145:
has been used for about 40 years. All die casting machines have been designed with the use of WBD. Water-based release coatings generally dry slower than solvent-based release agents but present fewer health and safety concerns. Water-based release agents will be less expensive to ship because of their inherently non-flammable nature and satisfy most plant-safety goals. Solvent-based release coatings dry almost instantly but present serious health and safety concerns. Fumes from solvent-based release agents may be hazardous without proper ventilation of the work area. Most solvents used in release agents are flammable.
374:
mold as it is loaded. Diluted silicone typically has to be applied every cycle. Semi-permanent mold release builds a silicone matrix on the mold that becomes a barrier between the rubber and the metal surface of the mold. The matrix is created by the other ingredients in the semi-permanent mold release. Applications of semi-permanent mold release vary from every cycle to once daily applications depending on the compound being molded and the design and quality of the mold. Silicone-based rubber products, however, require a non-silicone based releasing agent.
94:
27:
159:
1980 was used as the foundation to build the current program. The intent of asphalt release agents is to eliminate harmful stripping products that come into contact with bituminous products and strip the asphalt (binding agent) from the aggregates causing potholes, raveling, and other detrimental pavement failures.
114:(VOC) reduction along with the elimination of health and safety concerns surrounding solvent-based release agents were primary drivers in the development of cosolvent mold release. Cosolvent based release agents combine the benefits of a solvent based system and the safety of water-based release agents.
373:
based. The decision on which to use has to do with lubricity and release. Water-diluted silicone is used when you have rubber sliding over a hot mold (sheets or slugs). The silicone keeps the rubber from sticking to the mold but just as important it lubricates the rubber so it will slide over the hot
135:
Sacrificial coatings must be applied before every cycle of a molding operation and are therefore considered more labor intensive. Most molders will prefer semi-permanent coatings to sacrificial coatings, especially when molding rubber and plastic parts. These coatings contain fewer solid ingredients,
122:
One of the key attributes of a release agent is its degree of permanence: how long will it last before reapplication is necessary. A semi-permanent release agent does not need to be reapplied for every cycle of a molding operation and even works better when it is not over-applied to the mold surface.
144:
Release agents may be water or solvent-based and use of either will depend on the personal preference of the molder, plant safety regulations, hazardous materials shipping costs, state, local, or federal regulations, and/or desired drying times of the release coating. Water-based die lubricant (WBD)
73:
Release agents provide a barrier between a molding surface and the substrate, facilitating separation of the cured part from the mold. Without such a barrier, the substrate would become fused to the mold surface, resulting in difficult clean-up and dramatic loss in production efficiency. Even when a
158:
Asphalt release agents are chemical products developed and manufactured as alternatives to diesel and solvents commonly used for cleaning equipment associated with hot mix asphaltic concrete (HMAC) production and placement on government and private facilities. The United States Oil
Pollution Act of
126:
How many releases can be achieved before reapplication is necessary varies by process, material, and application method. In order to achieve multiple releases per application, the semi-permanent release coating generally must be applied to a clean, dry surface free of dirt, rust, grime or previous
211:
available in fresh concrete. A soapy film is created which prevents adhesion. Because it is a chemically reactive process, there is generally little to no residue or non-reacted product left on the forming surface or concrete which provides for a cleaner process.
74:
release agent is used, factors such as irregular applications or improper release agent choice may have a dramatic effect on the quality and consistency of the finished product. Many kinds of release agents are used. They are
345:
to prevent adhesives from bonding to the plastic surface. Some release agents, also known as de-molding agent, form oil, parting agent or form releaser, are substances used in
386:. These chemicals aid in keeping collections of polymeric materials from sticking together. Typical that are used for stacked sheets or rolls of plastics. They inhibit
353:
that aid in the separation of a mould from the material being moulded and reduce imperfections in the moulded surface. Slip
Additives are similarly used to prevent thin
502:
273:
Mold release agent also can be used in die casting or metal forging process of metal, such as aluminum, aluminum alloy, zinc, zinc alloy, magnesium, etc.
