580:
479:
320:
308:
498:
380:
289:
219:
297:
599:
52:
369:
651:
276:, became more intolerant of Protestantism. The Huguenots responded by establishing independent political and military structures, establishing diplomatic contacts with foreign powers, and openly revolting against central power. The Huguenot rebellions came after two decades of internal peace under Henry IV, following the intermittent
346:
Feeling their survival was at stake, the
Huguenots gathered in La Rochelle on 25 December. At this Huguenot General Assembly in La Rochelle the decision was taken to forcefully resist the Royal threat, and to establish a "state within the state", with an independent military commandment and
632:, with the objective of controlling the approaches to La Rochelle, and of encouraging the rebellion in the city. Buckingham ultimately ran out of money and support, and his army was weakened by diseases. The English intervention ended with the unsuccessful
561:, was signed between the city of La Rochelle and King Louis XIII on 5 February 1626, preserving religious freedom but imposing some guaranties against possible future upheavals: in particular, La Rochelle was prohibited from keeping a naval fleet.
547:. Through these deeds, he was recognized as the head of the Huguenots, and named himself "Admiral of the Protestant Church". The French Navy on the contrary was now completely depleted, leaving the central government vulnerable.
524:, and as a strong fleet was being prepared in Blavet for the eventuality of a siege of the city. The threat of a future siege on the city of La Rochelle was obvious, both to Soubise and the people of La Rochelle.
692:
The
Huguenot rebellions were implacably suppressed by the French crown. As a consequence, the Huguenots lost their political power, helping to strengthen the central government, which continued on a path toward
647:
and with gradually diminishing help from
England. During the siege, the population of La Rochelle decreased from 27,000 to 5,000 due to casualties, famine, and disease. Surrender was unconditional.
617:
The third and last
Huguenot rebellion started with an English military intervention aimed at encouraging an upheaval against the French king. The rebels had received the backing of the English king
643:. Cardinal Richelieu acted as the commander of the besieging troops (during times when the King was absent). Residents of La Rochelle resisted for 14 months, under the leadership of the mayor
390:
In 1621, Louis XIII moved to eradicate what he considered an open rebellion against his power. He led an army to the south, first succeeding in capturing the
Huguenot city of
351:, an ardent proponent of open conflict with the King. In that period, the Huguenots were defiant of the Crown, displaying intentions to become independent on the model of the
628:
with a fleet of 80 ships. In June 1627 Buckingham organised a landing on the nearby island of Île de Ré with 6,000 men in order to help the
Huguenots, thus starting an
40:
110:
550:
The
Huguenot city of La Rochelle voted to join Soubise on 8 August. These events would end with the defeat of the fleets of La Rochelle and Soubise, and the full
100:
33:
665:, the inhabitants were massacred or expelled, and the city was burnt to the ground. Louis XIII finally achieved a decisive victory in the
252:(Huguenots), mainly located in southwestern France, revolted against royal authority. The uprising occurred a decade after the death of
527:
In
February 1625, Soubise led a second Huguenot revolt against Louis XIII, and, after publishing a manifesto, invaded and occupied the
395:
80:
26:
697:. The Huguenots retained the religious freedoms authorised in the Edict of Nantes, but Louis XIV would later suppress these, and
625:
535:, although he could not take the fort after a three weeks siege. Soubise then returned to Ré with 15 ships and soon occupied the
960:
933:
890:
863:
811:
784:
731:
633:
592:
570:
433:
383:
125:
676:, the Huguenots lost their territorial, political, and military rights, but retained the religious freedom granted by the
579:
1029:
1015:
1001:
987:
698:
661:
Rohan continued to resist in
Southern France, where the forces of Louis XIII continued to intervene in 1629. In the
355:: "If the citizens, abandoned to their guidance, were threatened in their rights and creeds, they would imitate the
629:
531:, near La Rochelle. From there he sailed up to Brittany where he led a successful attack on the royal fleet in the
340:
159:
343:
in
October 1620. The government was replaced by a French-style parliament in which only Catholics could sit.
1044:
855:
Dictionary of Battles and Sieges: A Guide to 8,500 Battles from Antiquity Through the Twenty-first Century
636:. After a last attack on Saint-Martin they were repulsed with heavy casualties, and left in their ships.
512:
did not, however, uphold the terms of the Treaty of Montpellier, sparking renewed Huguenot resentment.
478:
482:
399:
432:
started to harass royal vessels and bases. The Royal fleet met with the fleet of La Rochelle in the
222:
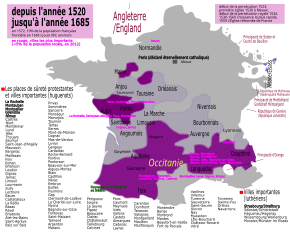
Areas controlled and contested by Huguenots are marked purple and blue on this map of modern France.
