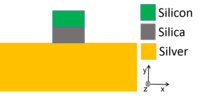78:
52:
74:
structure. The aim of designing the hybrid plasmonic waveguide was to combine these two different wave guiding schemes and achieve high light confinement without suffering large loss. Many different variations of this structure have been proposed. Many other types of hybrid plasmonic waveguides have been proposed since then to improve light confinement ability or to reduce fabrication complexity.
98:, which is confined near the metal surface. When these two structures are brought close to each other, the dielectric waveguide mode supported by the silicon nanowire couples to the surface plasmon mode supported by the metal surface. As a result of this mode coupling, light becomes highly confined in the region between the metal and the high index region (silicon nanowire).
111:, it can also confine light in the low index medium. Combination of these attractive features has stimulated worldwide research activity on the application of this new guiding scheme. Some notable examples of such applications are compact lasers, electro optic modulators, biosensors, polarization control devices, and thermo-optic switches.
73:
to confine light near a metal surface. The light confinement ability of plasmonic waveguides is not limited by diffraction, and, as a result, they can confine light to very small volumes. However, these guides suffer significant propagation loss because of the presence of metal as part of the guiding
94:. The most commonly used hybrid plasmonic waveguide consists of a silicon nanowire placed very near a metal surface and separated by a low index region. The silicon waveguide supports dielectric waveguide mode, which is mostly confined in silicon. The metal surface supports
106:
Hybrid plasmonic waveguide provides large confinement of light at a lower loss compared to many previously reported plasmonic waveguides. It is also compatible with silicon photonics technology, and can be integrated with silicon waveguides on the same chip. Similar to a
68:
to confine light in a high index region. They can guide light over a long distance with very low loss, but their light confinement ability is limited by diffraction. Plasmonic waveguides, on the other hand, use
320:
Y. Bian; Z. Zheng; X. Zhao; L. Liu; Y. Su; J. Liu; J. Zhu; T. Zhou (2013). "Nanoscale light guiding in a silicon-based hybrid plasmonic waveguide that incorporates an inverse metal ridge".
725:
F. Lou; L. Thylen; L. Wosinski (2013). Cheben, Pavel; Čtyroký, Jiří; Molina-Fernandez, Iñigo (eds.). "Hybrid plasmonic microdisk resonators for optical interconnect applications".
226:
R. F. Oulton; V. J. Sorger; D. A. Genov; D. F. P. Pile; X. Zhang (2008). "A hybrid plasmonic waveguide for subwavelength confinement and long range propagation".
682:
D. Perron; M. Wu; C. Horvath; D. Bachman; V. Van (2011). "All-plasmonic switching based on thermal nonlinearity in a polymer plasmonic microring resonator".
212:
631:
J. N. Caspers; J. S. Aitchison; M. Mojahedi (2013). "Experimental demonstration of an integrated hybrid plasmonic polarization rotator".
363:
M. Z. Alam; J. S. Aitchison; M. Mojahedi (2014). "A marriage of convenience: Hybridization of plasmonic and dielectric waveguide modes".
584:"Design of on-chip hybrid plasmonic Mach-Zehnder interferometer for temperature and concentration detection of chemical solution"
407:
65:
206:
406:
R. F. Oulton; V. J. Sorger; T. Zentgraf; R-M. Ma; C. Gladden; L. Dai; G. Bartal; X. Zhang (2009).
162:
W. L Barnes (2006). "Surface plasmon–polariton length scales: A route to sub-wavelength optics".
273:"A silicon-based hybrid plasmonic waveguide with a metal cap for a nano-scale light confinement"
734:
691:
640:
536:
487:
422:
372:
329:
284:
235:
171:
136:
25:
8:
778:
81:
Guided power density in a hybrid plasmonic waveguide. Light propagates in the z-direction
738:
695:
644:
540:
491:
426:
376:
333:
288:
239:
175:
140:
773:
750:
664:
608:
583:
559:
524:
505:
456:
388:
345:
90:
The operation of the hybrid plasmonic waveguides can be explained using the concept of
127:
D. K. Gramotnev; S. I. Bozhevolnyi (2010). "Plasmonics beyond the diffraction limit".
754:
707:
656:
613:
564:
448:
349:
302:
196:
21:
668:
509:
392:
183:
742:
699:
648:
603:
595:
554:
544:
495:
438:
430:
380:
337:
292:
251:
243:
179:
144:
33:
460:
55:
Cross section of hybrid plasmonic waveguide. Power propagates in the z direction.
