806:
800:
28:
794:
109:
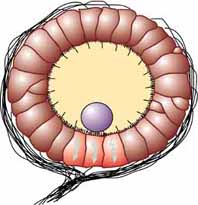
In other words, the statolith shifts as the animal moves. Any movement large enough to throw the organism off balance causes the statolith to brush against tiny bristles which in turn send a message to the brain to correct its balance.
20:
1041:
662:
352:
Levi, R.; Varona, P.; Arshavsky, Y. I.; Rabinovich, M. I.; Selverston, A. I. (2004). "Dual
Sensory-Motor Function for a Molluskan Statocyst Network".
1046:
259:
Lowe, B. (1997). "The role of Ca2+ in deflection-induced excitation of motile, mechanoresponsive balancer cilia in the ctenophore statocyst".
564:
849:
430:
Deliagina, Tatiana G.; Arshavsky, Yuri I.; Orlovsky, Grigori N. (1998). "Control of spatial orientation in a mollusc".
98:
causes it to push against the setae when the animal accelerates. Deflection of setae by the statolith in response to
557:
504:
805:
799:
793:
834:
185:
550:
1171:
1166:
1161:
854:
844:
518:
1036:
1031:
1176:
106:, providing feedback to the animal on change in orientation and allowing balance to be maintained.
387:
Cohen, M. J. (1960). "The response patterns of single receptors in the crustacean statocyst".
1138:
138:
33:
652:
1126:
164:
8:
1110:
875:
765:
750:
729:
714:
582:
689:
412:
311:
218:
745:
979:
914:
486:
447:
404:
369:
276:
241:
159:
45:
416:
1134:
1105:
1015:
904:
894:
819:
814:
724:
699:
478:
439:
396:
361:
334:
307:
268:
232:
Spangenberg, D. B. (1986). "Statolith formation in
Cnidaria: effects of cadmium on
214:
27:
1000:
972:
962:
957:
945:
930:
870:
775:
719:
637:
532:
294:
Ehlers, U. (1997). "Ultrastructure of the statocysts in the apodous sea cucumber
86:. The statocyst consists of a sac-like structure containing a mineralised mass (
1067:
889:
880:
839:
704:
694:
482:
113:
It may have been present in the common ancestor of cnidarians and bilaterians.
338:
1155:
1092:
642:
451:
325:
Clarke, M. R. (2009). "The cephalopod statolithan—introduction to its form".
154:
423:
272:
1051:
950:
709:
609:
490:
408:
400:
373:
245:
205:
Morton, B. (2009). "Statocyst structure in the
Anomalodesmata (Bivalvia)".
82:
49:
365:
280:
1005:
760:
1142:
1097:
909:
899:
647:
604:
573:
122:
77:
73:
69:
65:
61:
465:
Israelsson, O. (2007). "Ultrastructural aspects of the 'statocyst' of
1130:
770:
619:
614:
542:
179:
168:
995:
967:
57:
443:
327:
Journal of the Marine
Biological Association of the United Kingdom
885:
657:
173:
134:
130:
99:
95:
53:
31:
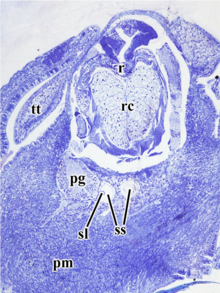
Statocysts (ss) and statolith (sl) inside the head of sea snail
1010:
103:
469:(Deuterostomia) cast doubt on its function as a georeceptor".
141:
for instance can hear low-frequency sounds between 30 and 500
755:
351:
126:
145:
when the water temperature is above 8 °C (46 °F).
19:
91:
429:
389:
Proceedings of the Royal
Society B: Biological Sciences
142:
519:"How Squid Hear: It's All in the Motion of the Ocean"
16:Statocysts are also balancing organs in arthropods
1153:
505:"Scientists Find that Squid Can Detect Sounds"
558:
231:
565:
551:
464:
176:, an equivalent structure in vertebrates.
90:) and numerous innervated sensory hairs (
26:
18:
80:, A similar structure is also found in
1154:
572:
324:
293:
204:
546:
386:
845:Flotation devices ("secondary fins")
258:
13:
1137:) → Juvenile → Subadult → Adult •
312:10.1111/j.1463-6395.1997.tb01127.x
219:10.1111/j.1469-7998.1985.tb05633.x
14:
1188:
298:(Holothuroidea, Echinodermata)".
