899:
99:
137:
237:, where the specific instruction that took the exception can be determined, can restart or re-execute at the point of the exception. However, those that experience imprecise exceptions generally cannot restart or re-execute, as the system cannot determine the specific instruction that took the exception.
205:
to correctly perform out-of-order execution. All general-purpose and reservation station registers hold either a real value or a placeholder value. If a real value is unavailable to a destination register during the issue stage, a placeholder value is initially used. The placeholder value is a tag
1373:
Reservation stations take on the responsibility of waiting for operands in the presence of data dependencies and other inconsistencies such as varying storage access time and circuit speeds, thus freeing up the functional units. This improvement overcomes long floating point delays and memory
209:
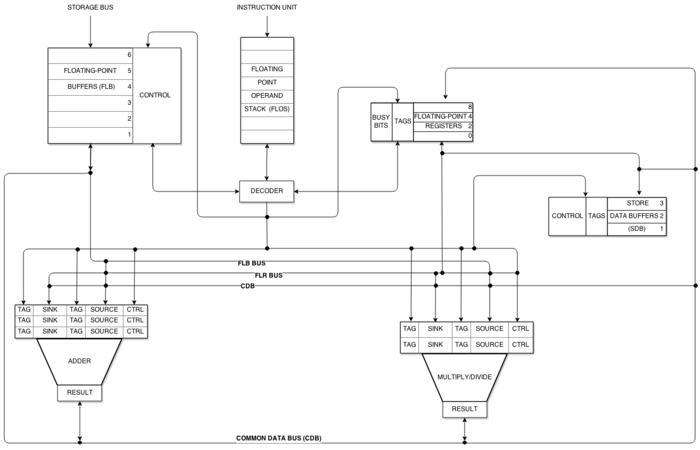
Each functional unit has a single reservation station. Reservation stations hold information needed to execute a single instruction, including the operation and the operands. The functional unit begins processing when it is free and when all source operands needed for an instruction are real.
1374:
accesses. In particular the algorithm is more tolerant of cache misses. Additionally, programmers are freed from implementing optimized code. This is a result of the common data bus and reservation station working together to preserve dependencies as well as encouraging concurrency.
911:
In the execute stage, the instruction operations are carried out. Instructions are delayed in this step until all of their operands are available, eliminating RAW hazards. Program correctness is maintained through effective address calculation to prevent hazards through memory.
1421:
Proliferation of mass-market software meant that programmers would not want to compile for a specific pipeline structure. The algorithm can function with any pipeline architecture and thus software requires few architecture-specific modifications.
118:
Functional units can access the result of any operation without involving a floating-point-register, allowing multiple units waiting on a result to proceed without waiting to resolve contention for access to register file read
1558:
334:
Otherwise, we can assume the operands are not in the registers, and so use virtual values. The functional unit must calculate the real value to keep track of the functional units that produce the operand.
318:
In the issue stage, instructions are issued for execution if all operands and reservation stations are ready or else they are stalled. Registers are renamed in this step, eliminating WAR and WAW hazards.
1411:
Tomasulo's algorithm was implemented in the System/360 Model 91 architecture. Outside of IBM, it went unused for several years. However, it saw a vast increase in usage during the 1990s for 3 reasons:
114:
The Common Data Bus (CDB) connects reservation stations directly to functional units. According to
Tomasulo it "preserves precedence while encouraging concurrency". This has two important effects:
218:
Practically speaking, there may be exceptions for which not enough status information about an exception is available, in which case the processor may raise a special exception, called an
1370:
The concepts of reservation stations, register renaming, and the common data bus in
Tomasulo's algorithm presents significant advancements in the design of high-performance computers.
193:
raised by these instructions, occur in the same order as they would on an in-order processor, regardless of the fact that they are being executed out-of-order (i.e. non-sequentially).
206:
indicating which reservation station will produce the real value. When the unit finishes and broadcasts the result on the CDB, the placeholder will be replaced with the real value.
1399:
An equally important improvement in the algorithm is the design is not limited to a specific pipeline structure. This improvement allows the algorithm to be more widely adopted by
72:
for all execution units, and a common data bus (CDB) on which computed values broadcast to all reservation stations that may need them. These developments allow for improved
1415:
Once caches became commonplace, the algorithm's ability to maintain concurrency during unpredictable load times caused by cache misses became valuable in processors.
