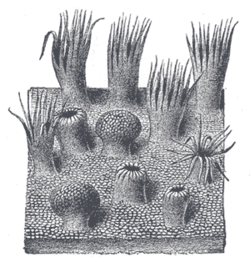
419:) are dome-shaped structures on the human tongue that vary in number from 8 to 12. They are situated on the surface of the tongue immediately in front of the foramen cecum and sulcus terminalis, forming a row on either side; the two rows run backward and medially, and meet in the midline. Each papillae consists of a projection of mucous membrane from 1 to 2 mm. wide, attached to the bottom of a circular depression of the mucous membrane; the margin of the depression is elevated to form a wall (vallum), and between this and the papilla is a circular sulcus termed the fossa. The papilla is shaped like a truncated cone, the smaller end being directed downward and attached to the tongue, the broader part or base projecting a little above the surface of the tongue and being studded with numerous small secondary papillae and covered by stratified
439:. The function of the secretion is presumed to flush materials from the base of circular depression to ensure that taste buds can respond to changing stimuli rapidly. The circumvallate papillae get special afferent taste innervation from cranial nerve IX, the glossopharyngeal nerve, even though they are anterior to the sulcus terminalis. The rest of the anterior two-thirds of the tongue gets taste innervation from the chorda tympani of cranial nerve VII, distributed with the lingual nerve of cranial nerve V.
867:
807:
831:
855:
843:
819:
40:
404:
336:
256:
44:
Anatomic landmarks of the tongue. Filiform papillae cover most of the dorsal surface of the anterior 2/3 of the tongue, with fungiform interspaced. Just in front of the sulcus terminalis lies a V-shaped line of circumvallate papillae, and on the posterior aspects of the lateral margins of the tongue
221:
are the most numerous of the lingual papillae. They are fine, small, cone-shaped papillae found on the anterior surface of the tongue. They are responsible for giving the tongue its texture and are responsible for the sensation of touch. Unlike the other kinds of papillae, filiform papillae do not
246:
These papillae have a whitish tint, owing to the thickness and density of their epithelium. This epithelium has undergone a peculiar modification as the cells have become cone–like and elongated into dense, overlapping, brush-like threads. They also contain a number of elastic fibers, which render
447:
Lingual papillae, particularly filiform papillae, are thought to increase the surface area of the tongue and to increase the area of contact and friction between the tongue and food. This may increase the tongue's ability to manipulate a bolus of food, and also to position food between the teeth
53:
189:
that give it its characteristic rough texture. The four types of papillae on the human tongue have different structures and are accordingly classified as circumvallate (or vallate), fungiform, filiform, and foliate. All except the filiform papillae are associated with
57:
Semidiagrammatic view of a portion of the mucous membrane of the tongue. Two fungiform papillae are shown. On some of the filiform papillae the epithelial prolongations stand erect, in one they are spread out, and in three they are folded
791:
Seven types of papillae are described in domestic mammals, with their presence and distribution being species-specific: -Mechanical papillae: filiform, conical, lentiform, marginal; -Taste papillae: fungiform, circumvallate, foliate
366:
and so are softer, and bear many taste buds. They are usually bilaterally symmetrical. Sometimes they appear small and inconspicuous, and at other times they are prominent. Because their location is a high risk site for
469:
In some diseases, there can be depapillation of the tongue, where the lingual papillae are lost, leaving a smooth, red and possibly sore area. Examples of depapillating oral conditions include
243:
which has fine secondary threads. Heavy keratinization of filiform papillae, occurring for instance in cats, gives the tongue a roughness that is characteristic of these animals.
211:
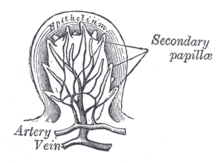
612:(rampart, wall), and means "having a raised edge surrounding a depression". This refers to the circular mucosal elevation which surrounds the circumvallate papillae.
150:
485:
is often used synonymously with depapillation. Where the entire dorsal surface of the tongue has lost its papillae, this is sometimes termed "bald tongue".
354:, There are four or five vertical folds, and their size and shape is variable. The foliate papillae appear as a series of red colored, leaf–like ridges of
202:
In living subjects, lingual papillae are more readily seen when the tongue is dry. There are four types of papillae present on the tongue in humans:
806:
346:
are short vertical folds and are present on each side of the tongue. They are located on the sides at the back of the tongue, just in front of the
247:
them firmer and more elastic than the other types of papillae. The larger and longer papillae of this group are sometimes termed papillae conicae.
