37:
252:
Hermann, Dirk M. et al. Afferent projections to the rat nuclei raphe magnus, raphe pallidus and reticularis gigantocellularis pars demonstrated by iontophoretic application of choleratoxin (subunit b). Journal of
Chemical Neuroanatomy Volume 13, Issue 1, June 1997, Pages
196:
The nucleus raphe pallidus has recently been shown to be involved in the activation of a fever as an immunoreaction. It has been implied that the preoptic area is constantly inhibiting the raphe pallidus, especially the rostral portion, with
204:
When the preoptic area receives immune signals from the body, the inhibition stops and the rostral portion of the nucleus raphe pallidus excites the intermediolateral cell column, which induces a fever.
271:
Zaretsky, Dmitry V. et al. Microinjection of muscimol into raphe pallidus suppresses tachycardia associated with air stress in conscious rats. Journal of
Physiology (2003), 546.1, pp. 243-250
190:
262:
Nakamura, Kazuhiro et al. The
Rostral Raphe Pallidus Nucleus Mediates Pyrogenic Transmission from the Preoptic Area. The Journal of Neuroscience, June 1, 2002, 22(11):4600-4610
225:
In both of these cases, GABA is mediating two different sympathetic responses, so clearly the nucleus raphe pallidus is a far more a complex nucleus than previously thought.
135:
615:
111:
675:
650:
655:
168:
17:
41:
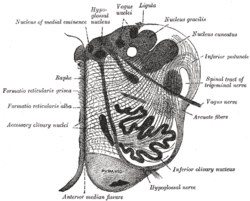
Section of the medulla oblongata at about the middle of the olive. (Raphe nuclei not labeled, but 'raphe' labeled at left.)
707:
298:
142:
712:
620:
176:
555:
550:
540:
535:
413:
130:
727:
680:
476:
418:
381:
215:
Microinjections of a GABA-a antagonist into the nucleus raphe pallidus, induces an increased heart rate.
777:
371:
722:
717:
471:
466:
448:
376:
86:
632:
354:
69:
486:
212:
response, an extremely high heart rate known to be incited by emotional or psychological stress.
756:
739:
118:
106:
576:
325:
291:
744:
183:
8:
702:
670:
610:
581:
530:
520:
403:
164:
481:
366:
361:
308:
525:
408:
344:
284:
443:
438:
99:
74:
349:
771:
665:
660:
186:
123:
734:
627:
502:
234:
694:
316:
276:
209:
148:
81:
172:
93:
219:
208:
The nucleus raphe pallidus has also been known to mediate the
182:
Also, the nucleus raphe pallidus receives afferents from the
57:
198:
36:
222:, inhibit tachycardia in rats under air-stress stimuli.
218:Conversely, microinjections of muscimol, a GABA-a
769:
292:
306:
299:
285:
35:
551:Descending dorsal longitudinal fasciculus
536:Ascending dorsal longitudinal fasciculus
169:Paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus
163:receives afferent connections from the
14:
770:
189:, median preoptic nucleus and lateral
280:
191:paragigantocellular reticular nuclei
24:
25:
789:
175:, lateral hypothalamic area, and
143:Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy
177:parvocellular reticular nucleus
556:Medial longitudinal fasciculus
541:Medial longitudinal fasciculus
265:
256:
246:
13:
1:
414:Dorsal nucleus of vagus nerve
240:
681:Inferior cerebellar peduncle
477:Rostral ventromedial medulla
7:
419:Inferior salivatory nucleus
228:
10:
794:
472:Arcuate nucleus of medulla
693:
643:
603:
596:
566:
510:
501:
467:Ventral respiratory group
457:
449:Accessory cuneate nucleus
431:
392:
333:
324:
315:
171:, central nucleus of the
141:
129:
117:
105:
92:
80:
68:
56:
51:
46:
34:
29:
633:Inferior olivary nucleus
355:Dorsal respiratory group
651:Posterior median sulcus
616:Anterior median fissure
18:Nucleus raphes pallidus
757:Perihypoglossal nuclei
161:nucleus raphe pallidus
63:nucleus raphe pallidus
30:Nucleus raphe pallidus
656:Posterolateral sulcus
577:Olivocerebellar tract
487:Pre-Bötzinger complex
621:Anterolateral sulcus
703:Reticular formation
671:Hypoglossal trigone
582:Rubro-olivary tract
531:Juxtarestiform body
521:Sensory decussation
