45:
347:. Accumulating fluid in the interstitial space (interstitial edema) is caused by increased microvascular pressure and permeability, a positive feedback loop mechanism resulting in an associated in increasing the rate of microvascular filtration into the interstitial space. Decreased lymphatic drainage due to blockage can compound these effects. Interstitial edema can prevent oxygen diffusion across tissue and in the brain, kidney and intestines lead to the onset of compartment syndrome.
237:. The structure of the gel reticulum plays a role in the distribution of solutes across the interstitium, as the microstructure of the extracellular matrix in some parts excludes larger molecules (exclusion volume). The density of the collagen matrix fluctuates with the fluid volume of the interstitium. Increasing fluid volume is associated with a decrease in matrix fiber density, and a lower exclusion volume.
180:), serve a variety of structural and immune functions. Fibroblasts synthesize the production of structural molecules as well as enzymes that break down polymeric molecules. Such structural components exist both for the general interstitium of the body, and within individual organs, such as the myocardial interstitium of the
331:
refers to increased interstitial flow causing a neutral or reversed pressure differential between blood vessels and healthy tissue, limiting the distribution of intravenous drugs to tumors, which under other circumstances display a high-pressure gradient at their periphery.
200:
extend into the interstitium. The fluid spaces communicate with draining lymph nodes, although they do not have lining cells or structures of lymphatic channels. Interstitial fluid entering the lymphatic system becomes
195:
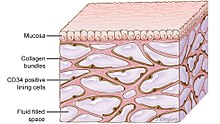
The interstitium in the submucosae of visceral organs, the dermis, superficial fascia, and perivascular adventitia are fluid-filled spaces supported by a collagen bundle lattice. Blind end, highly permeable, lymphatic
240:
The total fluid volume of the interstitium during health is about 20% of body weight, but this space is dynamic and may change in volume and composition during immune responses and in conditions such as
268:
interstitium facilitates solute and water transport between blood and urine in the vascular and tubular elements of the kidneys, and water reabsorption through changes in solute concentrations and
261:
and lungs to 21 to 24 mmHg in the liver, kidney and myocardium. Generally, increasing interstitial volume is associated with increased interstitial pressure and microvascular filtration.
678:
Benias, Petros C.; Wells, Rebecca G.; Sackey-Aboagye, Bridget; Klavan, Heather; Reidy, Jason; Buonocore, Darren; Miranda, Markus; Kornacki, Susan; Wayne, Michael (2018-03-27).
279:
The composition and chemical properties of the interstitial fluid vary among organs and undergo changes in chemical composition during normal function, as well as during
323:, the interstitial fluid and lymph system are sites where disease mechanisms may develop. Interstitial fluid flow is associated with the migration of cancer cells to
276:
associated with the spread of electrical events. The pulmonary interstitium allows for fluctuations in lung volume between inspiration and expiration.
424:
Wiig, H; Swartz, M. A (2012). "Interstitial fluid and lymph formation and transport: Physiological regulation and roles in inflammation and cancer".
328:
217:
The interstitial fluid is a reservoir and transportation system for nutrients and solutes distributing among organs, cells, and
335:
Changes in interstitial volume and pressure play critical roles in the onset of conditions like shock and inflammation. During
826:
477:
389:
382:
The interstitium and microvascular exchange. In: Handbook of
Physiology. The Cardiovascular System. Microcirculation
384:(sect. 2; pt. 1; chapt. 12; vol. IV ed.). Bethesda, MD: American Physiological Society. pp. 521–547.
1040:
156:-like reticulum. Collagen bundles of the extracellular matrix form scaffolding with a high tensile strength.
1045:
48:
Three-dimensional schematic of the interstitium, a fluid-filled space supported by a network of collagen
1050:
169:
157:
747:
205:, which is transported through lymphatic vessels until it empties into the microcirculation and the
339:, digestive enzymes and inflammatory agents diffuse to the interstitial space, then drain into the
257:. Interstitial fluid pressure is variable, ranging from -1 to -4 mmHg in tissues like the skin,
296:
258:
27:
577:"Changes in the myocardial interstitium and contribution to the progression of heart failure"
344:
691:
356:
109:
97:
8:
937:
Berggreen, E; Wiig, H (2014). "Lymphatic function and responses in periodontal disease".
