29:
57:
97:
The clinical presentation of intestinal lymphangiectasia can range from asymptomatic to severe, implying a broad clinical spectrum. Some patients may exhibit minimal or subtle clinical features, diverging from the "textbook" presentations often associated with severe cases in adults. This variability
90:
fluid into the intestines leads to the loss of lymphocytes, immunoglobulins, and proteins, causing lymphopenia, hypogammaglobulinemia, and hypoalbuminemia, respectively. The loss of proteins contributes to the development of protein-losing enteropathy, a major clinical manifestation of this disease.
93:
Patients with intestinal lymphangiectasia present with a range of symptoms, significantly influenced by the extent of protein loss. Chronic diarrhea and malabsorption are common symptoms. The loss of protein can lead to edema, particularly in the legs and abdomen, due to decreased oncotic pressure.
89:
The pathophysiology of intestinal lymphangiectasia is centered around the dilation of the lymphatic vessels in the intestinal mucosa, submucosa, and sometimes the mesentery. This dilation impedes the normal flow of lymph from the intestines back to the circulatory system. The overflow of lymphatic
77:
in cases where there is no secondary cause. The primary defect lies in the inability of the lymphatic system to adequately drain lymph, resulting in its subsequent accumulation and leakage into the intestinal lumen. This condition, first described by
Waldmann in 1961, is typically diagnosed in
233:
has been shown to reduce symptom effects. This diet, however, is not a cure. If the diet is stopped, the symptoms will eventually reappear. Medication is also used to treat this disease, including
Octreotide, Sirolimus, Anti-plasmin and, at least in one case, Trametinib.
94:
Nutritional deficiencies may develop due to malabsorption, leading to growth retardation in children and weight loss in adults. Immune abnormalities resulting from lymphocyte loss can predispose patients to recurrent infections.
815:
212:
indicating dilated lacteals. Computerized tomography (CT) can show low attenuation material within the bowel walls which corresponds to lipid-containing chylous fluid within the dilated lymphatic vessels.
550:
Kull P, Hess R, Craig L, Saunders H, Washabau R (2001). "Clinical, clinicopathologic, radiographic, and ultrasonographic characteristics of intestinal lymphangiectasia in dogs: 17 cases (1996-1998)".
274:
493:
Nishino, Koichi; Yoshimi, Kaku; Shibuya, Tomoyoshi; Hayashi, Takuo; Mitani, Keiko; Kobayashi, Etsuko; Ichikawa, Masako; Asao, Tetsuhiko; Suzuki, Yohei; Sato, Tadashi; Shiota, Satomi (2017-04-15).
869:
612:
Sutherland-Smith J, Penninck D, Keating J, Webster C (2007). "Ultrasonographic intestinal hyperechoic mucosal striations in dogs are associated with lacteal dilation".
495:"Protein-losing Enteropathy Caused by Intestinal or Colonic Lymphangiectasia Complicated by Sporadic Lymphangioleiomyomatosis: A Report of Two Cases"
862:
855:
98:
underscores the importance of considering PIL in differential diagnoses, even when clinical manifestations are not severe or typical.
172:
can also lead to inflammation of the lymphatics and lymphangiectasia through migration of inflammatory cells through the lymphatics.
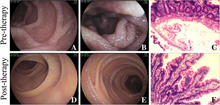
1153:
950:
1022:
780:
1093:
279:
469:
1163:
78:
infancy or early childhood. However, it can also manifest in adults, exhibiting a broad spectrum of clinical symptoms.
1125:
585:
Fogle, Jonathan E.; Bissett, Sally A. (May 2007). "Mucosal
Immunity and Chronic Idiopathic Enteropathies in Dogs".
28:
647:
Awiwi, Muhammad O.; Naik, Sagar (7 June 2022). "Tyrosine Kinase
Inhibitor–related Intestinal Lymphangiectasia".
1038:
1120:
1012:
243:
169:
69:, also known as "lymphangiectasis", is a pathologic dilation of lymph vessels. When it occurs in the
56:
830:
201:
157:
1017:
847:
242:
Dog breeds commonly affected by lymphangiectasia and/or protein-losing enteropathy include the
1158:
1078:
1115:
1105:
8:
1098:
977:
819:
247:
1110:
1083:
1073:
984:
900:
731:
696:
672:
527:
494:
474:
Proceedings of the 28th World
Congress of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association
453:
418:
402:
367:
824:
325:
937:
910:
905:
895:
878:
776:
718:
676:
664:
629:
625:
594:
567:
532:
514:
510:
440:
389:
329:
308:
Waldmann, T.A.; Steinfeld, J.L.; Dutcher, T.F.; Davidson, J.D.; Gordon, R.S. (2008).