881:Hepatopancreas (digestive gland)
804:
798:
792:
533:"Squid shown to be able to hear"
850:Funnel–mantle locking apparatus
525:
511:
497:
261:Journal of Experimental Biology
182:, a similar structure in plants
23:Drawing of the statocyst system
1037:Nuchal folds (occipital folds)
1032:Nuchal crest (occipital crest)
458:
380:
345:
318:
287:
252:
225:
198:
1:
191:
1143:Protoconch (embryonic shell)
238:Scanning Electron Microscopy
186:Sensory organs of gastropods
7:
148:
10:
1193:
483:10.1016/j.tice.2007.03.002
354:Journal of Neurophysiology
116:
1121:
1085:
1060:
1024:
988:
938:
927:
863:
827:
813:
790:
738:
682:
675:
630:
597:
590:
581:
339:10.1017/S0025315400041345
48:present in some aquatic
46:balance sensory receptor
273:10.1242/jeb.200.11.1593
167:, similar structure in
129:, statocysts provide a
401:10.1098/rspb.1960.0020
296:Leptosynapta inhaerens
37:
24:
1124:Developmental stages:
1016:Spadix and antispadix
900:Nephridia ("kidneys")
366:10.1152/jn.00753.2003
139:longfin inshore squid
34:Gigantopelta chessoia
30:
22:
267:(Pt 11): 1593–1606.
1111:Squid giant synapse
137:. As a result, the
133:-like mechanism to
94:). The statolith's
1042:Occipital membrane
915:Pericardial glands
610:Argonautid eggcase
521:. 2 February 2011.
207:Journal of Zoology
38:
25:
1172:Arthropod anatomy
1167:Cnidarian anatomy
1162:Vestibular system
1149:
1148:
1081:
1080:
980:Suckers and hooks
923:
922:
905:Nidamental glands
835:Dermal structures
788:
787:
784:
783:
671:
670:
438:(6681): 172–175.
165:Müllerian vesicle
160:Inertial guidance
1184:
1135:Doratopsis stage
1106:Squid giant axon
1025:Occipital region
936:
935:
876:Ctenidia (gills)
871:Branchial hearts
864:Internal anatomy
828:External anatomy
825:
824:
808:
802:
796:
680:
679:
595:
594:
588:
587:
567:
560:
553:
544:
543:
537:
536:
529:
523:
522:
515:
509:
508:
501:
495:
494:
462:
456:
455:
427:
421:
420:
384:
378:
377:
349:
343:
342:
322:
316:
315:
291:
285:
284:
256:
250:
249:
240:(4): 1609–1618.
229:
223:
222:
202:
169:loxodid ciliates
1192:
1191:
1187:
1186:
1185:
1183:
1182:
1181:
1177:Mollusc anatomy
1152:
1151:
1150:
1145:
1117:
1102:Nervous system
1077:
1056:
1047:Olfactory organ
1020:
984:
929:
919:
859:
818:
809:
803:
797:
780:
734:
667:
638:Belemnoid guard
626:
615:Nautiloid shell
577:
571:
541:
540:
531:
530:
526:
517:
516:
512:
503:
502:
498:
471:Tissue and Cell
463:
459:
428:
424:
385:
381:
350:
346:
323:
319:
292:
288:
257:
253:
230:
226:
203:
199:
194:
151:
119:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1190:
1180:
1179:
1174:
1169:
1164:
1147:
1146:
1122:
1119:
1118:
1116:
1115:
1114:
1113:
1108:
1100:
1095:
1093:Chromatophores
1089:
1087:
1083:
1082:
1079:
1078:
1076:
1075:
1070:
1064:
1062:
1058:
1057:
1055:
1054:
1049:
1044:
1039:
1034:
1028:
1026:
1022:
1021:
1019:
1018:
1013:
1008:
1003:
998:
992:
990:
986:
985:
983:
982:
977:
976:
975:
970:
965:
955:
954:
953:
942:
940:
939:Brachial crown
933:
925:
924:
921:
920:
918:
917:
912:
907:
902:
897:
892:
883:
878:
873:
867:
865:
861:
860:
858:
857:
852:
847:
842:
837:
831:
829:
822:
811:
810:
791:
789:
786:
785:
782:
781:
779:
778:
773:
768:
763:
758:
753:
748:
742:
740:
736:
735:
733:
732:
727:
722:
717:
712:
707:
702:
697:
692:
686:
684:
677:
673:
672:
669:
668:
666:
665:
660:
655:
650:
645:
640:
634:
632:
628:
627:
625:
624:
623:
622:
612:
607:
605:Ammonoid shell
601:
599:
592:
585:
579:
578:
570:
569:
562:
555:
547:
539:
538:
524:
510:
496:
477:(3): 171–177.
457:
422:
395:(946): 30–49.
379:
360:(1): 336–345.
344:
333:(3): 701–712.