866:
795:
Foliate papillae are fairly rudimentary structures in humans, representing evolutionary vestiges of similar structures in many other mammals.
114:
1142:
990:
1109:
1084:
1057:
225:
They appear as very small, conical or cylindrical surface projections, and are arranged in rows which lie parallel to the
387:, are scattered over the mucous membrane of their surface. Serous glands drain into the folds and clean the taste buds.
1320:
954:
906:
1032:
854:
842:
769:
714:
656:
598:
517:
17:
1350:
1135:
1302:
145:
1272:
516:
the foliate papillae appear swollen. This may occur due to mechanical irritation, or as a reaction to an
818:
226:
138:
1371:
1128:
474:
133:
1267:
1230:
486:
308:
157:
121:
109:
976:
1074:
945:
Susan
Standring (editor in chief)] (2008). "Chapter 33: NECK AND UPPER AERODIGESTIVE TRACT".
830:
304:
428:
407:
Circumvallate papilla in vertical section, showing arrangement of the taste-buds and nerves
376:
8:
420:
316:
271:, generally red in color. They are found on the tip of the tongue, scattered amongst the
964:
347:
1104:(7th, updated and extended ed.). Stuttgart ; New York: Georg Thieme Verlag.
1247:
1212:
1188:
1105:
1080:
1053:
1028:
950:
902:
470:
300:
272:
236:
222:
contain taste buds. They cover most of the front two-thirds of the tongue's surface.
1325:
1242:
1193:
1152:
737:
685:
621:
572:
380:
351:
320:
339:
Magnified diagram of a vertical section through some foliate papillae in a rabbit.
1376:
1183:
1178:
1173:
901:. illustrations by Netter FH. Philadelphia, Pa.: Saunders Elsevier. p. 402.
525:
424:
384:
102:
812:
The mouth. The cheeks have been slit transversely and the tongue pulled forward.
554:
543:
1220:
521:
388:
312:
288:
232:
1365:
126:
1277:
1225:
1025:
Oral and maxillofacial medicine : the basis of diagnosis and treatment
520:. Other sources state that foliate papilitis refers to inflammation of the
392:
1345:
505:
Papillitis refers to inflammation of the papillae, and sometimes the term
1235:
506:
449:
368:
355:
163:
494:
490:
453:
359:
240:
944:
435:
secretion into the base of the circular depression, which acts like a
1168:
1027:(3rd ed.). Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. pp. 401, 402.
478:
324:
292:
276:
275:
but are mostly present on the tip and sides of the tongue. They have
191:
371:, and their tendency to occasionally swell, they may be mistaken as
1312:
1294:
1282:
1120:
96:
1102:
Veterinary anatomy of domestic animals: textbook and colour atlas
872:
A picture showing filiform papillae taken using a USB microscope.
363:
39:
1160:
947:
Gray's anatomy : the anatomical basis of clinical practice
560:
432:
268:
229:. At the tip of the tongue, these rows become more transverse.
186:
72:
279:
on their upper surface which can distinguish the five tastes:
372:
296:
280:
84:
758:
645:
391:
are found immediately behind the foliate papillae and, when
27:
Structure giving the tongue its characteristic rough texture
1259:
1079:(7th ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences APAC. p. 34.
703:
700:
694:
587:
436:
403:
335:
284:
255:
210:
52:
636:
752:
746:
639:
630:
581:
783:(thread), and means "shaped like a filament or thread".
1072:
1052:. Baltimore, MD.: Lippincott, Williams, and Wilkins.
770:
755:
743:
715:
691:
657:
642:
633:
627:
599:
749:
706:
697:
590:
584:
578:
259:
Fungiform papillae, magnified and sectional diagram.
1047:
949:(40th ed.). : Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier.
761:
740:
688:
648:
624:
575:
185:) are small structures on the upper surface of the
1363:
940:
938:
676:, and means "shaped like a mushroom or fungus".
303:. The fungiform papillae are innervated by the
936:
934:
932:
930:
928:
926:
924:
922:
920:
918:
860:Floor of mouth. Deep dissection. Anterior view.
848:Floor of mouth. Deep dissection. Anterior view.