122:
Hazard
Detection and control execution are distributed. The reservation stations control when an instruction can execute, rather than a single dedicated hazard unit.
1617:
1699:
245:
The three stages listed below are the stages through which each instruction passes from the time it is issued to the time its execution is complete.
1024:
If the result is available, then: write it on the CDB and from there into the registers and any reservation stations waiting for this result
1418:
Dynamic scheduling and branch speculation from the algorithm enables improved performance as processors issued more and more instructions.
323:
Retrieve the next instruction from the head of the instruction queue. If the instruction operands are currently in the registers, then
309:
Qi - the reservation station whose result should be stored in this register (if blank or 0, no values are destined for this register)
1382:
1426:
Many modern processors implement dynamic scheduling schemes that are variants of
Tomasulo's original algorithm, including popular
1017:
In the write Result stage, ALU operations results are written back to registers and store operations are written back to memory.
1386:
154:
1377:
By tracking operands for instructions in the reservation stations and register renaming in hardware the algorithm minimizes
1572:
1640:
176:
1678:
290:
Qj, Qk - the reservation station that will produce the relevant source operand (0 indicates the value is in Vj, Vk)
1729:
1393:
1588:
928:
Else, if the instruction is a store then: wait for the value to be stored before sending it to the memory unit
1448:
916:
If one or more of the operands is not yet available then: wait for operand to become available on the CDB.
922:
Compute the effective address when the base register is available, and place it in the load/store buffer
329:
Else, as there is no available functional unit, stall the instruction until a station or buffer is free.
227:
158:
147:
1378:
87:
17:
1641:"Differences between Tomasulo's algorithm and dynamic scheduling in Intel Core microarchitecture"
1396:. This improves performance by reducing wasted time that would otherwise be required for stalls.
54:
189:
Instructions are issued sequentially so that the effects of a sequence of instructions, such as
1709:
223:
42:
1476:
1390:
936:
190:
34:
1522:
1403:
processors. Additionally, the algorithm is easily extended to enable branch speculation.
8:
1724:
69:
58:
106:
The following are the concepts necessary to the implementation of
Tomasulo's algorithm:
1504:
73:
1568:
1496:
202:
65:
1029:
Else, if the instruction was a store then: write the data to memory during this step
898:
1508:
1488:
939:(ALU) operation then: execute the instruction at the corresponding functional unit
925:
If the instruction is a load then: execute as soon as the memory unit is available
1703:
1442:
83:
46:
45:
and enables more efficient use of multiple execution units. It was developed by
1479:(Jan 1967). "An Efficient Algorithm for Exploiting Multiple Arithmetic Units".
1400:
1718:
1500:
919:
When all operands are available, then: if the instruction is a load or store
77:
226:
implementations, as processor state is changed only in program order (see
1670:
257:
RegisterStat - Register Status; contains information about the registers.
1492:
98:
277:
r - reservation station or buffer that the instruction is assigned to
38:
1564:
296:
A - used to hold the memory address information for a load or store
326:
If a matching functional unit is available, issue the instruction.
1430:
1427:
1618:
Intel 64 and IA-32 Architectures
Software Developer's Manual
76:
of instructions that would otherwise stall under the use of
287:
Op - represents the operation being performed on operands
50:
1710:
HASE Java applet simulation of the
Tomasulo's algorithm
64:
The major innovations of
Tomasulo’s algorithm include
157:. Please help to ensure that disputed statements are
41:for dynamic scheduling of instructions that allows
1556:
1716:
1557:Hennessy, John L.; Patterson, David A. (2012).
1560:Computer Architecture: A Quantitative Approach
281:
1552:
1550:
1548:
1546:
1544:
1471:
1469:
1467:
1465:
1406:
971:Compute result: operands are in Vj and Vk
93:
1700:Dynamic Scheduling - Tomasulo's Algorithm
1365:
303:
293:Vj, Vk - the value of the source operands
177:Learn how and when to remove this message
53:in 1967 and was first implemented in the
1475:
1021:If the instruction was an ALU operation
1012:
897:
240:
153:Relevant discussion may be found on the
97:
27:Computer architecture hardware algorithm
1541:
1481:IBM Journal of Research and Development
1462:
299:Busy - 1 if occupied, 0 if not occupied
228:Classic RISC pipeline § Exceptions
222:. Imprecise exceptions cannot occur in
90:in 1997 for his work on the algorithm.
