1084:
by two days. The treaty commissioners, Laird and
Macleod, arrived September 16 along with the Siksika, Stoney-Nakoda and Tsuut’ina. They all agreed to wait two days for the remaining nations to arrive. On September 19 the negotiations began between the commissioners and the five nations. Laird and Macleod began their side of the negotiations with stating the facts about the decline in the buffalo population and how he proposed to help the Indigenous people by introducing new laws to protect the buffalo. The importance of the buffalo to the Indigenous people was high due to their dependence on the buffalo for food. Laird proposed new laws to protect the buffalo along with helping and teaching the Indigenous people how to learn more about agriculture and ranching that would allow a way to transition from becoming less dependent on the buffalo. Laird said to the Indigenous people that the buffalo would soon be gone and it was important for them to move into agriculture and ranching lifestyles and that the government would support them for doing this.
1140:
as many expected. The winters following the signing of Treaty 7 were very harsh on the
Indigenous people and their nomadic lifestyle. The nations were still waiting on the government to state what land they will be able to claim. They suffered through disease outbreaks and starvation. Once the nations received the land they were given, it largely was unsuitable. The reserves led to poverty, food shortages and residential schools. Missionaries arrived to provide day schools and residential schools on the reserves. Issues arose with the reserves that included the lack of space for the number of people, fears the Canadian Pacific Railway would be constructed on their new land and that the land was insufficient and unsuitable. These were the main concerns of the Treaty Seven First Nations. The Treaty Seven First Nations had been given their reserves and plenty of aid from the missionaries but the promised help from the government that was stated in the treaty would take years to fully receive.
1118:
way to allow for a connection to be established between the
Indigenous people and the newcomers to Canada through the crown. Their interpretation of the treaties were guided by their need for support from the crown and protection to ensure the survival of their people and culture. Indigenous people did not support the viewpoint of the Canadian government as they found it to be narrow minded and restrictive when they felt as though they were looking for a broader sense of financial and general support for their people. The Indigenous people viewed the treaty as a covenant. The Canadian government viewed it as a contract. The difference between a contract and a covenant is that a covenant is conceived under a deity and therefore has a spiritual context and boundedness that includes a higher power as not only a participant but also a guarantor.
1122:
made smaller or larger depending on family size). The treaty outlined the rivers that each
Indigenous band could use including their shipments, docking and any other uses for the rivers. $ 12 from the Queen was designated to each person who was part of any other of the above-mentioned tribes and other amounts of money to people of higher power such as chiefs. Each nation would receive $ 2000 every year for the benefit of the tribe so long as it is necessary. Every three years the chiefs would be recognized by way of medals, flags or suits. The Queen would pay for teachers when children on reserves desired teachers and there was a means for education. The treaty dictated the number of cows per family depending on the number of persons. And finally, the Queen reserved the right to punish any Indian who violated the treaty.
904:
319:
1153:
the time strongly advocated for the treaty to be a written document but the tradition of the
Indigenous people was, and still is, an oral one. Due to the treaty being a written document, it is possible that other negotiations were made, which may have persuaded the Nations to sign the treaty, but were not officially reported. These conventional differences lead many to believe the Indigenous populations did not fully understanding the scope and ramifications of the treaties. It is speculated that if the Indigenous people involved had been properly informed of what was entailed in the documents, they would not have agreed to or signed these treaties.
1149:
the available resources. As well, the support from the
Canadian government to help transition to an agricultural lifestyle did not occur as promised, the reserves that the Nations were relocated to had land where they could not support the requirements of the Nations. Additionally, psychological damages from residential schools, and the attempted erasure of Indigenous cultures, have created immeasurable and unseen damages in the lives of the Indigenous population. All these implications of the treaties have contributed to the level of poverty and grievances experienced on the reserves and by Indigenous peoples today.
778:
1114:
treaty, all nations retained the right to use the land for hunting. However, due to their rapidly depleting population of buffalo, the
Indigenous people wanted to learn more about agriculture and how to cultivate their own produce seeing they would be more sedentary without the buffalo herds. The government brought money, cattle and the promise of education with the intention of teaching Indigenous people the Western ways of living so that they would be able to sustain their populations without the buffalo.
2695:
767:
247:
1033:
2905:
1742:
1092:, the leader of the Kainai Nation and a trusted friend of Macleod before making any decisions with the treaty. Once Red Crow arrived, Crowfoot explained to him to the best of his abilities about what he believed the treaty to be about. Once Crowfoot explained to Red Crow about the treaty and its terms, the treaty was agreed upon by all the leaders and was signed on September 22, 1877. The treaty involved 130,000 km of land stretching from the
68:
170:
27:
2915:
1131:
through the
Indigenous peoples' land. The Canadian government began the treaty talks to build the railway and for the expansion of settlement. The immediate responses after the treaty was signed from the Canadian government officials was that "since the treaty the Indians appeared more contented and friendly than ever". The government's main concern was about the
1016:
would mean for their communities. They saw the numbered treaties as an association with the monarchy and as a way for them to gain the government's protection of their land and resources before
American settlers came to take over their territories. They were able to trust that the Queen and her people would keep their word because the
1064:(Sarcee). Treaty 7 was the last of a series of treaties that were signed during the 1870s. It was the last treaty signed between the Crown and the First Nations for the next 20 years. This series of treaties during the 1870s was to determine the division of land. The negotiations of the treaty took place between
1152:
Special consideration must be given to the differences of cultures as pertains to negotiations. When comparing the difference in cultures during the treaty signing, it is possible the
