689:
on motor learning have noted that while consolidation occurs over a period of 4–6 hours during sleep, this is also true during waking hours, which may negate any role of sleep in learning. In this sense sleep would serve no special purpose to enhance consolidation of memories because it occurs independently of sleep. Other studies have examined the process of replay which has been described as a reactivation of patterns that were stimulated during a learning phase. Replay has been demonstrated in the hippocampus and this has lent support to the notion that it serves a consolidation purpose. However, replay is not specific to sleep and both rats and primates show signs during restful-awake periods. Also, replay may simply be residual activation in areas that were involved previously in the learning phase and may have no actual effect on consolidation. This reactivation of the memory traces has also been seen in non-REM sleep specifically for hippocampus-dependant memories. Researchers have noted strong reactivation of the hippocampus during sleep immediately after a learning task. This reactivation led to enhanced performance on the learned task. One such experiment had participants learn word pair associations (declarative memories) before either retention periods of sleep or periods of wakefulness. Researchers found that retrieval expectancy played a role as to whether participants were able to retain the information, as the participants that had been told about the delayed retrieval test performed better. However, their research showed that sleep was more likely to benefit the consolidation of memories if the information was relevant to future events or behaviors. Researchers following this line of work have come to assume that
511:
storage of episodic memories, can be established in structures apart from the hippocampal system such as the neo-cortex in the process of consolidation. Hence, while proper hippocampal functioning is necessary for the retention and retrieval of episodic memories, it is less necessary during the encoding and use of semantic memories. As memories age there are long-term interactions between the hippocampus and neo-cortex and this leads to the establishment of aspects of memory within structures aside from the hippocampus. MTT thus states that both episodic and semantic memories rely on the hippocampus and the latter becomes somewhat independent of the hippocampus during consolidation. An important distinction between MTT and the standard model is that the standard model proposes that all memories become independent of the hippocampus after several years. However, Nadel and
Moscovitch have shown that the hippocampus was involved in memory recall for all remote
367:
course of four days in one room, and the last was taught the class over the course of four days in different rooms. The subjects were tested five days later in a completely new setting. The results of the experiment were that taking the class over a period of four days was much more effective than taking it in one single mass. Interestingly, the group that took the course over four days and in different rooms performed the best in the final retention test out of all the groups." This shows that spacing out study sessions and studying in different environments helps with retention as it provides time for the brain to consolidate the information without being interrupted by new information. The benefits of spacing were also demonstrated in an earlier study by Reder and
Anderson (1982) which yielded similar results, confirming the spacing effect’s relevance and effects on learning.
592:(BLA) is involved in the encoding of significant experiences and has been directly linked to memorable events. Extensive evidence suggests that stress hormones such as epinephrine play a critical role in consolidating new memories and this is why stressful memories are recalled vividly. Studies by Gold and van Buskirk provided initial evidence for this relationship when they showed that injections of epinephrine into subjects following a training period resulted in greater long-term retention of task related memories. This study also provided evidence that the level of epinephrine injected was related to the level of retention suggesting that the level of stress or emotionality of the memory plays a role on the level of retention. It is suggested that epinephrine affects memory consolidation by activating the amygdala and studies have shown that
576:
on tasks and exhibit learning without the subject being aware that the training had ever taken place. This introduces a dissociation between the two forms of memory and the fact that one form can exist absent the other suggests separate mechanisms are involved in consolidation. Squire has proposed the procedural knowledge is consolidated in some cases by the extrapyramidal motor system. Squire demonstrated that intact learning of certain motor, perceptual, and cognitive skills can be retained in patients with amnesia. They also retain the ability to be influenced by priming effects without the patients being able to consciously recall any training session occurring.
837:). Following the same method that Nader and his associates used, Brunet induced anxiety responses in the patients by having them listen to a 30 second recording describing the circumstances of their traumatic experiences. The patients were shortly thereafter injected with propranolol, a drug that blocks stress hormone receptors in the amygdala which is implicated in neurologically representing the emotional content of memories. These patients experienced a significant reduction in PTSD symptoms months after treatment. These findings were confirmed in later studies done in 2009 by Kindt and colleagues and in 2010 by Schiller and colleagues.
550:
hippocampal damage show traces of memories and this has been used as support for the standard model because it suggests that memories are retained apart from the hippocampal system. Nadel and
Moscovitch argue that these retained memories have lost the richness of experience and exist as depersonalized events that have been semanticized over time. They suggest that this instead provides support for their notion that episodic memories rely significantly on the hippocampal system but semantic memories can be established elsewhere in the brain and survive hippocampal damage.
830:
shock. Groups of rats were then injected with anisomycin, an antibiotic that restricts protein synthesis, at different points in time. The rats that were injected with anisomycin after consolidation had taken place, retained the fear reaction to the tone. However, the rats that were injected before consolidation and reconsolidation could take place, did not retain the fear response when they heard the tone again later. It seems that interference that is made before memories are consolidated affect the way they are remembered later.
55:
479:
continually leading to strong connections between the two. Since the hippocampus can only support memories temporarily the remaining activation will be seen only in the neocortex which is able to support memory indefinitely. Squire and
Alvarez took the temporally graded nature of patients with retrograde amnesia as support for the notion that once a connection has been established within the neocortex the hippocampus is no longer required, but this process is dynamic and extends for several years.
529:
in the functional magnetic resonance imaging have allowed them to improve their distinction between the hippocampus and the entorhinal cortex which they claim is more enduring in its activation from remote memory retrieval. They also criticize the use of memories during testing which cannot be confirmed as accurate. Finally, they state that the initial interview in the scanner acted as an encoding event as such differences between recent and remote memories would be obscured.
99:
2940:
5208:
887:
debate and a detailed review of this field it had been concluded that reconsolidation was a real phenomenon. Tronson and Taylor compiled a lengthy summary of multiple reconsolidation studies, noting a number of studies were unable to show memory impairments due to blocked reconsolidation. However the need for standardized methods was underscored as in some learning tasks such as
5196:
694:
researchers have looked at the role growth hormones play in the consolidation of memories, particularly those of procedural and declarative memories. They found that although growth hormones support general brain systems and memory functioning, it is still unclear if growth hormones play a role in the formation and processing of particular memories during sleep periods.
78:. He noted the "curious fact... that the interval of a single night will greatly increase the strength of the memory," and presented the possibility that "... the power of recollection .. undergoes a process of ripening and maturing during the time which intervenes." The process of consolidation was later proposed based on clinical data illustrated in 1882 by
314:, which are suggested to underlie memory formation. LTP is also considered to be an important mechanism in terms of maintaining memories within brain regions, and therefore is thought to be involved in learning. There is compelling evidence that LTP is critical for Pavlovian fear conditioning in rats suggesting that it mediates
470:, representing the hippocampus-dependent stage. During this stage the hippocampus is 'teaching' the cortex more and more about the information and when the information is recalled it strengthens the cortico-cortical connection thus making the memory hippocampus-independent. Therefore, from one week and beyond the initial
85:, "progressive destruction advances progressively from the unstable to the stable". This idea was elaborated on by William H. Burnham a few years later in a paper on amnesia integrating findings from experimental psychology and neurology. Coining of the term "consolidation" is credited to the German researchers
236:(shown, for example, in goldfish), and as such it is considered the 'fast' type of consolidation. It is also referred to as 'initial consolidation'. As soon as six hours after training, memories become impervious to interferences that disrupt synaptic consolidation and the formation of long-term memory.
688:
regions; whereas the post-training awake group had no such improvements. It has been theorized that this may be related more-so to a process of synaptic consolidation rather than systems consolidation because of the short-term nature of the process involved. Researchers examining the effect of sleep
683:
related tasks. In one study testing finger-tapping, people were split into two groups and tested post-training with or without intervening sleep; results concluded that sleep post-training increases both speed and accuracy in this particular task, while increasing the activation of both cortical and
575:
however has been said to function separate from this system as it relies primarily on motor areas of the brain. The implicit nature of procedural knowledge allows it to exist absent from the conscious awareness that the information is there. Amnesic patients have shown retained ability to be trained
515:
memories no matter of their age. An important point they make while interpreting the results is that activation in the hippocampus was equally as strong regardless of the fact that the memories recalled were as old as 45 years prior to the date of the experiment. This is complicated by the fact that
493:
involved in the initial encoding of the memory. In this sense the MTL would act as a relay station for the various perceptual input that make up a memory and stores it as a whole event. After this has occurred the MTL directs information towards the neocortex to provide a permanent representation of
195:
have revolutionized the study of consolidation. Providing additional support is the study of functional brain activity in humans which has revealed that the activity of brain regions changes over time after a new memory is acquired. This change can occur as quickly as a couple hours after the memory
671:
More recent studies, however, have looked at the relationship between slow-wave sleep and memory consolidation, rather than REM sleep. One study found that low levels of acetylcholine found in the central nervous system, which are present during slow-wave sleep, aid in the consolidation of memories
528:
Haist, Gore, and Mao, sought to examine the temporal nature of consolidation within the hippocampus to test MTT against the standard view. They found that the hippocampus does not substantially contribute to the recollection of remote memories after a period of a few years. They claim that advances
478:
where it becomes permanently stored. In this view the hippocampus can perform the task of storing memories temporarily because the synapses are able to change quickly whereas the neocortical synapses change over time. Consolidation is thus the process whereby the hippocampus activates the neocortex
829:
for new consolidation, i.e., re-consolidation of the old memory. Nader, Schafe, and Le Doux (2000) demonstrated that the reconsolidation process may make memories more malleable than previously believed. Nader and his colleagues trained rats to be afraid of a tone by pairing the tone with a small
549:
need to be distinguished as relying on two different memory systems. When episodic information is encoded there are semantic aspects of the memory that are encoded as well and this is proposed as an explanation of the varying gradients of memory loss seen in amnesic patients. Amnesic patients with
886:
Some studies have supported this theory, while others have failed to demonstrate disruption of consolidated memory after retrieval. Negative results may be examples of conditions where memories are not susceptible to a permanent disruption, thus a determining factor of reconsolidation. After much
366:
One study that demonstrates this effect was conducted in 1984 by Smith and
Rothkopf. In this experiment, subjects were sorted into three groups to test retention and learning. "Each group was taught the same 8 hour statistics class, but one group was taught the class in one day, the next over the
612:
have the opposite effect on the enhancement of memory consolidation. The BLA is thought to be actively involved in memory consolidation and is influenced strongly by stress hormones resulting in increased activation and as such increased memory retention. The BLA then projects to the hippocampus
510:
and addresses perceived shortcomings of the standard model with respect to the dependency of the hippocampus. MTT argues that the hippocampus is always involved in the retrieval and storage of episodic memories. It is thought that semantic memories, including basic information encoded during the
1034:
In the decade between 2005 and 2015, at least five groups argued the notion that memory reconsolidation can be used to treat psychological problems. Three of these groups have proposed that the wide variety of different psychotherapies produce permanent change in clients to the extent that they
163:
suggesting that recently acquired memories of as long as a couple years could remain in the MTL prior to consolidation into other brain areas. Research into other patients with resections of the MTL have shown a positive relationship between the degree of memory impairment and the extent of MTL
693:
are a by-product of the reactivation of the brain areas and this can explain why dreams may be unrelated to the information being consolidated. The dream experience itself is not what enhances memory performance but rather it is the reactivation of the neural circuits that causes this. Other
94:
after they found that new information learned could disrupt information previously learnt if not enough time had passed to allow the old information to be consolidated. This led to the suggestion that new memories are fragile in nature but as time passes they become solidified.
227:
that lasts for at least 24 hours. Synaptic consolidation is achieved faster than systems consolidation (which is assumed to take weeks, months, or even to years to be accomplished). There is evidence to suggest that synaptic consolidation takes place within minutes to hours of
422:
in a more permanent form of storage. Systems consolidation is a slow dynamic process that can take anywhere from one to two decades to be fully formed in humans, unlike synaptic consolidation that only takes minutes to hours for new information to stabilize into memories.
1035:
manage to activate this same neurobiological mechanism of reconsolidation in a way that leads to deconsolidation. One example of this is the Lefkoe Method, created in 1985 by Morty Lefkoe, president and founder of the Lefkoe
Institute. Memory reconsolidation may be a
3051:
Brunet, Alain; Orr, Scott P.; Tremblay, Jacques; Robertson, Kate; Nader, Karim; Pitman, Roger K. (2008). "Effect of post-retrieval propranolol on psychophysiologic responding during subsequent script-driven traumatic imagery in post-traumatic stress disorder".