255:
209:
118:
45:
1132:
1088:
1050:
967:
957:
927:
726:
708:
656:
621:
559:
522:
506:
448:
430:
397:
379:
321:
309:
126:
122:
74:
1027:
1007:
835:
110:
917:
713:
563:
221:
In the case of primary intestinal lymphangiectasia, a diet of low-fat and high-
180:
Diagnosis is through biopsy. The presence of hypoproteinemia, decreased blood
205:
1147:
989:
722:
518:
444:
393:
333:
165:
152:
malformation of the lymphatics. Secondary lymphangiectasia may be caused by
130:
1058:
972:
668:
633:
598:
571:
536:
189:
161:
660:
435:
384:
962:
310:"The Role of the Gastrointestinal System in "Idiopathic Hypoproteinemia""
185:
37:
807:
1068:
999:
181:
160:(CVP) causing abnormal lymph drainage. Increased CVP can be caused by
149:
73:
it is known as intestinal lymphangiectasia, colloquially recognized as
770:
611:
141:. Rupture of the lymphatics causes protein loss into the intestines.
197:
153:
70:
50:
945:
230:
587:
Compendium on
Continuing Education for the Practicing Veterinarian
1032:
922:
697:"The Update of Treatment for Primary Intestinal Lymphangiectasia"
251:
226:
222:
193:
138:
114:
877:
307:
887:
747:
291:
McGavin/ Zachary (2007), Pathologic Basis of
Veterinary Disease
200:
and calcium, and secondary to low protein binding of calcium.
106:
145:
492:
419:"Primary intestinal lymphangiectasia (Waldmann's disease)"
134:
701:
584:
156:
or cancer causing lymphatic obstruction, or increased
549:
797:
417:Vignes, Stéphane; Bellanger, Jérôme (2008-02-22).
771:Ettinger, Stephen J.; Feldman, Edward C. (1995).
1145:
416:
133:syndrome of the small intestine, especially of
863:
764:
593:(5). Veterinary Learning Systems: 290–302.
285:
870:
856:
372:World Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology
55:
27:
730:
712:
646:
526:
452:
434:
401:
383:
196:) is also seen due to poor absorption of
773:Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine
775:(4th ed.). W.B. Saunders Company.
694:
467:
368:"Intestinal lymphangiectasia in adults"
365:
1146:
951:Asplenia with cardiovascular anomalies
470:"Protein-Losing Enteropathies in Dogs"
1023:Intranodal palisaded myofibroblastoma
851:
690:
688:
686:
84:
578:
361:
359:
357:
355:
353:
351:
349:
347:
345:
343:
303:
301:
299:
297:
695:Kwon, Yiyoung; Kim, Mi Jin (2021).
13:
683:
14:
1175:
793:
423:Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases
340:
294:
1126:Postmastectomy lymphangiosarcoma
1094:Lymphedema–distichiasis syndrome
626:10.1111/j.1740-8261.2007.00204.x
511:10.2169/internalmedicine.56.7769
1154:Dermal and subcutaneous growths
745:
739:
640:
605:
1039:Template:Respiratory pathology
543:
486:
461:
410:
268:
1:
746:PIL, Unraveling Adult-Onset.
326:10.1016/s0016-5085(19)35130-3
261:
237:
748:"Unraveling Adult-Onset PIL"
366:Freeman, Hugh James (2011).
280:Dorland's Medical Dictionary
216:
175:
7:
1121:Postinflammatory lymphedema
1013:Generalized lymphadenopathy
881:: organ and vessel diseases
244:Soft-Coated Wheaten Terrier
10:
1180:
714:10.5223/pghn.2021.24.5.413
564:10.2460/javma.2001.219.197
170:Inflammatory bowel disease
36:Lymphangiectasia shown on
1164:Lymphatic vessel diseases
1049:
998:
936:
886:
801:
468:Steiner, Jörg M. (2003).
44:
35:
26:
21:
188:support the diagnosis.