1099:
1136:
1073:Rajendran A; Sundaram S (10 February 2014).
1066:
1018:
1016:
1014:
1012:
1010:
915:
899:Netter's head and neck anatomy for dentistry
892:
890:
888:
886:
778:
723:
671:
665:
607:
552:
1143:
1129:
51:
38:
1007:
883:
728:(leafy), and means "shaped like a leaf".
500:
398:
1022:
896:
459:
402:
334:
254:
209:
497:may cause depapillation of the tongue.
14:
1364:
395:, cause a prominence of the papillae.
1124:
250:
178:
1150:
798:
205:
1076:Shafer's Textbook of Oral Pathology
824:Papillae and other tongue landmarks
481:. The term glossitis, particularly
330:
267:are club shaped projections on the
24:
1321:Posterior limb of internal capsule
25:
1388:
991:"Tongue | Gastrointestinal Tract"
518:upper respiratory tract infection
865:
853:
841:
829:
817:
805:
786:
736:
684:
620:
571:
464:
239:cores with a keratin–containing
235:, they are made up of irregular
547:is derived from the Latin word
1093:
1048:Ross, H R; Pawlina, W (2011).
1041:
983:
551:meaning "tongue" or "speech".
13:
1:
1303:Ventral posteromedial nucleus
877:
536:
307:, more specifically via the
214:Filiform papilla, magnified.
197:
7:
1273:Medial parabrachial nucleus
1050:Histology: A text and atlas
442:
10:
1393:
664:) is from the Latin words
531:
1351:Special visceral afferent
1338:
1311:
1293:
1258:
1211:
1204:
1159:
777:) is from the Latin word
722:) is from the Latin word
606:) is from the Latin word
509:is used interchangeably.
475:median rhomboid glossitis
156:
144:
132:
120:
108:
95:
83:
78:
68:
63:
50:
45:lie the foliate papillae.
37:
32:
559:is from Latin, meaning "
487:Nutritional deficiencies
358:. They are covered with
1268:Central tegmental tract
1100:König, Liebich (2020).
779:
724:
672:
666:
608:
553:
501:Papillitis/hypertrophy
413:circumvallate papillae
408:
399:Circumvallate papillae
340:
309:submandibular ganglion
299:. They have a core of
260:
215:
158:Anatomical terminology
460:Clinical significance
406:
338:
305:seventh cranial nerve
258:
213:
377:inflammatory disease
477:and other types of
423:. Ducts of lingual
421:squamous epithelium
317:geniculate ganglion
995:histologyguide.com
975:has generic name (
514:foliate papillitis
483:atrophic glossitis
429:Von Ebner's glands
409:
379:. Taste buds, the
348:palatoglossal arch
341:
265:fungiform papillae
261:
251:Fungiform papillae
216:
139:H3.04.01.0.03006
90:papillae linguales
1359:
1358:
1334:
1333:
1248:Gustatory nucleus
1189:Fungiform papilla
1111:978-3-13-242933-8
1086:978-81-312-3800-4
1059:978-0-7817-7200-6
1023:Scully C (2013).
897:Norton N (2007).