272:. The result of the gene expression is the lasting alteration of synaptic proteins, as well as synaptic remodeling and growth. In a short time-frame immediately following learning, the molecular cascade, expression and process of both transcription factors and
789:(ECT). This seemed to indicate the involvement of a re-consolidation process for excited memories, and that the operation active in ECT was the disruption of that process; here, of the reconsolidation of retrieved fear memories by shock administration.
516:
the hippocampus is constantly involved in the encoding of new events and activation due to this fact is hard to separate using baseline measures. Because of this, activation of the hippocampus during retrieval of distant memories may simply be a
22:
is a category of processes that stabilize a memory trace after its initial acquisition. A memory trace is a change in the nervous system caused by memorizing something. Consolidation is distinguished into two specific processes. The first,
662:
activity following an enriched or novel waking experience, thus increasing neuronal plasticity and therefore playing an essential role in the consolidation of memories. This has come into question in recent years however and studies on
667:
have shown that animals and humans who are denied REM sleep do not show deficits in task learning. It has been proposed that since the brain is in a non-memory encoding state during sleep, consolidation would be unlikely to occur.
955:
by lengthening the reactivation phase. There have also been concerns about the use of reconsolidation research to justify psychotherapy treatments, and the generalizability of basic reconsolidation research into the therapy room
359:, and enhances relational memory consolidation. When interpreted in the context of synaptic consolidation, mechanisms of synaptic strengthening may depend on the spacing of memory reactivation to allow sufficient time for
354:
has been found to enhance memory consolidation, specifically for relational memory. Experimental results suggest that distributing learning over the course of 24 hours decreases the rate of forgetting compared to
570:
recall of facts, episodes, and lists, and its storage typically connected with the mediotemporal lobe and the hippocampal systems as it includes the encoding of both semantic and episodic information of events.
89:
and Alfons
Pilzecker who rediscovered the concept that memory takes time to fixate or undergo "Konsolidierung" in their studies conducted between 1892 and 1900. The two proposed the perseveration-consolidation
621:. Studies appear to suggest that the amygdala effects the consolidation of memories through its influence with stress hormones and the projections to other brain areas implicated in memory consolidation.
394:. However, other results have shown that protein synthesis may not in fact be necessary for memory consolidation, as it has been found that the formation of memories can withstand vast amounts of
843:
In addition to fear memories, appetitive memories are also prone to reconsolidation episodes, which can likewise be disrupted; namely, after local administration of a protein activity inhibitor.
710:
that are involved in the information flow between relevant brain areas. A more complete understanding of these mechanics may possibly allow purposely enabling or strengthening this reactivation.
964:
Questions arose if reconsolidation was a unique process or merely another phase of consolidation. Both consolidation and reconsolidation can be disrupted by pharmacological agents (e.g. the
745:
Memory reconsolidation is the process of previously consolidated memories being recalled and actively consolidated. It is a distinct process that serves to maintain, strengthen and modify
390:, weaken memory, suggesting that protein synthesis is required for memory consolidation. Additionally, reports have suggested that the effects of protein synthesis inhibitors also inhibit
924:
are more difficult to run than typical consolidation experiments as disruption of a previously consolidated memory must be shown to be specific to the reactivation of the original
2634:
Gais, Steffen; Hüllemann, Philipp; Hallschmid, Manfred; Born, Jan (2006). "Sleep-dependent surges in growth hormone do not contribute to sleep-dependent memory consolidation".
617:
was administered to the hippocampus, enhanced consolidation was seen during food-rewarded maze tasks. The opposite effect was also seen when the amygdala was inactivated using
765:
stable after retrieval is complete. It is believed that post-retrieval stabilization is different and distinct from consolidation, despite its overlap in function (e.g.
874:. Further studies have demonstrated an analogue of memory reconsolidation in spinal cord pain processing pathways, suggesting a general role for reconsolidation in the
147:
the patient began to suffer from memory impairments. Molaison lost the ability to encode and consolidate newly learned information leading researchers to conclude the
2685:
Rasch, Björn H.; Born, Jan; Gais, Steffen (2006-05-01). "Combined
Blockade of Cholinergic Receptors Shifts the Brain from Stimulus Encoding to Memory Consolidation".
3319:
Gräff J; Joseph NF; Horn ME; Samiei A; Meng J; Seo J; Rei D; Bero AW; Phan TX; Wagner F; Holson E; Xu J; Sun J; Neve RL; Mach RH; Haggarty SJ; Tsai LH. (Jan 2014).
781:
The theory of reconsolidation has been debated for many years and is still controversial. Reconsolidation was first conceptualized in light of the discovery that
846:
Since those breakthrough studies were done, there have been several others to probe the theory of memory reconsolidation. Subjects in these studies, along with
4187:
Nadel, L; Samsonovich, A; Ryan, L; Moscovitch, M (2000). "Multiple trace theory of human memory: Computational, neuroimaging, and neuropsychological results".
276:, are susceptible to disruptions. Disruptions caused by specific drugs, antibodies and gross physical trauma can block the effects of synaptic consolidation.
840:
These studies done by Nader and others seem to suggest that as memories are being remembered, they are fragile, as if experiencing them for the first time.
4007:
Tse, D.; Langston, R. F.; Kakeyama, M.; Bethus, I.; Spooner, P. A.; Wood, E. R.; Witter, M. P.; Morris, R. G. M. (2007). "Schemas and Memory
Consolidation".
1470:
Okuda, K.; Højgaard, K.; Privitera, R.; Bayraktar, G.; Takeuchi, T. (2020). "Initial memory consolidation and the synaptic tagging and capture hypothesis".
902:. Under this possibility, traditional disruptions of reconsolidation might actually maintain the original memory trace but preventing the consolidation of
822:, but not by infusions made six hours afterwards. It was concluded that consolidated fear memory, when reactivated, enters a changeable state that requires
3576:
Centonze, Diego; Siracusano, Alberto; Calabresi, Paolo; Bernardi, Giorgio (October 2005). "Removing pathogenic memories: a neurobiology of psychotherapy".
3844:
796:
agent (leads to memory loss). These studies found it to be effective on retrieved memories when administered directly after the retrieval of a memory.
3213:"Activation of PKCzeta and PKMzeta in the nucleus accumbens core is necessary for the retrieval, consolidation and reconsolidation of the drug memory"
753:. Once memories undergo the process of consolidation and become part of long-term memory, they are thought of as stable. However, the retrieval of a
4796:
2235:
Gold, Paul E.; Van
Buskirk, Roderick B. (February 1975). "Facilitation of time-dependent memory processes with posttrial epinephrine injections".
431:
The standard model of systems consolidation has been summarized by Squire and Alvarez (1995); it states that when novel information is originally
3622:
3095:
Kindt, Merel; Soeter, Marieke; Vervliet, Bram (2009-02-15). "Beyond extinction: erasing human fear responses and preventing the return of fear".
675:
Recent studies have examined the relationship between REM sleep and procedural learning consolidation. In particular studies have been done on
134:
2369:"Involvement of amygdala pathways in the influence of post-training intra-amygdala norepinephrine and peripheral epinephrine on memory storage"
2094:
Haist, F.; Bowden Gore, J. B.; Mao, H. (2001). "Consolidation of human memory over decades revealed by functional magnetic resonance imaging".
1196:
Nader, K.; Schafe, G. E.; LeDoux, J. E. (2000). "Fear memories require protein synthesis in the amygdala for reconsolidation after retrieval".
482:
Squire and Alvarez also proposed the idea that MTL structures play a role in the consolidation of memories within the neocortex by providing a
702:
Memory consolidation during sleep via reactivation of prior experiences and information is associated with sleep signatures of cortical "slow
3837:
But for a more hesitant view of the role of memory reconsolidation in psychotherapy that criticizes some of the claims of Ecker et al., see:
944:
is not just due to task impairment caused by the procedure, which can be demonstrated by testing control groups in absence of the original
31:, occurs on a small scale in the synaptic connections and neural circuits within the first few hours after learning. The second process is
4379:
5574:
5245:
1399:
Milner, B.; Corkin, S.; Teuber, H. -L. (1968). "Further analysis of the hippocampal amnesic syndrome: 14-year follow-up study of H.M".
4660:
4150:
McIntyre, C. K.; Power, A. N. E.; Roozendaal, B.; McGaugh, J. L. (2006). "Role of the Basolateral Amygdala in Memory Consolidation".
2464:
Walker, M.P.; Stickgold, R.; Alsop, D.; Gaab, N.; Schlaug, G. (2005). "Sleep-dependent motor memory plasticity in the human brain".
737:, suggest that a waking experience prior to sleep can have an enduring effect in the brain, due to an increase of neuroplasticity.
3146:
Schiller, Daniela; Monfils, Marie-H.; Raio, Candace M.; Johnson, David C.; LeDoux, Joseph E.; Phelps, Elizabeth A. (2009-12-09).
913:
modifications may also prevent reconsolidation in some cases. The removal of these epigenetic modifications with inhibitors of
2295:
1911:
1829:
5503:
3656:
1148:
Bramham, C. R.; Messaoudi, E. (2005). "BDNF function in adult synaptic plasticity: The synaptic consolidation hypothesis".
4210:
4870:
3696:"Memory reconsolidation, emotional arousal and the process of change in psychotherapy: new insights from brain science"
1052:
1580:"Food for thought: The role of dietary flavonoids in enhancing human memory, learning and neuro-cognitive performance"
3822:
1723:
Smith, Steven M.; Rothkopf, Ernst Z. (1984). "Contextual Enrichment and Distribution of Practice in the Classroom".
773:). Memory modification needs to be demonstrated in the retrieval in order for this independent process to be valid.
4255:
2192:
McGaugh, J. L.; Roozendaal, B. (2002). "Role of adrenal stress hormones in forming lasting memories in the brain".
608:
will block the retention of memory effects seen previously. This is supported by the fact that beta-adrenoreceptor
398:, suggesting that this criterion of protein synthesis as necessary for memory consolidation is not unconditional.
3695:
2957:
Solyom, L.; Kenny, F.; Ledwidge, B. (1969). "Psychotherapy: Evaluation of a New Treatment Paradigm for Phobias".
1932:
Squire, L. R.; Alvarez, P. (1995). "Retrograde amnesia and memory consolidation: A neurobiological perspective".
1072:
786:
733:
after pre-exposure to an enriched environment. Results from studies testing the effects of zif268 on mice brains
2422:"The basolateral amygdala is a cofactor in memory enhancement produced by intrahippocampal glutamate injections"
5238:
4743:
3703:
834:
792:
Further studies investigated the concept, using ECT to test for reconsolidation; ECT was already known as an
5345:
3529:"A requirement for the immediate early gene zif268 in reconsolidation of recognition memory after retrieval"
2316:"Modulating effects of posttraining epinephrine on memory: involvement of the amygdala noradrenergic system"
4791:
4692:
4579:
1620:
833:
Brunet and colleagues (2008) studied patients that had been diagnosed with Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (
2044:
Nadel, L.; Moscovitch, M. (1997). "Memory consolidation, retrograde amnesia and the hippocampal complex".
613:
resulting in a strengthened memory. This relationship was studied by Packard and Chen who found that when
237:
28:
5340:
395:
383:
3413:"Directly reactivated, but not indirectly reactivated, memories undergo reconsolidation in the amygdala"
2884:"Endogenous memory reactivation during sleep in humans is clocked by slow oscillation-spindle complexes"
4917:
4842:
4675:
3000:
Nader, Karim; Schafe, Glenn E.; LeDoux, Joseph E. (2000). "The labile nature of consolidation theory".
2798:
Wilhelm, Ines; Diekelmann, Susanne; Molzow, Ina; Ayoub, Amr; Mölle, Matthias; Born, Jan (2011-02-02).
5231:
3966:"Hippocampal replay in the awake state: A potential substrate for memory consolidation and retrieval"
1040:
4029:
2857:
2478:
5407:
5268:
4955:
4900:
4875:
4705:
4682:
4632:
4537:
4201:
1062:
79:
5528:
4642:
4408:
3922:
3368:
Patihis, L. (2015). "Let's be skeptical about reconsolidation and emotional arousal in therapy".