404:Hypoglossal nucleus
165:periaqueductal gray
573:Descending tracts
778:Medulla oblongata
765:
764:
689:
688:
592:
591:
497:
496:
482:Botzinger complex
427:
426:
367:Vestibular nuclei
362:Gustatory nucleus
157:
156:
152:
16:(Redirected from
785:
601:
600:
526:Medial lemniscus
508:
507:
409:Nucleus ambiguus
397:
345:Solitary nucleus
338:
331:
330:
322:
321:
301:
294:
287:
278:
277:
272:
269:
263:
260:
254:
250:
149:edit on Wikidata
146:
39:
27:
26:
21:
793:
792:
788:
787:
786:
784:
783:
782:
768:
767:
766:
761:
708:Gigantocellular
685:
676:Medial eminence
639:
588:
562:
493:
453:
444:Cuneate nucleus
439:Gracile nucleus
423:
393:
388:
334:
311:
307:Anatomy of the
305:
275:
270:
266:
261:
257:
251:
247:
243:
231:
153:
42:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
791:
781:
780:
763:
762:
760:
759:
754:
753:
752:
747:
742:
732:
731:
730:
725:
720:
715:
710:
699:
697:
691:
690:
687:
686:
684:
683:
678:
673:
668:
663:
658:
653:
647:
645:
641:
640:
638:
637:
636:
635:
625:
624:
623:
618:
607:
605:
598:
594:
593:
590:
589:
587:
586:
585:
584:
579:
570:
568:
564:
563:
561:
560:
559:
558:
553:
545:
544:
543:
538:
533:
528:
523:
514:
512:
505:
499:
498:
495:
494:
492:
491:
490:
489:
484:
479:
474:
469:
461:
459:
455:
454:
452:
451:
446:
441:
435:
433:
429:
428:
425:
424:
422:
421:
416:
411:
406:
400:
398:
390:
389:
387:
386:
385:
384:
379:
374:
364:
359:
358:
357:
352:
341:
339:
328:
326:Cranial nuclei
319:
313:
312:
304:
303:
296:
289:
281:
274:
273:
264:
255:
244:
242:
239:
238:
237:
230:
227:
155:
154:
145:
139:
138:
133:
127:
126:
121:
115:
114:
109:
103:
102:
97:
90:
89:
84:
78:
77:
72:
66:
65:
60:
54:
53:
49:
48:
44:
43:
40:
32:
31:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
790:
779:
776:
775:
773:
758:
755:
751:
748:
746:
743:
741:
738:
737:
736:
733:
729:
726:
724:
721:
719:
716:
714:
713:Parvocellular
711:
709:
706:
705:
704:
701:
700:
698:
696:
692:
682:
679:
677:
674:
672:
669:
667:
666:Vagal trigone
664:
662:
661:Area postrema
659:
657:
654:
652:
649:
648:
646:
642:
634:
631:
630:
629:
626:
622:
619:
617:
614:
613:
612:
609:
608:
606:
602:
599:
595:
583:
580:
578:
575:
574:
572:
571:
569:
565:
557:
554:
552:
549:
548:
546:
542:
539:
537:
534:
532:
529:
527:
524:
522:
519:
518:
516:
515:
513:
509:
506:
504:
500:
488:
485:
483:
480:
478:
475:
473:
470:
468:
465:
464:
463:
462:
460:
456:
450:
447:
445:
442:
440:
437:
436:
434:
430:
420:
417:
415:
412:
410:
407:
405:
402:
401:
399:
396:
391:
383:
380:
378:
375:
373:
370:
369:
368:
365:
363:
360:
356:
353:
351:
348:
347:
346:
343:
342:
340:
337:
332:
329:
327:
323:
320:
318:
314:
310:
302:
297:
295:
290:
288:
283:
282:
279:
268:
259:
249:
245:
236:
233:
232:
226:
223:
221:
216:
213:
211:
206:
202:
200:
194:
192:
188:
187:preoptic area
185:
180:
178:
174:
170:
166:
162:
150:
144:
140:
137:
134:
132:
128:
125:
122:
120:
116:
113:
110:
108:
104:
101:
98:
95:
91:
88:
85:
83:
79:
76:
73:
71:
67:
64:
61:
59:
55:
50:
45:
38:
33:
28:
19:
749:
735:Raphe nuclei
503:White matter
394:
335:
267:
258:
248:
235:Raphe nuclei
224:
217:
214:
207:
203:
195:
181:
160:
158:
112:A14.1.04.320
100:birnlex_1375
62:
317:Grey matter
210:tachycardia
52:Identifiers
728:Paramedian
241:References
82:NeuroNames
395:efferent:
336:afferent:
772:Category
750:Pallidus
740:Obscurus
517:Sensory
382:Inferior
229:See also
173:amygdala
94:NeuroLex
723:Lateral
718:Ventral
611:Pyramid
597:Surface
567:Ventral
458:Ventral
372:Lateral
309:medulla
220:agonist
75:D065848
47:Details
745:Magnus
547:Motor
511:Dorsal
432:Dorsal
377:Medial
184:medial
167:, the
628:Olive
604:Front
350:tract
147:[
136:72586
58:Latin
695:Grey
644:Back
253:1-21
199:GABA
159:The
124:6036
107:TA98
70:MeSH
131:FMA
119:TA2
87:741
774::
201:.
193:.
179:.
96:ID
300:e
293:t
286:v
151:]
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.