101:
225:aliments, supplemental
202:Medical ultrasonography
158:central venous pressure
144:The most common cause
121:and distension of the
113:shows dilation of the
1079:Congenital lymphedema
661:10.1148/radiol.220137
614:Vet Radiol Ultrasound
436:10.1186/1750-1172-3-5
385:10.4251/wjgo.v3.i2.19
148:lymphangiectasia was
1116:Factitial lymphedema
1106:Secondary lymphedema
752:lymphangiectasia.com
1018:Castleman's disease
248:Norwegian Lundehund
1111:Bullous lymphedema
1084:Lymphedema praecox
1074:Primary lymphedema
985:Splenic infarction
552:J Am Vet Med Assoc
275:"lymphangiectasia"
85:Signs and symptoms
75:Waldmann's disease
1141:
1140:
1051:Lymphatic vessels
911:DiGeorge syndrome
879:Lymphatic disease
845:
844:
782:978-0-7216-6795-9
499:Internal Medicine
256:Yorkshire Terrier
210:intestinal mucosa
123:lymphatic vessels
64:
63:
16:Medical condition
1171:
1133:Waldmann disease
1099:Milroy's disease
1089:Lymphedema tarda
1064:Lymphangiectasia
978:Banti's syndrome
968:Wandering spleen
958:Accessory spleen
928:Thymic carcinoma
872:
865:
858:
849:
848:
799:
798:
787:
786:
768:
762:
761:
759:
758:
743:
737:
736:
734:
716:
692:
681:
680:
644:
638:
637:
609:
603:
602:
582:
576:
575:
547:
541:
540:
530:
490:
484:
483:
481:
480:
465:
459:
458:
456:
438:
414:
408:
407:
405:
387:
363:
338:
337:
314:Gastroenterology
305:
292:
289:
283:
272:
184:, and decreased
137:and fat-soluble
129:flow leads to a
67:Lymphangiectasia
60:
59:
31:
22:Lymphangiectasia
19:
18:
1179:
1178:
1174:
1173:
1172:
1170:
1169:
1168:
1144:
1143:
1142:
1137:
1045:
1028:Kikuchi disease
1008:Lymphadenopathy
994:
932:
882:
876:
846:
841:
840:
810:
796:
791:
790:
783:
769:
765:
756:
754:
744:
740:
693:
684:
645:
641:
610:
606:
583:
579:
548:
544:
491:
487:
478:
476:
466:
462:
415:
411:
364:
341:
306:
295:
290:
286:
273:
269:
264:
240:
219:
178:
164:or right-sided
111:small intestine
104:
87:
81:
54:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1177:
1167:
1166:
1161:
1156:
1139:
1138:
1136:
1135:
1130:
1129:
1128:
1123:
1118:
1113:
1103:
1102:
1101:
1096:
1091:
1086:
1081:
1071:
1066:
1061:
1055:
1053:
1047:
1046:
1044:
1043:
1042:
1041:
1030:
1025:
1020:
1015:
1010:
1004:
1002:
996:
995:
993:
992:
987:
982:
981:
980:
970:
965:
960:
955:
954:
953:
942:
940:
934:
933:
931:
930:
925:
920:
918:Ectopic thymus
915:
914:
913:
903:
898:
892:
890:
884:
883:
875:
874:
867:
860:
852:
843:
842:
839:
838:
827:
811:
806:
805:
803:
802:Classification
795:
794:External links
792:
789:
788:
781:
763:
738:
682:
639:
604:
577:
558:(2): 197–202.
542:
505:(8): 943–948.
485:
460:
409:
339:
320:(3): 197–207.
293:
284:
266:
265:
263:
260:
239:
236:
218:
215:
177:
174:
103:
100:
86:
83:
62:
61:
48:
42:
41:
33:
32:
24:
23:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1176:
1165:
1162:
1160:
1157:
1155:
1152:
1151:
1149:
1134:
1131:
1127:
1124:
1122:
1119:
1117:
1114:
1112:
1109:
1108:
1107:
1104:
1100:
1097:
1095:
1092:
1090:
1087:
1085:
1082:
1080:
1077:
1076:
1075:
1072:
1070:
1067:
1065:
1062:
1060:
1057:
1056:
1054:
1052:
1048:
1040:
1036:
1035:
1034:
1031:
1029:
1026:
1024:
1021:
1019:
1016:
1014:
1011:
1009:
1006:
1005:
1003:
1001:
997:
991:
990:Splenic tumor
988:
986:
983:
979:
976:
975:
974:
971:
969:
966:
964:
961:
959:
956:
952:
949:
948:
947:
944:
943:
941:
939:
935:
929:
926:
924:
921:
919:
916:
912:
909:
908:
907:
904:
902:
899:
897:
894:
893:
891:
889:
885:
880:
873:
868:
866:
861:
859:
854:
853:
850:
837:
833:
832:
828:
826:
822:
821:
817:
813:
812:
809:
804:
800:
784:
778:
774:
767:
753:
749:
742:
733:
728:
724:
720:
715:
710:
706:
702:
698:
691:
689:
687:
678:
674:
670:
666:
662:
658:
655:(2): 220137.
