552:
other toward phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine. Glycerophospholipids are generally metabolized in several steps with different intermediates. The very first step in this metabolism involves the addition or transfer of the fatty acid chains to the glycerol backbone to form the first intermediate, lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). LPA then becomes acylated to form the next intermediate phosphatidic acid (PA). PA can be dephosphorylated leading to the formation of diacylglycerol which is essential in the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine (PC). PC is one of the many species of glycerophospholipids. In a pathway called the
Kennedy pathway, the polar heads are added to complete the formation of the entire structure consisting of the polar head regions, the two fatty acid chains and the phosphate group attached to the glycerol backbone. In this Kennedy pathway, Choline is converted to CDP-Choline which drives the transfer of the polar head groups to complete the formation of PC. PC can then be further converted to other species of glycerophospholipids such as phosphatidylserine (PS) and phosphatidylethanolamine (PE).
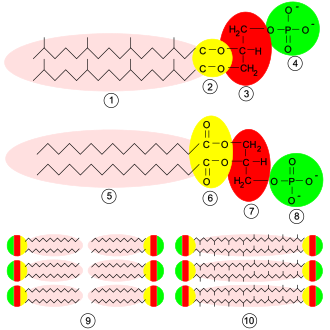
169:. The phosphate group forms an ester linkage to the glycerol. The long-chained hydrocarbons are typically attached through ester linkages in bacteria/eukaryotes and by ether linkages in archaea. In bacteria and procaryotes, the lipids consist of diesters commonly of C16 or C18 fatty acids. These acids are straight-chained and, especially for the C18 members, can be unsaturated. For archaea, the hydrocarbon chains have chain lengths of C10, C15, C20 etc. since they are derived from isoprene units. These chains are branched, with one methyl substituent per C5 subunit. These chains are linked to the glycerol phosphate by ether linkages. The two hydrocarbon chains attached to the glycerol are hydrophobic while the polar head, which mainly consists of the phosphate group attached to the third carbon of the glycerol backbone, is hydrophilic. This dual characteristic leads to the amphipathic nature of glycerophospholipids.
531:
plasmalogen. The main function of these classes of glycerophospholipids in the neural membranes is to provide stability, permeability and fluidity through specific alterations in their compositions. The glycerophospholipid composition of neural membranes greatly alters their functional efficacy. The length of glycerophospholipid acyl chain and the degree of saturation are important determinants of many membrane characteristics including the formation of lateral domains that are rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids. Receptor-mediated degradation of glycerophospholipids by phospholipases A(l), A(2), C, and D results in generation of second messengers, such as
359:. Cells will use this phosphatidylserine to enter cells via apoptotic mimicry. The structure of this lipid differs in plants and animals, regarding fatty acid composition. In addition, phosphatidylserine plays an important role in the human brain content, as it makes up 13–15% of the phospholipids in the human cerebral cortex. This lipid is found in a wide range of places. For example, in the human diet, about 130 mg are derived from phosphatidylserine. This has been said to have a positive impact on the brain, as it helps with reduced stress and improved memory.
502:. It is their specific distribution and catabolism that enables them carry out the biological response processes listed above. Their roles as storage centers for secondary messengers in the membrane is also a contributing factor to their ability to act as transporters. They also influence protein function. For example, they are important constituents of lipoproteins (soluble proteins that transport fat in the blood) hence affect their metabolism and function.
543:, modulation of activities of transporters, and membrane-bound enzymes. Marked alterations in neural membrane glycerophospholipid composition have been reported to occur in neurological disorders. These alterations result in changes in membrane fluidity and permeability. These processes along with the accumulation of lipid peroxides and compromised energy metabolism may be responsible for the neurodegeneration observed in neurological disorders.
20:
307:
phosphatidate. There is a negative charge on the phosphate and, in the case of choline or serine, a positive quaternary ammonium ion. (Serine also has a negative carboxylate group.) The presence of charges give a "head" with an overall charge. The phosphate ester portion ("head") is hydrophilic, whereas the remainder of the molecule, the fatty acid "tail", is hydrophobic. These are important components for the formation of lipid bilayers.