412:
285:
release agents are used to get slip effect of the paper from the processing equipment. A release agent may be applied on the process rolls (like the
483:
127:
coatings. This allows the release agent to properly bond to the mold and mold tooling, improving durability and longevity of the coating.
333:) are added to powdered and granulated drug compositions, to serve as a lubricant for mold release purposes during tabletting.
540:
246:
have been used, but in industrial food processing other chemicals might be used. The application is called bakery release.
171:
construction industry, form release agents prevent the adhesion of freshly placed concrete to the forming surface, usually
429:
567:
562:
111:
42:
used to prevent other materials from bonding to surfaces. Release agents aid in processes involving
448:
Stevens, Malcolm P. (1993). "Polymer
Additives: III. Surface Property and Processing Modifiers".
183:. In this application, there are two types of release agents available: barrier and reactive.
457:
358:
8:
357:
films from adhering to metal surfaces (or each other) during processing, for instance in
63:
461:
369:
There are two types of release agents used in the molding of rubber products. Both are
330:
536:
425:
346:
254:
221:
204:
528:
465:
417:
532:
208:
43:
20:
301:
523:
Pelzl, Bernhard; Wolf, Rainer; Kaul, Bansi Lal (2018). "Plastics, Additives".
556:
421:
308:
290:
87:
342:
286:
250:
67:
282:
79:
47:
38:(also mold release agent, release coating, or mold release coating) is a
354:
469:
387:
93:
370:
262:
258:
235:
190:
180:
168:
83:
55:
39:
350:
172:
51:
231:
503:"Water-Free Electrostatic Spray for High Pressure Die Casting"
297:
243:
176:
227:
194:
59:
239:
197:
or barrier between the forming surface and the concrete.
136:
and thus do not last as long as semi-permanent coatings.
75:
484:"Reduce VOC's in Automotive Seating molding operations"
30:
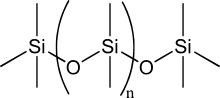
Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) is a typical release agent.
26:
226:
Release agents are used to aid in the separation of
311:
for pressure-sensitive adhesive laminates and tapes
203:are chemically active and work by the process of a
16:Substance applied to prevent adhesion to a surface
554:
525:Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry
413:Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry
522:
410:Lammerting, Helmut (2000). "Release Agents".
409:
139:
405:
403:
66:release. Release agents are one of many
92:
25:
447:
320:Food-grade release and packaging papers
207:between the release agent and the free
555:
500:
400:
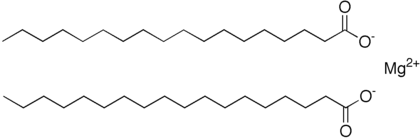
97:Magnesium stearate is a release agent.
443:
441:
19:For the pharmacological meaning, see
341:Release agents are coated onto some
70:used in the production of plastics.
13:
438:
377:
324:
215:
14:
579:
317:General industrial release papers
193:by the development of a physical
117:
268:
101:
230:from a cooking container after
148:
516:
494:
476:
382:Related to release agents are
265:release coatings may be used.
130:
1:
533:10.1002/14356007.a20_459.pub2
450:Journal of Chemical Education
393:
106:
7:
336:
162:
10:
584:
219:
153:
18:
364:
112:Volatile organic compound
510:Ultreaseal International
422:10.1002/14356007.a23_067
300:types are made with low
276:
416:. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH.
201:Reactive release agents
140:Water- or solvent-based
329:Release agents (e.g.,
187:Barrier release agents
98:
31:
220:Further information:
96:
29:
501:Butler, Tim (2011).
257:release agents like
175:, overlaid plywood,
462:1993JChEd..70..713S
488:Hightower Products
331:magnesium stearate
304:release coatings:
99:
32:
568:Process chemicals
563:Plastics industry
542:978-3-527-30673-2
527:. pp. 1–57.
