2254:
66:
36:
97:
435:
2266:
511:
366:
73:
43:
2242:
478:. Wiedmer's research suggested the possibility of Lake Atna being a serial generator of megafloods from glacial dam failures. One such possible flood originated from a catastrophic failure of a glacial dam 61 m (200 ft) in height at Tahneta Pass, located at the eastern end of Matanuska Valley. Wiedmer's maximum estimates of this flood place its size at a 2.0–3.3 × 10
2230:
345:(USGS). Based on sedimentary evidence, he concluded that there was a possibility of a large body of standing water being responsible for the deposits and that this could have been an arm of the sea. Alongside A. C. Spencer in 1901, he concluded – contrary to his earlier hypothesis – that these deposits occurred only in limited areas. This conclusion was supported by
458:, some distance from the Copper River Basin area. Pygmy whitefish are known to exist in remnant lakes of Lake Atna. This offered a clue as to a water connection that may have existed at some time in the past between Lake Atna and Lake George. Wiedmer also observed the presence of large, symmetrical hills in the
541:
origin deposits exist in many areas of the Copper River Basin. All major rivers present today occupy narrow valleys that have cut up to 137 m (449 ft) into the bottom of the basin. Lacustrine sediments of the lake are visible in many river bluffs throughout the basin. Several extant lakes
501:
into the Tok River, and down the Copper River itself. The
Susitna River outburst may have been responsible for a flood three to four times more intense than the Tahneta Pass outburst, at a 7.0–11.3 × 10ms discharge rate. This flood may have discharged nearly twice as much water as the Tahneta Pass
402:
exist in the basin indicating sustained lake levels at a maximum of 914 m (2,999 ft) above modern sea level and other lower levels including 750 m (2,460 ft), 700 m (2,300 ft), 580 m (1,900 ft), 550 m (1,800 ft) and 490 m (1,610 ft) above
356:
In 1954, Fred Howard Moffit noted that topographic conditions were favorable for the possibility of a large lake, but that specific evidence was lacking at that time. By 1957, geologists Oscar J. Ferrians and H.R. Schmoll concluded the basin had been resident to a large proglacial lake during the
425:
indicated that Lake Atna may have been a remnant of an earlier lake called Lake
Susitna. This was contradicted by Michael Wiedmer in 2011 who stated that no evidence exists for an independent Lake Susitna. The detailed history of the lake and its extent over time is a highly complex problem, as
373:
lacustrine, alluvial, and glacial deposits that fill the Copper River Basin. Most of the section seen in this view consists of finely laminated to indistinctly bedded sand, silt, and clay, with or without coarser material, that was deposited in glacial Lake
390:
forest. During the
Wisconsin glaciation, a multitude of glaciers extended into and blocked drainage exits from the Copper River Basin. The lake formed at least as early as 58 ka, during the Pleistocene period as a result of
558:, down to a maximum depth of 75 m (246 ft) in the central basin area. The postulated Matanuska Valley flood produced by Lake Atna 17,000 years ago may have been responsible for the deposition of a thin
473:
Wiedmer's resulting research was published in a 2010 paper titled "Late
Quaternary megafloods from Glacial Lake Atna, Southcentral Alaska, U.S.A.", with co-authors from the Quaternary Research Center at the
486:. The velocity estimates of this flood range from a minimum of 13 m/s (29 mph) to 57 m/s (130 mph). The flood released a maximum of 1,400 km (340 cu mi) of water into the
1250:
889:
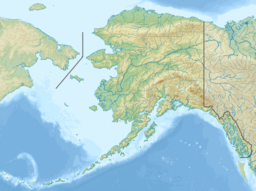
298:. The lake existed in several forms, with several prominent shorelines observable in modern geology. At its greatest extent, the lake surface area was approximately half the size of modern-day
414:, though it may have periodically topped its glacial dams. The final draining and disappearance of the lake likely happened no later than approximately 9.4 ka through the Copper River Valley.
1006:
1329:
1668:
1301:
1826:
418:
of departing ice sheets and the draining of Lake Atna from the basin remain uncertain, as detailed study of the shorelines in the basin has not been conducted.
967:
124:
1699:
1366:
607:
1197:
410:
During its early formation, the lake likely had no permanent outlet. The damming glaciers that created the lake became large enough that the lake was
398:
The highest surface level the lake achieved was 975 m (3,199 ft), based on sedimentation in the northwestern area of the basin. Multiple
1079:
551:
547:
65:
1126:
998:
562:
of clay and silt grains in the
Anchorage area. The collapse of this stratum caused catastrophic landslides in the Anchorage area during the
1678:
866:
2301:
890:"Reply to the comments of Reger, Lowell, and Evenson on "Late Quaternary megafloods from Glacial Lake Atna, Southcentral Alaska, U.S.A.""