949:
903:
892:
299:
176:
3321:"Epigenetic priming of memory updating during reconsolidation to attenuate remote fear memories"
2279:
2271:
1067:
5498:
5300:
5049:
5009:
4910:
4879:
4517:
4305:
4196:
4024:
3810:
Unlocking the Emotional Brain: Eliminating Symptoms at Their Roots Using Memory Reconsolidation
3578:
2473:
965:
875:
391:
303:
285:
4064:"Dreaming of a Learning Task is Associated with Enhanced Sleep-Dependent Memory Consolidation"
3397:
2743:"Dreaming of a Learning Task is Associated with Enhanced Sleep-Dependent Memory Consolidation"
2368:
2315:
5548:
5513:
5293:
5278:
5064:
4779:
4665:
4637:
4622:
4617:
4455:
1036:
988:
436:
291:
273:
265:
43:
over a period of weeks to years. Recently, a third process has become the focus of research,
86:
4948:
4932:
4811:
4569:
4522:
4512:
4248:
4075:
4016:
3760:
3483:
3424:
3224:
3211:
Crespo, J.A.; Stöckl, P.; Ueberall, F.; Marcel, J.; Saria, A.; Zernig, G. (February 2012).
3159:
2895:
2754:
2155:
1575:
1311:
1205:
1123:
984:
973:
722:
601:
589:
572:
351:
148:
8:
5543:
5079:
4979:
4670:
4554:
4502:
4470:
4450:
3472:"Independent cellular processes for hippocampal memory consolidation and reconsolidation"
2882:
Schreiner, Thomas; Petzka, Marit; Staudigl, Tobias; Staresina, Bernhard P. (2021-05-25).
1978:
Frankland, P. W.; Bontempi, B. (2005). "The organization of recent and remote memories".
1019:
995:
914:
597:
326:
307:
261:
241:
140:
107:
4079:
4020:
3764:
3487:
3428:
3228:
3163:
2899:
2758:
2159:
1532:
Tronson, N. C.; Taylor, J. R. (2007). "Molecular mechanisms of memory reconsolidation".
1315:
1209:
223:, when discussed in the context of synaptic consolidation, is conventionally said to be
219:
is one form of memory consolidation seen across all species and long-term memory tasks.
5176:
5161:
4999:
4944:
4937:
4905:
4806:
4801:
4753:
4731:
4700:
4527:
4222:
4175:
4163:
4138:
4113:
McGaugh, J. L. (2002). "Memory consolidation and the amygdala: A systems perspective".
4096:
4063:
4050:
3990:
3965:
3869:
3781:
3746:
3603:
3558:
3509:
3447:
3412:
3345:
3320:
3296:
3271:
3247:
3212:
3188:
3147:
3128:
3033:
2924:
2883:
2834:
2799:
2775:
2742:
2718:
2667:
2613:
2499:
2487:
2443:
2399:
2346:
2217:
2119:
2069:
2003:
1957:
1874:
1849:
1797:
1661:
1621:"Long-term potentiation in the amygdala: A mechanism for emotional learning and memory"
1557:
1495:
1229:
1173:
1110:
Dudai, Y. (2004). "The Neurobiology of Consolidations, Or, How Stable is the Engram?".
1023:
703:
676:
559:
257:
175:
in an effort to identify brain substrates critical for slow consolidation. Meanwhile,
156:
131:
36:
4126:
3545:
3528:
2548:
2523:
2248:
2205:
2057:
1639:
1376:
1351:
537:
Nadel and Moscovitch argued that when studying the structures and systems involved in
5467:
5444:
5437:
5417:
5412:
5397:
5370:
5315:
5283:
5212:
5200:
5171:
5019:
4890:
4865:
4821:
4748:
4726:
4627:
4564:
4532:
4507:
4475:
4460:
4370:
4340:
4278:
4214:
4167:
4130:
4101:
4042:
3995:
3873:
3861:
3839:
3828:
3818:
3786:
3720:
3595:
3550:
3501:
3452:
3393:
3385:
3350:
3301:
3252:
3193:
3175:
3120:
3112:
3077:
3069:
3065:
3025:
3017:
2982:
2974:
2929:
2911:
2839:
2821:
2780:
2710:
2702:
2659:
2651:
2605:
2553:
2491:
2447:
2391:
2387:
2338:
2334:
2291:
2252:
2209:
2171:
2111:
2061:
1995:
1949:
1945:
1907:
1879:
1825:
1789:
1781:
1740:
1702:
1653:
1601:
1549:
1499:
1487:
1452:
1412:
1381:
1327:
1273:
1221:
1165:
1127:
1057:
1011:
888:
826:
815:
803:
770:
664:
563:
447:
regions. Later the hippocampus' representations of this information become active in
432:
415:
375:
360:
330:
311:
253:
197:
188:
82:
4226:
4142:
4054:
3607:
3562:
3513:
2671:
2350:
2221:
2123:
1801:
1665:
1177:
1161:
5533:
5472:
5387:
5151:
5104:
5074:
5029:
4885:
4816:
4769:
4574:
4549:
4435:
4395:
4283:
4206:
4179:
4159:
4122:
4091:
4083:
4034:
3985:
3977:
3853:
3776:
3768:
3751:
3742:
3738:
3712:
3665:
3587:
3540:
3491:
3442:
3432:
3377:
3340:
3332:
3291:
3283:
3242:
3232:
3183:
3167:
3132:
3104:
3061:
3037:
3009:
2966:
2919:
2903:
2829:
2816:
2811:
2770:
2762:
2722:
2694:
2647:
2643:
2595:
2543:
2535:
2503:
2483:
2433:
2403:
2383:
2330:
2283:
2244:
2201:
2163:
2103:
2073:
2053:
2007:
1987:
1961:
1941:
1869:
1861:
1771:
1732:
1692:
1643:
1635:
1591:
1561:
1541:
1479:
1442:
1408:
1371:
1363:
1319:
1263:
1233:
1213:
1157:
1119:
766:
750:
630:
512:
295:
252:
The standard model of synaptic consolidation suggests that alterations of synaptic
220:
4062:
Wamsley, E. J.; Tucker, M.; Payne, J. D.; Benavides, J. A.; Stickgold, R. (2010).
2741:
Wamsley, E. J.; Tucker, M.; Payne, J. D.; Benavides, J. A.; Stickgold, R. (2010).
2629:
2627:
2617:
932:
of reactivation occurs in a limited time frame, which can be assessed by delaying
98:
5569:
5477:
5422:
5392:
5380:
5335:
5320:
5089:
5069:
5044:
5034:
4989:
4984:
4738:
4710:
4445:
4428:
4423:
4418:
4413:
4288:
4241:
3808:
3747:"Preventing the return of fear in humans using reconsolidation update mechanisms"
3272:"A spinal analogue of memory reconsolidation enables the erasure of hyperalgesia"
3237:
3148:"Preventing the return of fear in humans using reconsolidation update mechanisms"
2600:
2583:
1901:
1819:
1447:
1430:
1323:
863:
651:
546:
542:
507:
503:
487:
483:
452:
448:
444:
269:
229:
183:
possibly responsible for fast consolidation. In recent decades, advancements in
5156:
5120:
5014:
4612:
4559:
4385:
4355:
4335:
4322:
3336:
2970:
2944:
2907:
2698:
2624:
356:
346:
184:
111:
4087:
3912:
3716:
3591:
3381:
2766:
1865:
1760:"Effects of spacing and embellishment on memory for the main points of a text"
1736:
1596:
1579:
5563:
5432:
5310:
5305:
5135:
5125:
5099:
5094:
5054:
5039:
5004:
4927:
4774:
4602:
4465:
4440:
4403:
4360:
4350:
4345:
4330:
3857:
3832:
3691:
3179:
3116:
3073:
3021:
2978:
2915:
2858:"Press (re)play to remember: How the brain strengthens memories during sleep"
2825:
2706:
2655:
1785:
1744:
933:
929:
726:
707:
323:
192:
137:
4038:
3496:
3471:
3437:
2167:
102:
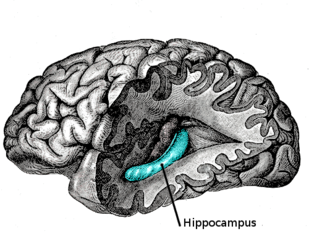
Lateral view of the hippocampus which is located in the medial temporal lobe
5375:
5166:
5130:
5084:
4994:
4837:
4652:
4607:
4594:
4584:
4544:
4264:
4218:
4171:
4134:
4105:
4046:
3999:
3865:
3790:
3724:
3599:
3554:
3505:
3456:
3389:
3354:
3305:
3256:
3197:
3124:
3081:
3029:
2933:
2843:
2784:
2714:
2663:
2609:
2557:
2524:"Brain Gene Expression During REM Sleep Depends on Prior Waking Experience"
2495:
2213:
2115:
1999:
1883:
1706:
1657:
1605:
1553:
1491:
1456:
1385:
1331:
1277:
1225:
1169:
1131:
925:
899:
799:
Later research, wherein fear memories had been established in rats through
754:
244:, is thought to be the cellular process underlying synaptic consolidation.
68:
67:
Memory consolidation was first referred to in the writings of the renowned
2986:
2395:
2342:
2256:
2175:
2065:
1953:
1793:
948:. Finally, it is important to rule out alternative explanations, such as
204:
dimension to the reorganization of the memory as it is represented in the
5352:
5325:
5288:
5024:
4895:
4849:
3649:"Transformative emotional sequence: towards a common principle of change"
3623:"Unlocking the emotional brain: finding the neural key to transformation"
1648:
1367:
1007:
910:
685:
680:
655:
647:
605:
463:
440:
411:
410:
consolidation. It is a reorganization process in which memories from the
171:
These studies were accompanied by the creation of animal models of human
123:
75:
40:
5523:
3772:
3171:
2270:
Gold, P. E.; McIntyre, C.; McNay, E.; Stefani, M.; Korol, D. L. (2001).
5362:
5059:
4922:
4489:
3687:
3648:
2539:
2438:
2421:
1821:
Cognitive Psychology: Connecting Mind, Research and Everyday Experience
1776:
1759:
1697:
1680:
969:
937:
936:
till six hours after reactivation. It is also useful to show that the
921:
819:
734:
593:
517:
475:
419:
91:
54:
3887:
3210:
2800:"Sleep Selectively Enhances Memory Expected to Be of Future Relevance"
2287:
1483:
1268:
1251:
5508:
5493:
5330:
5273:
5260:
4295:
3936:
3814:
3669:
3013:
1252:"Retrieval and reconsolidation: toward a neurobiology of remembering"
1217:
859:
800:
730:
635:
618:
614:
567:
553:
180:
152:
3981:
3287:
3108:
1991:
1545:
983:
is required for consolidation (but not reconsolidation) whereas the
891:, certain forms of memory reactivation could actually represent new
5518:
5427:
5223:
4784:
3575:
952:
945:
906:
895:
811:
746:
697:
659:
643:
609:
585:
471:
467:
387:
379:
334:
315:
233:
165:
144:
115:
72:
48:
2107:
1718:
1716:
994:
is required for reconsolidation but not consolidation. A similar
5538:
4497:
4211:
10.1002/1098-1063(2000)10:4<352::AID-HIPO2>3.0.CO;2-D
3917:
871:
867:
855:
793:
782:
490:
216:
172:
160:
127:
119:
2881:
642:
has been thought of to be an important concept in the overnight
5454:
4233:
3318:
1850:"Protein synthesis inhibition and memory: Formation vs amnesia"
1713:
1681:"Distributed learning enhances relational memory consolidation"
1469:
1015:
999:
991:
941:
807:
762:
758:
718:
579:
538:
407:
319:
240:, the long-lasting form of one of the best understood forms of
224:
4186:
4149:
502:
Multiple trace theory (MTT) builds on the distinction between
5401:
2939:
1302:
McGaugh, J. L. (2000). "Memory--a Century of Consolidation".