517:
164:
422:
331:
The first Huguenot rebellion was triggered by the re-establishment of Catholic rights in Huguenot
142:
105:
407:
277:
85:
551:
471:
558:
502:
184:
147:
950:
906:
853:
833:
801:
774:
748:
721:
923:
880:
680:. However, they were left at the mercy of the monarchy, unable to resist when the next king,
458:
to power as chief minister, which would mean more difficult times ahead for the Protestants.
440:
120:
307:
640:
618:
606:
574:
348:
300:
239:
206:
169:
115:
8:
681:
273:
684:, embarked on active persecution in the 1670s, and revoked the Edict of Nantes in 1685.
339:
in 1617, and the military annexation of Béarn to France in 1620, with the occupation of
602:
584:
455:
415:
359:
in their resistance to Spain, and defy all the power of the monarchy to reduce them." (
324:
312:
253:
90:
536:
319:
1025:
1011:
997:
983:
956:
929:
886:
859:
807:
780:
727:
694:
361:
75:
532:
467:
137:
666:
654:
189:
179:
677:
662:
520:, instead of dismantling it, right under the walls of the Huguenot stronghold of
261:
174:
528:
673:
497:
486:
372:
352:
95:
1038:
243:
425:
in which the population was massacred and the city was burnt to the ground.
292:
Huguenot regions (purple) and royal intervention (red) between 1620 and 1622
379:
18:
908:
The Penny Cyclopædia of the Society for the Diffusion of Useful Knowledge
644:
610:
521:
448:
429:
403:
356:
257:
201:
421:
After a lull, combat resumed with numerous atrocities in 1622, with the
509:
490:
336:
265:
249:
368:
288:
650:
622:
444:
411:
296:
246:
598:
218:
544:
235:
332:
51:
994:
Huguenot warrior: the life and times of Henri de Rohan, 1579–1638
803:
Huguenot Warrior: The Life and Times of Henri de Rohan, 1579–1638
980:
Siege Warfare: The Fortress in the Early Modern World, 1494–1660
776:
Siege Warfare: The Fortress in the Early Modern World, 1494-1660
952:
Europe's Physician: The Various Life of Sir Theodore de Mayerne
588:
540:
513:
391:
269:
591:
vanquishing the English army of Buckingham at the end of the
838:. Longman, Brown, Green, Longmans, and Roberts. p. 454.
753:. Longman, Brown, Green, Longmans, and Roberts. p. 454.
539:
as well, thus giving him command of the Atlantic coast from
402:
on 24 June. A small number of troops attempted to surround
461:
256:
who, himself originally a Huguenot before converting to
564:
283:
303:(1579–1638) was chosen as the leader of the rebellion.
242:, were a series of rebellions of the 1620s in which
447:and La Rochelle could be kept, but the fortress of
847:
845:
436:on 27 October 1622 in an inconclusive encounter.
1036:
921:
842:
443:ended hostilities. The Huguenot fortresses of
347:independent taxes, under the direction of the
885:. Cambridge University Press. pp. xiii.
715:
713:
639:The English intervention was followed by the
34:
948:
922:Litalien, Raymonde; Vaugeois, Denis (2004).
827:
825:
823:
768:
766:
764:
762:
760:
428:In La Rochelle, the fleet of the city under
311:Re-establishment of the Catholics in Béarn,
928:. McGill-Queen's Press – MQUP. p. 22.
779:. Routledge & Kegan Paul. p. 118.
48:
710:
41:
27:
949:Trevor-Roper, Hugh Redwald (2006-01-01).
820:
757:
649:
597:
578:
496:
477:
378:
367:
318:
306:
295:
287:
260:, had protected Protestants through the
217:
626:George Villiers, 1st Duke of Buckingham
414:, where he exhausted his troops in the
1037:
1022:The French wars of religion, 1562–1629
955:. Yale University Press. p. 289.
925:Champlain: The Birth of French America
882:The French Wars of Religion, 1562–1629
851:
799:
719:
831:
806:. Springer Netherlands. p. 108.
772:
746:
462:Second Huguenot rebellion (1625–1626)
410:, but Louis XIII then moved south to
22:
878:
565:Third Huguenot rebellion (1627–1629)
284:First Huguenot rebellion (1620–1622)
669:in June 1629, and Rohan submitted.