317:
300:Acta Zoologica
286:
251:
224:
196:
195:
193:
190:
189:
188:
183:
177:
171:
162:
157:
150:
147:
118:
115:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1189:
1178:
1175:
1173:
1170:
1168:
1165:
1163:
1160:
1159:
1157:
1144:
1140:
1136:
1132:
1128:
1125:
1120:
1112:
1109:
1107:
1104:
1103:
1101:
1099:
1096:
1094:
1091:
1090:
1088:
1084:
1074:
1071:
1069:
1066:
1065:
1063:
1059:
1053:
1050:
1048:
1045:
1043:
1040:
1038:
1035:
1033:
1030:
1029:
1027:
1023:
1017:
1014:
1012:
1009:
1007:
1004:
1002:
999:
997:
994:
993:
991:
989:Buccal region
987:
981:
978:
974:
971:
969:
966:
964:
961:
960:
959:
956:
952:
949:
948:
947:
944:
943:
941:
937:
934:
932:
926:
916:
913:
911:
908:
906:
903:
901:
898:
896:
895:Needham's sac
893:
891:
887:
884:
882:
879:
877:
874:
872:
869:
868:
866:
862:
856:
853:
851:
848:
846:
843:
841:
838:
836:
833:
832:
830:
826:
823:
821:
816:
812:
807:
801:
795:
777:
774:
772:
769:
767:
764:
762:
759:
757:
754:
752:
749:
747:
744:
743:
741:
737:
731:
728:
726:
723:
721:
718:
716:
713:
711:
708:
706:
703:
701:
698:
696:
693:
691:
688:
687:
685:
681:
678:
674:
664:
661:
659:
658:Spirula shell
656:
654:
653:Gladius (pen)
651:
649:
646:
644:
643:Cirrate shell
641:
639:
636:
635:
633:
629:
621:
618:
617:
616:
613:
611:
608:
606:
603:
602:
600:
596:
593:
589:
586:
584:
580:
575:
568:
563:
561:
556:
554:
549:
548:
545:
534:
528:
520:
514:
506:
500:
492:
488:
484:
480:
476:
472:
468:
461:
453:
449:
445:
444:10.1038/30251
441:
437:
433:
426:
418:
414:
410:
406:
402:
398:
394:
390:
383:
375:
371:
367:
363:
359:
355:
348:
340:
336:
332:
328:
321:
313:
309:
305:
301:
297:
290:
282:
278:
274:
270:
266:
262:
255:
247:
243:
239:
236:statoliths".
235:
228:
220:
216:
212:
208:
201:
197:
187:
184:
181:
178:
175:
172:
170:
166:
163:
161:
158:
156:
155:Accelerometer
153:
152:
146:
144:
140:
136:
132:
128:
124:
114:
111:
107:
105:
101:
97:
93:
89:
85:
84:
79:
75:
71:
67:
63:
59:
55:
51:
50:invertebrates
47:
43:
36:
35:
29:
21:
1123:
1072:
1052:Nuchal organ
951:Hectocotylus
840:Fins (wings)
746:Body chamber
710:Periostracum
527:
513:
499:
474:
470:
467:Xenoturbella
466:
460:
435:
431:
425:
392:
388:
382:
357:
353:
347:
330:
326:
320:
303:
299:
295:
289:
264:
260:
254:
237:
233:
227:
210:
206:
200:
120:
112:
108:
87:
83:Xenoturbella
81:
62:ctenophorans
52:, including
41:
39:
32:
1139:Egg fossils
1098:Photophores
1061:Other parts
1006:Odontophore
928:Head &
761:Phragmocone
123:cephalopods
74:crustaceans
70:cephalopods
66:echinoderms
1156:Categories
1073:Statocysts
910:Osphradium
648:Cuttlebone
574:Cephalopod
192:References
102:activates
78:gastropods
58:cnidarians
1131:Paralarva
958:Tentacles
771:Siphuncle
730:Umbilicus
715:Sculpture
620:Orthocone
452:0028-0836
306:: 61–68.
213:: 23–34.
180:Statocyte
88:statolith
42:statocyst
996:Aptychus
968:Dactylus
739:Internal
690:Aperture
683:External
676:Features
631:Internal
598:External
491:17434196
417:29494854
409:13849418
374:14507988
246:11539690
149:See also
54:bivalves
1086:General
886:Ink sac
751:Camerae
725:Sutures
576:anatomy
281:9202448
234:Aurelia
174:Otolith
131:cochlea
117:Hearing
104:neurons
100:gravity
96:inertia
1011:Radula
963:Carpus
820:funnel
817:&
815:Mantle
776:Whorls
700:Callus
663:Stylet
489:
450:
432:Nature
415:
407:
372:
279:
244:
127:squids
76:, and
1127:Spawn
973:Manus
931:limbs
766:Septa
756:Nacre
720:Spire
705:Lirae
591:Types
583:Shell
413:S2CID
125:like
92:setae
44:is a
1068:Eyes
1001:Beak
946:Arms
888:and
855:Tail
695:Apex
487:PMID
448:ISSN
405:PMID
370:PMID
277:PMID
242:PMID
135:hear
40:The
890:ink
479:doi
440:doi
436:393
397:doi
393:152
362:doi
335:doi
308:doi
269:doi
265:200
215:doi
211:206
121:In
72:,
1158::
1141:•
1129:→
485:.
475:39
473:.
446:.
434:.
411:.
403:.
391:.
368:.
358:91
356:.
331:58
329:.
304:78
302:.
275:.
263:.
209:.
143:Hz
68:,
64:,
60:,
56:,
1133:(
566:e
559:t
552:v
535:.
507:.
493:.
481::
454:.
442::
419:.
399::
376:.
364::
341:.
337::
314:.
310::
283:.
271::
248:.
221:.
217::
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.