851:
847:
690:
639:
456:
205:
2797:
806:, found that a consolidated fear memory can be brought to a
4061:
2740:
2633:
1352:"Loss of Recent Memory After Bilateral Hippocampal Lesions"
1003:
980:
976:
201:
179:
studies of selected brain areas began to shed light on the
35:, occurring on a much larger scale in the brain, rendering
3741:; Monfils, Marie-H.; Raio, Candace M.; Johnson, David C.;
3737:
3145:
3050:
302:
sensitivity, lasting minutes to even days. The process of
4006:
3913:"Eliminate Core Beliefs - Morty Lefkoe on the Today Show"
2276:
Memory consolidation: Essays in honor of James L. McGaugh
558:
Learning can be distinguished by two forms of knowledge:
3411:
Debiec, J.; Doyere, V.; Nader, K.; LeDoux, J.E. (2006).
3269:
3158:(7277). Springer Science and Business Media LLC: 49–53.
2463:
2269:
1899:
928:. Furthermore, it is important to demonstrate that the
290:
LTP can be thought of as the prolonged strengthening of
155:
involved in this process. Molaison also showed signs of
47:, in which previously consolidated memories can be made
3410:
3103:(3). Springer Science and Business Media LLC: 256–258.
3008:(3). Springer Science and Business Media LLC: 216–219.
761:
phase that then requires an active process to make the
130:
and their effect on memory. After Molaison underwent a
3685:
1770:(2). Springer Science and Business Media LLC: 97–102.
725:(IEG) thought to be involved in neuroplasticity by an
110:
started to emerge in the 1960s and 1970s. The case of
1900:
Roediger, H.L.; Dudai, Y.; Fitzpatrick, S.M. (2007).
917:
enabled the erasure of remote memories after recall.
3263:
2419:
474:
experience, the memory is slowly transferred to the
159:
spanning a period of about three years prior to the
3807:Ecker, Bruce; Ticic, Robin; Hulley, Laurel (2012).
3094:
2956:
2093:
2039:
2037:
1424:
1422:
1356:
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry
1029:
363:to occur, and thereby strengthen long-term memory.
3845:Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association
3470:Lee, J. L.; Everitt, B. J.; Thomas, K. L. (2004).
2272:"Neurochemical referees of dueling memory systems"
2035:
2033:
2031:
2029:
2027:
2025:
2023:
2021:
2019:
2017:
1398:
979:. However, recent amygdala research suggests that
959:
554:Declarative vs. procedural knowledge consolidation
3964:Carr, M. F.; Jadhav, S. P.; Frank, L. M. (2011).
3526:
2999:
2420:Packard, Mark G; Chen, Scott A (September 1999).
2367:Liang, KC; McGaugh, JL; Yao, HY (February 1990).
2313:
2191:
2187:
2185:
1977:
1813:
1811:
1195:
5561:
3806:
3469:
2314:Liang, KC; Juler, RG; McGaugh, JL (March 1986).
1463:
1431:"The consolidation and transformation of memory"
1419:
1345:
1343:
1341:
1147:
698:Cortical slow oscillation- and spindle-complexes
378:plays an important role in the formation of new
337:synaptic transmission that would result in LTP.
51:again through reactivation of the memory trace.
3963:
2366:
2234:
2043:
2014:
1297:
1295:
1293:
1291:
1289:
1287:
532:
520:of the subject encoding the study as an event.
3642:
3640:
2228:
2182:
2146:Squire, L. R. (1986). "Mechanisms of memory".
1927:
1925:
1923:
1808:
1428:
1349:
1143:
1141:
672:and therefore assist in the learning process.
329:appear to block the induction of both LTP and
5239:
4249:
3888:"How the Lefkoe Belief Process works, Part 1"
2684:
1931:
1757:
1722:
1678:
1531:
1338:
646:in humans by establishing information in the
126:and sparked massive interest in the study of
58:The line processes to make information memory
3802:
3800:
1973:
1971:
1284:
580:Emotional and stressful memory consolidation
406:Systems consolidation is the second form of
4380:The Magical Number Seven, Plus or Minus Two
3681:
3679:
3637:
3204:
1920:
1895:
1893:
1758:Reder, Lynne M.; Anderson, John R. (1982).
1138:
294:, and is known to produce increases in the
114:, formerly known as patient H.M., became a
5246:
5232:
4256:
4242:
4152:Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences
3527:Bozon, B.; Davis, S.; Laroche, S. (2003).
2736:
2734:
2732:
2517:
2515:
2513:
2415:
2413:
1527:
1525:
1523:
1521:
1519:
1517:
1515:
1513:
1511:
1509:
4200:
4095:
4028:
3989:
3797:
3780:
3544:
3495:
3446:
3436:
3344:
3295:
3246:
3236:
3187:
2923:
2833:
2815:
2774:
2599:
2577:
2575:
2573:
2571:
2569:
2567:
2547:
2477:
2459:
2457:
2437:
2362:
2360:
2141:
2139:
2137:
2135:
2133:
1968:
1873:
1817:
1775:
1696:
1647:
1595:
1446:
1375:
1267:
713:
279:
211:
3838:
3676:
3270:Bonin R. P. & De Koninck Y. (2014).
2959:Canadian Psychiatric Association Journal
2309:
2307:
2089:
2087:
2085:
2083:
1890:
497:
401:
306:is regarded as a contributing factor to
168:in the consolidating nature of the MTL.
97:
53:
16:Category of memory stabilizing processes
4112:
3745:; Phelps, Elizabeth A. (January 2010).
3646:
3367:
2729:
2521:
2510:
2410:
1843:
1841:
1574:
1568:
1506:
1429:Dudai, Y.; Karni, A.; Born, J. (2015).
1301:
1191:
1189:
1187:
1105:
1103:
1101:
1099:
1097:
1095:
1093:
1091:
1089:
1087:
566:. Declarative information includes the
5562:
2581:
2564:
2454:
2357:
2145:
2130:
1672:
1245:
1243:
1124:10.1146/annurev.psych.55.090902.142050
785:could often be eliminated by means of
624:
118:in studies of memory as it relates to
5227:
4237:
3620:
2304:
2263:
2080:
1618:
1612:
1392:
1109:
940:measure used to assess disruption of
333:and that fear conditioning increases
5253:
3842:(April 2015). "Commentary on Tuch".
3657:Journal of Psychotherapy Integration
3312:
1847:
1838:
1584:Proceedings of the Nutrition Society
1350:Scoville, W. B.; Milner, B. (1957).
1249:
1184:
1084:
435:and registered, memory of these new
370:
27:, which is thought to correspond to
1854:Neurobiology of Learning and Memory
1240:
1006:for consolidation was found in the
729:of the transcription factor during
658:. REM sleep elicits an increase in
426:
264:. These molecular cascades trigger
262:intracellular transduction cascades
164:removal which points to a temporal
13:
4164:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb07088.x
3957:
2488:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2005.04.007
1824:(4th ed.). Cengage Learning.
1731:(3). Informa UK Limited: 341–358.
740:
14:
5586:
5575:Unsolved problems in neuroscience
4661:Deese–Roediger–McDermott paradigm
2687:Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience
909:. Recent work has suggested that
898:rather than activation of an old
466:for up to one week after initial
414:region, where memories are first
340:
247:
29:late-phase long-term potentiation
5206:
5194:
4263:
3925:from the original on 2021-12-15.
3066:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2007.05.006
2938:
1679:Litman, L.; Davachi, L. (2008).
1472:European Journal of Neuroscience
1030:Reconsolidation in psychotherapy
260:are achieved through activating
3929:
3905:
3880:
3731:
3621:Ecker, Bruce (September 2008).
3614:
3569:
3520:
3463:
3404:
3361:
3139:
3088:
3054:Journal of Psychiatric Research
3044:
2993:
2950:
2875:
2850:
2791:
2678:
2584:"Memory Consolidation in Sleep"
2194:Current Opinion in Neurobiology
2046:Current Opinion in Neurobiology
1934:Current Opinion in Neurobiology
1751:
1162:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2005.06.003
960:Distinctions from consolidation
881:
787:electroconvulsive shock therapy
749:that are already stored in the
4871:Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model
4744:Memory and social interactions
2817:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3575-10.2011
2648:10.1016/j.psyneuen.2006.02.009
1053:Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model
1:
4127:10.1016/S0166-2236(02)02211-7
3704:Behavioral and Brain Sciences
3686:Lane, Richard D.; Ryan, Lee;
3546:10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00674-3
3370:Behavioral and Brain Sciences
2249:10.1016/S0091-6773(75)91784-8
2206:10.1016/S0959-4388(02)00306-9
2058:10.1016/S0959-4388(97)80010-4
1640:10.1016/S0166-2236(99)01465-4
1078:
810:state, by means of immediate
523:
455:(unconscious) recall like in
439:becomes retained in both the
5408:Perception as interpretation
4580:Retrieval-induced forgetting
3238:10.1371/journal.pone.0030502
2601:10.1016/j.neuron.2004.08.034
2388:10.1016/0006-8993(90)90400-6
2335:10.1016/0006-8993(86)91049-8
1946:10.1016/0959-4388(95)80023-9
1448:10.1016/j.neuron.2015.09.004
1413:10.1016/0028-3932(68)90021-3
1324:10.1126/science.287.5451.248
776:
533:Semantic vs. episodic memory
396:protein synthesis inhibition
384:protein synthesis inhibitors
39:memories independent of the
7:
3647:Welling, Hans (June 2012).
3060:(6). Elsevier BV: 503–506.
3002:Nature Reviews Neuroscience
2642:(6). Elsevier BV: 786–791.
1980:Nature Reviews Neuroscience
1906:. Oxford University Press.
1903:Science of Memory: Concepts
1534:Nature Reviews Neuroscience
1112:Annual Review of Psychology
1073:Sharp wave–ripple complexes
1046:
1041:many forms of psychotherapy
769:) and its mechanisms (e.g.
200:suggesting that there is a
10:
5591:
4918:Levels of Processing model
4843:World Memory Championships
4676:Lost in the mall technique
4523:dissociative (psychogenic)
3337:10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.020
2971:10.1177/070674376901400102
2908:10.1038/s41467-021-23520-2
2699:10.1162/jocn.2006.18.5.793
628:
462:Memory is retained in the
382:. Studies have shown that
344:
322:in mammals. Specifically,
283:
62:
5486:
5453:
5361:
5259:
5189:
5144:
5113:
4972:
4965:
4858:
4830:
4762:
4719:
4691:
4651:
4593:
4488:
4394:
4369:
4321:
4314:
4271:
4088:10.1016/j.cub.2010.03.027
3717:10.1017/S0140525X14000041
3382:10.1017/S0140525X14000272
2767:10.1016/j.cub.2010.03.027
1866:10.1016/j.nlm.2007.10.006
1737:10.1207/s1532690xci0103_4
1725:Cognition and Instruction
1597:10.1017/S0029665108007088
459:and 'offline' processes.
4956:The Seven Sins of Memory
4901:Intermediate-term memory
4706:Indirect tests of memory
4683:Recovered-memory therapy
4633:Misattribution of memory
3858:10.1177/0003065115579720
2636:Psychoneuroendocrinology
1818:Goldstein, E.B. (2014).
1150:Progress in Neurobiology
1002:for reconsolidation and
268:that lead to changes in
5529:Relational frame theory
5504:Higher nervous activity
4643:Source-monitoring error
4115:Trends in Neurosciences
4039:10.1126/science.1135935
3627:Psychotherapy Networker
3497:10.1126/science.1095760
3438:10.1073/pnas.0507168103
2804:Journal of Neuroscience
2168:10.1126/science.3086978
1628:Trends in Neurosciences
972:) and both require the
151:(MTL) was an important
122:and the removal of the
5499:Experiential avoidance
5050:George Armitage Miller
5010:Patricia Goldman-Rakic
3579:Molecular Neurobiology
2582:Vertes, R. P. (2004).
1764:Memory & Cognition
876:central nervous system
714:Zif268 & REM sleep
451:(conscious) recall or
286:Long-term potentiation
280:Long-term potentiation
217:Synaptic consolidation
212:Synaptic consolidation
106:Systematic studies of
103:
59:
25:synaptic consolidation
5514:Ironic process theory
5279:Cognitive flexibility
5213:Philosophy portal
5201:Psychology portal
5065:Henry L. Roediger III
4666:False memory syndrome
4638:Misinformation effect
4618:Imagination inflation
3840:Alberini, Cristina M.