95:
70:
225:
108:
599:
767:
500:
475:
247:
148:
91:
525:"Miniature microring resonator sensor based on a hybrid plasmonic waveguide"
711:
660:
617:
568:
452:
443:
384:
341:
306:
256:
405:
703:
652:
473:
297:
272:
24:
that achieves strong light confinement by coupling the light guided by a
434:
746:
630:
549:
476:"Ultra-compact silicon nanophotonic modulator with broadband response"
29:
362:
681:
77:
37:
126:
45:
197:
M. Z. Alam, J. Meier, J.S. Aitchison, and M. Mojahedi (2007).
51:
319:
41:
724:
522:
474:
V. J. Sorger; N. D. L-Kimura; R-M. Ma; X. Zhang (2012).
581:
32:
waveguide. It is formed by separating a medium of high
201:. Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics (CLEO).
765:
729:. Integrated Optics: Physics and Simulations.
408:"Plasmon lasers at deep subwavelength scale"
211:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
164:Journal of Optics A: Pure and Applied Optics
270:
161:
199:Super mode propagation in low index medium
607:
558:
548:
499:
442:
296:
255:
85:
523:L. Zhou; X. Sun; X. Li; J. Chen (2011).
76:
50:
766:
13:
582:S. Ghosh; B. M. A. Rahman (2019).
14:
790:
588:Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical
40:) from a metal surface (usually
718:
675:
624:
575:
516:
101:
467:
399:
356:
313:
264:
219:
190:
155:
120:
1:
114:
7:
365:Laser and Photonics Reviews
10:
795:
64:Dielectric waveguides use
59:
18:hybrid plasmonic waveguide
600:10.1016/j.snb.2018.09.070
184:10.1088/1464-4258/8/4/S06
66:total internal reflection
501:10.1515/nanoph-2012-0009
248:10.1038/nphoton.2008.131
149:10.1038/nphoton.2009.282
385:10.1002/lpor.201300168
342:10.1002/pssa.201228682
271:D. Dai; S. He (2009).
86:Principle of operation
82:
56:
322:Phys. Status Solidi A
80:
54:
704:10.1364/OL.36.002731
653:10.1364/OL.38.004054
298:10.1364/OE.17.016646
26:dielectric waveguide
739:2013SPIE.8781E..0XL
696:2011OptL...36.2731P
645:2013OptL...38.4054C
541:2011Senso..11.6856Z
492:2012Nanop...1...17S
435:10.1038/nature08364
427:2009Natur.461..629O
377:2014LPRv....8..394A
334:2013PSSAR.210.1424B
289:2009OExpr..1716646D
283:(19): 16646–16653.
240:2008NaPho...2.....O
176:2006JOptA...8S..87B
141:2010NaPho...4...83G
747:10.1117/12.2017108
550:10.3390/s110706856
83:
57:
48:) by a small gap.
690:(14): 2731–2733.
639:(20): 4054–4057.
421:(7264): 629–632.
22:optical waveguide
786:
759:
758:
722:
716:
715:
679:
673:
672:
628:
622:
621:
611:
579:
573:
572:
562:
552:
535:(7): 6856–6867.
520:
514:
513:
503:
471:
465:
464:
446:
412:
403:
397:
396:
360:
354:
353:
328:(7): 1424–1428.
317:
311:
310:
300:
268:
262:
261:
259:
228:Nature Photonics
223:
217:
216:
210:
202:
194:
188:
187:
159:
153:
152:
129:Nature Photonics
124:
34:refractive index
794:
793:
789:
788:
787:
785:
784:
783:
764:
763:
762:
723:
719:
680:
676:
629:
625:
580:
576:
521:
517:
472:
468:
410:
404:
400:
361:
357:
318:
314:
269:
265:
224:
220:
207:cite conference
204:
203:
195:
191:
160:
156:
125:
121:
117:
104:
96:surface plasmon
88:
71:surface plasmon
62:
12:
11:
5:
792:
782:
781:
776:
761:
760:
717:
684:Optics Letters
674:
633:Optics Letters
623:
594:(7): 490–502.