Indigenous population could have been misinformed or misguided, whether unwittingly or intentionally. The settlers at
1148:
Overall, the treaty did not have the positive impact for Indigenous peoples that they initially believed it would. The buffalo disappeared at a rapid rate, and some Nations trespassed on other Nations' land to hunt, and the number of settlers that came to the area increased, putting further strain on
1130:
The implications at the time of the treaty were seen in two different ways, through the government's point of view and the Indigenous people's point of view. The Canadian government wanted the treaty to take place to allow them to build the railway across Canada. It was required that the railway went
1139:
The implications for the Indigenous people after the signing of the treaty are seen through their suffering and hardship. The buffalo disappeared more rapidly than expected and the promised support from the Canadian government to transition into an agriculture lifestyle did not happen as quickly and
1156:
The Canadian government has been attempting to reconcile with the Indigenous people of Canada. In the 1982 constitutional amendment, the government provided protection to the Indigenous people and the treaty rights of the Indigenous people of Canada. However, all the nations involved in the eleven
1121:
The treaty outlined specifics as to rights of Indigenous people and support and protection of the Queen. These included rights that Indigenous people could hunt and fish and had provisions on their land. Their lands would be divided into one square mile for each family of five people (this would be
1117:
Opinions on what the treaties mean differ across groups. Government officials have been cited as saying that the treaties were contracts allowing the Canadian government to take control of Indigenous lands in return for other types of compensation. Indigenous people thought that the treaties were a
1113:
The government wanted the land for the purposes of building a railroad through western Canada. The written treaty covered roughly 130,000 km of land from the Rocky Mountains to the west, the Cypress Hills to the east, the Red Deer River to the north, and the US border to the south. Through the
1083:
The signing of the treaty took place at the Blackfoot crossing, a location on their territory. This location was a bit problematic for some of the other nations due to it being quite far from their hunting grounds. The distance factor led to the meeting to discuss the negotiations being pushed back
990:
The Canadian government wanted to build a railway, but to proceed, they had to acquire the land from the Indigenous people. The government brought forward the idea of a treaty to the Indigenous people who resided on the land on the plains that was needed for the railway. There were already treaties
986:
hunting which allowed people to sustain themselves and their culture. Buffalo were the foundation of not only the economy of the people of the plains but also of their culture and way of life. The buffalo provided the people of the plains with food, clothing and warmth, fuel and sacred objects. The
1104:
and the US border. The terms of the treaty stated that all nations still maintained the right to hunt on the land and in exchange for giving up the land each nation was to receive reserves of 1 square mile (2.6 km) per family of five and in proportion to that number depending on whether the
1015:
were killing both the old and the young, and it was becoming increasingly difficult to control the spread of diseases to which there was no native immunity. The plains people and their leaders were also concerned about their future and culture and what the influx of American settlers and traders
981:
In the late 1800s, five Indigenous nations were situated along the southern parts of western Canada. The five nations were the Blackfoot, Piegans, Sarcee, Cree, and Blood. They were nomadic populations, which allowed them to move freely following the buffalo herds from which they gained a lot of
1076:(commissioner of the NWMP) who were acting as the Crown's treaty commissioners. The First Nations representatives were largely from the Blackfoot confederacy due to their inhabiting the majority of the land being sought after. The First Nations' representative was the Blackfoot nation, who sent
876:), promised annual payments, provisions, or both, from the Crown to the tribes and promised continued hunting and trapping rights on the "tract surrendered". In exchange, the tribes ceded their rights to their traditional territory, of which they had earlier been recognized as the owners.
982:
their resources and were able to live. The five Nations owned their lands and used them for hunting grounds as well as for settlement areas. Their territories started in the southern parts of Alberta and Saskatchewan as well as northern Montana. These plains included vast
987:
buffalo were a pivotal part of their way of life and greatly diminished due to overhunting in the plains. By 1879, the buffalo could no longer be found in any significant numbers across the plains leading the people to have different needs and require other ways of life.
994:
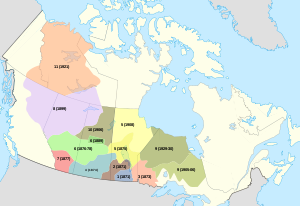
A series of eleven treaties made between the Canadian government and Indigenous peoples from 1871 to 1921. The Indigenous groups in the west were involved in treaties 1-7, which were established between 1871 and 1877. The treaties covered the area between the
1006:
The leaders of the plains were interested in the treaty because they had concerns about the course of their lives. People had become aware that their resources were rapidly depleting due to overhunting and commercialization of the usage of animals with the
899:
that were transferred to Canada in 1870, including the part that became Alberta in 1905. The British government, in an exchange of letters at the time of the transfer, sought assurances that Canada would provide the Crown's obligation to First Nations.
1135:
and that it would be built. The construction began in the 1880s and it was completed. The implications for the government of Canada have not been seen until more recent years as it has been trying to reconcile with the Indigenous people of Canada.
1087:
There was also discussion surround annual payments, reserve land and education. The Indigenous leaders and their nations were greatly concerned about continuing to be able to hunt and fish across all of the land. Crowfoot waited for the arrival of
1157:
treaties throughout Canada have since been in communications with the government about issues with their land surrenders, improperly performed surveys and fraudulent deals. As of 2018, the talks between the two parties were still ongoing.
865:. Chief Crowfoot was one of the signatories to Treaty 7. Another signing on this treaty occurred on December 4, 1877, to accommodate some Blackfoot leaders who were not present at the primary September 1877 signing.
2264:
1105:
family was larger or smaller. Along with the exchange of land an immediate payment was given to every man, woman and child and the promise of annual payments of $ 25 to the nation's chief.