361:
320:
308:
121:
695:
1007:
977:"Interstitial fluid flow in cancer: implications for disease progression and treatment"
976:
923:
893:
865:
856:
818:
782:
720:
679:
655:
630:
601:
576:
547:
512:
222:
108:
of organs. The role of the interstitium in solute concentration, protein transport and
81:
77:
1012:
994:
954:
913:
881:
822:
806:
787:
769:
725:
707:
660:
606:
552:
534:
441:
385:
336:
141:
93:
16:
In anatomy, a fluid-filled space between a structural barrier and internal structures
473:
The
Interstitium. In: Capillary Fluid Exchange: Regulation, Functions, and Pathology
1035:
1002:
984:
946:
919:
889:
860:
852:
814:
777:
759:
715:
699:
650:
642:
596:
588:
542:
524:
433:
316:
254:
249:. The amount of interstitial fluid varies from about 50% of the tissue weight in
69:
950:
57:
703:
471:
437:
764:
592:
529:
1029:
998:
773:
711:
680:"Structure and Distribution of an Unrecognized Interstitium in Human Tissues"
538:
292:
234:
61:
44:
1016:
958:
791:
729:
664:
610:
556:
445:
284:
273:
269:
149:
117:
912:
Matthes, Stephanie A.; Hadley, Ryan; Roman, Jesse; White, Eric S. (2015).
33:
646:
206:
989:
915:
Comparative
Biology of the Normal Lung Extracellular Matrix - Chapter 20
324:
280:
173:
161:
145:
105:
340:
218:
197:
177:
165:
153:
60:
fluid-filled space existing between a structural barrier, such as a
880:
Haschek, Wanda M.; Rousseaux, Colin G.; Wallig, Matthew A. (2010),
230:
133:
288:
226:
137:
85:
805:
Moe, Orson W.; Giebisch, Gerhard H.; Seldin, Donald W. (2009),
748:"A Modern View of the Interstitial Space in Health and Disease"
677:
513:"A Modern View of the Interstitial Space in Health and Disease"
312:
265:
242:
185:
73:
469:
343:
lymphatic system and enter into circulation, contributing to
246:
202:
181:
113:
101:
89:
112:
impacts human pathology and physiological responses such as
250:
189:
65:
132:
The non-fluid parts of the interstitium are predominantly
96:
and supporting tissues within the body – called the
911:
476:. San Rafael, CA: Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences.
272:
gradients. The myocardial interstitium participates in
879:
635:
Clinical
Journal of the American Society of Nephrology
574:
92:
system. The interstitial compartment is composed of
847:Breshears, Melanie A.; Confer, Anthony W. (2017).
804:
1027:
379:
100:– that are situated outside the blood and
846:
628:
975:Munson, Jennifer; Shieh, Adrian (2014-08-01).
245:, and specifically within the interstitium of
936:
882:"Cardiovascular and Skeletal Muscle Systems"
974:
329:enhanced permeability and retention effects
470:Scallan J; Huxley VH; Korthuis RJ (2010).
423:
1006:
988:
864:
781:
763:
719:
654:
600:
546:
528:
465:
463:
461:
459:
457:
455:
624:
622:
620:
188:, and the pulmonary interstitium of the
43:
745:
570:
568:
566:
510:
1028:
631:"Physiology of the Renal Interstitium"
452:
419:
417:
415:
413:
411:
409:
407:
405:
403:
401:
970:
968:
886:Fundamentals of Toxicologic Pathology
671:
617:
225:communicating between cells, and for
741:
739:
563:
506:
504:
502:
500:
498:
496:
494:
80:. The fluid in this space is called
746:Stewart, Randolph H. (2020-11-05).
511:Stewart, Randolph H. (2020-11-05).
398:
373:
68:, and internal structures, such as
13:
965:
924:10.1016/b978-0-12-404577-4.00020-5
894:10.1016/b978-0-12-370469-6.00012-x
857:10.1016/b978-0-323-35775-3.00011-4
819:10.1016/b978-0-12-449851-8.00003-6
14:
1062:
851:. Elsevier. pp. 617–681.e1.
736:
491:
629:Zeisberg, M; Kalluri, R (2015).
575:Eckhouse SR; Spinale FG (2012).