406:under the Count of Soissons in the
16:Rebellions in the Kingdom of France
13:
634:siege of Saint-Martin-de-Ré (1627)
593:siege of Saint-Martin-de-Ré (1627)
571:Siege of Saint-Martin-de-Ré (1627)
434:Naval battle of Saint-Martin-de-Ré
384:Naval battle of Saint-Martin-de-Ré
14:
1056:
1024:Cambridge University Press, 2005
1010:Greenwood Publishing Group, 2007
483:Benjamin de Rohan, duc de Soubise
454:The year 1624 saw the arrival of
400:Benjamin de Rohan, duc de Soubise
1008:Dictionary of Battles and Sieges
858:. Greenwood Press. p. 572.
516:reinforced the fortification of
50:
942:
911:. C. Knight. 1842. p. 268.
272:of his Italian Catholic mother
915:
899:
872:
800:Clarke, Jack A. (1967-07-31).
793:
740:
1:
972:
557:After long negotiations, the
394:, and then succeeding in the
879:Holt, Mack P. (2005-10-13).
720:Sturdy, D. J. (2002-02-01).
687:
630:Anglo-French War (1627–1629)
396:siege of Saint-Jean-d'Angély
7:
773:Duffy, Christopher (1979).
723:Fractured Europe: 1600–1721
10:
1061:
832:Crowe, Eyre Evans (1863).
747:Crowe, Eyre Evans (1863).
568:
465:
323:Louis XIII in the failed
66:
704:
505:on September 16th, 1625.
501:Capture of Île de Ré by
398:against Rohan's brother
408:Blockade of La Rochelle
278:French Wars of Religion
230:, sometimes called the
726:. Wiley. p. 125.
658:
614:
595:
506:
503:Charles, Duke of Guise
494:
485:led the occupation of
451:had to be dismantled.
387:
376:
328:
316:
304:
293:
223:
852:Jaques, Tony (2007).
835:The History of France
750:The History of France
653:
601:
582:
500:
481:
441:Treaty of Montpellier
423:Siege of Nègrepelisse
382:
371:
322:
310:
299:
291:
221:
121:Treaty of Montpellier
672:By the terms of the
641:siege of La Rochelle
607:Siege of La Rochelle
575:Siege of La Rochelle
552:Capture of Ré island
472:Capture of Ré island
207:War of the Camisards
1045:Huguenot rebellions
301:Henri, duc de Rohan
228:Huguenot rebellions
81:Saint-Jean-d'Angély
58:Huguenot rebellions
992:Jack Alden Clarke
978:Christopher Duffy
659:
615:
603:Cardinal Richelieu
596:
585:Henri de Schomberg
507:
495:
456:Cardinal Richelieu
416:Siege of Montauban
388:
386:on 27 October 1622
377:
329:
325:siege of Montauban
317:
313:Melchior Tavernier
305:
294:
224:
160:Saint-Martin-de-Ré
126:Saint-Martin-de-Ré
962:978-0-300-11263-4
935:978-0-7735-2850-5
892:978-1-139-44767-6
865:978-0-313-33536-5
813:978-90-247-0193-3
786:978-0-7100-8871-0
733:978-0-631-20513-5
362:Mercure de France
215:
214:
1052:
982:Routledge, 1979
967:
966:
946:
940:
939:
919:
913:
912:
903:
897:
896:
876:
870:
869:
849:
840:
839:
829:
818:
817:
797:
791:
790:
770:
755:
754:
744:
738:
737:
717:
699:revoke the edict
533:Battle of Blavet
468:Battle of Blavet
274:Marie de' Medici
264:. His successor
61:
59:
54:
43:
36:
29:
20:
19:
1060:
1059:
1055:
1054:
1053:
1051:
1050:
1049:
1035:
1034:
996:Springer, 1967
975:
970:
963:
947:
943:
936:
920:
916:
905:
904:
900:
893:
877:
873:
866:
850:
843:
830:
821:
814:
798:
794:
787:
771:
758:
745:
741:
734:
718:
711:
707:
690:
678:Edict of Nantes
663:siege of Privas
621:, who sent his
577:
569:Main articles:
567:
559:Treaty of Paris
489:in defiance of
474:
466:Main articles:
464:
439:Meanwhile, the
286:
262:Edict of Nantes
216:
211:
148:Treaty of Paris
62:
57:
55:
49:
47:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1058:
1048:
1047:
1033:
1032:
1018:
1004:
990:
974:
971:
969:
968:
961:
941:
934:
914:
898:
891:
871:
864:
841:
819:
812:
792:
785:
756:
739:
732:
708:
706:
703:
689:
686:
674:Peace of Alais
566:
563:
554:by September.
463:
460:
373:Siege of Royan
353:Dutch Republic
285:
282:
280:of 1562–1598.