2884:
2453:
240:
Treaty and Supplementary Treaty No. 7 between Her Majesty the Queen and the Blackfeet and Other Indian Tribes, at the Blackfoot Crossing of Bow River and Fort Macleod
2889:
2311:
1171:
1036:
Presentation copy of the original Treaty 7. Printed on parchment. Text in black and red; blue and red border. Sourced from the Bruce Peel Special Collections at
806:
703:
370:
180:
1754:
427:
1731:
753:
1069:
728:
632:
1383:
1298:
1420:"The Indian Residential Schools Settlement Agreement's Common Experience Payment and Healing: A Qualitative Study Exploring Impacts on Recipients"
2969:
2607:
602:
2827:
597:
399:
2694:
516:
365:
799:
2179:
771:
496:
387:
872:
signed between First Nations and the Crown between 1871 and 1921. The treaty established a delimited area of land for the tribes (a
999:(northern Ontario, southern Manitoba) to the Rocky Mountains (northeastern British Columbia and interior Plains of Alberta) to the
196:
506:
382:
1466:
1724:
1571:
612:
521:
486:
450:
1455:
1419:
903:
2029:
1491:
921:
792:
733:
627:
544:
511:
476:
935:
1770:
969:
491:
2832:
2600:
1762:
1217:"Copy of Treaty & Supplementary Treaty No. 7 Between Her Majesty The Queen and The Blackfeet and Other Indian Tribes"
2569:
879:
Britain had transferred whatever jurisdiction over "Indians and lands reserved for the Indians" it may have had to the
132:
1717:
1344:
549:
360:
221:
151:
104:
54:
748:
2411:
2049:
1964:
738:
461:
2727:
2510:
471:
422:
184:
111:
2908:
2593:
2209:
2134:
1969:
89:
650:
2846:
2837:
1544:
1037:
675:
670:
622:
432:
377:
2974:
2721:
2486:
2249:
665:
617:
308:
118:
2964:
2356:
2159:
1709:
1249:
2939:
2918:
2474:
2458:
2279:
2254:
2224:
2169:
1979:
1685:
1564:
1057:
559:
2852:
2391:
2381:
2244:
2199:
1984:
1401:
1216:
1017:
607:
100:
85:
40:
2416:
2371:
2104:
1949:
1745:
1358:
Branch, Government of Canada; Indigenous and Northern Affairs Canada; Communications (2008-11-03).
1132:
585:
1359:
2954:
2949:
2376:
2341:
2331:
2326:
2316:
2214:
2114:
2084:
2079:
2059:
2054:
1974:
1008:
892:
846:
831:
417:
329:
188:
78:
1274:
849:
in 1875. It was concluded on September 22 and December 4, 1877. The agreement was signed at the
2959:
2944:
2498:
2406:
2336:
2194:
2074:
2069:
2044:
1097:
1021:
888:
1191:
2616:
2515:
2479:
2421:
2284:
2204:
2124:
1994:
1886:
1689:
1557:
945:
827:
2794:
2789:
2437:
2289:
2099:
1798:
1693:
1528:
884:
318:
1741:
991:
in place between other Indigenous groups and the government. This was the seventh treaty.
8:
2396:
2361:
2346:
2301:
2294:
2269:
2239:
2229:
2184:
2089:
1852:
1697:
1680:
2680:
2574:
1061:
1044:
Treaty 7 was signed in September 1877 between the Crown and the five First Nations: the
963:
590:
2804:
2784:
2711:
2632:
2119:
1783:
880:
850:
268:
1549:
1273:
Branch, Government of Canada; Indigenous and Northern Affairs Canada; Communications.
343:
125:
2764:
2164:
2154:
2139:
2064:
1999:
1901:
1581:
1377:
1292:
996:
869:
841:. The idea of developing treaties for Blackfoot lands was brought to Blackfoot chief
481:
2656:
2491:
2094:
1891:
1860:
1430:
1053:
896:
1502:
2858:
2799:
2149:
1940:
1865:
1779:
1534:
1166:
1093:
834:
680:
655:
392:
2739:
2651:
2646:
2541:
2034:
2019:
2014:
1758:
1675:
1670:
1101:
1045:
957:
951:
908:
873:
858:
743:
708:
577:
2933:
2641:
2009:
1954:
1845:
1805:
1665:
1073:
1049:
941:
925:
782:
685:
501:
466:
46:
2503:
1000:
983:
554:
437:
272:
1739:
2759:
2754:
2674:
2549:
1065:
660:
2585:
246:
2869:
2533:
1821:
443:
2749:
2109:
1838:
1814:
1788:
1649:
1644:
854:
823:
539:
456:
67:
2865:
2821:
1925:
1909:
1878:
1831:
1639:
1634:
1624:
1619:
1614:
1609:
1604:
1599:
1089:
1077:
1012:
842:
862:
838:
1456:"The Residential School Experience: Syndrome or Historic Trauma"
1591:
1535:
Alberta Online Encyclopedia Website: Treaty 7: Past and Present
929:
336:
1032:
1825:
1793:
1539:
1579:
1172:
Monarchy of Canada and the Indigenous peoples of Canada
861:
reserve, approximately 75 km (47 mi) east of
287:
2843:
War against the Crow and Gros Ventre (circa 1861–1867)
1489:
1360:"Treaty Texts: Treaty and Supplementary Treaty no. 7"
1020:
had done well in keeping American traders out of the
915:
1529:
Treaty Texts - Treaty and Supplementary Treaty no. 7
1490:
Wesley-Esquimaux, Cynthia C.; Smolewski, Magdalena.
954:(Blackfoot / Piikáni / Aapatohsipikáni / Niitsítapi)
92:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
1070:lieutenant governor of the North-West Territories
2931:
2864:Peace with the Cree, circa 1871, (symbolized by
1027:
1003:(north of Yukon and the Northwest Territories).
16:Treaty between First Nations and Canadian Crown
2875:US land annexation, migration to Canada (1874)
1275:"Treaty Research Report - Treaty Seven (1877)"
972:(Stoney First Nation / Nakoda / Îyârhe Nakoda)
938:(Stoney First Nation / Nakoda / Îyârhe Nakoda)
907:A brass medal commemorating the treaty in the
2601:
1725:
1565:
883:in the 1840s. This authority devolved to the
800:
1382:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
1297:: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (
1125:
55:Learn how and when to remove these messages
2828:1775–1782 North American smallpox epidemic
2608:
2594:
1732:
1718:
1572:
1558:
1080:to make the negotiations on their behalf.
807:
793:
245:
2657:Amskapi Pikuni, South Piegan or Blackfeet
2615:
2180:Lesser Slave Lake Indian Regional Council
1453:
837:in what is today the southern portion of
288:§ List of the Treaty 7 First Nations
222:Learn how and when to remove this message
152:Learn how and when to remove this message
2265:Stoney Nakoda - Tsuut'ina Tribal Council
1492:"Historic Trauma and Aboriginal Healing"
1031:
902:
183:: vague phrasing that often accompanies
1318:
891:in 1867 and applied to the area of the
2970:Indigenous peoples of the Great Plains
2932:
1417:
1357:
1108:
451:Indigenous and Northern Affairs Canada
2647:Piikani, Northern Peigan or Blackfoot
2589:
2030:Confederacy of Treaty 6 First Nations
1713:
1553:
1189:
477:Missing and Murdered Indigenous Women
2914:
1399:
1395:
1393:
1338:
1336:
1334:
1332:
1330:
1323:. Heritage House Publishing Company.