325:. Choline is the alcohol, with a positively charged quaternary ammonium, bound to the phosphate, with a negative charge. Lecithins are present in all living organisms. An egg yolk has a high concentration of lecithins, which are commercially important as an emulsifying agent in products such as mayonnaise. Lecithins are also present in brain and nerve tissue.
172:
They are usually organized into a bilayer in membranes with the polar hydrophilic heads sticking outwards to the aqueous environment and the non-polar hydrophobic tails pointing inwards. Glycerophospholipids consist of various diverse species which usually differ slightly in structure. The most basic
294:
are a type of phosphoglyceride. The first carbon of glycerol has a hydrocarbon chain attached via an ether, not ester, linkage. The linkages are more resistant to chemical attack than ester linkages are. The second (central) carbon atom has a fatty acid linked by an ester. The third carbon links to
551:
The metabolism of glycerophospholipids is different in eukaryotes, tumor cells, and prokaryotes. Synthesis in prokaryotes involves the synthesis of glycerophospholipids phosphatidic acid and polar head groups. Phosphatidic acid synthesis in eukaryotes is different, there are two routes, one to the
530:
Neural membranes contain several classes of glycerophospholipids which turnover at different rates with respect to their structure and localization in different cells and membranes. There are three major classes namely; 1-alkyl-2-acyl glycerophospholipid, 1,2-diacyl glycerophospholipid and
306:
are lipids in which the first two carbon atoms of the glycerol are fatty acid esters, and the 3 is a phosphate ester. The phosphate serves as a link to another alcohol-usually ethanolamine, choline, serine, or a carbohydrate. The identity of the alcohol determines the subcategory of the
398:. The glycolipids include phosphatidyl sugars where the alcohol functional group is part of a carbohydrate. Phosphatidyl sugars are present in plants and certain microorganisms. A carbohydrate is very hydrophilic due to the large number of hydroxyl groups present.
173:
structure is a phosphatidate. This species is an important intermediate in the synthesis of many phosphoglycerides. The presence of an additional group attached to the phosphate allows for many different phosphoglycerides.
497:
Apart from their function in cell membranes, they function in other cellular processes such as signal induction and transport. In regards to signaling, they provide the precursors for prostanglandins and other
416:
consists of two identifiable layers, or "leaflets", each of which is made up of an ordered row of glycerophospholipid molecules. The composition of each layer can vary widely depending on the type of cell.
176:
By convention, structures of these compounds show the 3 glycerol carbon atoms vertically with the phosphate attached to carbon atom number three (at the bottom). Plasmalogens and phosphatidates are examples.
411:
Glycerophospholipids are the main structural component of biological membranes. Their amphipathic nature drives the formation of the lipid bilayer structure of membranes. The cell membrane seen under the
1100:
Farooqui, AA; Horrocks, LA; Farooqui, T (June 2000). "Glycerophospholipids in brain: their metabolism, incorporation into membranes, functions, and involvement in neurological disorders".
997:"Scientific Opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to phosphatidyl serine (ID 552, 711, 734, 1632, 1927) pursuant to Article 13(1) of Regulation (EC) No 1924/2006 | EFSA"
825:
Ecker, Josef; Liebisch, Gerhard (April 2014). "Application of stable isotopes to investigate the metabolism of fatty acids, glycerophospholipid and sphingolipid species".
340:
in eukaryotic cell membranes and gives molecules a negative charge. Its importance relies in its role in activating sensory receptors that correlate with taste functions.
1136:
775:
Montealegre, Cristina; Verardo, Vito; Luisa Marina, María; Caboni, Maria
Fiorenza (March 2014). "Analysis of glycerophosphate- and sphingolipids by CE".
539:, platelet activating factor and diacylglycerol. Thus, neural membrane phospholipids are a reservoir for second messengers. They are also involved in
745:
378:
of nerve cell axons in animal cell membranes. Sphingomyelin can be found in eggs or bovine brain. This sphingolipid is synthesized at the
922:
1376:
1060:
Hermansson, Martin; Hokynar, Kati; Somerharju, Pentti (July 2011). "Mechanisms of glycerophospholipid homeostasis in mammalian cells".