240:Henri de Rohan
213:
212:
210:
209:
204:
198:
197:
193:
192:
187:
182:
177:
172:
167:
165:Pont du Feneau
162:
156:
155:
151:
150:
145:
140:
134:
133:
129:
128:
123:
118:
113:
108:
103:
98:
93:
88:
83:
78:
72:
71:
67:
64:
63:
46:
45:
38:
31:
23:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1057:
1046:
1043:
1042:
1040:
1031:
1030:0-521-83872-X
1027:
1023:
1020:Mack P. Holt
1019:
1017:
1016:0-313-33538-9
1013:
1009:
1005:
1003:
1002:90-247-0193-7
999:
995:
991:
989:
988:0-7100-8871-X
985:
981:
977:
976:
964:
958:
954:
953:
945:
937:
931:
927:
926:
918:
910:
909:
902:
894:
888:
884:
883:
875:
867:
861:
857:
856:
848:
846:
837:
836:
828:
826:
824:
815:
809:
805:
804:
796:
788:
782:
778:
777:
769:
767:
765:
763:
761:
752:
751:
743:
735:
729:
725:
724:
716:
714:
709:
702:
700:
696:
685:
683:
679:
675:
670:
668:
667:siege of Alès
664:
657:in June 1629.
656:
655:Siege of Alès
652:
648:
646:
642:
637:
635:
631:
627:
624:
620:
612:
608:
604:
600:
594:
590:
586:
581:
576:
572:
562:
560:
555:
553:
548:
546:
542:
538:
534:
530:
525:
523:
519:
515:
511:
504:
499:
492:
488:
484:
480:
476:
473:
469:
459:
457:
452:
450:
446:
442:
437:
435:
431:
426:
424:
419:
417:
413:
409:
405:
401:
397:
393:
385:
381:
374:
370:
366:
364:
363:
358:
354:
350:
344:
342:
338:
334:
326:
321:
314:
309:
302:
298:
290:
281:
279:
275:
271:
267:
263:
259:
255:
251:
248:
245:
241:
237:
233:
229:
220:
208:
205:
203:
200:
199:
195:
194:
191:
190:Peace of Alès
188:
186:
183:
181:
178:
176:
173:
171:
168:
166:
163:
161:
158:
157:
153:
152:
149:
146:
144:
141:
139:
136:
135:
131:
130:
127:
124:
122:
119:
117:
114:
112:
111:Saint-Antonin
109:
107:
104:
102:
99:
97:
94:
92:
89:
87:
84:
82:
79:
77:
74:
73:
69:
68:
65:
60:
53:
44:
39:
37:
32:
30:
25:
24:
21:
1021:
1007:
1006:Tony Jaques
993:
979:
951:
944:
924:
917:
907:
901:
881:
874:
854:
834:
802:
795:
775:
749:
742:
722:
691:
671:
660:
638:
616:
556:
549:
537:Ile d'Oléron
529:island of Ré
526:
508:
475:
453:
438:
427:
420:
389:
360:
349:Duc de Rohan
345:
330:
268:, under the
231:
227:
225:
106:Nègrepelisse
56:
645:Jean Guiton
611:Henri Motte
522:La Rochelle
449:Montpellier
430:Jean Guiton
404:La Rochelle
258:Catholicism
250:Protestants
202:Dragonnades
170:La Rochelle
116:Montpellier
86:La Rochelle
973:References
695:absolutism
518:Fort Louis
510:Louis XIII
491:Louis XIII
337:Louis XIII
266:Louis XIII
234:after the
232:Rohan Wars
101:Saint-Foix
701:in 1685.
688:Aftermath
682:Louis XIV
623:favourite
619:Charles I
583:Marshall
487:Île de Ré
445:Montauban
412:Montauban
247:Calvinist
196:Aftermath
185:Montauban
143:Ré island
91:Montauban
1039:Category
545:Bordeaux
254:Henry IV
236:Huguenot
605:at the
327:in 1621
270:regency
238:leader
154:1627–29
70:1621–22
1028:
1014:
1000:
986:
959:
932:
889:
862:
810:
783:
730:
613:, 1881
589:Toiras
541:Nantes
514:Toiras
392:Saumur
375:, 1622
315:, 1620
244:French
175:Privas
138:Blavet
76:Saumur
705:Notes
357:Dutch
333:Béarn
96:Royan
1026:ISBN
1012:ISBN
998:ISBN
984:ISBN
957:ISBN
930:ISBN
887:ISBN
860:ISBN
808:ISBN
781:ISBN
728:ISBN
587:and
573:and
470:and
226:The
180:Alès
132:1625
543:to
341:Pau
335:by
1041::
844:^
822:^
759:^
712:^
609:,
418:.
365:)
965:.
938:.
895:.
868:.
816:.
789:.
736:.
493:.
42:e
35:t
28:v
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.