32:
206:
Depending upon the treatment required, it is sometimes most appropriate to wait until later in life for a surgical remedy – the childhood growth of the face may highlight or increase the symptoms. When surgery is required, particularly when there is a severe disfiguration of the jaw, it is common to
115:
It can be thought of as a particularly severe form of HFM, in which extracranial anomalies are present to some extent. Some of the internal organs (especially the heart, kidneys, and lungs) may be underdeveloped, or in some cases even absent altogether. The affected organs are typically on the same
214:, or costochondral graft. The treatment is based on the type of severity for these patients. According to Pruzanksky's classification, if the patient has moderate to severe symptoms, then surgery is preferred. If patient has mild symptoms, then a functional appliance is generally used.
461:
446:
189:
Type II : The condyle and ramus are small, the head of the condyle is flattened, the glenoid fossa is absent, the condyle is hinged on a flat, often convex, infratemporal surface, the coronoid may be
119:
While there is no universally accepted grading scale, the OMENS scale (standing for
Orbital, Mandible, Ear, Nerves and Soft tissue) was developed to help describe the heterogeneous
116:
side as the affected facial features, but bilateral involvement occurs in approximately 10% of cases. Deformities of the vertebral column such as scoliosis may also be observed.
76:. It usually occurs on one side of the face, but both sides are sometimes affected. If severe, it may result in difficulties in breathing due to obstruction of the
221:, the goal of treatment in hemifacial microsomia is to elongate the deficient jaw bone to restore facial symmetry and correct the slanting bite (occlusion).
169:. This restricts the developmental ability of that area of the face. Currently there are no definitive reasons for the development of the condition.
100:
The clinical presentation of HFM is quite variable. The severity may depend on the extent of the area with an insufficient blood supply
210:
According to literature, HFM patients can be treated with various treatment options such as functional therapy with an appliance,
104:, and the gestational age of the fetus at which this occurs. In some people, the only physical manifestation may be a small and
476:
138:
84:. With an incidence in the range of 1:3500 to 1:4500, it is the second most common birth defect of the face, after
309:
Figueroa, AA; Pruzansky, S (1982). "The external ear, mandible and other components of hemifacial microsomia".
514:
423:
291:
344:
Hansen, PR (1999). "Orthodontic management of the patient undergoing mandibular distraction osteogenesis".
193:
Type III: The ramus is reduced to a thin lamina of bone or is completely absent. There is no evidence of a
154:
272:
109:
85:
72:
that affects the development of the lower half of the face, most commonly the ears, the mouth and the
225:
89:
399:
487:
211:
108:. In more severe cases, multiple parts of the face may be affected. Some people with HFM may have
519:
134:
379:
186:
Type I : Mild hypoplasia of the ramus, and the body of the mandible is slightly affected.
165:
to the face. This can be caused by physical trauma, though there is some evidence of it being
292:"TMJ Surgery in India | Hemifacial microsomia Treatment in India | TMJ Surgery Cost in India"
49:
8:
465:
262:
124:
69:
410:
267:
218:
470:
413:" at the Children's Hospital and Health System of Wisconsin. Accessed 20 January 2008.
357:
322:
361:
326:
137:
is not typically seen in people with HFM. Hemifacial microsomia sometimes results in
44:
353:
318:
31:
492:
508:
455:
182:
Figueroa and
Pruzanksky classified HFM patients into three different types:
365:
330:
158:
81:
438:
53:
120:
380:"Hemifacial Microsomia | Cosmetic Surgery in India | Balaji Dental"
166:
162:
128:
105:
73:
424:
GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on
Craniofacial Microsomia Overview
402:" at the Tennessee Craniofacial Center. Accessed 20 January 2008.
77:
481:
450:
150:
39:
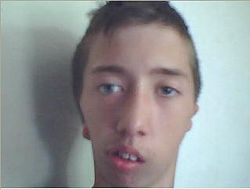
Bilateral (both sides) hemifacial microsomia in an adolescent
194:
384:
296:
16:
Birth defect which affects the lower half of the face
428:
236:
The condition is also known by various other names:
308:
217:According to Dr. Harry Pepe, a pediatrician from
506:
112:and decreased visual acuity or even blindness.
157:, when some form of vascular problem such as
302:
207:use a rib graft to help correct the shape.