576:
1158:
Dolce V, Cappello AR, Lappano R, Maggiolini M (November 2011). "Glycerophospholipid synthesis as a novel drug target against cancer".
295:
an ethanolamine or choline by means of a phosphate ester. These compounds are key components of the membranes of muscles and nerves.
1232:
141:
in a de novo pathway. The term glycerophospholipid signifies any derivative of glycerophosphoric acid that contains at least one
1366:
1358:
1350:
1144:
1337:
1332:
1327:
67:
40:
689:"Diversity and function of membrane glycerophospholipids generated by the remodeling pathway in mammalian cells"
117:, of which its composition affects membrane structure and properties. Two major classes are known: those for
646:
1225:
310:
Phosphatidylethanolamines, phosphatidylcholines, and other phospholipids are examples of phosphatidates.
1403:
1022:
1532:
1305:
862:"Thematic Review Series: Glycerolipids. Acyltransferases in bacterial glycerophospholipid synthesis"
1537:
1280:
1199:
440:
1195:
1527:
1218:
1479:
379:
1300:
1295:
515:
333:
138:
916:
Alfieri A, Imperlini E, Nigro E, Vitucci D, Orrù S, Daniele A, Buono P, Mancini A (2017).
8:
1285:
561:
455:
413:
318:
162:
106:
1461:
1290:
977:. Part I. Fatty Acid, Neutral Fats, Long-Chain Alcohols and Long-Chain Bases § Lip-1.13
946:
917:
888:
861:
800:
723:
688:
478:
chains. In the cell membrane, the two layers of phospholipids are arranged as follows:
444:
348:
202:
43:
1113:
1038:
1271:
1175:
1117:
1077:
1042:
996:
951:
893:
842:
804:
792:
728:
710:
669:
624:
616:
511:
471:
224:) of the glycero-molecule is determined intuitively by the residues on the positions
755:
1167:
1109:
1069:
1034:
941:
931:
918:"Effects of Plant Oil Interesterified Triacylglycerols on Lipemia and Human Health"
883:
873:
834:
784:
759:
750:
718:
700:
661:
608:
166:
110:
1073:
838:
687:
Hishikawa, Daisuke; Hashidate, Tomomi; Shimizu, Takao; Shindou, Hideo (May 2014).
665:
436:
383:
240:
186:
1205:
1171:
1497:
878:
596:
532:
490:
352:
194:
1521:
1441:
1046:
754:, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "
714:
620:
459:
375:
367:
303:
216:
The advantage of this particular notation is that the spatial configuration (
763:
1245:
1179:
1121:
1081:
955:
897:
846:
796:
788:
732:
673:
628:
571:
566:
493:
head groups are placed at the inner and outer surfaces of the cell membrane
463:
371:
102:
654:
Biochimica et
Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids
1432:
1418:
1398:
1389:
936:
612:
536:
499:
483:
475:
422:
395:
291:
1210:
705:
185:
In general, glycerophospholipids use an "sn" notation, which stands for
1502:
374:, which contains a backbone of sphingoid bases. It can be found in the
248:
540:
427:
356:
266:
position. Animal fats more often have saturated fatty acids in the 2-
122:
774:
1466:
1253:
322:
118:
98:
19:
970:
859:
205:. The numbering follows the one of Fischer's projections, being 1-
1492:
432:
337:
126:
686:
647:"Archaeal phospholipids: Structural properties and biosynthesis"
454:
side (the side on the exterior of the cell) consists mainly of
1157:
486:
tails point to each other and form a fatty, hydrophobic center
1241:
519:
154:
114:
915:
1059:
597:"Understanding the diversity of membrane lipid composition"
146:
518:
of one substance into another. This is sometimes used in
1099:
254:
Most vegetable oils have unsaturated fatty acids in the
968:
975:
470:
Each glycerophospholipid molecule consists of a small
394:
There are many other phospholipids, some of which are
180:
645:Caforio, Antonella; Driessen, Arnold J.M. (2017).
406:
258:-2 position, with saturated fatty acids in the 1-
82:, lipid bilayer of bacteria and eukaryotes;
1519:
644:
595:Harayama, Takeshi; Riezman, Howard (May 2018).