799:Additional images
471:geographic tongue
319:ascending to the
301:connective tissue
273:filiform papillae
237:connective tissue
227:sulcus terminalis
219:Filiform papillae
206:Filiform papillae
172:
171:
167:
18:Filiform papillae
16:(Redirected from
1384:
1372:Gustatory system
1326:Gustatory cortex
1243:Solitary nucleus
1209:
1208:
1194:Filiform papilla
1145:
1138:
1131:
1122:
1121:
1116:
1115:
1097:
1091:
1090:
1070:
1064:
1063:
1045:
1039:
1038:
1020:
1005:
1004:
1002:
1001:
987:
981:
980:
974:
970:
968:
960:
942:
913:
912:
894:
869:
857:
845:
836:Foliate papillae
833:
821:
809:
782:
773:
768:
767:
764:
763:
760:
757:
754:
751:
748:
745:
742:
727:
718:
713:
712:
709:
708:
705:
702:
699:
696:
693:
690:
675:
669:
660:
655:
654:
651:
650:
647:
644:
641:
638:
635:
632:
629:
626:
611:
602:
597:
596:
593:
592:
589:
586:
583:
580:
577:
558:
417:vallate papillae
344:Foliate papillae
331:Foliate papillae
321:solitary nucleus
180:
175:Lingual papillae
164:edit on Wikidata
161:
55:
42:
33:Lingual papillae
30:
29:
21:
1392:
1391:
1387:
1386:
1385:
1383:
1382:
1381:
1362:
1361:
1360:
1355:
1330:
1307:
1289:
1254:
1200:
1184:Foliate papilla
1179:Vallate papilla
1174:Lingual papilla
1155:
1149:
1119:
1112:
1098:
1094:
1087:
1071:
1067:
1060:
1046:
1042:
1035:
1021:
1008:
999:
997:
989:
988:
984:
972:
971:
962:
961:
957:
943:
916:
909:
895:
884:
880:
873:
870:
861:
858:
849:
846:
837:
834:
825:
822:
813:
810:
801:
789:
771:
739:
735:
716:
687:
683:
670:(mushroom) and
658:
623:
619:
600:
574:
570:
539:
534:
526:lymphoid tissue
503:
467:
462:
452:(chewing) and
445:
425:salivary glands
401:
389:Lingual tonsils
385:gustatory sense
333:
253:
208:
200:
168:
59:
46:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1390:
1380:
1379:
1374:
1357:
1356:
1354:
1353:
1348:
1342:
1340:
1336:
1335:
1332:
1331:
1329:
1328:
1323:
1317:
1315:
1309:
1308:
1306:
1305:
1299:
1297:
1291:
1290:
1288:
1287:
1286:
1285:
1280:
1270:
1264:
1262:
1256:
1255:
1253:
1252:
1251:
1250:
1240:
1239:
1238:
1233:
1228:
1221:Solitary tract
1217:
1215:
1206:
1202:
1201:
1199:
1198:
1197:
1196:
1191:
1186:
1181:
1171:
1165:
1163:
1157:
1156:
1148:
1147:
1140:
1133:
1125:
1118:
1117:
1110:
1092:
1085:
1065:
1058:
1040:
1033:
1006:
982:
956:978-0443066849
955:
914:
908:978-1929007882
907:
881:
879:
876:
875:
874:
871:
864:
862:
859:
852:
850:
847:
840:
838:
835:
828:
826:
823:
816:
814:
811:
804:
800:
797:
788:
785:
538:
535:
533:
530:
522:lingual tonsil
502:
499:
466:
463:
461:
458:
444:
441:
400:
397:
332:
329:
313:chorda tympani
252:
249:
233:Histologically
207:
204:
199:
196:
170:
169:
160:
154:
153:
148:
142:
141:
136:
130:
129:
124:
118:
117:
112:
106:
105:
100:
93:
92:
87:
81:
80:
76:
75:
70:
66:
65:
61:
60:
56:
48:
47:
43:
35:
34:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1389:
1378:
1375:
1373:
1370:
1369:
1367:
1352:
1349:
1347:
1344:
1343:
1341:
1337:
1327:
1324:
1322:
1319:
1318:
1316:
1314:
1310:
1304:
1301:
1300:
1298:
1296:
1292:
1284:
1281:
1279:
1276:
1275:
1274:
1271:
1269:
1266:
1265:
1263:
1261:
1257:
1249:
1246:
1245:
1244:
1241:
1237:
1234:
1232:
1229:
1227:
1224:
1223:
1222:
1219:
1218:
1216:
1214:
1210:
1207:
1203:
1195:
1192:
1190:
1187:
1185:
1182:
1180:
1177:
1176:
1175:
1172:
1170:
1167:
1166:
1164:
1162:
1158:
1154:
1146:
1141:
1139:
1134:
1132:
1127:
1126:
1123:
1113:
1107:
1103:
1096:
1088:
1082:
1078:
1077:
1069:
1061:
1055:
1051:
1044:
1036:
1034:9780702049484
1030:
1026:
1019:
1017:
1015:
1013:
1011:
996:
992:
986:
978:
966:
958:
952:
948:
941:
939:
937:
935:
933:
931:
929:
927:
925:
923:
921:
919:
910:
904:
900:
893:
891:
889:
887:
882:
868:
863:
856:
851:
844:
839:
832:
827:
820:
815:
808:
803:
802:
796:
793:
787:Other animals
784:
781:
776:
775:
766:
733:
729:
726:
721:
720:
711:
681:
677:
674:
668:
663:
662:
653:
617:
613:
610:
605:
604:
595:
568:
564:
562:
557:
556:
550:
546:
545:
529:
527:
523:
519:
515:
510:
508:
498:
496:
492:
488:
484:
480:
476:
472:
465:Depapillation
457:
455:
451:
440:
438:
434:
430:
426:
422:
418:
414:
405:
396:
394:
390:
386:
382:
378:
374:
370:
365:
361:
357:
353:
349:
345:
337:
328:
326:
322:
318:
314:
310:
306:
302:
298:
294:
290:
286:
282:
278:
274:
270:
266:
257:
248:
244:
242:
238:
234:
230:
228:
223:
220:
212:
203:
195:
193:
188:
184:
176:
165:
159:
155:
152:
149:
147:
143:
140:
137:
135:
131:
128:
125:
123:
119:
116:
113:
111:
107:
104:
101:
98:
94:
91:
88:
86:
82:
77:
74:
71:
67:
62:
54:
49:
41:
36:
31:
19:
1346:Basic tastes
1278:Hypothalamus
1101:
1095:
1075:
1068:
1049:
1043:
1024:
998:. Retrieved
994:
985:
946:
898:
794:
790:
734:(pronounced
731:
730:
682:(pronounced
679:
678:
618:(pronounced
615:
614:
569:(pronounced
566:
565:
548:
542:
540:
513:
511:
504:
482:
468:
446:
416:
412:
410:
393:hyperplastic
343:
342:
264:
262:
245:
231:
224:
218:
217:
201:
182:
174:
173:
115:A05.1.04.013
103:birnlex_4102
89:
1151:Anatomy of
973:|last=
524:, which is
507:hypertrophy
450:mastication
427:, known as
369:oral cancer
79:Identifiers
1366:Categories
1000:2023-02-19
878:References
495:B vitamins
491:folic acid
454:swallowing
360:epithelium
277:taste buds
241:epithelium
192:taste buds
1169:Taste bud
965:cite book
616:Fungiform
541:The term
537:Etymology
489:of iron,
479:glossitis
381:receptors
325:brainstem
198:Structure
1313:cerebrum
1295:thalamus
1283:Amygdala
732:Filiform
725:foliatus
661:-jif-orm
443:Function
431:empty a
97:NeuroLex
1213:medulla
774:-if-orm
719:-lee-ət
680:Foliate
567:Vallate
555:Papilla
544:lingual
532:History
448:during
383:of the
364:keratin
362:, lack
350:of the
323:in the
183:papilla
69:Part of
64:Details
1377:Tongue
1161:Tongue
1108:
1083:
1056:
1031:
953:
905:
667:fungus
609:vallum
561:nipple
549:lingua
493:, and
433:serous
373:tumors
356:mucosa
352:fauces
315:, and
295:, and
289:bitter
269:tongue
187:tongue
73:Tongue
1339:Other
1153:taste
780:filum
673:forma
297:umami
293:salty
281:sweet
162:[
151:54819
85:Latin
1260:pons
1205:Path
1106:ISBN
1081:ISBN
1054:ISBN
1029:ISBN
977:help
951:ISBN
903:ISBN
603:-ayt
437:moat
415:(or
411:The
285:sour
263:The
127:2837
110:TA98
1226:VII
772:FIL
759:ɔːr
717:FOH
659:FUN
646:ɔːr
601:VAL
563:".
512:In
375:or
179:sg.
146:FMA
122:TA2
58:in.
1368::
1231:IX
1009:^
993:.
969::
967:}}
963:{{
917:^
885:^
695:oʊ
637:dʒ
588:eɪ
528:.
473:,
456:.
327:.
311:,
291:,
287:,
283:,
194:.
181::
134:TH
99:ID
1236:X
1144:e
1137:t
1130:v
1114:.
1089:.
1062:.
1037:.
1003:.
979:)
959:.
911:.
765:/
762:m
756:f
753:ɪ
750:l
747:ɪ
744:f
741:ˈ
738:/
710:/
707:t
704:ə
701:i
698:l
692:f
689:ˈ
686:/
652:/
649:m
643:f
640:ɪ
634:n
631:ʌ
628:f
625:ˈ
622:/
594:/
591:t
585:l
582:æ
579:v
576:ˈ
573:/
177:(
166:]
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.