733:
201:
2291:
494:
34 m (112 ft) in height, with crests of the dunes 0.8 km (0.50 mi) and more apart. The dunes still exist today.
1359:
382:, the region saw significant tectonic uplift through which the ancestral Copper River maintained its course. Sometime before 40
35:
1231:
671:
Schrader, F. C. (1900). "A Reconnaissance of a Part of Prince
William Sound and the Copper River District, Alaska, in 1898".
1292:
1352:
2321:
2316:
443:
679:
956:
342:
599:
403:
modern sea level. At its greatest extent, the lake surface area was approximately half the size of modern-day
1575:
1158:
2004:
322:
2296:
2077:
2067:
1445:
1414:
758:
Ferrian, Oscar J. Jr. (1957). "Extensive proglacial lake of
Wisconsin Age in the Copper River Basin".
2326:
2214:
2198:
2163:
1069:
575:
534:
422:
2306:
475:
459:
415:
357:
Wisconsin glaciation. The lake was named Lake Atna by geologist D. J. Nichols of the USGS in 1965.
346:
1071:
Model for Late
Wisconsinan Massive Outburst Flooding, Tok River Valley, Northeastern Alaska Range
1344:
395:
along the middle and lower valleys of the river, impounding the lake in the Copper River Basin.
2188:
1915:
1910:
858:
563:
338:
326:
722:
2168:
2153:
1984:
1880:
1875:
1763:
1753:
1693:
1673:
678:(Report). Part VII – Explorations in Alaska in 1898. Government Printing House. p. 402.
483:
287:
205:
176:
156:
1075:
1821:
1265:
1173:
904:
502:
outburst. The postulated glacial dam height for this flood was 346 m (1,135 ft).
451:
369:
The bluffs near the confluence of the Gakona and Copper Rivers expose nearly 300 ft of the
295:
8:
2311:
315:
110:
2110:
1269:
1177:
908:
325:. Old deposits from one of these floods may have added to the destruction caused by the
1189:
920:
307:
1277:
1157:
Wiedmer, Michael; Montgomery, David R.; Gillespie, Alan R.; Greenberg, Harvey (2010),
888:
Wiedmer, Michael; Montgomery, David R.; Gillespie, Alan R.; Greenberg, Harvey (2011).
490:
region over the span of a week. The intensity of the release was such that it created
1896:
1393:
1320:
1193:
924:
311:
302:, and possibly much larger. The basin of the lake lay within an area bordered by the
291:
2148:
1251:"Facies architecture within a regional glaciolacustrine basin: Copper River, Alaska"
290:, an area roughly centered around 245 km (152 mi) northeast of modern-day
2234:
1989:
1934:
1885:
1870:
1273:
1181:
912:
251:
1216:
2087:
1782:
1729:
1658:
1473:
1378:
487:
447:
399:
392:
383:
283:
279:
193:
161:
1185:
1159:"Late Quaternary megafloods from Glacial Lake Atna, Southcentral Alaska, U.S.A."
916:
2246:
1999:
1994:
1842:
1831:
1811:
1806:
1739:
1714:
1663:
1627:
1622:
1530:
1483:
467:
497:
Other glacial dam outbursts may have occurred down the
Susitna River, through
2285:
2270:
2100:
2062:
2032:
2027:
1905:
1865:
1860:
1850:
1816:
1787:
1643:
1617:
1525:
1520:
1478:
515:
498:
197:
139:
126:
2258:
2173:
2105:
2095:
1968:
1954:
1748:
1709:
1704:
1638:
1594:
1565:
1560:
1551:
1468:
1435:
1430:
1398:
672:
543:
455:
434:
404:
303:
299:
1294:
A Geologic Guide to
Wrangell–Saint EliasNational Park and Preserve, Alaska
2158:
2072:
2057:
2037:
1963:
1944:
1855:
1797:
1773:
1719:
1688:
1683:
1653:
1633:
1609:
1599:
1570:
1375:
673:
Twentieth Annual report of the United States Geological Survey, 1898–1899
350:
101:
Map showing one of the possible extents (pale green) of ancient Lake Atna
2193:
2052:
2047:
2042:
2019:
2009:
1939:
1925:
1758:
1724:
1488:
555:
538:
370:
2265:
177:
1648:
1585:
1504:
526:
411:
187:
1440:
1156:
1112:
1055:
1043:
1027:
887:
825:
723:"Geology of the Eastern Part of the Alaska Range and Adjacent Area"
658:
637:
519:
510:
365:
1076:
The Geological Society of America (GSA) 2010 Denver Annual Meeting
96:
1374:
559:
463:
379:
2120:
1127:"Research shows part of Alaska inundated by ancient megafloods"
999:"Research shows part of Alaska inundated by ancient megafloods"
387:
2183:
466:
origin. This led Wiedmer to investigate the possibility of a
257:
2178:
1300:, U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey,
566:
contributing to the collapse of structures built above it.