2888:Nature Communications
2528:Learning & Memory
598:beta-andrenoreceptors
498:Multiple trace theory
402:Systems consolidation
310:and in the growth of
292:synaptic transmission
274:immediate early genes
266:transcription factors
101:
57:
37:hippocampus-dependent
33:systems consolidation
4570:Motivated forgetting
3941:The Lefkoe Institute
3937:"About Morty Lefkoe"
3892:The Lefkoe Institute
3692:Greenberg, Leslie S.
2522:Ribeiro, S. (1999).
1848:Gold, P. E. (2008).
1368:10.1136/jnnp.20.1.11
989:immediate early gene
985:transcription factor
974:transcription factor
723:Immediate early gene
573:Procedural knowledge
352:Distributed learning
177:neuropharmacological
149:medial temporal lobe
20:Memory consolidation
5544:Thought suppression
5080:Arthur P. Shimamura
4980:Richard C. Atkinson
4797:Effects of exercise
4671:Memory implantation
4555:Interference theory
4471:Selective retention
4451:Meaningful learning
4080:2010CBio...20..850W
4021:2007Sci...316...76T
3970:Nature Neuroscience
3773:10.1038/nature08637
3765:2010Natur.463...49S
3592:10.1385/MN:32:2:123
3488:2004Sci...304..839L
3429:2006PNAS..103.3428D
3229:2012PLoSO...730502C
3172:10.1038/nature08637
3164:2010Natur.463...49S
3097:Nature Neuroscience
2900:2021NatCo..12.3112S
2759:2010CBio...20..850W
2160:1986Sci...232.1612S
2154:(4758): 1612–1619.
2096:Nature Neuroscience
1316:2000Sci...287..248M
1210:2000Natur.406..722N
1020:double dissociation
1014:. However, not all
996:double dissociation
915:histone deacetylase
625:Sleep consolidation
588:, specifically the
418:, are moved to the
386:administered after
308:synaptic plasticity
242:synaptic plasticity
108:anterograde amnesia
5177:Andriy Slyusarchuk
5000:Hermann Ebbinghaus
4906:Involuntary memory
4807:Memory improvement
4792:Effects of alcohol
4754:Transactive memory
4732:Politics of memory
4701:Exceptional memory
2540:10.1101/lm.6.5.500
2439:10.3758/BF03332131
2237:Behavioral Biology
1777:10.3758/bf03209210
1698:10.1101/lm.1132008
1619:Maren, S. (1999).
1024:object recognition
757:can cause another
636:Rapid eye movement
590:basolateral region
486:area for multiple
258:membrane potential
157:retrograde amnesia
145:epileptic symptoms
104:
60:
5557:
5556:
5316:Critical thinking
5284:Cognitive liberty
5221:
5220:
5185:
5184:
5172:Cosmos Rossellius
5020:Marcia K. Johnson
4891:Exosomatic memory
4876:Context-dependent
4866:Absent-mindedness
4749:Memory conformity
4727:Collective memory
4628:Memory conformity
4565:Memory inhibition
4484:
4483:
4476:Tip of the tongue
3943:. 18 January 2008
3743:LeDoux, Joseph E.
3739:Schiller, Daniela
3482:(5672): 839–843.
2862:medicalxpress.com
2297:978-1-55798-783-9
2288:10.1037/10413-012
2102:(11): 1139–1145.
1913:978-0-19-972751-3
1831:978-1-305-17699-7
1576:Spencer, J. P. E.
1484:10.1111/ejn.14902
1310:(5451): 248–251.
1269:10.1101/lm.7.2.73
1250:Sara, SJ (2000).
1204:(6797): 722–726.
1058:Coherence therapy
1012:fear conditioning
966:protein synthesis
889:fear conditioning
827:protein synthesis
816:protein synthesis
814:infusions of the
804:fear conditioning
771:protein synthesis
665:sleep deprivation
376:Protein synthesis
371:Protein synthesis
361:protein synthesis
331:fear conditioning
312:synaptic strength
254:protein synthesis
189:molecular biology
83:Law of Regression
5582:
5254:Mental processes
5248:
5241:
5234:
5225:
5224:
5211:
5210:
5209:
5199:
5198:
5197:
5152:Jonathan Hancock
5105:Robert Stickgold
5075:Richard Shiffrin
5030:Elizabeth Loftus
4970:
4969:
4886:Childhood memory
4693:Research methods
4575:Repressed memory
4550:Forgetting curve
4538:transient global
4409:Autobiographical
4319:
4318:
4258:
4251:
4244:
4235:
4234:
4230:
4204:
4183:
4146:
4109:
4099:
4058:
4032:
4003:
3993:
3952:
3951:
3949:
3948:
3933:
3927:
3926:
3909:
3903:
3902:
3900:
3899:
3884:
3878:
3877:
3836:
3804:
3795:
3794:
3784:
3735:
3729:
3728:
3700:
3683:
3674:
3673:
3670:10.1037/a0027786
3653:
3644:
3635:
3634:
3618:
3612:
3611:
3573:
3567:
3566:
3548:
3524:
3518:
3517:
3499:
3467:
3461:
3460:
3450:
3440:
3423:(9): 3428–3433.
3408:
3402:
3401:
3365:
3359:
3358:
3348:
3331:(1–2): 261–276.
3316:
3310:
3309:
3299:
3282:(8): 1043–1045.
3267:
3261:
3260:
3250:
3240:
3208:
3202:
3201:
3191:
3143:
3137:
3136:
3092:
3086:
3085:
3048:
3042:
3041:
3014:10.1038/35044580
2997:
2991:
2990:
2954:
2948:
2943:Available under
2942:
2937:
2927:
2879:
2873:
2872:
2870:
2868:
2854:
2848:
2847:
2837:
2819:
2810:(5): 1563–1569.
2795:
2789:
2788:
2778:
2738:
2727:
2726:
2682:
2676:
2675:
2631:
2622:
2621:
2603:
2579:
2562:
2561:
2551:
2519:
2508:
2507:
2481:
2461:
2452:
2451:
2441:
2417:
2408:
2407:
2373:
2364:
2355:
2354:
2320:
2311:
2302:
2301:
2267:
2261:
2260:
2232:
2226:
2225:
2189:
2180:
2179:
2143:
2128:
2127:
2091:
2078:
2077:
2041:
2012:
2011:
1975:
1966:
1965:
1929:
1918:
1917:
1897:
1888:
1887:
1877:
1845:
1836:
1835:
1815:
1806:
1805:
1779:
1755:
1749:
1748:
1720:
1711:
1710:
1700:
1676:
1670:
1669:
1651:
1625:
1616:
1610:
1609:
1599:
1572:
1566:
1565:
1529:
1504:
1503:
1478:(8): 6826–6849.
1467:
1461:
1460:
1450:
1426:
1417:
1416:
1401:Neuropsychologia
1396:
1390:
1389:
1379:
1347:
1336:
1335:
1299:
1282:
1281:
1271:
1247:
1238:
1237:
1218:10.1038/35021052
1193:
1182:
1181:
1145:
1136:
1135:
1107:
1018:tasks show this
920:Reconsolidation
850:, have included
751:long-term memory
631:Sleep and memory
513:autobiographical
296:neurotransmitter
221:Long-term memory
124:hippocampal zone
5590:
5589:
5585:
5584:
5583:
5581:
5580:
5579:
5560:
5559:
5558:
5553:
5482:
5449:
5357:
5336:Problem solving
5321:Decision-making
5255:
5252:
5222:
5217:
5207:
5205:
5195:
5193:
5181:
5162:Dominic O'Brien
5140:
5109:
5090:Susumu Tonegawa
5070:Daniel Schacter
5045:Eleanor Maguire
5035:Geoffrey Loftus
4990:Stephen J. Ceci
4985:Robert A. Bjork
4961:
4880:state-dependent
4854:
4826:
4758:
4739:Cultural memory
4715:
4711:Memory disorder
4687:
4647:
4589:
4480:
4390:
4365:
4310:
4267:
4262:
4068:Current Biology
4030:10.1.1.385.8987
4015:(5821): 76–82.
3982:10.1038/nn.2732
3960:
3958:Further reading
3955:
3946:
3944:
3935:
3934:
3930:
3921:. 7 July 2009.
3911:
3910:
3906:
3897:
3895:
3886:
3885:
3881:
3825:
3805:
3798:
3759:(7277): 49–53.
3736:
3732:
3698:
3684:
3677:
3651:
3645:
3638:
3619:
3615:
3574:
3570:
3525:
3521:
3468:
3464:
3409:
3405:
3366:
3362:
3317:
3313:
3288:10.1038/nn.3758
3268:
3264:
3209:
3205:
3144:
3140:
3109:10.1038/nn.2271
3093:
3089:
3049:
3045:
2998:
2994:
2955:
2951:
2880:
2876:
2866:
2864:
2856:
2855:
2851:
2796:
2792:
2747:Current Biology
2739:
2730:
2683:
2679:
2632:
2625:
2580:
2565:
2520:
2511:
2479:10.1.1.471.2164
2462:
2455:
2418:
2411:
2371:
2365:
2358:
2318:
2312:
2305:
2298:
2268:
2264:
2233:
2229:
2190:
2183:
2144:
2131:
2092:
2081:
2042:
2015:
1992:10.1038/nrn1607
1976:
1969:
1930:
1921:
1914:
1898:
1891:
1846:
1839:
1832:
1816:
1809:
1756:
1752:
1721:
1714:
1677:
1673:
1634:(12): 561–567.
1623:
1617:
1613:
1573:
1569:
1546:10.1038/nrn2090
1530:
1507:
1468:
1464:
1427:
1420:
1397:
1393:
1348:
1339:
1300:
1285:
1248:
1241:
1194:
1185:
1146:
1139:
1108:
1085:
1081:
1049:
1032:
962:
884:
779:
743:
741:Reconsolidation
716:
700:
654:regions of the
633:
627:
582:
556:
547:episodic memory
543:semantic memory
541:consolidation,
535:
526:
508:episodic memory
504:semantic memory
500:
429:
404:
373:
357:massed learning
349:
343:
298:production and
288:
282:
270:gene expression
256:and changes in
250:
230:memory encoding
214:
65:
45:reconsolidation
17:
12:
11:
5:
5588:
5578:
5577:
5572:
5555:
5554:
5552:
5551:
5546:
5541:
5536:
5531:
5526:
5524:Mental fatigue
5521:
5516:
5511:
5506:
5501:
5496:
5490:
5488:
5484:
5483:
5481:
5480:
5475:
5470:
5465:
5459:
5457:
5451:
5450:
5448:
5447:
5442:
5441:
5440:
5435:
5430:
5420:
5415:
5410:
5405:
5395:
5390:
5385:
5384:
5383:
5373:
5367:
5365:
5359:
5358:
5356:
5355:
5350:
5349:
5348:
5343:
5333:
5328:
5323:
5318:
5313:
5308:
5303:
5298:
5297:
5296:
5286:
5281:
5276:
5271:
5265:
5263:
5257:
5256:
5251:
5250:
5243:
5236:
5228:
5219:
5218:
5216:
5215:
5203:
5190:
5187:
5186:
5183:
5182:
5180:
5179:
5174:
5169:
5164:
5159:
5157:Paul R. McHugh
5154:
5148:
5146:
5142:
5141:
5139:
5138:
5133:
5128:
5123:
5117:
5115:
5111:
5110:
5108:
5107:
5102:
5097:
5092:
5087:
5082:
5077:
5072:
5067:
5062:
5057:
5052:
5047:
5042:
5037:
5032:
5027:
5022:
5017:
5015:Ivan Izquierdo
5012:
5007:
5002:
4997:
4992:
4987:
4982:
4976:
4974:
4967:
4963:
4962:
4960:
4959:
4952:
4942:
4941:
4940:
4930:
4925:
4920:
4915:
4914:
4913:
4903:
4898:
4893:
4888:
4883:
4873:
4868:
4862:
4860:
4856:
4855:
4853:
4852:
4847:
4846:
4845:
4834:
4832:
4828:
4827:
4825:
4824:
4819:
4814:
4809:
4804:
4799:
4794:
4789:
4788:
4787:
4782:
4772:
4766:
4764:
4760:
4759:
4757:
4756:
4751:
4746:
4741:
4736:
4735:
4734:
4723:
4721:
4717:
4716:
4714:
4713:
4708:
4703:
4697:
4695:
4689:
4688:
4686:
4685:
4680:
4679:
4678:
4668:
4663:
4657:
4655:
4649:
4648:
4646:
4645:
4640:
4635:
4630:
4625:
4620:
4615:
4613:Hindsight bias
4610:
4605:
4599:
4597:
4591:
4590:
4588:
4587:
4582:
4577:
4572:
4567:
4562:
4560:Memory erasure
4557:
4552:
4547:
4542:
4541:
4540:
4535:
4530:
4525:
4520:
4518:post-traumatic
4515:
4510:
4505:
4494:
4492:
4486:
4485:
4482:
4481:
4479:
4478:
4473:
4468:
4463:
4458:
4456:Personal-event
4453:
4448:
4443:
4438:
4433:
4432:
4431:
4426:
4421:
4411:
4406:
4400:
4398:
4392:
4391:
4389:
4388:
4386:Working memory
4383:
4375:
4373:
4367:
4366:
4364:
4363:
4358:
4356:Motor learning
4353:
4348:
4343:
4338:
4333:
4327:
4325:
4316:
4312:
4311:
4309:
4308:
4303:
4298:
4292:
4291:
4286:
4281:
4275:
4273:
4272:Basic concepts
4269:
4268:
4261:
4260:
4253:
4246:
4238:
4232:
4231:
4202:10.1.1.90.9696
4184:
4147:
4121:(9): 456–461.