654:
650:
643:
635:
631:
627:
623:
619:
615:
608:
600:
596:
592:
588:
581:
573:
569:
565:
561:
557:
553:
546:
538:
534:
529:
524:
520:
516:
512:
508:
504:
500:
496:
489:
475:
471:
464:
455:
450:
446:
442:
437:
432:
428:
424:
420:
413:
404:
399:
395:
391:
386:
381:
377:
373:
369:
362:
360:
358:
356:
354:
352:
350:
348:
346:
344:
335:
331:
327:
323:
319:
315:
311:
304:
302:
300:
298:
288:
282:
281:
276:
271:
267:
259:
257:
253:
249:
245:
235:
232:
228:
224:
214:
211:
207:
203:
199:
195:
191:
187:
183:
173:
171:
167:
166:heart failure
163:
159:
155:
151:
147:
142:
140:
136:
132:
131:malabsorption
128:
124:
120:
116:
112:
108:
99:
95:
91:
82:
79:
76:
72:
68:
58:
52:
49:
47:
43:
39:
34:
30:
25:
20:
1159:Dog diseases
1063:
1059:Lymphangitis
973:Splenomegaly
829:
814:
772:
766:
755:. Retrieved
751:
741:
704:
700:
652:
648:
642:
617:
613:
607:
590:
586:
580:
555:
551:
545:
502:
498:
488:
477:. Retrieved
473:
463:
426:
422:
412:
375:
371:
317:
313:
287:
278:
270:
241:
229:and certain
220:
190:Hypocalcemia
179:
162:pericarditis
143:
105:
96:
92:
88:
80:
66:
65:
963:Polysplenia
901:Hyperplasia
620:(1): 51–7.
186:cholesterol
182:lymphocytes
125:. Reduced
38:enteroscopy
1148:Categories
1069:Lymphedema
1000:Lymph node
906:Hypoplasia
757:2023-11-30
707:(5): 413.
479:2007-03-20
262:References
238:In animals
206:striations
154:granulomas
150:congenital
71:intestines
723:2234-8646
677:249432951
649:Radiology
519:0918-2918
445:1750-1172
394:1948-5204
378:(2): 19.
334:0016-5085
217:Treatment
204:may show
198:vitamin D
176:Diagnosis
51:Angiology
46:Specialty
946:Asplenia
669:35670716
634:17236361
599:17724983
572:11469575
537:28420844
231:vitamins
139:vitamins
115:lacteals
1033:Tonsils
923:Thymoma
896:Abscess
836:D008200
732:8443852
528:5465412
454:2288596
403:3046182
252:Basenji
227:calcium
223:protein
208:in the
194:calcium
117:of the
109:of the
938:Spleen
888:Thymus
779:
729:
721:
675:
667:
632:
597:
570:
535:
525:
517:
451:
443:
400:
392:
332:
254:, and
107:Biopsy
53:
825:457.1
673:S2CID
429:(1).
192:(low
127:lymph
119:villi
102:Cause
1037:see
831:MeSH
820:9-CM
777:ISBN
719:ISSN
665:PMID
630:PMID
595:PMID
568:PMID
533:PMID
515:ISSN
441:ISSN
390:ISSN
330:ISSN
816:ICD
727:PMC
709:doi
657:doi
653:305
622:doi
560:doi
556:219
523:PMC
507:doi
449:PMC
431:doi
398:PMC
380:doi
322:doi
277:at
168:.
135:fat
1150::
834::
823::
750:.
725:.
717:.
705:24
703:.
699:.
685:^
671:.
663:.
651:.
628:.
618:48
616:.
591:29
589:.
566:.
554:.
531:.
521:.
513:.
503:56
501:.
497:.
472:.
447:.
439:.
425:.
421:.
396:.
388:.
374:.
370:.
342:^
328:.
318:41
316:.
312:.
296:^
258:.
250:,
246:,
146:of
871:e
864:t
857:v
818:-
808:D
785:.
760:.
735:.
711::
679:.
659::
636:.
624::
601:.
574:.
562::
539:.
509::
482:.
457:.
433::
427:3
406:.
382::
376:3
336:.
324::
40:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.