1314:
1312:
1310:
1308:
1268:
1266:
1264:
1262:
1243:
1241:
1239:
1237:
1235:
1233:
1231:
1229:
163:
90:adding citations to reliable sources
61:
20:
13:
2570:List of Indian reserves in Alberta
1272:
1247:
960:(Blackfoot / Siksiká / Niitsítapi)
916:List of the Treaty 7 First Nations
14:
2986:
1522:
1454:Robertson, Lloyd Hawkeye (2006).
1390:
1342:
1327:
1305:
1259:
1226:
260:September 22 and December 4, 1877
36:This article has multiple issues.
2913:
2904:
2903:
2693:
1740:
776:
765:
317:
168:
66:
25:
2728:Fort Belknap Indian Reservation
1483:
1447:
423:British Columbia Treaty Process
77:needs additional citations for
44:or discuss these issues on the
2135:Kee Tas Kee Now Tribal Council
1411:
1351:
1209:
1190:Tesar, Alex (August 9, 2016).
1183:
1:
2885:Starvation winter (1883–1884)
2847:Treaty of Fort Laramie (1868)
2838:Treaty of Fort Laramie (1851)
1531:from the Government of Canada
1499:Aboriginal Healing Foundation
1427:Aboriginal Healing Foundation
1250:"Compact, Contract, Covenant"
1177:
1038:University of Alberta Library
1028:Negotiations and treaty terms
2722:Blackfeet Indian Reservation
2468:Not headquartered in Alberta
1321:The Great Blackfoot Treaties
428:Crown and Indigenous peoples
7:
2833:1837–1838 smallpox epidemic
2357:Western Cree Tribal Council
1160:
942:Blood Tribe (Kainai Nation)
666:Indigenous English Dialects
10:
2991:
2459:Lubicon Lake Indian Nation
2225:North Peace Tribal Council
1686:Stoney Nakoda First Nation
976:
868:Treaty 7 is one of eleven
195:Such statements should be
2899:
2853:Battle of the Belly River
2813:
2777:
2737:
2709:
2702:
2691:
2665:
2630:
2623:
2565:
2526:
2467:
2446:
2430:
2392:Yellowhead Tribal Council
2390:
2355:
2310:
2263:
2223:
2178:
2165:Whitefish Lake (Atikameg)
2133:
2080:Whitefish Lake (Goodfish)
2028:
1993:
1948:
1937:
1900:
1876:
1769:
1752:
1658:
1589:
1319:Dempsey, Hugh A. (2015).
1196:The Canadian Encyclopedia
1143:
1018:North-West Mounted Police
772:Indigenous North Americas
295:
278:
264:
256:
244:
239:
2855:(against the Cree, 1870)
2447:Not federally recognized
1950:Athabasca Tribal Council
1746:First Nations in Alberta
1659:Treaty Seven Nations
1133:Canadian Pacific Railway
1126:Implications at the time
822:is an agreement between
550:Indigenous personalities
2890:Sweetgrass Hills Treaty
1540:Treaty 7 Tribal Council
1364:www.rcaanc-cirnac.gc.ca
893:North-Western Territory
2312:Tribal Chiefs Ventures
1771:Ethnolinguistic groups
1041:
1022:North-West Territories
948:/ Káínaa / Niitsítapi)
912:
2675:Gros Ventre or Atsina
2617:Blackfoot Confederacy
2250:Little Red River Cree
1995:Blackfoot Confederacy
1887:Blackfoot Confederacy
1690:Bearspaw First Nation
1418:Reimer, Gwen (2010).
1279:www.aadnc-aandc.gc.ca
1035:
922:Bearspaw First Nation
906:
857:, at the present-day
251:The Numbered Treaties
2790:Gros Ventre language
2652:Siksika or Blackfoot
1773:(by language family)
1694:Chiniki First Nation
1545:Article on Treaty #7
1009:Hudson's Bay Company
966:(Sarcee / Tsúūt'ínà)
936:Chiniki First Nation
885:government of Canada
826:and several, mainly
676:Aboriginal syllabics
651:Indigenous languages
197:clarified or removed
86:improve this article
2881:(with Canada, 1877)
2824:(circa 1730s-1800s)
2681:Tsuutʼina or Sarcee
1965:Athabasca Chipewyan
1938:Tribal councils and
1698:Wesley First Nation
1671:Pikani First Nation
1109:Immediate aftermath
1011:. Diseases such as
970:Wesley First Nation
926:Stoney First Nation
704:Traditional beliefs
545:Indigenous cultures
388:Residential schools
378:Settler colonialism
236:
2965:History of Alberta
2861:(by US Army, 1870)
2805:Blackfoot religion
2795:Tsuutʼina language
2785:Blackfoot language
2633:Blackfoot-speaking
2454:Aseniwuche Winewak
1584:: Treaty Seven
1402:"Copy of Treaty 7"
1042:
913:
881:Province of Canada
851:Blackfoot Crossing
309:Indigenous peoples
269:Blackfoot Crossing
234:
2940:Numbered Treaties
2927:
2926:
2773:
2772:
2689:
2688:
2677:(circa 1793–1861)
2624:Tribes or Nations
2583:
2582:
2561:
2560:
2554:
2546:
2538:
2519:
2507:
2495:
2483:
2400:
2365:
2320:
2273:
2233:
2188:
2155:Lubicon Lake Band
2143:
2038:
2003:
1970:Chipewyan Prairie
1958:
1930:
1922:
1914:
1902:Numbered Treaties
1707:
1706:
1582:Numbered Treaties
1400:Dunhamel, Roger.