574:
515:
466:
398:
371:(3): 394–408.
355:
312:
263:
234:(8): 496–500.
218:
189:
154:
118:
116:
113:
109:slot-waveguide
103:
100:
87:
84:
61:
58:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
791:
780:
777:
775:
772:
771:
769:
756:
752:
748:
744:
740:
736:
732:
728:
721:
713:
709:
705:
701:
697:
693:
689:
685:
678:
670:
666:
662:
658:
654:
650:
646:
642:
638:
634:
627:
619:
615:
610:
605:
601:
597:
593:
589:
585:
578:
570:
566:
561:
556:
551:
546:
542:
538:
534:
530:
526:
519:
511:
507:
502:
497:
493:
489:
485:
481:
480:Nanophotonics
477:
470:
462:
458:
454:
450:
445:
444:10044/1/19116
440:
436:
432:
428:
424:
420:
416:
409:
402:
394:
390:
386:
382:
378:
374:
370:
366:
359:
351:
347:
343:
339:
335:
331:
327:
323:
316:
308:
304:
299:
294:
290:
286:
282:
278:
274:
267:
258:
257:10044/1/19117
253:
249:
245:
241:
237:
233:
229:
222:
214:
208:
200:
193:
185:
181:
177:
173:
169:
165:
158:
150:
146:
142:
138:
134:
130:
123:
119:
112:
110:
99:
97:
93:
92:mode coupling
79:
75:
72:
67:
53:
49:
47:
43:
39:
35:
31:
27:
23:
19:
730:
726:
720:
687:
683:
677:
636:
632:
626:
591:
587:
577:
532:
528:
518:
486:(1): 17–22.
483:
479:
469:
418:
414:
401:
368:
364:
358:
325:
321:
315:
280:
277:Opt. Express
276:
266:
231:
227:
221:
198:
192:
167:
163:
157:
135:(2): 83–91.
132:
128:
122:
105:
102:Applications
89:
63:
17:
15:
779:Plasmonics
768:Categories
733:: 87810X.
727:Proc. SPIE
170:(4): S87.
115:References
774:Photonics
755:119802655
350:115148678
36:(usually
30:plasmonic
712:21765524
669:26909408
661:24321921
618:22163989
569:22163989
510:10431638
453:19718019
393:54036931
307:19770880
735:Bibcode
692:Bibcode
641:Bibcode
609:3231671
560:3231671
537:Bibcode
529:Sensors
488:Bibcode
423:Bibcode
373:Bibcode
330:Bibcode
285:Bibcode
236:Bibcode
172:Bibcode
137:Bibcode
60:History
38:silicon
753:
710:
667:
659:
616:
606:
567:
557:
508:
461:912028
459:
451:
415:Nature
391:
348:
305:
46:silver
28:and a
20:is an
751:S2CID
665:S2CID
506:S2CID
457:S2CID
411:(PDF)
389:S2CID
346:S2CID
731:8781
708:PMID
657:PMID
614:PMID
565:PMID
449:PMID
303:PMID
213:link
42:gold
743:doi
700:doi
649:doi
604:PMC
596:doi
592:279
555:PMC
545:doi
496:doi
439:hdl
431:doi
419:461
381:doi
338:doi
326:210
293:doi
252:hdl
244:doi
180:doi
145:doi
44:or
770::
749:.
741:.
706:.
698:.
688:36
686:.
663:.
655:.
647:.
637:38
635:.
612:.
602:.
590:.
586:.
563:.
553:.
543:.
533:11
531:.
527:.
504:.
494:.
482:.
478:.
455:.
447:.
437:.
429:.
417:.
413:.
387:.
379:.
367:.
344:.
336:.
324:.
301:.
291:.
281:17
279:.
275:.
250:.
242:.
230:.
209:}}
205:{{
178:.
166:.
143:.
131:.
16:A
757:.
745::
737::
714:.
702::
694::
671:.
651::
643::
620:.
598::
571:.
547::
539::
512:.
498::
490::
484:1
463:.
441::
433::
425::
395:.
383::
375::
369:8
352:.
340::
332::
309:.
295::
287::
260:.
254::
246::
238::
232:2
215:)
186:.
182::
174::
168:8
151:.
147::
139::
133:4
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.