243:First and second branchial arch syndrome
507:
343:
394:
88:. HFM shares many similarities with
13:
246:Oral-mandibular-auricular syndrome
14:
531:
417:
224:Patients can also benefit from a
177:
139:temporomandibular joint disorders
405:
311:Journal of Maxillofacial Surgery
30:
95:
372:
337:
284:
231:
149:The condition develops in the
1:
358:10.1016/S1073-8746(99)80039-5
323:10.1016/S0301-0503(82)80042-8
278:
201:
172:
80:—sometimes even requiring a
7:
256:
106:underdeveloped external ear
10:
536:
110:sensorineural hearing loss
86:cleft lip and cleft palate
432:
226:Bone Anchored Hearing Aid
163:insufficient blood supply
153:at approximately 4 weeks
90:Treacher Collins syndrome
43:
38:
29:
24:
346:Seminars in Orthodontics
249:Otomandibular dysostosis
240:Lateral facial dysplasia
212:distraction osteogenesis
144:
252:Craniofacial microsomia
135:Intellectual disability
273:Parry–Romberg syndrome
411:Hemifacial Microsomia
400:Hemifacial Microsomia
62:Hemifacial microsomia
25:Hemifacial microsomia
515:Congenital disorders
50:Craniofacial surgery
386:. 17 February 2018.
263:Condylar hypoplasia
123:that makes up this
70:congenital disorder
298:. 19 January 2019.
268:Goldenhar syndrome
219:Hollywood, Florida
502:
501:
59:
58:
19:Medical condition
527:
430:
429:
408:
397:
388:
387:
376:
370:
369:
341:
335:
334:
306:
300:
299:
288:
34:
22:
21:
535:
534:
530:
529:
528:
526:
525:
524:
505:
504:
503:
498:
497:
441:
420:
391:
378:
377:
373:
342:
338:
307:
303:
290:
289:
285:
281:
259:
234:
204:
180:
175:
155:gestational age
147:
98:
20:
17:
12:
11:
5:
533:
523:
522:
520:Rare syndromes
517:
500:
499:
496:
495:
484:
473:
458:
442:
437:
436:
434:
433:Classification
427:
426:
419:
418:External links
416:
415:
414:
403:
390:
389:
371:
336:
301:
282:
280:
277:
276:
275:
270:
265:
258:
255:
254:
253:
250:
247:
244:
241:
233:
230:
203:
200:
199:
198:
191:
187:
179:
178:Classification
176:
174:
171:
159:blood clotting
146:
143:
97:
94:
57:
56:
47:
41:
40:
36:
35:
27:
26:
18:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
532:
521:
518:
516:
513:
512:
510:
494:
490:
489:
485:
483:
479:
478:
474:
472:
468:
467:
463:
459:
457:
453:
452:
448:
444:
443:
440:
435:
431:
425:
422:
421:
412:
407:
404:
401:
396:
393:
392:
385:
381:
375:
367:
363:
359:
355:
351:
347:
340:
332:
328:
324:
320:
317:(4): 200–11.
316:
312:
305:
297:
293:
287:
283:
274:
271:
269:
266:
264:
261:
260:
251:
248:
245:
242:
239:
238:
237:
229:
227:
222:
220:
215:
213:
208:
196:
192:
188:
185:
184:
183:
170:
168:
164:
160:
156:
152:
142:
140:
136:
132:
130:
126:
122:
117:
113:
111:
107:
103:
93:
91:
87:
83:
79:
75:
71:
67:
63:
55:
51:
48:
46:
42:
37:
33:
28:
23:
486:
475:
460:
445:
406:
395:
383:
374:
352:(1): 25–34.
349:
345:
339:
314:
310:
304:
295:
286:
235:
223:
216:
209:
205:
181:
148:
133:
118:
114:
101:
99:
96:Presentation
65:
61:
60:
232:Terminology
82:tracheotomy
509:Categories
279:References
167:hereditary
54:pediatrics
202:Treatment
173:Diagnosis
161:leads to
121:phenotype
45:Specialty
366:10371937
257:See also
228:(BAHA).
129:syndrome
125:sequence
102:in utero
74:mandible
493:D006053
331:6961179
190:absent.
78:trachea
68:) is a
482:164210
364:
329:
471:758.0
151:fetus
145:Cause
488:MeSH
477:OMIM
466:9-CM
362:PMID
327:PMID
462:ICD
456:Q90
447:ICD
354:doi
319:doi
195:TMJ
127:or
66:HFM
511::
491::
480::
469::
454::
451:10
382:.
360:.
348:.
325:.
315:10
313:.
294:.
141:.
131:.
92:.
52:,
464:-
449:-
439:D
409:"
398:"
368:.
356::
350:5
333:.
321::
197:.
64:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.