14:
1717:
1671:"Pipelined and Out-of-Order Execution"
1668:
1632:
1610:
983:& r is head of load-store queue
271:rs, rt - source registration numbers
196:
130:
126:
906:
274:imm - sign extended immediate field
24:
1662:
263:Mem - Value of memory at address A
109:
25:
1741:
1706: (archived December 25, 2017)
1693:
313:
1638:
1523:"Robert Tomasulo – Award Winner"
268:rd - destination register number
135:
1681:from the original on 2018-07-03
1620:(Report). Intel. September 2014
902:Example of Tomasulo's algorithm
1581:
1515:
102:Tomasulo's floating point unit
13:
1:
1598:. Washington University. 2006
1455:
1449:Instruction-level parallelism
213:
80:or other earlier algorithms.
1669:Savard, John J. G. (2018) .
965:(RS.Qj = 0) and (RS.Qk = 0)
935:Else, the instruction is an
7:
1436:
10:
1746:
282:Reservation Station Fields
260:regs - Value of register x
201:Tomasulo's algorithm uses
248:
233:Programs that experience
1311:
1060:
986:
963:
793:
762:
614:
365:
1407:Applications and legacy
254:RS - Reservation Status
94:Implementation concepts
55:IBM System/360 Model 91
1730:Instruction processing
1477:Tomasulo, Robert Marco
1366:Algorithm improvements
1305:Execution complete at
1053:Execution complete at
1045:Action or bookkeeping
955:Action or bookkeeping
903:
350:Action or bookkeeping
304:Register Status Fields
103:
43:out-of-order execution
1589:"CSE P548 - Tomasulo"
1391:computer architecture
1381:(RAW) and eliminates
1050:FP operation or load
1013:Stage 3: write result
998:Load step 1 complete
988:RS.A ← RS.Vj + RS.A;
937:arithmetic logic unit
901:
241:Instruction lifecycle
101:
35:computer architecture
1057:& CDB available
146:factual accuracy is
88:Eckert–Mauchly Award
70:reservation stations
31:Tomasulo's algorithm
1493:10.1147/rd.111.0025
1035:
945:
340:
220:imprecise exception
59:floating point unit
1039:Instruction state
1033:
977:Load/store step 1
949:Instruction state
943:
904:
344:Instruction state
338:
235:precise exceptions
104:
74:parallel execution
1487:(1). IBM: 25–33.
1383:write-after-write
1363:
1362:
1307:r & RS.Qk = 0
1010:
1009:
896:
895:
203:register renaming
197:Register renaming
187:
186:
179:
127:Instruction order
66:register renaming
16:(Redirected from
1737:
1689:
1687:
1686:
1656:
1655:
1653:
1651:
1636:
1630:
1629:
1627:
1625:
1614:
1608:
1607:
1605:
1603:
1593:
1585:
1579:
1578:
1554:
1539:
1538:
1536:
1534:
1519:
1513:
1512:
1473:
1387:Write-after-Read
1379:read-after-write
1357:
1354:
1351:
1348:
1345:
1342:
1339:
1336:
1333:
1330:
1327:
1324:
1321:
1318:
1315:
1308:
1295:
1292:
1289:
1286:
1283:
1280:
1277:
1274:
1271:
1268:
1265:
1262:
1259:
1256:
1253:
1250:
1247:
1244:
1241:
1238:
1235:
1232:
1229:
1226:
1223:
1220:
1217:
1214:
1211:
1208:
1205:
1202:
1199:
1196:
1193:
1190:
1187:
1184:
1181:
1178:
1175:
1172:
1169:
1166:
1163:
1160:
1157:
1154:
1151:
1148:
1145:
1142:
1139:
1136:
1133:
1130:
1127:
1124:
1121:
1118:
1115:
1112:
1109:
1106:
1103:
1100:
1097:
1094:
1091:
1088:
1085:
1082:
1079:
1076:
1073:
1070:
1067:
1064:
1056:
1036:
1032:
1005:
982:
946:
942:
907:Stage 2: execute
