:
715:
714:
708:
706:
702:
698:
693:
691:
687:
683:
679:
675:
671:
668:that deliver
667:
650:
647:
644:
641:
638:
635:
633:
630:
628:
625:
624:
622:
619:
612:
609:
606:
603:
602:
600:
597:
592:
589:
586:
583:
582:
580:
577:
576:
574:
571:
570:
569:
566:
565:
564:
556:
553:
551:
547:
543:
538:
528:
526:
522:
518:
508:
506:
502:
498:
494:
490:
485:
483:
479:
475:
471:
467:
463:
459:
455:
451:
436:
429:
426:
422:
419:
415:
414:
413:
411:
407:
397:
394:
385:
381:
379:
375:
366:
357:
355:
351:
347:
343:
339:
335:
331:
327:
323:
319:
315:
311:
307:
303:
299:
295:
291:
287:
283:
279:
270:
264:Cardiac veins
261:
258:
254:
249:
247:
243:
239:
235:
231:
227:
223:
219:
214:
212:
208:
204:
200:
196:
192:
188:
184:
180:
172:
165:
161:
147:
145:
141:
137:
133:
129:
125:
121:
117:
116:Cardiac veins
113:
109:
105:
101:
97:
93:
89:
78:
72:
68:
65:
62:
60:
56:
51:
46:
45:Blood vessels
41:
36:
31:
19:
1535:
1524:Blood supply
1396:heart valves
1358:
1355:aortic sinus
1351:aortic valve
1343:mitral valve
1326:
1300:
1285:infundibulum
1257:fossa ovalis
1249:right atrium
1236:
993:. Retrieved
963:
959:
949:
924:
920:
892:
870:
866:
855:
843:. Retrieved
828:
800:
799:
705:heart attack
694:
690:heart muscle
663:
562:
554:
537:vasodilation
534:
519:myocardium (
514:
486:
470:right atrium
454:mitral valve
447:
433:
403:
395:
391:
382:
371:
322:right atrium
275:
250:
215:
210:
177:
104:heart muscle
87:
86:
1479:Pericardium
1388:Endocardium
1335:left atrium
1239:venae cavae
1229:Right heart
1080:interatrial
921:Circulation
684:. When the
517:ventricular
458:left atrium
452:attach the
374:anastomoses
360:Anastomoses
316:, from the
234:anastomoses
53:Identifiers
1567:Cardiology
1556:Categories
1406:Myocardium
1319:Left heart
1149:ventricles
796:References
780:Cardiology
678:myocardium
464:) and the
348:, and the
318:myocardium
308:, and the
232:, forming
211:epicardial
138:linked to
112:oxygenated
845:11 August
651:#2 (PL#2)
645:#1 (PL#1)
388:Variation
284:from the
150:Structure
1572:Arteries
1221:Chambers
1116:Internal
1096:borders
1075:coronary
990:19966048
754:See also
686:arteries
680:are the
593:#2 (OM2)
587:#1 (OM1)
559:Branches
542:ischemia
525:diastole
501:ischemia
472:and the
460:and the
439:Function
378:atheroma
244:causing
144:embolism
96:arteries
1434:AV node
1424:SA node
1053:Surface
1046:General
981:2838558
941:7882478
676:to the
666:vessels
521:systole
330:anatomy
320:to the
278:vessels
110:supply
94:in the
90:is the
64:D003326
1380:Layers
1295:), →
1176:valves
995:26 May
988:
978:
939:
899:
877:CHORUS
836:
805:book:
701:angina
672:-rich
670:oxygen
623:(RCA)
601:(LAD)
581:(LCX)
546:angina
408:– the
340:, the
336:, the
328:. The
314:oxygen
304:, the
300:, the
296:, the
1361:aorta
1341:) →
1181:cusps
1127:atria
1100:right
1070:sulci
1039:heart
872:00460
803:CC BY
703:or a
674:blood
639:(PDA)
568:Aorta
290:veins
286:heart
282:blood
120:brain
100:veins
75:[
1363:and
1357:) →
1305:and
1275:) →
1105:left
1065:apex
1060:base
997:2021
986:PMID
937:PMID
897:ISBN
847:2014
834:ISBN
664:The
448:The
276:The
201:and
199:left
193:and
98:and
59:MeSH
976:PMC
968:doi
964:298
929:doi
875:at
692:.
1558::
1349:→
1345:→
1333:→
1299:→
1291:,
1287:,
1279:→
1271:,
1267:,
1263:,
1259:,
1255:,
1247:→
1241:,
984:.
974:.
962:.
958:.
935:.
925:91
923:.
911:^
883:^
816:^
613:#2
607:#1
1367:)
1359:(
1353:(
1337:(
1331:)
1327:(
1309:)
1301:(
1283:(
1251:(
1245:)
1237:(
1030:e
1023:t
1016:v
999:.
970::
943:.
931::
905:.
849:.
79:]
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.