184:, the renal interstitium of the
172:and inflammatory cells, such as
152:that are cross-linked to form a
930:
905:
873:
840:
752:Frontiers in Veterinary Science
517:Frontiers in Veterinary Science
480:from the original on 2021-02-08
981:Cancer Management and Research
918:. Elsevier. pp. 387–402.
888:, Elsevier, pp. 319–376,
811:Genetic Diseases of the Kidney
798:
1:
367:
813:, Elsevier, pp. 39–73,
212:
127:
7:
951:10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.12.006
380:Bert JL; Pearce RH (1984).
350:
170:interstitial cells of Cajal
10:
1067:
939:Experimental Cell Research
704:10.1038/s41598-018-23062-6
438:10.1152/physrev.00037.2011
302:
765:10.3389/fvets.2020.609583
593:10.1016/j.hfc.2011.08.012
530:10.3389/fvets.2020.609583
26:
21:
297:chronic kidney disease
88:, and drains into the
84:, comprises water and
49:
28:Anatomical terminology
807:"Logic of the Kidney"
426:Physiological Reviews
345:systemic inflammation
287:, and development of
136:types I, III, and V,
47:
1041:Extracellular matrix
647:10.2215/CJN.00640114
357:Extracellular matrix
110:hydrostatic pressure
98:extracellular matrix
990:10.2147/CMAR.S65444
696:2018NatSR...8.4947B
362:Extracellular fluid
321:periodontal disease
223:signaling molecules
164:, dendritic cells,
1046:Matrices (biology)
849:The Urinary System
684:Scientific Reports
315:, kidney disease,
158:Interstitial cells
142:glycosaminoglycans
82:interstitial fluid
78:circulatory system
50:
1051:Tissues (biology)
828:978-0-12-449851-8
641:(10): 1831–1840.
337:hypovolemic shock
311:, heart disease,
235:immune regulation
233:participating in
102:lymphatic vessels
42:
41:
37:
1058:
1021:
1020:
1010:
992:
972:
963:
962:
934:
928:
927:
909:
903:
902:
901:
900:
877:
871:
870:
868:
844:
838:
837:
836:
835:
802:
796:
795:
785:
767:
743:
734:
733:
723:
675:
669:
668:
658:
626:
615:
614:
604:
572:
561:
560:
550:
532:
508:
489:
488:
486:
485:
467:
450:
449:
421:
396:
395:
377:
317:immune disorders
283:, conditions of
253:to about 10% in
34:edit on Wikidata
31:
19:
18:
1066:
1065:
1061:
1060:
1059:
1057:
1056:
1055:
1026:
1025:
1024:
973:
966:
935:
931:
910:
906:
898:
896:
878:
874:
845:
841:
833:
831:
829:
803:
799:
744:
737:
676:
672:
627:
618:
581:Heart Fail Clin
573:
564:
509:
492:
483:
481:
468:
453:
422:
399:
392:
378:
374:
370:
353:
307:In people with
305:
274:ionic exchanges
255:skeletal muscle
215:
130:
38:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1064:
1054:
1053:
1048:
1043:
1038:
1023:
1022:
964:
929:
904:
872:
839:
827:
797:
735:
670:
616:
562:
490:
451:
432:(3): 1005–60.
397:
390:
371:
369:
366:
365:
364:
359:
352:
349:
304:
301:
214:
211:
129:
126:
40:
39:
30:
24:
23:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1063:
1052:
1049:
1047:
1044:
1042:
1039:
1037:
1034:
1033:
1031:
1018:
1014:
1009:
1004:
1000:
996:
991:
986:
982:
978:
971:
969:
960:
956:
952:
948:
944:
940:
933:
925:
921:
917:
916:
908:
895:
891:
887:
883:
876:
867:
862:
858:
854:
850:
843:
830:
824:
820:
816:
812:
808:
801:
793:
789:
784:
779:
775:
771:
766:
761:
757:
753:
749:
742:
740:
731:
727:
722:
717:
713:
709:
705:
701:
697:
693:
689:
685:
681:
674:
666:
662:
657:
652:
648:
644:
640:
636:
632:
625:
623:
621:
612:
608:
603:
598:
594:
590:
586:
582:
578:
571:
569:
567:
558:
554:
549:
544:
540:
536:
531:
526:
522:
518:
514:
507:
505:
503:
501:
499:
497:
495:
479:
475:
474:
466:
464:
462:
460:
458:
456:
447:
443:
439:
435:
431:
427:
420:
418:
416:
414:
412:
410:
408:
406:
404:
402:
393:
391:0-683-07202-1
387:
383:
376:
372:
363:
360:
358:
355:
354:
348:
346:
342:
338:
333:
330:
326:
322:
318:
314:
310:
309:lung diseases
300:
298:
294:
293:heart failure
290:
286:
282:
277:
275:
271:
267:
262:
260:
256:
252:
248:
244:
238:
236:
232:
228:
224:
220:
210:
208:
207:venous system
204:
199:
193:
191:
187:
183:
179:
175:
171:
167:
163:
159:
155:
151:
150:proteoglycans
147:
143:
139:
135:
125:
123:
119:
115:
111:
107:
103:
99:
95:
91:
87:
83:
79:
75:
71:
67:
63:
62:cell membrane
59:
55:
46:
35:
29:
25:
20:
980:
945:(2): 130–7.