594:
54:, a bacterial or eukaryotic phospholipid:
971:"Nomenclature of Lipids, Recommendations 1976"
911:
909:
907:
193:appear in the nomenclature, by convention the
1226:
1095:
1093:
1091:
824:
1151:
820:
818:
816:
814:
386:with a larger concentration on the outside.
923:International Journal of Molecular Sciences
904:
860:Yong-Mei Zhang and Charles O. Rock (2008).
1233:
1219:
1088:
577:1,2-Dioleoyl-sn-glycerophosphoethanolamine
1240:
1198:at the U.S. National Library of Medicine
945:
935:
887:
877:
811:
722:
704:
640:
638:
525:
510:Glycerophospholipids can also act as an
505:
270:, with unsaturated fatty acids in the 1-
18:
1023:"Sphingomyelin breakdown and cell fate"
86:, lipid monolayer of some archaea.
1520:
1134:
635:
137:Glycerophospholipids are derived from
1214:
1020:
962:
601:Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology
1137:"Metabolism of glycerophospholipids"
197:of the second carbon of glycerol (2-
13:
751:Compendium of Chemical Terminology
336:makes up a small component of the
105:. They are the main component of
14:
1549:
1189:
27:, an archaeal phospholipid:
1135:Garcia, Christina (2011-06-30).
969:Moss G.P. (www version) (1976).
181:Nomenclature and stereochemistry
1128:
1102:Chemistry and Physics of Lipids
1053:
1014:
989:
247:-glycero-1-phosphoric acid are
1160:Current Molecular Pharmacology
1027:Trends in Biochemical Sciences
853:
768:
739:
680:
588:
407:Functions and use in membranes
1:
1114:10.1016/s0009-3084(00)00128-6
1074:10.1016/j.plipres.2011.02.004
1039:10.1016/S0968-0004(96)10056-6
1021:Testi, Roberto (1996-12-01).
839:10.1016/j.plipres.2014.01.002
582:
546:
522:making and ice-cream making.
132:
666:10.1016/j.bbalip.2016.12.006
209:the carbon at the top and 3-
189:numbering. When the letters
7:
1281:-ethanolamine/cephalin (PE)
1172:10.2174/1874467211104030167
555:
447:, and phosphatidylinositol.
281:
10:
1554:
1404:Platelet-activating factor
1062:Progress in Lipid Research
879:10.1194/jlr.R800005-JLR200
827:Progress in Lipid Research
431:side (the side facing the
125:and a separate family for
113:cells. They are a type of
58:, fatty acid chains;
1488:
1475:
1457:
1450:
1431:
1414:
1388:
1317:
1270:
1252:
693:Journal of Lipid Research
165:attached to the glycerol
1200:Medical Subject Headings
474:head group and two long
441:phosphatidylethanolamine
74:, phosphate group.
50:, phosphate group.
31:, isoprene chains;
764:10.1351/goldbook.G02648
401:
382:and is enriched at the
213:the one at the bottom.
62:, ester linkages;
35:, ether linkages;
1286:-choline/lecithin (PC)
789:10.1002/elps.201300534
421:For example, in human
201:) is on the left on a
87:
1480:Lysophosphatidic acid
1260:Glycerophospholipids/
526:Presence in the brain
506:Use in emulsification
380:endoplasmic reticulum
23:Membrane structures.
22:
1196:Glycerophospholipids
937:10.3390/ijms19010104
613:10.1038/nrm.2017.138
334:Phosphatidylinositol
329:Phosphatidylinositol
319:Phosphatidylcholines
314:Phosphatidylcholines
139:glycerol-3-phosphate
107:biological membranes
91:Glycerophospholipids
756:glycerophospholipid
706:10.1194/jlr.R046094
562:Biological membrane
456:phosphatidylcholine
439:consists mainly of
414:electron microscope
390:Other phospholipids
1462:Inositol phosphate
1318:Phosphoinositides:
1206:Diagram at uca.edu
1001:www.efsa.europa.eu
445:phosphatidylserine
349:Phosphatidylserine
344:Phosphatidylserine
203:Fischer projection
88:
1515:
1514:
1511:
1510:
1427:
1426:
1262:Phosphoglycerides
660:(11): 1325–1339.