470:10.1021/ed070p713
255:greaseproof paper
222:Non-stick surface
205:chemical reaction
575:
547:
546:
520:
514:
513:
507:
498:
492:
491:
480:
474:
473:
445:
436:
435:
407:
238:. Traditionally
583:
582:
578:
577:
576:
574:
573:
572:
553:
552:
551:
550:
543:
521:
517:
505:
499:
495:
482:
481:
477:
446:
439:
432:
408:
401:
396:
384:blocking agents
380:
378:Blocking agents
367:
339:
327:
325:Pharmaceuticals
279:
271:
224:
218:
216:Food processing
165:
156:
151:
142:
133:
120:
109:
104:
24:
21:releasing agent
17:
12:
11:
5:
581:
571:
570:
565:
549:
548:
541:
515:
493:
475:
437:
430:
398:
397:
395:
392:
379:
376:
366:
363:
338:
335:
326:
323:
322:
321:
318:
315:
314:Casting papers
312:
309:Release liners
302:surface energy
281:In industrial
278:
275:
270:
267:
217:
214:
164:
161:
155:
152:
150:
147:
141:
138:
132:
129:
119:
118:Semi-permanent
116:
108:
105:
103:
100:
88:metallic soaps
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
580:
569:
566:
564:
561:
560:
558:
544:
538:
534:
530:
526:
519:
511:
504:
497:
489:
485:
479:
471:
467:
463:
459:
455:
451:
444:
442:
433:
427:
423:
419:
415:
414:
406:
404:
399:
391:
389:
385:
375:
372:
362:
360:
356:
352:
348:
344:
343:plastic films
334:
332:
319:
316:
313:
310:
307:
306:
305:
303:
299:
294:
292:
291:paper coating
288:
284:
274:
269:Metal casting
266:
264:
260:
256:
252:
247:
245:
241:
237:
233:
229:
223:
213:
210:
206:
202:
198:
196:
192:
188:
184:
182:
178:
174:
170:
160:
146:
137:
128:
124:
115:
113:
102:Functionality
95:
91:
89:
85:
81:
77:
71:
69:
65:
61:
58:release, and
57:
53:
49:
45:
41:
37:
36:release agent
28:
22:
524:
518:
509:
496:
487:
478:
453:
449:
411:
383:
381:
368:
359:film blowing
340:
328:
295:
289:) or in the
287:yankee dryer
280:
272:
251:bakery paper
248:
225:
200:
199:
186:
185:
166:
157:
149:Applications
143:
134:
125:
121:
110:
72:
35:
33:
283:papermaking
131:Sacrificial
80:fatty ester
557:Categories
456:(9): 713.
431:3527306730
394:References
355:polyolefin
388:cold flow
107:Cosolvent
84:silicones
68:additives
54:release,
50:release,
46:release,
371:silicone
337:Plastics
263:silicone
259:catalyst
236:roasting
191:adhesion
189:prevent
181:aluminum
169:concrete
163:Concrete
56:adhesive
48:die-cast
40:chemical
490:. 2020.
458:Bibcode
351:casting
347:molding
261:-cured
173:plywood
167:In the
154:Asphalt
52:plastic
539:
428:
365:Rubber
232:baking
86:, and
506:(PDF)
298:paper
296:Some
277:Paper
244:flour
209:limes
177:steel
76:waxes
537:ISBN
426:ISBN
349:and
228:food
195:film
90:.
62:and
60:tire
44:mold
529:doi
466:doi
418:doi
390:.
253:or
249:In
242:or
240:fat
234:or
179:or
64:web
559::
535:.
508:.
486:.
464:.
454:70
452:.
440:^
424:.
402:^
361:.
293:.
82:,
78:,
34:A
545:.
531::
512:.
472:.
468::
460::
434:.
420::
23:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.