997:Lake of the Woods
870:Numbered Treaties
817:
816:
783:Canada portal
729:Index of articles
482:Numbered Treaties
303:
302:
232:
231:
224:
214:
213:
162:
161:
154:
136:
59:
2982:
2975:Tsuut'ina Nation
2917:
2916:
2907:
2906:
2892:(with USA, 1887)
2707:
2706:
2697:
2628:
2627:
2610:
2603:
2596:
2587:
2586:
2575:Métis in Alberta
2552:
2544:
2536:
2513:
2501:
2489:
2477:
2394:
2359:
2327:Beaver Lake Cree
2317:Beaver Lake Cree
2314:
2267:
2227:
2182:
2137:
2055:Beaver Lake Cree
2032:
1997:
1952:
1946:
1945:
1941:band governments
1928:
1920:
1912:
1892:Iron Confederacy
1744:
1734:
1727:
1720:
1711:
1710:
1681:Tsuut'ina Nation
1574:
1567:
1560:
1551:
1550:
1517:
1516:
1514:
1513:
1507:
1501:. Archived from
1496:
1487:
1481:
1480:
1478:
1477:
1471:
1465:. Archived from
1460:
1451:
1445:
1444:
1442:
1441:
1435:
1429:. Archived from
1424:
1415:
1409:
1408:
1406:
1397:
1388:
1387:
1381:
1373:
1371:
1370:
1355:
1349:
1348:
1340:
1325:
1324:
1316:
1303:
1302:
1296:
1288:
1286:
1285:
1270:
1257:
1256:
1254:
1245:
1224:
1223:
1221:
1213:
1207:
1206:
1204:
1202:
1187:
964:Tsuutʼina Nation
932:/ Îyârhe Nakoda)
835:band governments
809:
802:
795:
781:
780:
779:
770:
769:
768:
487:Royal Commission
393:Indian hospitals
366:Pre-colonization
321:
305:
304:
249:
237:
233:
227:
220:
209:
206:
200:
172:
171:
164:
157:
150:
146:
143:
137:
135:
94:
70:
62:
51:
29:
28:
21:
2990:
2989:
2985:
2984:
2983:
2981:
2980:
2979:
2930:
2929:
2928:
2923:
2895:
2868:'s adoption of
2859:Marias Massacre
2809:
2800:Blackfeet music
2769:
2733:
2724:(South Piegans)
2698:
2685:
2661:
2619:
2614:
2584:
2579:
2557:
2522:
2511:Smith's Landing
2463:
2442:
2426:
2386:
2351:
2306:
2259:
2219:
2174:
2150:Loon River Cree
2129:
2070:Ermineskin Cree
2024:
1989:
1939:
1933:
1896:
1872:
1765:
1748:
1738:
1708:
1703:
1654:
1585:
1578:
1525:
1520:
1511:
1509:
1505:
1494:
1488:
1484:
1475:
1473:
1469:
1458:
1452:
1448:
1439:
1437:
1433:
1422:
1416:
1412:
1404:
1398:
1391:
1375:
1374:
1368:
1366:
1356:
1352:
1341:
1328:
1317:
1306:
1290:
1289:
1283:
1281:
1271:
1260:
1252:
1246:
1227:
1219:
1215:
1214:
1210:
1200:
1198:
1188:
1184:
1180:
1167:Making Treaty 7
1163:
1146:
1128:
1111:
1094:Rocky Mountains
1030:
979:
918:
813:
777:
775:
774:
766:
764:
759:
758:
724:
716:
715:
699:
691:
690:
656:Inuit languages
646:
638:
637:
578:Indian reserves
573:
565:
564:
535:
527:
526:
497:Specific claims
492:Self-government
453:
413:
405:
404:
356:
310:
252:
228:
217:
216:
215:
210:
204:
201:
194:
173:
169:
158:
147:
141:
138:
95:
93:
83:
71:
30:
26:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2988:
2978:
2977:
2972:
2967:
2962:
2957:
2955:Siksika Nation
2952:
2950:Piikani Nation
2947:
2942:
2925:
2924:
2922:
2921:
2911:
2900:
2897:
2896:
2894:
2893:
2887:
2882:
2876:
2873:
2862:
2856:
2850:
2844:
2841:
2835:
2830:
2825:
2817:
2815:
2811:
2810:
2808:
2807:
2802:
2797:
2792:
2787:
2781:
2779:
2775:
2774:
2771:
2770:
2768:
2767:
2765:Tsuu T'ina 145
2762:
2757:
2752:
2746:
2744:
2735:
2734:
2732:
2731:
2730:(Gros Ventres)
2725:
2718:
2716:
2704:
2700:
2699:
2692:
2690:
2687:
2686:
2684:
2683:
2678:
2671:
2669:
2663:
2662:
2660:
2659:
2654:
2649:
2644:
2642:Kanai or Blood
2638:
2636:
2625:
2621:
2620:
2613:
2612:
2605:
2598:
2590:
2581:
2580:
2578:
2577:
2572:
2566:
2563:
2562:
2559:
2558:
2556:
2555:
2547:
2539:
2530:
2528:
2524:
2523:
2521:
2520:
2508:
2496:
2484:
2471:
2469:
2465:
2464:
2462:
2461:
2456:
2450:
2448:
2444:
2443:
2441:
2440:
2434:
2432:
2428:
2427:
2425:
2424:
2419:
2414:
2409:
2403:
2401:
2388:
2387:
2385:
2384:
2379:
2374:
2368:
2366:
2353:
2352:
2350:
2349:
2344:
2339:
2334:
2329:
2323:
2321:
2308:
2307:
2305:
2304:
2299:
2298:
2297:
2292:
2287:
2276:
2274:
2261:
2260:
2258:
2257:
2252:
2247:
2242:
2236:
2234:
2221:
2220:
2218:
2217:
2212:
2207:
2202:
2197:
2191:
2189:
2176:
2175:
2173:
2172:
2167:
2162:
2160:Peerless Trout
2157:
2152:
2146:
2144:
2131:
2130:
2128:
2127:
2122:
2117:
2112:
2107:
2102:
2097:
2092:
2087:
2082:
2077:
2072:
2067:
2062:
2057:
2052:
2047:
2041:
2039:
2026:
2025:
2023:
2022:
2017:
2012:
2006:
2004:
1991:
1990:
1988:
1987:
1982:
1977:
1972:
1967:
1961:
1959:
1943:
1935:
1934:
1932:
1931:
1923:
1915:
1906:
1904:
1898:
1897:
1895:
1894:
1889:
1883:
1881:
1874:
1873:
1871:
1870:
1869:
1868:
1858:
1857:
1856:
1849:
1842:
1835:
1819:
1818:
1817:
1812:
1811:
1810:
1803:
1791:
1776:
1774:
1767:
1766:
1755:Cultural areas
1753:
1750:
1749:
1737:
1736:
1729:
1722:
1714:
1705:
1704:
1702:
1701:
1683:
1678:
1676:Siksika Nation
1673:
1668:
1662:
1660:
1656:
1655:
1653:
1652:
1647:
1642:
1637:
1632:
1627:
1622:
1617:
1612:
1607:
1602:
1596:
1594:
1587:
1586:
1577:
1576:
1569:
1562:
1554:
1548:
1547:
1542:
1537:
1532:
1524:
1523:External links
1521:
1519:
1518:
1482:
1446:
1410:
1389:
1350:
1326:
1304:
1258:
1225:
1208:
1181:
1179:
1176:
1175:
1174:
1169:
1162:
1159:
1145:
1142:
1127:
1124:
1110:
1107:
1102:Red Deer River
1029:
1026:
978:
975:
974:
973:
967:
961:
958:Siksika Nation
955:
952:Piikani Nation
949:
939:
933:
917:
914:
909:Glenbow Museum
859:Siksika Nation
847:John McDougall
815:
814:
812:
811:
804:
797:
789:
786:
785:
761:
760:
757:
756:
751:
746:
741:
736:
731:
725:
722:
721:
718:
717:
714:
713:
712:
711:
709:Inuit religion
700:
697:
696:
693:
692:
689:
688:
683:
678:
673:
668:
663:
658:
653:
647:
644:
643:
640:
639:
636:
635:
630:
625:
620:
615:
610:
605:
600:
595:
594:
593:
588:
580:
574:
571:
570:
567:
566:
563:
562:
557:
552:
547:
542:
536:
533:
532:
529:
528:
525:
524:
519:
514:
509:
504:
499:
494:
489:
484:
479:
474:
469:
464:
459:
454:
449:
447:
440:
435:
430:
425:
420:
418:Indigenous law
414:
411:
410:
407:
406:
403:
402:
400:Reconciliation
397:
396:
395:
390:
385:
375:
374:
373:
363:
357:
354:
353:
350:
349:
348:
347:
340:
333:
323:
322:
314:
313:
301:
300:
297:
293:
292:
291:
290:
285:
280:
276:
275:
266:
262:
261:
258:
254:
253:
250:
242:
241:
230:
229:
212:
211:
176:
174:
167:
160:
159:
74:
72:
65:
60:
34:
33:
31:
24:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2987:
2976:
2973:
2971:
2968:
2966:
2963:
2961:
2960:1877 treaties
2958:
2956:
2953:
2951:
2948:
2946:
2945:Kainai Nation
2943:
2941:
2938:
2937:
2935:
2920:
2912:
2910:
2902:
2901:
2898:
2891:
2888:
2886:
2883:
2880:
2877:
2874:
2871:
2867:
2863:
2860:
2857:
2854:
2851:
2848:
2845:
2842:
2839:
2836:
2834:
2831:
2829:
2826:
2823:
2819:
2818:
2816:
2812:
2806:
2803:
2801:
2798:
2796:
2793:
2791:
2788:
2786:
2783:
2782:
2780:
2776:
2766:
2763:
2761:
2758:
2756:
2753:
2751:
2748:
2747:
2745:
2742:
2741:
2736:
2729:
2726:
2723:
2720:
2719:
2717:
2714:
2713:
2708:
2705:
2701:
2696:
2682:
2679:
2676:
2673:
2672:
2670:
2668:
2667:Later members
2664:
2658:
2655:
2653:
2650:
2648:
2645:
2643:
2640:
2639:
2637:
2635:
2634:
2629:
2626:
2622:
2618:
2611:
2606:
2604:
2599:
2597:
2592:
2591:
2588:
2576:
2573:
2571:
2568:
2567:
2564:
2551:
2548:
2543:
2540:
2535:
2532:
2531:
2529:
2525:
2517:
2512:
2509:
2505:
2500:
2497:
2493:
2488:
2485:
2481:
2476:
2475:Acho Dene Koe
2473:
2472:
2470:
2466:
2460:
2457:
2455:
2452:
2451:
2449:
2445:
2439:
2436:
2435:
2433:
2429:
2423:
2420:
2418:
2415:
2413:
2410:
2408:
2405:
2404:
2402:
2398:
2393:
2389:
2383:
2382:Sturgeon Lake
2380:
2378:
2375:
2373:
2370:
2369:
2367:
2363:
2358:
2354:
2348:
2345:
2343:
2340:
2338:
2335:
2333:
2330:
2328:
2325:
2324:
2322:
2318:
2313:
2309:
2303:
2300:
2296:
2293:
2291:
2288:
2286:
2283:
2282:
2281:
2280:Stoney Nakoda
2278:
2277:
2275:
2271:
2266:
2262:
2256:
2253:
2251:
2248:
2246:
2243:
2241:
2238:
2237:
2235:
2231:
2226:
2222:
2216:
2213:
2211:
2208:
2206:
2203:
2201:
2198:
2196:
2193:
2192:
2190:
2186:
2181:
2177:
2171:
2170:Woodland Cree
2168:
2166:
2163:
2161:
2158:
2156:
2153:
2151:
2148:
2147:
2145:
2141:
2136:
2132:
2126:
2123:
2121:
2118:
2116:
2113:
2111:
2108:
2106:
2103:
2101:
2098:
2096:
2093:
2091:
2088:
2086:
2083:
2081:
2078:
2076:
2073:
2071:
2068:
2066:
2063:
2061:
2058:
2056:
2053:
2051:
2048:
2046:
2043:
2042:
2040:
2036:
2031:
2027:
2021:
2018:
2016:
2013:
2011:
2008:
2007:
2005:
2001:
1996:
1992:
1986:
1983:
1981:
1980:Fort McMurray
1978:
1976:
1973:
1971:
1968:
1966:
1963:
1962:
1960:
1956:
1955:Fort McMurray
1951:
1947:
1944:
1942:
1936:
1927:
1924:
1919:
1916:
1911:
1908:
1907:
1905:
1903:
1899:
1893:
1890:
1888:
1885:
1884:
1882:
1880:
1875:
1867:
1864:
1863:
1862:
1859:
1855:
1854:
1850:
1848:
1847:
1843:
1841:
1840:
1836:
1834:
1833:
1829:
1828:
1827:
1823:
1820:
1816:
1813:
1809:
1808:
1804:
1802:
1801:
1797:
1796:
1795:
1792:
1790:
1787:
1786:
1785:
1781:
1778:
1777:
1775:
1772:
1768:
1764:
1760:
1756:
1751:
1747:
1743:
1735:
1730:
1728:
1723:
1721:
1716:
1715:
1712:
1699:
1695:
1691:
1687:
1684:
1682:
1679:
1677:
1674:
1672:
1669:
1667:
1666:Kainai Nation
1664:
1663:
1661:
1657:
1651:
1648:
1646:
1643:
1641:
1638:
1636:
1633:
1631:
1628:
1626:
1623:
1621:
1618:
1616:
1613:
1611:
1608:
1606:
1603:
1601:
1598:
1597:
1595:
1593:
1588:
1583:
1575:
1570:
1568:
1563:
1561:
1556:
1555:
1552:
1546:
1543:
1541:
1538:
1536:
1533:
1530:
1527:
1526:
1508:on 2016-09-14
1504:
1500:
1493:
1486:
1472:on 2016-08-26
1468:
1464:
1457:
1450:
1436:on 2016-09-09
1432:
1428:
1421:
1414:
1403:
1396:
1394:
1385:
1379:
1365:
1361:
1354:
1346:
1343:Tesar, Alex.
1339:
1337:
1335:
1333:
1331:
1322:
1315:
1313:
1311:
1309:
1300:
1294:
1280:
1276:
1269:
1267:
1265:
1263:
1251:
1248:Miller, J.r.
1244:
1242:
1240:
1238:
1236:
1234:
1232:
1230:
1218:
1212:
1197:
1193:
1186:
1182:
1173:
1170:
1168:
1165:
1164:
1158:
1154:
1150:
1141:
1137:
1134:
1123:
1119:
1115:
1106:
1103:
1099:
1098:Cypress Hills
1095:
1091:
1085:
1081:
1079:
1075:
1074:James Macleod
1071:
1067:
1063:
1059:
1058:Stoney-Nakoda
1055:
1051:
1048:(Blackfoot),
1047:
1039:
1034:
1025:
1023:
1019:
1014:
1010:
1004:
1002:
998:
992:
988:
985:
971:
968:
965:
962:
959:
956:
953:
950:
947:
943:
940:
937:
934:
931:
927:
923:
920:
919:
910:
905:
901:
898:
897:Rupert's Land
894:
890:
889:Confederation
886:
882:
877:
875:
871:
866:
864:
860:
856:
852:
848:
844:
840:
836:
833:
829:
825:
821:
810:
805:
803:
798:
796:
791:
790:
788:
787:
784:
773:
763:
762:
755:
752:
750:
747:
745:
742:
740:
739:First Nations
737:
735:
732:
730:
727:
726:
720:
719:
710:
707:
706:
705:
702:
701:
695:
694:
687:
686:Inuit grammar
684:
682:
679:
677:
674:
672:
669:
667:
664:
662:
659:
657:
654:
652:
649:
648:
642:
641:
634:
633:Pacific Coast
631:
629:
626:
624:
621:
619:
616:
614:
611:
609:
606:
604:
601:
599:
596:
592:
589:
587:
584:
583:
581:
579:
576:
575:
569:
568:
561:
558:
556:
553:
551:
548:
546:
543:
541:
538:
537:
531:
530:
523:
520:
518:
517:Organizations
515:
513:
510:
508:
505:
503:
502:Treaty rights
500:
498:
495:
493:
490:
488:
485:
483:
480:
478:
475:
473:
470:
468:
467:Land defender
465:
463:
460:
458:
455:
452:
448:
446:
445:
441:
439:
436:
434:
433:Health Policy
431:
429:
426:
424:
421:
419:
416:
415:
409:
408:
401:
398:
394:
391:
389:
386:
384:
381:
380:
379:
376:
372:
369:
368:
367:
364:
362:
359:
358:
352:
351:
346:
345:
341:
339:
338:
334:
332:
331:
330:First Nations
327:
326:
325:
324:
320:
316:
315:
312:
307:
306:
298:
294:
289:
286:
283:
282:
281:
277:
274:
270:
267:
263:
259:
255:
248:
243:
238:
226:
223:
208:
198:
192:
190:
186:
182:
177:This article
175:
166:
165:
156:
153:
145:
134:
131:
127:
124:
120:
117:
113:
110:
106:
103: –
102:
98:
97:Find sources:
91:
87:
81:
80:
75:This article
73:
69:
64:
63:
58:
56:
49:
48:
43:
42:
37:
32:
23:
22:
19:
2878:
2738:
2712:Reservations
2710:
2666:
2631:
2431:Unaffiliated
2347:Kehewin Cree
2210:Sucker Creek
2090:Kehewin Cree
1985:Mikisew Cree
1917:
1851:
1844:
1837:
1830:
1806:
1799:
1629:
1510:. Retrieved
1503:the original
1498:
1485:
1474:. Retrieved
1467:the original
1462:
1449:
1438:. Retrieved
1431:the original
1426:
1413:
1367:. Retrieved
1363:
1353:
1320:
1282:. Retrieved
1278:
1211:
1199:. Retrieved
1195:
1185:
1155:
1151:
1147:
1138:
1129:
1120:
1116:
1112:
1086:
1082:
1043:
1005:
1001:Beaufort Sea
993:
989:
980:
878:
867:
832:First Nation
819:
818:
572:Demographics
555:Country food
442:
438:Idle No More
342:
335:
328:
273:Fort Macleod
218:
202:
189:unverifiable
181:weasel words
178:
148:
139:
129:
122:
115:
108:
96:
84:Please help
79:verification
76:
52:
45:
39:
38:Please help
35:
18:
2760:Siksika 146
2755:Piikani 147
2703:Communities
2120:Samson Cree
2115:Saddle Lake
1877:Historical
1839:Dënesųłı̨ne
1463:Pimatisiwin
1201:February 5,
1066:David Laird
681:Chinuk pipa
661:Chinuk Wawa
645:Linguistics
628:Territories
598:Atlantic CA
462:Land claims
191:information
2934:Categories
2870:Poundmaker
2849:(with USA)
2840:(with USA)
2534:Papaschase
2527:Terminated
2499:Onion Lake
2487:Kelly Lake
2397:Morinville
2377:Horse Lake
2362:Valleyview
2342:Heart Lake
2230:High Level
2215:Swan River
2185:Slave Lake
2095:Louis Bull
2085:Heart Lake
2065:Enoch Cree
1975:Fort McKay
1822:Athapascan
1784:Algonquian
1512:2023-09-11
1476:2023-09-11
1440:2023-09-10
1369:2021-01-18
1345:"Treaty 7"
1284:2018-03-29
1192:"Treaty 7"
1178:References
1056:(Peigan),
734:Indigenous
472:Land title
444:Indian Act
112:newspapers
101:"Treaty 7"
41:improve it
2820:War with
2750:Blood 148
2542:Sharphead
2407:Alexander
2337:Frog Lake
2332:Cold Lake
2302:Tsuut'ina
2270:Tsuut'ina
2245:Dene Tha'
2200:Kapawe'no
2195:Driftpile
2075:Frog Lake
2060:Cold Lake
2045:Alexander
1853:Tsuut'ina
1846:Dene Tha'
1815:Saulteaux
1789:Blackfoot
1763:Subarctic
1650:Treaty 11
1645:Treaty 10
1590:Numbered
1062:Tsuut’ina
1052:(Blood),
946:Blackfoot
855:Bow River
828:Blackfoot
824:the Crown
698:Religions
457:Land Back
311:in Canada
205:June 2022
179:contains
142:June 2022
47:talk page
2909:Category
2879:Treaty 7
2872:in 1873)
2866:Crowfoot
2822:Shoshone
2743:(Canada)
2740:Reserves
2438:Bigstone
2422:Sunchild
2417:O'Chiese
2372:Duncan's
2285:Bearspaw
2255:Tallcree
2205:Sawridge
2140:Atikameg
2125:Sunchild
2105:O'Chiese
2000:Standoff
1926:Treaty 8
1918:Treaty 7
1910:Treaty 6
1879:polities
1807:Woodland
1640:Treaty 9
1635:Treaty 8
1630:Treaty 7
1625:Treaty 6
1620:Treaty 5
1615:Treaty 4
1610:Treaty 3
1605:Treaty 2
1600:Treaty 1
1592:Treaties
1378:cite web
1293:cite web
1161:See also
1090:Red Crow
1078:Crowfoot
1013:smallpox
843:Crowfoot
820:Treaty 7
522:Politics
512:Case law
507:Genocide
412:Politics
383:Genocide
371:Genetics
361:Timeline
296:Language
265:Location
235:Treaty 7
2919:Commons
2814:History
2778:Culture
2290:Chiniki
2100:Montana
2020:Siksika
2015:Piikani
1832:Daneẕaa
1096:to the
1054:Piikani
1046:Siksika
984:buffalo
977:Context
911:, 1877.
874:reserve
863:Calgary
853:of the
839:Alberta
534:Culture
355:History
299:English
279:Parties
126:scholar
2553:(1958)
2550:Michel
2545:(1897)
2537:(1891)
2412:Alexis
2295:Wesley
2240:Beaver
2050:Alexis
2010:Kainai
1929:(1899)
1921:(1877)
1913:(1876)
1866:Nakoda
1861:Siouan
1800:Plains
1759:Plains
1144:Legacy
1100:, the
1072:) and
1060:, and
1050:Kainai
930:Nakoda
284:Canada
257:Signed
185:biased
128:
121:
114:
107:
99:
2035:Enoch
1780:Algic
1506:(PDF)
1495:(PDF)
1470:(PDF)
1459:(PDF)
1434:(PDF)
1423:(PDF)
1405:(PDF)
1253:(PDF)
1220:(PDF)
754:Stubs
749:Métis
744:Inuit
723:Index
591:Métis
560:Music
344:Métis
337:Inuit
133:JSTOR
119:books
2715:(US)
2110:Paul
1826:Dene
1794:Cree
1580:The
1384:link
1299:link
1203:2018
895:and
671:NAPA
105:news
887:at
845:by
582:AB
540:Art
187:or
88:by
2936::
2516:NT
2504:SK
2492:BC
2480:NT
1824:/
1782:/
1761:,
1757::
1696:/
1692:/
1497:.
1461:.
1425:.
1392:^
1380:}}
1376:{{
1362:.
1329:^
1307:^
1295:}}
1291:{{
1277:.
1261:^
1228:^
1194:.
1024:.
928:/
830:,
623:SK
618:QC
613:ON
608:MB
603:BC
586:FN
271:,
50:.
2609:e
2602:t
2595:v
2518:)
2514:(
2506:)
2502:(
2494:)
2490:(
2482:)
2478:(
2399:)
2395:(
2364:)
2360:(
2319:)
2315:(
2272:)
2268:(
2232:)
2228:(
2187:)
2183:(
2142:)
2138:(
2037:)
2033:(
2002:)
1998:(
1957:)
1953:(
1733:e
1726:t
1719:v
1700:)
1688:(
1573:e
1566:t
1559:v
1515:.
1479:.
1443:.
1407:.
1386:)
1372:.
1347:.
1301:)
1287:.
1255:.
1222:.
1205:.
1068:(
1040:.
944:(
924:(
808:e
801:t
794:v
225:)
219:(
207:)
203:(
199:.
193:.
155:)
149:(
144:)
140:(
130:·
123:·
116:·
109:·
82:.
57:)
53:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.