512:emulsifying agent
450:By contrast, the
223:
219:
95:phosphoglycerides
1545:
1533:Membrane biology
1455:
1454:
1268:
1267:
1235:
1228:
1221:
1212:
1211:
1184:
1183:
1155:
1149:
1148:
1143:. Archived from
1132:
1126:
1125:
1097:
1086:
1085:
1057:
1051:
1050:
1018:
1012:
1011:
1009:
1008:
993:
987:
986:
984:
982:
966:
960:
959:
949:
939:
913:
902:
901:
891:
881:
872:(9): 1867–1874.
857:
851:
850:
822:
809:
808:
772:
766:
743:
737:
736:
726:
708:
684:
678:
677:
651:
642:
633:
632:
592:
351:is important in
221:
217:
1553:
1552:
1548:
1547:
1546:
1544:
1543:
1542:
1538:Glycerol esters
1518:
1517:
1516:
1507:
1484:
1471:
1446:
1423:
1410:
1384:
1380:
1370:
1362:
1354:
1347:
1313:
1261:
1257:
1248:
1239:
1192:
1187:
1156:
1152:
1133:
1129:
1098:
1089:
1058:
1054:
1033:(12): 468–471.
1019:
1015:
1006:
1004:
995:
994:
990:
980:
978:
967:
963:
914:
905:
858:
854:
823:
812:
777:Electrophoresis
773:
769:
744:
740:
685:
681:
649:
643:
636:
593:
589:
585:
558:
549:
528:
508:
437:plasma membrane
409:
404:
384:plasma membrane
355:, specifically
284:
241:phosphoric acid
183:
135:
17:
16:Class of lipids
12:
11:
5:
1551:
1541:
1540:
1535:
1530:
1513:
1512:
1509:
1508:
1506:
1505:
1500:
1498:Phosphocholine
1495:
1489:
1486:
1485:
1483:
1482:
1476:
1473:
1472:
1470:
1469:
1464:
1458:
1452:
1448:
1447:
1445:
1444:
1438:
1436:
1429:
1428:
1425:
1424:
1422:
1421:
1415:
1412:
1411:
1409:
1408:
1407:
1406:
1395:
1393:
1386:
1385:
1383:
1382:
1378:
1374:
1373:
1372:
1368:
1364:
1360:
1356:
1352:
1345:
1342:
1341:
1340:
1335:
1330:
1321:
1319:
1315:
1314:
1312:
1311:
1310:
1309:
1301:-inositol (PI)
1298:
1296:-glycerol (PG)
1293:
1288:
1283:
1277:
1275:
1265:
1250:
1249:
1238:
1237:
1230:
1223:
1215:
1209:
1208:
1203:
1191:
1190:External links
1188:
1186:
1185:
1166:(3): 167–175.
1150:
1147:on 2012-03-23.
1141:We Sapiens.org
1127:
1087:
1068:(3): 240–257.
1052:
1013:
988:
961:
903:
852:
810:
783:(6): 779–792.
767:
738:
699:(5): 799–807.
679:
634:
607:(5): 281–296.