530:
491:
266:
321:
Lake Atna may have generated several of the largest ever
514:
The Copper River Basin as it is now, looking east from
604:
University of Alaska Fairbanks – Geophysical Institute
386:, the basin was free of water and ice, and covered in
554:. Much of the unconsolidated fill of the basin is in
263:
438:
Map showing geographic features related to Lake Atna
341:
undertook a study of the Copper River Basin for the
260:
254:
442:In 2005, Michael Wiedmer, then a biologist at the
223:8,900–24,000 km (3,400–9,300 sq mi)
751:
542:in the basin are remnants of the lake, including
421:In 2006, John Jangala, an archaeologist with the
2283:
1322:Geoarchaeology of Glacial Lakes Susitna and Atna
1217:"Glacial Lake Atna, Copper River Basin, Alaskan"
117:
789:
787:
785:
670:
231:2,300–6,000 km (550–1,440 cu mi)
1360:
1068:Hubbard, Trent D.; Reger, Richard D. (2010).
806:
804:
802:
482:ms (2.0–3.3 million cubic meters per second)
353:deposits in the central region of the basin.
294:. The lake formed, and dispersed, during the
1067:
840:
838:
836:
834:
782:
1039:
1037:
1035:
821:
819:
704:
702:
700:
593:
591:
1367:
1353:
992:
990:
988:
799:
654:
652:
650:
648:
646:
633:
631:
629:
627:
625:
1124:
996:
831:
714:
1214:
1032:
816:
793:
708:
697:
588:
509:
470:down the valley from ancient Lake Atna.
433:
364:
1290:
1248:
1100:
985:
844:
810:
776:
757:
643:
622:
505:
282:that initially formed approximately 58
2284:
770:
760:Geological Society of America Bulletin
720:
1348:
1318:
1307:from the original on 20 February 2017
1203:from the original on 15 December 2017
944:
600:"Spillways of an ancient Alaska lake"
360:
1237:from the original on 31 January 2017
1082:from the original on 31 January 2017
1009:from the original on 1 February 2017
973:from the original on 3 February 2017
739:from the original on 31 January 2017
685:from the original on 31 January 2017
610:from the original on 31 January 2017
429:
239:975 m (3,199 ft) (maximum)
1264:(20–22), Elsevier Inc.: 2237–2279,
426:further investigation is required.
13:
2302:Glacial lakes of the United States
1328:, Alaska Journal of Anthropology,
1125:Stricherz, Vince (29 April 2010).
997:Stricherz, Vince (29 April 2010).
964:Alaska Department of Fish and Game
859:"Searching for signs of Lake Atna"
606:. University of Alaska Fairbanks.
597:
454:. This lake sits near the face of
444:Alaska Department of Fish and Game
14:
2338:
2292:Former lakes of the United States
1230:, U.S. Geological Survey: 85–88,
869:from the original on 23 July 2012
72:
42:
2264:
2252:
2240:
2228:
1332:from the original on 1 July 2021
250:
95:
71:
64:
41:
34:
1224:U.S. Geological Survey Circular
1215:Ferrians, Oscar J. Jr. (1989),
1118:
1106:
1094:
1061:
1049:
1021:
949:
938:
881:
856:
850:
522:. Lake Atna covered this basin.
343:United States Geological Survey
664:
450:which had been collected from
1:
1576:Proglacial lakes of Minnesota
1278:10.1016/S0277-3791(02)00027-6
1172:(3), Elsevier Inc.: 413–424,
581:
446:, was shown the carcass of a
349:in 1905, who had studied the
1249:Bennett, Matthew R. (2002),
1005:. University of Washington.
721:Moffit, Fred Howard (1954).
407:, and possibly much larger.