890:
887:
884:
881:
878:
875:
872:
869:
866:
863:
860:
857:
854:
851:
848:
845:
842:
839:
836:
833:
830:
827:
824:
821:
818:
815:
812:
809:
806:
803:
800:
797:
781:
778:
775:
772:
769:
766:
750:
747:
744:
741:
738:
735:
732:
729:
726:
723:
720:
717:
714:
711:
708:
705:
702:
699:
696:
693:
690:
687:
684:
681:
678:
675:
672:
669:
666:
663:
660:
657:
654:
651:
648:
645:
642:
639:
636:
633:
630:
627:
624:
621:
618:
610:
597:
594:
591:
588:
585:
582:
579:
576:
573:
570:
567:
564:
561:
558:
555:
552:
549:
546:
543:
540:
537:
534:
531:
528:
525:
522:
519:
516:
513:
510:
507:
504:
501:
498:
495:
492:
489:
486:
483:
480:
477:
474:
471:
468:
465:
462:
459:
456:
453:
450:
447:
444:
441:
438:
435:
432:
429:
426:
423:
420:
417:
414:
411:
408:
405:
402:
399:
396:
393:
390:
387:
384:
381:
378:
375:
372:
369:
361:
341:
337:
182:
175:
171:
168:
162:
159:reliably sourced
139:
138:
131:
21:
1745:
1744:
1740:
1739:
1738:
1736:
1735:
1734:
1715:
1714:
1704:Wayback Machine
1696:
1684:
1682:
1665:
1663:Further reading
1660:
1659:
1649:
1647:
1637:
1633:
1623:
1621:
1616:
1615:
1611:
1601:
1599:
1591:
1587:
1586:
1582:
1575:
1563:. Waltham, MA:
1555:
1542:
1532:
1530:
1521:
1520:
1516:
1474:
1463:
1458:
1443:Re-order buffer
1439:
1409:
1368:
1359:
1358:
1355:
1352:
1349:
1346:
1343:
1340:
1337:
1334:
1331:
1328:
1325:
1322:
1319:
1316:
1313:
1306:
1297:
1296:
1293:
1290:
1287:
1284:
1281:
1278:
1275:
1272:
1269:
1266:
1263:
1260:
1257:
1254:
1251:
1248:
1245:
1242:
1239:
1236:
1233:
1230:
1227:
1224:
1221:
1218:
1215:
1212:
1209:
1206:
1203:
1200:
1197:
1194:
1191:
1188:
1185:
1182:
1179:
1176:
1173:
1170:
1167:
1164:
1161:
1158:
1155:
1152:
1149:
1146:
1143:
1140:
1137:
1134:
1131:
1128:
1125:
1122:
1119:
1116:
1113:
1110:
1107:
1104:
1101:
1098:
1095:
1092:
1089:
1086:
1083:
1080:
1077:
1074:
1071:
1068:
1065:
1062:
1054:
1015:
1003:
990:
989:
980:
967:
966:
909:
892:
891:
888:
885:
882:
879:
876:
873:
870:
867:
864:
861:
858:
855:
852:
849:
846:
843:
840:
837:
834:
831:
828:
825:
822:
819:
816:
813:
810:
807:
804:
801:
798:
795:
783:
782:
779:
776:
773:
770:
767:
764:
752:
751:
748:
745:
742:
739:
736:
733:
730:
727:
724:
721:
718:
715:
712:
709:
706:
703:
700:
697:
694:
691:
688:
685:
682:
679:
676:
673:
670:
667:
664:
661:
658:
655:
652:
649:
646:
643:
640:
637:
634:
631:
628:
625:
622:
619:
616:
608:
599:
598:
595:
592:
589:
586:
583:
580:
577:
574:
571:
568:
565:
562:
559:
556:
553:
550:
547:
544:
541:
538:
535:
532:
529:
526:
523:
520:
517:
514:
511:
508:
505:
502:
499:
496:
493:
490:
487:
484:
481:
478:
475:
472:
469:
466:
463:
460:
457:
454:
451:
448:
445:
442:
439:
436:
433:
430:
427:
424:
421:
418:
415:
412:
409:
406:
403:
400:
397:
394:
391:
388:
385:
382:
379:
376:
373:
370:
367:
359:
316:
306:
284:
251:
243:
216:
199:
183:
172:
166:
163:
152:
144:This section's
140:
136:
129:
112:
110:Common data bus
96:
84:Robert Tomasulo
47:Robert Tomasulo
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
1743:
1733:
1732:
1727:
1713:
1712:
1707:
1695:
1694:External links
1692:
1691:
1690:
1664:
1661:
1658:
1657:
1639:Yoga, Adarsh.