586:
584:
581:
580:
579:
574:
569:
564:
557:
554:
548:
545:
533:prostaglandins
527:
524:
507:
504:
495:
494:
487:
468:
467:
448:
408:
405:
403:
400:
392:
391:
365:
364:
353:cell signaling
346:
345:
331:
330:
316:
315:
304:Phosphatidates
301:
300:
299:Phosphatidates
289:
288:
283:
280:
195:hydroxyl group
187:stereospecific
182:
179:
134:
131:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1550:
1539:
1536:
1534:
1531:
1529:
1528:Phospholipids
1526:
1525:
1523:
1504:
1501:
1499:
1496:
1494:
1491:
1490:
1487:
1481:
1478:
1477:
1474:
1468:
1465:
1463:
1460:
1459:
1456:
1453:
1449:
1443:
1442:Sphingomyelin
1440:
1439:
1437:
1434:
1430:
1420:
1417:
1416:
1413:
1405:
1402:
1401:
1400:
1397:
1396:
1394:
1391:
1387:
1381:
1375:
1371:
1365:
1363:
1357:
1355:
1349:
1348:
1343:
1339:
1336:
1334:
1331:
1329:
1326:
1325:
1323:
1322:
1320:
1316:
1307:
1304:
1303:
1302:
1299:
1297:
1294:
1292:
1289:
1287:
1284:
1282:
1279:
1278:
1276:
1273:
1272:Phosphatidyl-
1269:
1266:
1263:
1255:
1251:
1247:
1246:phospholipids
1243:
1236:
1231:
1229:
1224:
1222:
1217:
1216:
1213:
1207:
1204:
1201:
1197:
1194:
1193:
1181:
1177:
1173:
1169:
1165:
1161:
1154:
1146:
1142:
1138:
1131:
1123:
1119:
1115:
1111:
1107:
1103:
1096:
1094:
1092:
1083:
1079:
1075:
1071:
1067:
1063:
1056:
1048:
1044:
1040:
1036:
1032:
1028:
1024:
1017:
1002:
998:
992:
976:
972:
965:
957:
953:
948:
943:
938:
933:
929:
925:
924:
919:
912:
910:
908:
899:
895:
890:
885:
880:
875:
871:
867:
863:
856:
848:
844:
840:
836:
832:
828:
821:
819:
817:
815:
806:
802:
798:
794:
790:
786:
782:
778:
771:
765:
761:
757:
753:
752:
747:
742:
734:
730:
725:
720:
716:
712:
707:
702:
698:
694:
690:
683:
675:
671:
667:
663:
659:
655:
648:
641:
639:
630:
626:
622:
618:
614:
610:
606:
602:
598:
591:
587:
578:
575:
573:
570:
568:
565:
563:
560:
559:
553:
544:
542:
538:
534:
523:
521:
517:
513:
503:
501:
492:
488:
485:
481:
480:
479:
477:
473:
465:
461:
460:sphingomyelin
457:
453:
449:
446:
442:
438:
434:
430:
429:
424:
420:
419:
418:
415:
399:
397:
389:
388:
387:
385:
381:
377:
376:myelin sheath
373:
370:is a type of
369:
368:Sphingomyelin
363:Sphingomyelin
362:
361:
360:
358:
354:
350:
343:
342:
341:
339:
335:
328:
327:
326:
324:
320:
313:
312:
311:
308:
305:
298:
297:
296:
293:
286:
285:
279:
277:
273:
269:
265:
261:
257:
252:
250:
246:
242:
238:
233:
231:
227:
214:
212:
208:
204:
200:
196:
192:
188:
178:
174:
170:
168:
164:
161:-alk-1'-enyl
160:
156:
152:
148:
144:
140:
130:
128:
124:
120:
116:
112:
108:
104:
103:phospholipids
100:
96:
92:
85:
81:
77:
73:
69:
65:
61:
57:
53:
49:
45:
42:
38:
34:
30:
26:
21:
1390:Ether lipids
1291:-serine (PS)
1259:
1163:
1159:
1153:
1145:the original
1140:
1130:
1105:
1101:
1065:
1061:
1055:
1030:
1026:
1016:
1005:. Retrieved
1003:. 2010-10-19
1000:
991:
979:. Retrieved
974:
964:
927:
921:
869:
865:
855:
830:
826:
780:
776:
770:
749:
741:
696:
692:
682:
657:
653:
604:
600:
590:
572:Glycerolipid
567:Phospholipid
550:
529:
509:
500:leukotrienes
496:
469:
464:sphingolipid
462:, a type of
451:
426:
423:erythrocytes
410:
393:
372:sphingolipid
366:
347:
332:
317:
309:
302:
292:Plasmalogens
290:
287:Plasmalogens
275:
271:
267:
263:
259:
255:
253:
244:
236:
235:For example
234:
229:
225:
215:
210:
206:
198:
190:
184:
175:
171:
158:
150:
142:
136:
94:
90:
89:
83:
79:
75:
71:
63:
59:
55:
51:
47:
36:
32:
28:
24:
1451:Metabolites
1433:Sphingosine
1419:Cardiolipin
1399:Plasmalogen
1108:(1): 1–29.