942:
938:
932:
914:
907:
897:, retrieved
885:
875:
848:
842:
832:, retrieved
810:
800:
755:
751:
687:
683:
673:
638:
634:
584:
580:
520:
516:
482:. Retrieved
472:
429:
425:
381:
375:
334:
306:
285:inflammation
278:
263:
239:
216:
194:
131:
118:inflammation
72:, including
54:interstitium
53:
51:
22:Interstitium
690:(1): 4947.
587:(1): 7–20.
327:sites. The
281:body growth
270:hydrostatic
219:capillaries
198:capillaries
174:macrophages
162:fibroblasts
1030:Categories
899:2024-04-22
834:2024-04-22
484:2018-03-29
368:References
341:mesenteric
325:metastatic
178:mast cells
166:adipocytes
146:hyaluronan
144:, such as
106:parenchyma
94:connective
58:contiguous
999:1179-1322
774:2297-1769
712:2045-2322
539:2297-1769
259:intestine
231:cytokines
213:Functions
154:honeycomb
128:Structure
1017:25170280
959:24503053
792:33251275
730:29588511
665:25813241
611:22108723
557:33251275
478:Archived
446:22811424
351:See also
291:, as in
289:diseases
227:antigens
134:collagen
104:and the
76:and the
1036:Anatomy
1008:4144982
983:: 317.
866:7271189
783:7674635
721:5869738
692:Bibcode
656:4594057
602:3227393
548:7674635
303:Disease
160:(e.g.,
138:elastin
86:solutes
74:muscles
64:or the
1015:
1005:
997:
957:
863:
825:
790:
780:
772:
728:
718:
710:
663:
653:
609:
599:
555:
545:
537:
444:
388:
319:, and
313:cancer
247:tumors
243:cancer
221:, for
186:kidney
140:, and
70:organs
266:renal
203:lymph
182:heart
122:shock
114:edema
90:lymph
56:is a
32:[
1013:PMID
995:ISSN
955:PMID
823:ISBN
788:PMID
770:ISSN
726:PMID
708:ISSN
661:PMID
607:PMID
553:PMID
535:ISSN
442:PMID
386:ISBN
295:and
264:The
251:skin
229:and
190:lung
176:and
148:and
120:and
66:skin
52:The
1003:PMC
985:doi
947:doi
943:325
920:doi
890:doi
861:PMC
853:doi
815:doi
778:PMC
760:doi
716:PMC
700:doi
651:PMC
643:doi
597:PMC
589:doi
543:PMC
525:doi
434:doi
1032::
1011:.
1001:.
993:.
979:.
967:^
953:.
941:.
884:,
859:.
821:,
809:,
786:.
776:.
768:.
758:.
754:.
750:.
738:^
724:.
714:.
706:.
698:.
686:.
682:.
659:.
649:.
639:10
637:.
633:.
619:^
605:.
595:.
583:.
579:.
565:^
551:.
541:.
533:.
523:.
519:.
515:.
493:^
454:^
440:.
430:92
428:.
400:^
299:.
209:.
192:.
168:,
124:.
116:,
1019:.
987::
961:.
949::
926:.
922::
892::
869:.
855::
817::
794:.
762::
756:7
732:.
702::
694::
688:8
667:.
645::
613:.
591::
585:8
559:.
527::
521:7
487:.
448:.
436::
394:.
36:]
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.