1631:
1609:
1596:washington.edu
1580:
1574:978-0123838728
1573:
1540:
1514:
1460:
1459:
1457:
1454:
1453:
1452:
1446:
1438:
1435:
1424:
1423:
1419:
1416:
1408:
1405:
1401:multiple-issue
1367:
1364:
1361:
1360:
1312:
1309:
1303:
1299:
1298:
1061:
1058:
1051:
1047:
1046:
1043:
1040:
1031:
1030:
1027:
1026:
1025:
1014:
1011:
1008:
1007:
999:
996:
992:
991:
987:
984:
978:
974:
973:
968:
964:
961:
957:
956:
953:
950:
941:
940:
933:
932:
931:
930:
929:
926:
917:
908:
905:
894:
893:
794:
791:
789:
785:
784:
763:
760:
758:
754:
753:
615:
612:
605:
604:Load or Store
601:
600:
366:
363:
356:
352:
351:
348:
345:
336:
335:
332:
331:
330:
327:
315:
314:Stage 1: issue
312:
311:
310:
305:
302:
301:
300:
297:
294:
291:
288:
283:
280:
279:
278:
275:
272:
269:
265:
264:
261:
258:
255:
250:
247:
242:
239:
215:
212:
198:
195:
185:
184:
143:
141:
134:
128:
125:
124:
123:
120:
111:
108:
95:
92:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1742:
1731:
1728:
1726:
1723:
1722:
1720:
1711:
1708:
1705:
1701:
1698:
1697:
1680:
1676:
1672:
1667:
1666:
1646:
1642:
1635:
1619:
1613:
1597:
1590:
1584:
1576:
1570:
1566:
1562:
1561:
1553:
1551:
1549:
1547:
1545:
1528:
1524:
1518:
1510:
1506:
1502:
1498:
1494:
1490:
1486:
1482:
1478:
1472:
1470:
1468:
1466:
1461:
1450:
1447:
1444:
1441:
1440:
1434:
1432:
1429:
1420:
1417:
1414:
1413:
1412:
1404:
1402:
1397:
1395:
1392:
1388:
1384:
1380:
1375:
1371:
1310:
1304:
1301:
1300:
1059:
1052:
1049:
1048:
1044:
1041:
1038:
1037:
1028:
1023:
1022:
1020:
1019:
1018:
1006:
1000:
997:
994:
993:
985:
979:
976:
975:
972:
969:
962:
960:FP operation
959:
958:
954:
951:
948:
947:
938:
934:
927:
924:
923:
921:
920:
918:
915:
914:
913:
900:
792:
790:
787:
786:
761:
759:
756:
755:
613:
606:
603:
602:
364:
357:
355:FP operation
354:
353:
349:
346:
343:
342:
333:
328:
325:
324:
322:
321:
320:
308:
307:
298:
295:
292:
289:
286:
285:
276:
273:
270:
267:
266:
262:
259:
256:
253:
252:
246:
238:
236:
231:
229:
225:
221:
211:
207:
204:
194:
192:
181:
178:
170:
167:December 2023
160:
156:
150:
149:
142:
133:
132:
121:
117:
116:
115:
107:
100:
91:
89:
86:received the
85:
81:
79:
78:scoreboarding
75:
71:
68:in hardware,
67:
62:
60:
56:
52:
48:
44:
40:
36:
32:
19:
1683:. Retrieved
1674:
1648:. Retrieved
1644:
1634:
1622:. Retrieved
1612:
1600:. Retrieved
1595:
1583:
1559:
1531:. Retrieved
1526:
1517:
1484:
1480:
1425:
1410:
1398:
1376:
1372:
1369:
1111:RegisterStat
1078:RegisterStat
1034:Pseudocode
1016:
1001:
995:Load step 2
970:
944:Pseudocode
910:
835:RegisterStat
802:RegisterStat
765:RegisterStat
656:RegisterStat
623:RegisterStat
581:RegisterStat
503:RegisterStat
470:RegisterStat
407:RegisterStat
374:RegisterStat
317:
244:
234:
232:
219:
217:
208:
200:
188:
173:
164:
145:
113:
105:
82:
63:
30:
29:
1645:The boozier
1042:Wait until
952:Wait until
788:Store only
347:Wait until
339:Pseudocode
1725:Algorithms
1719:Categories
1685:2018-07-16
1624:8 December
1602:8 December
1533:8 December
1527:ACM Awards
1456:References
1385:(WAW) and
1002:Read from
757:Load only
214:Exceptions
191:exceptions
1675:quadibloc
1501:0018-8646
981:RS.Qj = 0
155:talk page
39:algorithm
37:hardware
1679:Archived
1565:Elsevier
1437:See also
358:Station
224:in-order
148:disputed
18:Tomasulo
1702:at the
1650:4 April
1509:8445049
1433:chips.