930:(1): E104.
866:J Lipid Res
537:eicosanoids
514:to promote
484:hydrophobic
476:hydrophobic
396:glycolipids
249:enantiomers
239:-glycero-3-
1522:Categories
1503:Citicoline
1007:2023-11-29
583:References
547:Metabolism
452:exoplasmic
278:position.
133:Structures
123:eukaryotes
111:eukaryotic
68:D-glycerol
41:L-glycerol
1047:0968-0004
833:: 14–31.
805:205804071
715:0022-2275
621:1471-0080
541:apoptosis
516:dispersal
435:) of the
428:cytosolic
357:apoptosis
323:lecithins
274:and/or 3-
262:and/or 3-
1467:Inositol
1435:backbone
1367:PI(4,5)P
1359:PI(3,5)P
1351:PI(3,4)P
1256:backbone
1254:Glycerol
1180:21222647
1122:10878232
1082:21382416
956:29301208
898:18369234
847:24462586
797:24301713
733:24646950
674:28007654
629:29410529
556:See also
282:Examples
119:bacteria
99:glycerol
70:moiety;
1493:Choline
947:5796054
889:2515527
724:3995458
433:cytosol
338:cytosol
228:-1 and
163:residue
127:archaea
101:-based
66:,
39:,
1338:PI(5)P
1333:PI(4)P
1328:PI(3)P
1306:glyco-
1242:Lipids
1202:(MeSH)
1178:
1120:
1080:
1045:
981:27 Sep
954:
944:
896:
886:
845:
803:
795:
731:
721:
713:
672:
627:
619:
167:moiety
76:Bottom
52:Middle
44:moiety
1308:(GPI)
801:S2CID
746:IUPAC
650:(PDF)
520:candy
491:ionic
472:polar
157:, or
155:alkyl
149:, or
115:lipid
1324:PIP
1176:PMID
1118:PMID
1078:PMID
1043:ISSN
983:2023
952:PMID
894:PMID
843:PMID
793:PMID
729:PMID
711:ISSN
670:PMID
658:1862
625:PMID
617:ISSN
489:the
482:the
458:and
425:the
402:Uses
321:are
243:and
232:-3.
191:"sn"
147:acyl
121:and
97:are
1377:PIP
1344:PIP
1168:doi
1110:doi
1106:106
1070:doi
1035:doi
942:PMC
932:doi
884:PMC
874:doi
835:doi
785:doi
760:doi
758:".
719:PMC
701:doi
662:doi
609:doi
220:or
109:in
93:or
25:Top
1524::
1244::
1174:.
1162:.
1139:.
1116:.
1104:.
1090:^
1076:.
1066:50
1064:.
1041:.
1031:21
1029:.
1025:.
999:.
973:.
950:.
940:.
928:19
926:.
920:.
906:^
892:.
882:.
870:49
868:.
864:.
841:.
831:54
829:.
813:^
799:.
791:.
781:35
779:.
748:,
727:.
717:.
709:.
697:55
695:.
691:.
668:.
656:.
652:.
637:^
623:.
615:.
605:19
603:.
599:.
535:,
443:,
276:sn
272:sn
268:sn
264:sn
260:sn
256:sn
251:.
245:sn
237:sn
230:sn
226:sn
211:sn
207:sn
199:sn
129:.
84:10
78::
46:;
1392::
1379:3
1369:2
1361:2
1353:2
1346:2
1274::
1264:)
1258:(
1234:e
1227:t
1220:v
1182:.
1170::
1164:4
1124:.
1112::
1084:.
1072::
1049:.
1037::
1010:.
985:.
958:.
934::
900:.
876::
849:.
837::
807:.
787::
762::
735:.
703::
676:.
664::
631:.
611::
466:.
222:L
218:D
159:O
153:-
151:O
145:-
143:O
80:9
72:8
64:7
60:6
56:5
48:4
37:3
33:2
29:1
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.