332:
323:glacial lake outburst floods
286:(thousand years ago) in the
7:
1186:10.1016/j.yqres.2010.02.005
917:10.1016/j.yqres.2010.09.003
569:
10:
2343:
1446:West Siberian Glacial Lake
1258:Quaternary Science Reviews
1149:
1133:. University of Washington
730:Geological Survey Bulletin
16:Prehistoric lake in Alaska
2322:Pleistocene United States
2317:Natural history of Alaska
2223:
2215:List of prehistoric lakes
2207:
2199:Great Tehuelche Paleolake
2141:
2119:
2086:
2018:
1977:
1953:
1924:
1894:
1840:
1796:
1772:
1738:
1608:
1584:
1550:
1543:
1513:
1497:
1461:
1454:
1423:
1407:
1386:
1291:Winkler, Gary R. (2000),
576:List of prehistoric lakes
423:Bureau of Land Management
416:Isostatic rebound effects
235:
227:
219:
215:
175:
167:
155:
116:
106:
94:
85:Show map of North America
28:
23:
1319:Smith, Gerad M. (2019),
476:University of Washington
347:Walter Curran Mendenhall
1669:Lake Houghton (glacial)
1911:Kankakee Outwash Plain
1827:Glacial Lake Sammamish
564:1964 Alaska earthquake
523:
439:
375:
339:Frank Charles Schrader
327:1964 Alaska earthquake
314:to the south, and the
140:62.28444°N 145.75000°W
1876:Lake Jordan (Montana)
1764:Glacial Lake Missoula
1754:Glacial Lake Columbia
1694:Nipissing Great Lakes
1674:Glacial Lake Iroquois
513:
437:
368:
2235:Geography portal
2005:Lake Nantucket Sound
1822:Glacial Lake Russell
506:Remnants and effects
296:Wisconsin glaciation
278:) was a prehistoric
208:depending on period.
145:62.28444; -145.75000
1270:2002QSRv...21.2237B
1178:2010QuRes..73..413W
1166:Quaternary Research
1113:Wiedmer et al. 2010
1056:Wiedmer et al. 2010
1044:Wiedmer et al. 2010
1028:Wiedmer et al. 2010
966:. State of Alaska.
909:2011QuRes..75..303W
897:Quaternary Research
826:Wiedmer et al. 2010
766:(12, part 2): 1726.
659:Wiedmer et al. 2010
638:Wiedmer et al. 2010
316:Talkeetna Mountains
136: /
111:Southcentral Alaska
2247:History portal
1700:Early Lake Ontario
524:
440:
376:
361:Geological history
308:Wrangell Mountains
306:to the north, the
288:Copper River Basin
171:Copper River Basin
55:Show map of Alaska
2297:Geology of Alaska
2279:
2278:
2271:Oceans portal
2137:
2136:
1807:Glacial Lake Hood
1696:(Multiple basins)
1630:(Multiple basins)
1539:
1538:
1394:Lake Makgadikgadi
957:"Pygmy Whitefish"
430:Megaflood history
312:Chugach Mountains
310:to the east, the
292:Anchorage, Alaska
243:
242:
236:Surface elevation
2334:
2327:Proglacial lakes
2269:
2268:
2259:Lakes portal
2257:
2256:
2255:
2245:
2244:
2243:
2233:
2232:
2231:
2111:Lake San Agustín
1990:Lake Connecticut
1935:Lake Monongahela
1886:Lake Musselshell
1871:Lake Great Falls
1548:
1547:
1459:
1458:
1381:and related seas
1379:proglacial lakes
1369:
1362:
1355:
1346:
1345:
1340:
1339:
1337:
1327:
1315:
1314:
1312:
1306:
1299:
1287:
1286:
1284:
1255:
1245:
1244:
1242:
1236:
1221:
1211:
1210:
1208:
1202:
1163:
1143:
1142:
1140:
1138:
1122:
1116:
1110:
1104:
1098:
1092:
1091:
1089:
1087:
1065:
1059:
1053:
1047:
1041:
1030:
1025:
1019:
1018:
1016:
1014:
994:
983:
982:
980:
978:
972:
961:
953:
947:
942:
936:
935:
933:
931:
894:
885:
879:
878:
876:
874:
854:
848:
842:
829:
823:
814:
808:
797:
791:
780:
774:
768:
767:
755:
749:
748:
746:
744:
738:
727:
718:
712:
706:
695:
694:
692:
690:
684:
677:
668:
662:
656:
641:
635:
620:
619:
617:
615:
595:
535:glaciolacustrine
481:
460:Matanuska Valley
274:; also known as
273:
272:
269:
268:
265:
262:
259:
256:
179:
178:Primary outflows
151:
150:
148:
147:
146:
141:
137:
134:
133:
132:
129:
119:
99:
86:
75:
74:
68:
56:
45:
44:
38:
21:
20:
2342:
2341:
2337:
2336:
2335:
2333:
2332:
2331:
2307:Lakes of Alaska
2282:
2281:
2280:
2275:
2263:
2253:
2251:
2241:
2239:
2229:
2227:
2219:
2203:
2133:
2115:
2088:Rio Grande rift
2082:
2014:
1973:
1949:
1920:
1890:
1836:
1792:
1783:Lake Bonneville
1768:
1734:
1730:Lake Whittlesey
1659:Early Lake Erie
1604:
1580:
1535:
1509:
1493:
1474:Baltic Ice Lake
1450:
1419:
1403:
1382:
1373:
1343:
1335:
1333:
1325:
1310:
1308:
1304:
1297:
1282:
1280:
1253:
1240:
1238:
1234:
1219:
1206:
1204:
1200:
1161:
1152:
1147:
1146:
1136:
1134:
1123:
1119:
1111:
1107:
1099:
1095:
1085:
1083:
1066:
1062:
1054:
1050:
1042:
1033:
1026:
1022:
1012:
1010:
995:
986:
976:
974:
970:
959:
955:
954:
950:
943:
939:
929:
927:
892:
886:
882:
872:
870:
855:
851:
843:
832:
824:
817:
809:
800:
792:
783:
775:
771:
756:
752:
742:
740:
736:
725:
719:
715:
707:
698:
688:
686:
682:
675:
669:
665:
657:
644:
636:
623:
613:
611:
596:
589:
584:
572:
508:
479:
448:pygmy whitefish
432:
393:glacial damming
363:
335:
280:proglacial lake
253:
249:
211:
194:Matanuska River
162:Proglacial lake
144:
142:
138:
135:
130:
127:
125:
123:
122:
102:
90:
89:
88:
87:
84:
83:
82:
81:
80:
76:
59:
58:
57:
54:
53:
52:
51:
50:
46:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2340:
2330:
2329:
2324:
2319:
2314:
2309:
2304:
2299:
2294:
2277:
2276:
2274:
2273:
2261:
2249:
2237:
2224:
2221:
2220:
2218:
2217:
2211:
2209:
2205:
2204:
2202:
2201:
2196:
2191:
2186:
2181:
2176:
2171:
2166:
2161:
2156:
2151:
2149:Lake Ballivián
2145:
2143:
2139:
2138:
2135:
2134:
2132:
2131:
2125:
2123:
2117:
2116:
2114:
2113:
2108:
2103:
2098:
2092:
2090:
2084:
2083:
2081:
2080:
2075:
2070:
2065:
2060:
2055:
2050:
2045:
2040:
2035:
2030:
2024:
2022:
2016:
2015:
2013:
2012:
2007:
2002:
2000:Lake Merrimack
1997:
1995:Lake Hitchcock
1992:
1987:
1981:
1979:
1975:
1974:
1972:
1971:
1966:
1960:
1958:
1951:
1950:
1948:
1947:
1942:
1937:
1931:
1929:
1922:
1921:
1919:
1918:
1916:Lake Wisconsin
1913:
1908:
1902:
1900:
1892:
1891:
1889:
1888:
1883:
1878:
1873:
1868:
1863:
1858:
1853:
1847:
1845:
1843:Missouri River
1838:
1837:
1835:
1834:
1832:Lake Skokomish
1829:
1824:
1819:
1814:
1812:Lake Nisqually
1809:
1803:
1801:
1794:
1793:
1791:
1790:
1785:
1779:
1777:
1770:
1769:
1767:
1766:
1761:
1756:
1751:
1745:
1743:
1740:Columbia River
1736:
1735:
1733:
1732:
1727:
1722:
1717:
1715:Lake Tonawanda
1712:
1707:
1702:
1697:
1691:
1686:
1681:
1676:
1671:
1666:
1664:Lake Frontenac
1661:
1656:
1651:
1646:
1641:
1636:
1631:
1628:Lake Algonquin
1625:
1623:Lake Admiralty
1620:
1614:
1612:
1606:
1605:
1603:
1602:
1597:
1591:
1589:
1582:
1581:
1579:
1578:
1573:
1568:
1563:
1557:
1555:
1545:
1541:
1540:
1537:
1536:
1534:
1533:
1531:Lake Pickering
1528:
1523:
1517:
1515:
1511:
1510:
1508:
1507:
1501:
1499:
1495:
1494:
1492:
1491:
1486:
1484:Mastogloia Sea
1481:
1476:
1471:
1465:
1463:
1456:
1452:
1451:
1449:
1448:
1443:
1438:
1433:
1427:
1425:
1421:
1420:
1418:
1417:
1411:
1409:
1405:
1404:
1402:
1401:
1396:
1390:
1388:
1384:
1383:
1372:
1371:
1364:
1357:
1349:
1342:
1341:
1316:
1288:
1246:
1212:
1153:
1151:
1148:
1145:
1144:
1117:
1105:
1103:, p. 2237
1093:
1060:
1048:
1031:
1020:
984:
948:
937:
880:
849:
830:
815:
798:
781:
779:, p. 2240
769:
750:
732:. 989-D: 159.