4110:
4074:(9): 850–855.
4059:
4004:
3976:(2): 147–153.
3959:
3956:
3954:
3953:
3928:
3904:
3879:
3852:(2): 317–330.
3823:
3796:
3730:
3675:
3664:(2): 109–136.
3636:
3613:
3586:(2): 123–132.
3568:
3539:(4): 695–701.
3519:
3462:
3403:
3360:
3311:
3262:
3203:
3138:
3087:
3043:
2992:
2949:
2874:
2849:
2790:
2753:(9): 850–855.
2728:
2693:(5): 793–802.
2677:
2623:
2594:(1): 135–148.
2563:
2534:(5): 500–510.
2509:
2472:(4): 911–917.
2453:
2432:(3): 377–385.
2409:
2356:
2303:
2296:
2262:
2243:(2): 145–153.
2227:
2200:(2): 205–210.
2181:
2129:
2079:
2052:(2): 217–227.
2013:
1986:(2): 119–130.
1967:
1940:(2): 169–177.
1919:
1912:
1889:
1860:(3): 201–211.
1837:
1830:
1807:
1750:
1712:
1691:(9): 711–716.
1671:
1611:
1590:(2): 238–252.
1567:
1540:(4): 262–275.
1505:
1462:
1418:
1407:(3): 215–234.
1391:
1337:
1283:
1239:
1183:
1137:
1082:
1080:
1077:
1076:
1075:
1070:
1065:
1060:
1055:
1048:
1045:
1031:
1028:
961:
958:
883:
880:
870:, and various
778:
775:
742:
739:
715:
712:
708:sleep spindles
699:
696:
626:
623:
581:
578:
555:
552:
534:
531:
525:
522:
499:
496:
428:
427:Standard model
425:
403:
400:
372:
369:
347:Spacing effect
345:Main article:
342:
341:Spacing effect
339:
284:Main article:
281:
278:
249:
248:Standard model
246:
238:Late-phase LTP
213:
210:
187:preparations,
112:Henry Molaison
64:
61:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
5587:
5576:
5573:
5571:
5568:
5567:
5565:
5550:
5547:
5545:
5542:
5540:
5537:
5535:
5532:
5530:
5527:
5525:
5522:
5520:
5517:
5515:
5512:
5510:
5507:
5505:
5502:
5500:
5497:
5495:
5492:
5491:
5489:
5485:
5479:
5476:
5474:
5471:
5469:
5466:
5464:
5463:Consolidation
5461:
5460:
5458:
5456:
5452:
5446:
5443:
5439:
5436:
5434:
5431:
5429:
5426:
5425:
5424:
5421:
5419:
5416:
5414:
5411:
5409:
5406:
5403:
5399:
5396:
5394:
5391:
5389:
5386:
5382:
5379:
5378:
5377:
5374:
5372:
5369:
5368:
5366:
5364:
5360:
5354:
5351:
5347:
5344:
5342:
5339:
5338:
5337:
5334:
5332:
5329:
5327:
5324:
5322:
5319:
5317:
5314:
5312:
5311:Consciousness
5309:
5307:
5306:Comprehension
5304:
5302:
5299:
5295:
5292:
5291:
5290:
5287:
5285:
5282:
5280:
5277:
5275:
5272:
5270:
5267:
5266:
5264:
5262:
5258:
5249:
5244:
5242:
5237:
5235:
5230:
5229:
5226:
5214:
5204:
5202:
5192:
5191:
5188:
5178:
5175:
5173:
5170:
5168:
5165:
5163:
5160:
5158:
5155:
5153:
5150:
5149:
5147:
5143:
5137:
5136:Clive Wearing
5134:
5132:
5129:
5127:
5124:
5122:
5119:
5118:
5116:
5112:
5106:
5103:
5101:
5100:Endel Tulving
5098:
5096:
5095:Anne Treisman
5093:
5091:
5088:
5086:
5083:
5081:
5078:
5076:
5073:
5071:
5068:
5066:
5063:
5061:
5058:
5056:
5055:Brenda Milner
5053:
5051:
5048:
5046:
5043:
5041:
5040:James McGaugh
5038:
5036:
5033:
5031:
5028:
5026:
5023:
5021:
5018:
5016:
5013:
5011:
5008:
5006:
5005:Sigmund Freud
5003:
5001:
4998:
4996:
4993:
4991:
4988:
4986:
4983:
4981:
4978:
4977:
4975:
4971:
4968:
4964:
4958:
4957:
4953:
4950:
4949:retrospective
4946:
4943:
4939:
4936:
4935:
4934:
4931:
4929:
4928:Muscle memory
4926:
4924:
4921:
4919:
4916:
4912:
4909:
4908:
4907:
4904:
4902:
4899:
4897:
4894:
4892:
4889:
4887:
4884:
4881:
4877:
4874:
4872:
4869:
4867:
4864:
4863:
4861:
4857:
4851:
4848:
4844:
4841:
4840:
4839:
4836:
4835:
4833:
4829:
4823:
4820:
4818:
4815:
4813:
4810:
4808:
4805:
4803:
4800:
4798:
4795:
4793:
4790:
4786:
4783:
4781:
4778:
4777:
4776:
4775:Art of memory
4773:
4771:
4768:
4767:
4765:
4761:
4755:
4752:
4750:
4747:
4745:
4742:
4740:
4737:
4733:
4730:
4729:
4728:
4725:
4724:
4722:
4718:
4712:
4709:
4707:
4704:
4702:
4699:
4698:
4696:
4694:
4690:
4684:
4681:
4677:
4674:
4673:
4672:
4669:
4667:
4664:
4662:
4659:
4658:
4656:
4654:
4650:
4644:
4641:
4639:
4636:
4634:
4631:
4629:
4626:
4624:
4623:Memory biases
4621:
4619:
4616:
4614:
4611:
4609:
4606:
4604:
4603:Confabulation
4601:
4600:
4598:
4596:
4595:Memory errors
4592:
4586:
4583:
4581:
4578:
4576:
4573:
4571:
4568:
4566:
4563:
4561:
4558:
4556:
4553:
4551:
4548:
4546:
4543:
4539:
4536:
4534:
4531:
4529:
4526:
4524:
4521:
4519:
4516:
4514:
4513:post-hypnotic
4511:
4509:
4506:
4504:
4501:
4500:
4499:
4496:
4495:
4493:
4491:
4487:
4477:
4474:
4472:
4469:
4467:
4466:Rote learning
4464:
4462:
4459:
4457:
4454:
4452:
4449:
4447:
4444:
4442:
4441:Hyperthymesia
4439:
4437:
4434:
4430:
4427:
4425:
4422:
4420:
4417:
4416:
4415:
4412:
4410:
4407:
4405:
4404:Active recall
4402:
4401:
4399:
4397:
4393:
4387:
4384:
4381:
4377:
4376:
4374:
4372:
4368:
4362:
4359:
4357:
4354:
4352:
4349:
4347:
4344:
4342:
4339:
4337:
4334:
4332:
4329:
4328:
4326:
4324:
4320:
4317:
4313:
4307:
4304:
4302:
4301:Consolidation
4299:
4297:
4294:
4293:
4290:
4287:
4285:
4282:
4280:
4277:
4276:
4274:
4270:
4266:
4259:
4254:
4252:
4247:
4245:
4240:
4239:
4236:
4228:
4224:
4220:
4216:
4212:
4208:
4203:
4198:
4195:(4): 352–68.
4194:
4190:
4185:
4181:
4177:
4173:
4169:
4165:
4161:
4157:
4153:
4148:
4144:
4140:
4136:
4132:
4128:
4124:
4120:
4116:
4111:
4107:
4103:
4098:
4093:
4089:
4085:
4081:
4077:
4073:
4069:
4065:
4060:
4056:
4052:
4048:
4044:
4040:
4036:
4031:
4026:
4022:
4018:
4014:
4010:
4005:
4001:
3997:
3992:
3987:
3983:
3979:
3975:
3971:
3967:
3962:
3961:
3942:
3938:
3932:
3924:
3920:
3919:
3914:
3908:
3893:
3889:
3883:
3875:
3871:
3867:
3863:
3859:
3855:
3851:
3847:
3846:
3841:
3834:
3830:
3826:
3824:9780415897167
3820:
3816:
3812:
3811:
3803:
3801:
3792:
3788:
3783:
3778:
3774:
3770:
3766:
3762:
3758:
3754:
3753:
3748:
3744:
3740:
3734:
3726:
3722:
3718:
3714:
3710:
3706:
3705:
3697:
3693:
3689:
3682:
3680:
3671:
3667:
3663:
3659:
3658:
3650:
3643:
3641:
3632:
3628:
3624:
3617:
3609:
3605:
3601:
3597:
3593:
3589:
3585:
3581:
3580:
3572:
3564:
3560:
3556:
3552:
3547:
3542:
3538:
3534:
3530:
3523:
3515:
3511:
3507:
3503:
3498:
3493:
3489:
3485:
3481:
3477:
3473:
3466:
3458:
3454:
3449:
3444:
3439:
3434:
3430:
3426:
3422:
3418:
3414:
3407:
3399:
3395:
3391:
3387:
3383:
3379:
3375:
3371:
3364:
3356:
3352:
3347:
3342:
3338:
3334:
3330:
3326:
3322:
3315:
3307:
3303:
3298:
3293:
3289:
3285:
3281:
3277:
3273:
3266:
3258:
3254:
3249:
3244:
3239:
3234:
3230:
3226:
3223:(2): e30502.
3222:
3218:
3214:
3207:
3199:
3195:
3190:
3185:
3181:
3177:
3173:
3169:
3165:
3161:
3157:
3153:
3149:
3142:
3134:
3130:
3126:
3122:
3118:
3114:
3110:
3106:
3102:
3098:
3091:
3083:
3079:
3075:
3071:
3067:
3063:
3059:
3055:
3047:
3039:
3035:
3031:
3027:
3023:
3019:
3015:
3011:
3007:
3003:
2996:
2988:
2984:
2980:
2976:
2972:
2968:
2964:
2960:
2953:
2946:
2941:
2935:
2931:
2926:
2921:
2917:
2913:
2909:
2905:
2901:
2897:
2893:
2889:
2885:
2878:
2863:
2859:
2853:
2845:
2841:
2836:
2831:
2827:
2823:
2818:
2813:
2809:
2805:
2801:
2794:
2786:
2782:
2777:
2772:
2768:
2764:
2760:
2756:
2752:
2748:
2744:
2737:
2735:
2733:
2724:
2720:
2716:
2712:
2708:
2704:
2700:
2696:
2692:
2688:
2681:
2673:
2669:
2665:
2661:
2657:
2653:
2649:
2645:
2641:
2637:
2630:
2628:
2619:
2615:
2611:
2607:
2602:
2597:
2593:
2589:
2585:
2578:
2576:
2574:
2572:
2570:
2568:
2559:
2555:
2550:
2545:
2541:
2537:
2533:
2529:
2525:
2518:
2516:
2514:
2505:
2501:
2497:
2493:
2489:
2485:
2480:
2475:
2471:
2467:
2460:
2458:
2449:
2445:
2440:
2435:
2431:
2427:
2426:Psychobiology
2423:
2416:
2414:
2405:
2401:
2397:
2393:
2389:
2385:
2382:(2): 225–33.