1394:hazards
607:Buffer
1571:
1507:
1499:
1431:x86-64
1389:(WAR)
1302:Store
1252:result
1177:result
1105:result
1004:Mem.A]
611:empty
362:empty
249:Legend
119:ports.
1592:(PDF)
1529:. ACM
1505:S2CID
1451:(ILP)
1445:(ROB)
1428:Intel
33:is a
1652:2016
1626:2014
1604:2014
1569:ISBN
1535:2014
1497:ISSN
1347:Busy
1285:Busy
1099:regs
868:Regs
850:else
740:Busy
689:Regs
671:else
569:Busy
536:Regs
518:else
437:Regs
419:else
1489:doi
1314:Mem
1276:});
1201:});
1126:});
746:yes
728:imm
575:yes
230:).
57:’s
51:IBM
49:at
1721::
1677:.
1673:.
1643:.
1594:.
1567:.
1543:^
1525:.
1503:.
1495:.
1485:11
1483:.
1464:^
1353:no
1341:RS
1335:Vk
1329:RS
1291:no
1279:RS
1264:Qk
1258:RS
1246:Vk
1240:RS
1225:Qk
1219:RS
1213:if
1189:Qj
1183:RS
1171:Vj
1165:RS
1150:Qj
1144:RS
1138:if
1117:Qi
1084:Qi
1072:if
889:};
880:Qk
874:RS
862:Vk
856:RS
841:Qi
829:Qk
823:RS
808:Qi
796:if
771:Qi
734:RS
716:RS
701:Qj
695:RS
683:Vj
677:RS
662:Qi
650:Qj
644:RS
629:Qi
617:if
587:Qi
563:RS
548:Qk
542:RS
530:Vk
524:RS
509:Qi
497:Qk
491:RS
476:Qi
464:if
449:Qj
443:RS
431:Vj
425:RS
413:Qi
401:Qj
395:RS
380:Qi
368:if
61:.
1688:.
1654:.
1628:.
1606:.
1577:.
1537:.
1511:.
1491::
1356:;
1350:←
1344:.
1338:;
1332:.
1326:←
1323:]
1320:A
1317:.
1294:;
1288:←
1282:.
1273:;
1270:0
1267:←
1261:.
1255:;
1249:←
1243:.
1237:{
1234:)
1231:r
1228:=
1222:.
1216:(
1210:(
1207:x
1204:∀
1198:;
1195:0
1192:←
1186:.
1180:;
1174:←
1168:.
1162:{
1159:)
1156:r
1153:=
1147:.
1141:(
1135:(
1132:x
1129:∀
1123:0
1120:=
1114:.
1108:;
1102:←
1096:{
1093:)
1090:r
1087:=
1081:.
1075:(
1069:(
1066:x
1063:∀
1055:r
886:0
883:←
877:.
871:;
865:←
859:.
853:{
847:}
844:;
838:.
832:←
826:.
820:{
817:)
814:0
811:¦
805:.
799:(
780:;
777:r
774:←
768:.
749:;
743:←
737:.
731:;
725:←
722:A
719:.
713:}
710:;
707:0
704:←
698:.
692:;
686:←
680:.
674:{
668:}
665:;
659:.
653:←
647:.
641:{
638:)
635:0
632:¦
626:.
620:(
609:r
596:;
593:r
590:←
584:.
578:;
572:←
566:.
560:}
557:;
554:0
551:←
545:.
539:;
533:←
527:.
521:{
515:}
512:;
506:.
500:←
494:.
488:{
485:)
482:0
479:¦
473:.
467:(
461:}
458:;
455:0
452:←
446:.
440:;
434:←
428:.
422:{
416:}
410:.
404:←
398:.
392:{
389:)
386:0
383:¦
377:.
371:(
360:r
180:)
174:(
169:)
165:(
161:.
151:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.