713:
696:
663:
642:
621:
586:
585:
583:
580:
579:
578:
571:
568:
507:
504:
484:discharge rate
462:, possibly of
431:
428:
362:
359:
334:
331:
241:
240:
237:
233:
232:
229:
225:
224:
221:
217:
216:
213:
212:
210:
209:
190:
183:
181:
173:
172:
169:
165:
164:
159:
153:
152:
120:
114:
113:
108:
104:
103:
100:
92:
91:
78:
77:
70:
69:
63:
62:
61:
60:
48:
47:
40:
39:
33:
32:
31:
30:
29:
26:
25:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2339:
2328:
2325:
2323:
2320:
2318:
2315:
2313:
2310:
2308:
2305:
2303:
2300:
2298:
2295:
2293:
2290:
2289:
2287:
2272:
2267:
2262:
2260:
2250:
2248:
2238:
2236:
2226:
2225:
2222:
2216:
2213:
2212:
2210:
2206:
2200:
2197:
2195:
2192:
2190:
2187:
2185:
2182:
2180:
2177:
2175:
2172:
2170:
2167:
2165:
2162:
2160:
2157:
2155:
2152:
2150:
2147:
2146:
2144:
2142:South America
2140:
2130:
2127:
2126:
2124:
2122:
2118:
2112:
2109:
2107:
2104:
2102:
2101:Lake Estancia
2099:
2097:
2094:
2093:
2091:
2089:
2085:
2079:
2078:Lake Thompson
2076:
2074:
2071:
2069:
2066:
2064:
2063:Lake Panamint
2061:
2059:
2056:
2054:
2051:
2049:
2046:
2044:
2041:
2039:
2036:
2034:
2033:Lake Corcoran
2031:
2029:
2028:Lake Cahuilla
2026:
2025:
2023:
2021:
2017:
2011:
2008:
2006:
2003:
2001:
1998:
1996:
1993:
1991:
1988:
1986:
1985:Lake Cape Cod
1983:
1982:
1980:
1976:
1970:
1967:
1965:
1962:
1961:
1959:
1956:
1952:
1946:
1943:
1941:
1938:
1936:
1933:
1932:
1930:
1927:
1923:
1917:
1914:
1912:
1909:
1907:
1906:Lake Kankakee
1904:
1903:
1901:
1898:
1893:
1887:
1884:
1882:
1881:Lake McKenzie
1879:
1877:
1874:
1872:
1869:
1867:
1866:Lake Glendive
1864:
1862:
1861:Lake Cut Bank
1859:
1857:
1854:
1852:
1851:Lake Chouteau
1849:
1848:
1846:
1844:
1839:
1833:
1830:
1828:
1825:
1823:
1820:
1818:
1817:Lake Puyallup
1815:
1813:
1810:
1808:
1805:
1804:
1802:
1799:
1795:
1789:
1788:Lake Lahontan
1786:
1784:
1781:
1780:
1778:
1775:
1771:
1765:
1762:
1760:
1757:
1755:
1752:
1750:
1747:
1746:
1744:
1741:
1737:
1731:
1728:
1726:
1723:
1721:
1718:
1716:
1713:
1711:
1708:
1706:
1703:
1701:
1698:
1695:
1692:
1690:
1687:
1685:
1682:
1680:
1677:
1675:
1672:
1670:
1667:
1665:
1662:
1660:
1657:
1655:
1652:
1650:
1647:
1645:
1644:Lake Chippewa
1642:
1640:
1637:
1635:
1632:
1629:
1626:
1624:
1621:
1619:
1618:Champlain Sea
1616:
1615:
1613:
1611:
1607:
1601:
1598:
1596:
1593:
1592:
1590:
1587:
1583:
1577:
1574:
1572:
1569:
1567:
1564:
1562:
1559:
1558:
1556:
1553:
1549:
1546:
1544:North America
1542:
1532:
1529:
1527:
1526:Lake Lapworth
1524:
1522:
1521:Lake Harrison
1519:
1518:
1516:
1514:Great Britain
1512:
1506:
1503:
1502:
1500:
1496:
1490:
1487:
1485:
1482:
1480:
1479:Littorina Sea
1477:
1475:
1472:
1470:
1467:
1466:
1464:
1460:
1457:
1453:
1447:
1444:
1442:
1439:
1437:
1434:
1432:
1429:
1428:
1426:
1422:
1416:
1415:Lake Washburn
1413:
1412:
1410:
1406:
1400:
1397:
1395:
1392:
1391:
1389:
1385:
1380:
1377:
1370:
1365:
1363:
1358:
1356:
1351:
1350:
1347:
1331:
1324:
1323:
1317:
1303:
1296:
1295:
1289:
1279:
1275:
1271:
1267:
1263:
1259:
1252:
1247:
1233:
1229:
1225:
1218:
1213:
1199:
1195:
1191:
1187:
1183:
1179:
1175:
1171:
1167:
1160:
1155:
1154:
1132:
1128:
1121:
1115:, p. 417
1114:
1109:
1102:
1097:
1081:
1077:
1073:
1072:
1064:
1058:, p. 421
1057:
1052:
1046:, p. 423
1045:
1040:
1038:
1036:
1029:
1024:
1008:
1004:
1000:
993:
991:
989:
969:
965:
958:
952:
946:
941:
926:
922:
918:
914:
910:
906:
902:
898:
891:
884:
868:
864:
860:
857:Ned, Rozell.
853:
846:
841:
839:
837:
835:
828:, p. 414
827:
822:
820:
813:, p. 121
812:
807:
805:
803:
795:
794:Ferrians 1989
790:
788:
786:
778:
773:
765:
761:
754:
735:
731:
724:
717:
710:
709:Ferrians 1989
705:
703:
701:
681:
674:
667:
661:, p. 422
660:
655:
653:
651:
649:
647:
640:, p. 418
639:
634:
632:
630:
628:
626:
609:
605:
601:
598:Rozell, Ned.
594:
592:
587:
577:
574:
573:
567:
565:
561:
557:
553:
549:
545:
540:
536:
532:
528:
521:
517:
516:Glenn Highway
512:
503:
500:
499:Mentasta Pass
495:
493:
489:
485:
477:
471:
469:
465:
461:
457:
453:
449:
445:
436:
427:
424:
419:
417:
413:
408:
406:
401:
396:
394:
389:
385:
381:
380:Miocene Epoch
372:
367:
358:
354:
352:
348:
344:
340:
330:
328:
324:
319:
318:to the west.
317:
313:
309:
305:
301:
297:
293:
289:
285:
281:
277:
271:
247:
238:
234:
230:
226:
222:
218:
214:
207:
203:
199:
198:Susitna River
195:
191:
189:
185:
184:
182:
180:
174:
170:
166:
163:
160:
158:
154:
149:
121:
115:
112:
109:
105:
98:
93:
67:
37:
27:
22:
19:
2174:Lake Minchin
2128:
2106:Lake Palomas
2096:Lake Alamosa
2068:Lake Russell
1969:Lake Passaic
1749:Lake Allison
1710:Lake Stanley
1705:Lake Saginaw
1639:Lake Chicago
1595:Lake Ojibway
1566:Lake Bassano
1561:Lake Agassiz
1552:Nelson River
1469:Ancylus Lake
1436:Lake Tengger
1431:Lake Bandung
1399:Lake Ptolemy
1334:, retrieved
1321:
1309:, retrieved
1293:
1281:, retrieved
1261:
1257:
1239:, retrieved
1227:
1223:
1205:, retrieved
1169:
1165:
1135:. Retrieved
1130:
1120:
1108:
1101:Bennett 2002
1096:
1084:. Retrieved
1070:
1063:
1051:
1023:
1011:. Retrieved
1002:
975:. Retrieved
963:
951:
940:
928:. Retrieved
900:
896:
883:
871:. Retrieved
862:
852:
847:, p. 81
845:Winkler 2000
811:Winkler 2000
796:, p. 87
777:Bennett 2002
772:
763:
759:
753:
741:. Retrieved
729:
716:
711:, p. 85
687:. Retrieved
666:
612:. Retrieved
603:
552:Tonsina Lake
548:Klutina Lake
544:Tazlina Lake
525:
496:
472:
456:Knik Glacier
441:
420:
409:
405:Lake Ontario
400:strand lines
397:
377:
355:
336:
320:
304:Alaska Range
300:Lake Ontario
275:
245:
244:
228:Water volume
220:Surface area
206:Copper River
168:Part of
18:
2159:Lake Escara
2073:Lake Tecopa
2058:Lake Mojave
2038:Lake Harper
1978:New England