2381:
2377:
2370:
2363:
2361:
2352:
2348:
2344:
2340:
2336:
2332:
2329:(1): 125–33.
2328:
2324:
2317:
2310:
2308:
2299:
2293:
2289:
2285:
2281:
2277:
2273:
2266:
2258:
2254:
2250:
2246:
2242:
2238:
2231:
2223:
2219:
2215:
2211:
2207:
2203:
2199:
2195:
2188:
2186:
2177:
2173:
2169:
2165:
2161:
2157:
2153:
2149:
2142:
2140:
2138:
2136:
2134:
2125:
2121:
2117:
2113:
2109:
2108:10.1038/nn739
2105:
2101:
2097:
2090:
2088:
2086:
2084:
2075:
2071:
2067:
2063:
2059:
2055:
2051:
2047:
2040:
2038:
2036:
2034:
2032:
2030:
2028:
2026:
2024:
2022:
2020:
2018:
2009:
2005:
2001:
1997:
1993:
1989:
1985:
1981:
1974:
1972:
1963:
1959:
1955:
1951:
1947:
1943:
1939:
1935:
1928:
1926:
1924:
1915:
1909:
1905:
1904:
1896:
1894:
1885:
1881:
1876:
1871:
1867:
1863:
1859:
1855:
1851:
1844:
1842:
1833:
1827:
1823:
1822:
1814:
1812:
1803:
1799:
1795:
1791:
1787:
1783:
1778:
1773:
1769:
1765:
1761:
1754:
1746:
1742:
1738:
1734:
1730:
1726:
1719:
1717:
1708:
1704:
1699:
1694:
1690:
1686:
1682:
1675:
1667:
1663:
1659:
1655:
1650:
1649:2027.42/56238
1645:
1641:
1637:
1633:
1629:
1622:
1615:
1607:
1603:
1598:
1593:
1589:
1585:
1581:
1577:
1571:
1563:
1559:
1555:
1551:
1547:
1543:
1539:
1535:
1528:
1526:
1524:
1522:
1520:
1518:
1516:
1514:
1512:
1510:
1501:
1497:
1493:
1489:
1485:
1481:
1477:
1473:
1466:
1458:
1454:
1449:
1444:
1440:
1436:
1432:
1425:
1423:
1414:
1410:
1406:
1402:
1395:
1387:
1383:
1378:
1373:
1369:
1365:
1361:
1357:
1353:
1346:
1344:
1342:
1333:
1329:
1325:
1321:
1317:
1313:
1309:
1305:
1298:
1296:
1294:
1292:
1290:
1288:
1279:
1275:
1270:
1265:
1261:
1257:
1253:
1246:
1244:
1235:
1231:
1227:
1223:
1219:
1215:
1211:
1207:
1203:
1199:
1192:
1190:
1188:
1179:
1175:
1171:
1167:
1163:
1159:
1156:(2): 99–125.
1155:
1151:
1144:
1142:
1133:
1129:
1125:
1121:
1117:
1113:
1106:
1104:
1102:
1100:
1098:
1096:
1094:
1092:
1090:
1088:
1083:
1074:
1071:
1069:
1066:
1064:
1061:
1059:
1056:
1054:
1051:
1050:
1044:
1042:
1038:
1037:common factor
1027:
1025:
1021:
1017:
1013:
1009:
1005:
1001:
997:
993:
990:
986:
982:
978:
975:
971:
967:
957:
954:
951:
947:
943:
939:
935:
931:
930:vulnerability
927:
923:
918:
916:
912:
908:
905:
901:
897:
894:
890:
879:
877:
873:
869:
865:
861:
857:
853:
849:
844:
841:
838:
836:
831:
828:
825:
821:
817:
813:
809:
805:
802:
797:
795:
790:
788:
784:
774:
772:
768:
764:
760:
756:
752:
748:
738:
736:
732:
728:
727:up-regulation
724:
720:
711:
709:
705:
695:
692:
687:
682:
678:
673:
669:
666:
661:
657:
653:
649:
645:
641:
637:
632:
622:
620:
616:
611:
607:
603:
599:
595:
591:
587:
577:
574:
569:
565:
561:
551:
548:
544:
540:
530:
521:
519:
514:
509:
505:
495:
492:
489:
485:
480:
477:
473:
469:
465:
460:
458:
454:
450:
446:
442:
438:
434:
424:
421:
417:
413:
409:
399:
397:
393:
389:
385:
381:
377:
368:
364:
362:
358:
353:
348:
338:
336:
332:
328:
325:
324:NMDA-receptor
321:
317:
313:
309:
305:
301:
297:
293:
287:
277:
275:
271:
267:
263:
259:
255:
245:
243:
239:
235:
231:
226:
222:
218:
209:
207:
203:
199:
194:
193:neurogenetics
190:
186:
182:
178:
174:
169:
167:
162:
158:
154:
150:
146:
143:to alleviate
142:
139:
138:temporal lobe
136:
133:
129:
128:brain lesions
125:
121:
117:
113:
109:
100:
96:
93:
88:
84:
81:
77:
74:
70:
56:
52:
50:
46:
42:
38:
34:
30:
26:
21:
5462:
5167:Ben Pridmore
5085:Larry Squire
4995:Susan Clancy
4954:
4838:Memory sport
4763:Other topics
4653:False memory
4608:Cryptomnesia
4585:Weapon focus
4545:Decay theory
4306:Neuroanatomy
4300:
4265:Human memory
4192:
4188:
4155:
4151:
4118:
4114:
4071:
4067:
4012:
4008:
3973:
3969:
3945:. Retrieved
3940:
3931:
3916:
3907:
3896:. Retrieved
3894:. 2010-02-03
3891:
3882:
3849:
3843:
3813:. New York:
3809:
3756:
3750:
3733:
3708:
3702:
3661:
3655:
3630:
3626:
3616:
3583:
3577:
3571:
3536:
3532:
3522:
3479:
3475:
3465:
3420:
3416:
3406:
3373:
3369:
3363:
3328:
3324:
3314:
3279:
3276:Nat Neurosci
3275:
3265:
3220:
3216:
3206:
3155:
3151:
3141:
3100:
3096:
3090:
3057:
3053:
3046:
3005:
3001:
2995:
2962:
2958:
2952:
2891:
2887:
2877:
2865:. Retrieved
2861:
2852:
2807:
2803:
2793:
2750:
2746:
2690:
2686:
2680:
2639:
2635:
2591:
2587:
2531:
2527:
2469:
2466:Neuroscience
2465:
2429:
2425:
2379:
2375:
2326:
2322:
2275:
2265:
2240:
2236:
2230:
2197:
2193:
2151:
2147:
2099:
2095:
2049:
2045:
1983:
1979:
1937:
1933:
1902:
1857:
1853:
1820:
1767:
1763:
1753:
1728:
1724:
1688:
1684:
1674:
1631:
1627:
1614:
1587:
1583:
1570:
1537:
1533:
1475:
1471:
1465:
1441:(1): 20–32.
1438:
1434:
1404:
1400:
1394:
1362:(1): 11–21.
1359:
1355:
1307:
1303:
1262:(2): 73–84.
1259:
1255:
1201:
1197:
1153:
1149:
1115:
1111:
1033:
963:
926:memory trace
919:
900:memory trace
885:
845:
842:
839:
832:
823:
798:
791:
780:
755:memory trace
744:
717:
704:oscillations
701:
674:
670:
634:
583:
557:
536:
527:
501:
494:the memory.
481:
461:
430:
405:
374:
365:
350:
335:amygdaloidal
289:
251:
215:
170:
105:
66:
44:
32:
24:
19:
18:
5353:Prospection
5326:Imagination
5289:Forecasting
5269:Association
5025:Eric Kandel
4973:Researchers
4945:Prospective
4896:Free recall
4850:Shas Pollak
4503:anterograde
4419:Declarative
4189:Hippocampus
4158:: 273–293.
3688:Nadel, Lynn
2894:(1): 3112.
2278:. pp.
1008:hippocampus
922:experiments
864:medaka fish
686:hippocampal
648:hippocampal
606:epinephrine
560:declarative
464:hippocampus
441:hippocampus
412:hippocampal
327:antagonists
76:Quintillian
71:teacher of
41:hippocampus
5564:Categories
5534:Mental set
5413:Peripheral
5363:Perception
5346:strategies
5060:Lynn Nadel
4938:intertrial
4923:Metamemory
4911:flashbacks
4831:In society
4528:retrograde
4490:Forgetting
4461:Procedural
4371:Short-term
4341:Eyewitness
3947:2020-10-23
3898:2020-10-23
2965:(1): 3–9.
1685:Learn. Mem
1256:Learn. Mem
1079:References
1068:Patient HM
1022:, such as
970:anisomycin
968:inhibitor
950:extinction
938:behavioral
911:epigenetic
904:extinction
893:extinction
882:Criticisms
820:anisomycin
818:inhibitor
735:postmortem
629:See also:
594:antagonism
564:procedural
524:Criticisms
518:by-product
476:neo-cortex
420:neo-cortex
92:hypothesis
5509:Intention
5494:Attention
5428:Harmonics
5381:RGB model
5331:Intuition
5301:Foresight
5294:affective
5274:Awareness
5261:Cognition
4812:Nutrition
4720:In groups
4533:selective
4508:childhood
4436:Flashbulb
4396:Long-term
4296:Attention
4197:CiteSeerX
4025:CiteSeerX
3874:207597244
3833:772112300
3815:Routledge
3180:0028-0836
3117:1097-6256
3074:0022-3956
3022:1471-003X
2979:0008-4824
2945:CC BY 4.0
2916:2041-1723
2826:0270-6474
2707:0898-929X
2656:0306-4530
2474:CiteSeerX
2448:143135085
2376:Brain Res
2323:Brain Res
1786:0090-502X
1745:0737-0008
1500:220469574
1118:: 51–86.
860:honeybees
801:Pavlovian
731:REM sleep
619:lidocaine
615:glutamate
602:injection
600:prior to
568:conscious
196:has been
181:molecules
153:structure
141:resection
132:bilateral
5549:Volition
5539:Thinking
5519:Learning
5468:Encoding
5114:Patients
4785:mnemonic
4780:chunking
4446:Implicit
4429:Semantic
4424:Episodic
4414:Explicit
4279:Encoding
4227:16979212
4219:10985275
4172:12724165
4143:32408870
4135:12183206
4106:20417102
4055:11943298
4047:17412951
4000:21270783
3923:Archived
3866:25922379
3791:20010606
3725:24827452
3694:(2015).
3608:20176022
3600:16215277
3563:17160003
3555:14622575
3514:24194409
3506:15073322
3457:16492789
3390:26050685
3355:24439381
3306:24997764
3257:22348011
3217:PLOS ONE
3198:20010606
3125:19219038
3082:17588604
3030:11257912
2934:34035303
2844:21289163
2785:20417102
2715:16768378
2672:14639873
2664:16621327
2610:15450166
2558:10541470
2496:15964485
2351:12361503
2222:10480860
2214:12015238
2124:24890684
2116:11600889
2000:15685217
1884:18054504
1802:46236858
1707:18772260
1666:18787168
1658:10542437
1606:18412998
1578:(2008).
1554:17342174
1492:32649022
1457:26447570
1386:13406589
1332:10634773
1278:10753974
1226:10963596
1178:22770640
1170:16099088
1132:14744210
1047:See also
1026:memory.
998:between
953:learning
946:learning
934:infusion
907:learning
896:learning
812:amygdala
747:memories
660:neuronal
652:cortical
644:learning
610:agonists
586:amygdala
488:cortical
472:training
468:learning
453:implicit
449:explicit
445:cortical
388:learning
380:memories
316:learning
300:receptor
234:learning
202:temporal
185:cellular
166:gradient
116:landmark
73:rhetoric
5473:Storage
5341:methods
4933:Priming
4859:Related
4802:Emotion
4498:Amnesia
4336:Eidetic
4323:Sensory
4284:Storage
4180:9879141
4097:2869395
4076:Bibcode
4017:Bibcode
4009:Science
3991:3215304
3918:YouTube
3782:3640262
3761:Bibcode
3484:Bibcode
3476:Science
3448:1413871
3425:Bibcode
3398:2677025
3376:: e21.
3346:3986862
3297:4978538
3248:3277594
3225:Bibcode
3189:3640262
3160:Bibcode
3133:5948908
3038:5765968
2987:4388484
2925:8149676
2896:Bibcode
2867:14 June
2835:6623736
2776:2869395
2755:Bibcode
2723:7584537
2504:3167159
2404:8665059
2396:2306613
2343:3955350
2257:1122202
2176:3086978
2156:Bibcode
2148:Science
2074:4802179
2066:9142752
2008:1115019
1962:9080102
1954:7620304
1875:2346577
1794:7087784
1562:1835412
1312:Bibcode
1304:Science
1234:4420637
1206:Bibcode
872:rodents
868:lymnaea
824:de novo
794:amnesic
783:phobias
777:History
767:storage
677:sensory
491:regions
484:binding
437:stimuli
433:encoded
416:encoded
198:encoded
173:amnesia
161:surgery
120:amnesia
80:Ribot's
63:History
5570:Memory
5478:Recall
5455:Memory
5445:Visual
5438:Speech
5418:Social
5398:Haptic
5371:Amodal
4966:People
4951:memory
4882:memory
4822:Trauma
4361:Visual
4351:Iconic
4346:Haptic
4331:Echoic
4289:Recall
4225:
4217:
4199:
4178:
4170:
4141:
4133:
4104:
4094:
4053:
4045:
4027:
3998:
3988:
3872:
3864:
3831:
3821:
3789:
3779:
3752:Nature
3723:
3711:: e1.
3606:
3598:
3561:
3553:
3533:Neuron
3512:
3504:
3455:
3445:
3396:
3388:
3353:
3343:
3304:
3294:
3255:
3245:
3196:
3186:
3178:
3152:Nature
3131:
3123:
3115:
3080:
3072:
3036:
3028:
3020:
2985:
2977:
2932:
2922:
2914:
2842:
2832:
2824:
2783:
2773:
2721:
2713:
2705:
2670:
2662:
2654:
2618:919482
2616:
2608:
2588:Neuron
2556:
2549:311304
2546:
2502:
2494:
2476:
2446:
2402:
2394:
2349:
2341:
2294:
2255:
2220:
2212:
2174:
2122:
2114:
2072:
2064:
2006:
1998:
1960:
1952:
1910:
1882:
1872:
1828:
1800:
1792:
1784:
1743:
1705:
1664:
1656:
1604:
1560:
1552:
1498:
1490:
1455:
1435:Neuron
1384:
1377:497229
1374:
1330:
1276:
1232:
1224:
1198:Nature
1176:
1168:
1130:
1063:Engram
1016:memory
1000:Zif268
992:Zif268
942:memory
856:chicks
848:humans
808:labile
763:memory
759:labile
721:is an
719:Zif268
706:" and
691:dreams
638:(REM)
539:memory
408:memory
320:memory
225:memory
191:, and
135:medial
87:Müller
49:labile
5487:Other
5433:Pitch
5423:Sound
5402:Touch
5388:Depth
5376:Color
5145:Other
4817:Sleep
4770:Aging
4315:Types
4223:S2CID
4176:S2CID
4139:S2CID
4051:S2CID
3870:S2CID
3699:(PDF)
3652:(PDF)
3604:S2CID
3559:S2CID
3510:S2CID
3129:S2CID
3034:S2CID
2719:S2CID
2668:S2CID
2614:S2CID
2500:S2CID
2444:S2CID
2400:S2CID
2372:(PDF)
2347:S2CID
2319:(PDF)
2218:S2CID
2120:S2CID
2070:S2CID
2004:S2CID
1958:S2CID
1798:S2CID
1662:S2CID
1624:(PDF)
1558:S2CID
1496:S2CID
1230:S2CID
1174:S2CID
852:crabs
681:motor
656:brain
640:sleep
457:sleep
206:brain
69:Roman
5393:Form
4947:and
4878:and
4215:PMID
4168:PMID
4131:PMID
4102:PMID
4043:PMID
3996:PMID
3862:PMID
3829:OCLC
3819:ISBN
3787:PMID
3721:PMID
3633:(5).
3596:PMID
3551:PMID
3502:PMID
3453:PMID
3417:PNAS
3394:SSRN
3386:PMID
3351:PMID
3325:Cell
3302:PMID
3253:PMID
3194:PMID
3176:ISSN
3121:PMID
3113:ISSN
3078:PMID
3070:ISSN
3026:PMID
3018:ISSN
2983:PMID
2975:ISSN
2930:PMID
2912:ISSN
2869:2021
2840:PMID
2822:ISSN
2781:PMID
2711:PMID
2703:ISSN
2660:PMID
2652:ISSN
2606:PMID
2554:PMID
2492:PMID
2392:PMID
2339:PMID
2292:ISBN
2253:PMID
2210:PMID
2172:PMID
2112:PMID
2062:PMID
1996:PMID
1950:PMID
1908:ISBN
1880:PMID
1826:ISBN
1790:PMID
1782:ISSN
1741:ISSN
1703:PMID
1654:PMID
1602:PMID
1550:PMID
1488:PMID
1453:PMID
1382:PMID
1328:PMID
1274:PMID
1222:PMID
1166:PMID
1128:PMID
1010:for
1004:BDNF
987:and
981:BDNF
977:CREB
835:PTSD
679:and
650:and
584:The
562:and
545:and
506:and
443:and
318:and
4207:doi
4160:doi
4156:985
4123:doi
4092:PMC
4084:doi
4035:doi
4013:316
3986:PMC
3978:doi
3854:doi
3777:PMC
3769:doi
3757:463
3713:doi
3666:doi
3588:doi
3541:doi
3492:doi
3480:304
3443:PMC
3433:doi
3421:103
3378:doi
3341:PMC
3333:doi
3329:156
3292:PMC
3284:doi
3243:PMC
3233:doi
3184:PMC
3168:doi
3156:463
3105:doi
3062:doi
3010:doi
2967:doi
2920:PMC
2904:doi
2830:PMC
2812:doi
2771:PMC
2763:doi
2695:doi
2644:doi
2596:doi
2544:PMC
2536:doi
2484:doi
2470:133
2434:doi
2384:doi
2380:508
2331:doi
2327:368
2284:doi
2280:219
2245:doi
2202:doi
2164:doi
2152:232
2104:doi
2054:doi
1988:doi
1942:doi
1870:PMC
1862:doi
1772:doi
1733:doi
1693:doi
1644:hdl
1636:doi
1592:doi
1542:doi
1480:doi
1443:doi
1409:doi
1372:PMC
1364:doi
1320:doi
1308:287
1264:doi
1214:doi
1202:406
1158:doi
1120:doi
1039:in
604:of
596:of
392:LTP
304:LTP
232:or
5566::
5131:NA
5126:KC
5121:HM
4221:.
4213:.
4205:.
4193:10
4191:.
4174:.
4166:.
4154:.
4137:.
4129:.
4119:25
4117:.
4100:.
4090:.
4082:.
4072:20
4070:.
4066:.
4049:.
4041:.
4033:.
4023:.
4011:.
3994:.
3984:.
3974:14
3972:.
3968:.
3939:.
3915:.
3890:.
3868:.
3860:.
3850:63
3848:.
3827:.
3817:.
3799:^
3785:.
3775:.
3767:.
3755:.
3749:.
3719:.
3709:38
3707:.
3701:.
3690:;
3678:^
3662:22
3660:.
3654:.
3639:^
3631:32
3629:.
3625:.
3602:.
3594:.
3584:32
3582:.
3557:.
3549:.
3537:40
3535:.
3531:.
3508:.
3500:.
3490:.
3478:.
3474:.
3451:.
3441:.
3431:.
3419:.
3415:.
3392:.
3384:.
3374:38
3372:.
3349:.
3339:.
3327:.
3323:.
3300:.
3290:.
3280:17
3278:.
3274:.
3251:.
3241:.
3231:.
3219:.
3215:.
3192:.
3182:.
3174:.
3166:.
3154:.
3150:.
3127:.
3119:.
3111:.
3101:12
3099:.
3076:.
3068:.
3058:42
3056:.
3032:.
3024:.
3016:.
3004:.
2981:.
2973:.
2963:14
2961:.
2928:.
2918:.
2910:.
2902:.
2892:12
2890:.
2886:.
2860:.
2838:.
2828:.
2820:.
2808:31
2806:.
2802:.
2779:.
2769:.
2761:.
2751:20
2749:.
2745:.
2731:^
2717:.
2709:.
2701:.
2691:18
2689:.
2666:.
2658:.
2650:.
2640:31
2638:.
2626:^
2612:.
2604:.
2592:44
2590:.
2586:.
2566:^
2552:.
2542:.
2530:.
2526:.
2512:^
2498:.
2490:.
2482:.
2468:.
2456:^
2442:.
2430:27
2428:.
2424:.
2412:^
2398:.
2390:.
2378:.
2374:.
2359:^
2345:.
2337:.
2325:.
2321:.
2306:^
2290:.
2282:.
2274:.
2251:.
2241:13
2239:.
2216:.
2208:.
2198:12
2196:.
2184:^
2170:.
2162:.
2150:.
2132:^
2118:.
2110:.
2098:.
2082:^
2068:.
2060:.
2048:.
2016:^
2002:.
1994:.
1982:.
1970:^
1956:.
1948:.
1936:.
1922:^
1892:^
1878:.
1868:.
1858:89
1856:.
1852:.
1840:^
1810:^
1796:.
1788:.
1780:.
1768:10
1766:.
1762:.
1739:.
1727:.
1715:^
1701:.
1689:15
1687:.
1683:.
1660:.
1652:.
1642:.
1632:22
1630:.
1626:.
1600:.
1588:67
1586:.
1582:.
1556:.
1548:.
1536:.
1508:^
1494:.
1486:.
1476:54
1474:.
1451:.
1439:88
1437:.
1433:.
1421:^
1403:.
1380:.
1370:.
1360:20
1358:.
1354:.
1340:^
1326:.
1318:.
1306:.
1286:^
1272:.
1258:.
1254:.
1242:^
1228:.
1220:.
1212:.
1200:.
1186:^
1172:.
1164:.
1154:76
1152:.
1140:^
1126:.
1116:55
1114:.
1086:^
1043:.
878:.
866:,
862:,
858:,
854:,
208:.
5404:)
5400:(
5247:e
5240:t
5233:v
4382:"
4378:"
4257:e
4250:t
4243:v
4229:.
4209::
4182:.
4162::
4145:.
4125::
4108:.
4086::
4078::
4057:.
4037::
4019::
4002:.
3980::
3950:.
3901:.
3876:.
3856::
3835:.
3793:.
3771::
3763::
3727:.
3715::
3672:.
3668::
3610:.
3590::
3565:.
3543::
3516:.
3494::
3486::
3459:.
3435::
3427::
3400:.
3380::
3357:.
3335::
3308:.
3286::
3259:.
3235::
3227::
3221:7
3200:.
3170::
3162::
3135:.
3107::
3084:.
3064::
3040:.
3012::
3006:1
2989:.
2969::
2947:.
2936:.
2906::
2898::
2871:.
2846:.
2814::
2787:.
2765::
2757::
2725:.
2697::
2674:.
2646::
2620:.
2598::
2560:.
2538::
2532:6
2506:.
2486::
2450:.
2436::
2406:.
2386::
2353:.
2333::
2300:.
2286::
2259:.
2247::
2224:.
2204::
2178:.
2166::
2158::
2126:.
2106::
2100:4
2076:.
2056::
2050:7
2010:.
1990::
1984:6
1964:.
1944::
1938:5
1916:.
1886:.
1864::
1834:.
1804:.
1774::
1747:.
1735::
1729:1
1709:.
1695::
1668:.
1646::
1638::
1608:.
1594::
1564:.
1544::
1538:8
1502:.
1482::
1459:.
1445::
1415:.
1411::
1405:6
1388:.
1366::
1334:.
1322::
1314::
1280:.
1266::
1260:7
1236:.
1216::
1208::
1180:.
1160::
1134:.
1122::
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.