1964:Lake Albany
1945:Teays River
1897:Mississippi
1856:Lake Circle
1798:Puget Sound
1774:Great Basin
1720:Lake Warren
1689:Lake Minong
1684:Lake Maumee
1654:Lake Duluth
1634:Lake Arkona
1610:Great Lakes
1600:Tyrrell Sea
1571:Lake Souris
1376:Pleistocene
452:Lake George
378:During the
351:Pleistocene
143: /
131:145°45′00″W
118:Coordinates
2312:Megafloods
2286:Categories
2194:Lake Tauca
2164:Inca Huasi
2053:Lake Modoc
2048:Lake Manly
2043:Lake Manix
2020:California
2010:Lake Stowe
1940:Lake Tight
1759:Lake Lewis
1725:Lake Wayne
1679:Lake Lundy
1489:Yoldia Sea
1462:Baltic Sea
1408:Antarctica
1336:2 November
1311:19 January
1283:19 January
1241:19 January
1207:19 January
1137:19 January
1086:19 January
1013:19 January
977:19 January
945:Smith 2019
930:19 January
903:(1): 303.
873:19 January
743:19 January
689:19 January
614:19 January
582:References
556:permafrost
539:lacustrine
371:Quaternary
276:Lake Ahtna
128:62°17′04″N
2129:Lake Atna
1649:Lake Dana
1586:James Bay
1505:Lake Komi
1194:129855432
925:128892602
527:Diamicton
468:megaflood
412:endorheic
337:In 1898,
333:Discovery
246:Lake Atna
202:Tok River
188:endorheic
79:Lake Atna
49:Lake Atna
24:Lake Atna
1928:drainage
1899:drainage
1588:drainage
1554:drainage
1441:Mundafan
1330:archived
1302:archived
1232:archived
1198:archived
1131:UW Today
1080:Archived
1007:Archived
1003:UW Today
968:Archived
867:Archived
734:Archived
680:Archived
608:Archived
570:See also
520:Mt. Drum
518:towards
107:Location
2208:Summary
2189:Salinas
1266:Bibcode
1174:Bibcode
1150:Sources
905:Bibcode
863:SitNews
560:stratum
531:glacial
488:Wasilla
464:fluvial
192:Later:
186:Early:
2169:Mataro
2154:Cabana
2121:Alaska
1957:valley
1955:Hudson
1895:Upper
1841:Upper
1800:system
1776:system
1742:system
1498:Russia
1455:Europe
1387:Africa
1192:
923:
550:, and
537:, and
480:
388:spruce
204:, and
2184:Sajsi
1326:(PDF)
1305:(PDF)
1298:(PDF)
1254:(PDF)
1235:(PDF)
1220:(PDF)
1201:(PDF)
1190:S2CID
1162:(PDF)
971:(PDF)
960:(PDF)
921:S2CID
893:(PDF)
737:(PDF)
726:(PDF)
683:(PDF)
676:(PDF)
492:dunes
374:Atna.
2179:Ouki
1926:Ohio
1424:Asia
1338:2019
1313:2017
1285:2017
1243:2017
1228:1026
1209:2017
1139:2017
1088:2017
1015:2017
979:2017
932:2017
875:2017
745:2017
691:2017
616:2017
157:Type
1274:doi
1182:doi
913:doi
2288::
1272:,
1262:21
1260:,
1256:,
1226:,
1222:,
1196:,
1188:,
1180:,
1170:73
1168:,
1164:,
1129:.
1078:.
1074:.
1034:^
1001:.
987:^
962:.
919:.
911:.
901:75
899:.
895:.
865:.
861:.
833:^
818:^
801:^
784:^
764:68
762:.
728:.
699:^
645:^
624:^
602:.
590:^
546:,
533:,
529:,
384:ka
329:.
284:ka
258:ɑː
200:,
196:,
1368:e
1361:t
1354:v
1276::
1268::
1184::
1176::
1141:.
1090:.
1017:.
981:.
934:.
915::
907::
877:.
747:.
693:.
618:.
270:/
267:ə
264:n
261:t
255:ˈ
252:/
248:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.