498:(also known as pleomorphic adenomas). Benign tumors are almost always cured by surgery. Very rarely, they may become cancer if left untreated for a long time or if they are not completely removed and grow back. It's not clear exactly how benign tumors become cancers. There are many types of salivary gland cancers. Normal salivary glands are made up of several different types of cells, and tumors can start in any of these cell types. Salivary gland cancers are named according to which of these cell types they most look like when seen under a microscope. The main types of cancers are described below. Doctors usually give salivary cancers a grade (from 1 to 3, or from low to high), based on how abnormal the cancers look under a microscope. The grade gives a rough idea of how quickly it is likely to grow and spread.
40:
314:
497:
Most salivary gland tumors are benign – that is, they are not cancer and will not spread to other parts of the body. These tumors are almost never life-threatening. There are many types of benign salivary gland tumors, with names such as adenomas, oncocytomas, Warthin tumors, and benign mixed tumors
321:
Adrenal adenomas are common, and are often found on the abdomen, usually not as the focus of investigation; they are usually incidental findings. About one in 10,000 is malignant. Thus, a biopsy is rarely called for, especially if the lesion is homogeneous and smaller than 3 centimeters. Follow-up
526:
A physician's response to detecting an adenoma in a patient will vary according to the type and location of the adenoma among other factors. Different adenomas will grow at different rates, but typically physicians can anticipate the rates of growth because some types of common adenomas progress
537:
upon removing adenomatous polyps from a patient. In the common case of removing one or two of these polyps from the colon from a patient with no particular risk factors for cancer, thereafter the best practice is to resume surveillance colonoscopy after 5–10 years rather than repeating it more
264:
or loss of normal differentiation of epithelium) irregular cells with hyperchromatic nuclei, stratified or pseudostratified nuclei, nucleolus, decreased mucosecretion, and mitosis. The architecture may be tubular, villous, or tubulo-villous. Basement membrane and muscularis mucosae are intact.
449:
Adenomas can also appear in the appendix. The condition is extremely rare. The most common version is called cystadenoma. They are usually discovered in the course of examination of the tissue following an appendectomy. If the appendix has ruptured and a tumor is present, this presents
252:
or polypoid adenoma. Adenomatous polyps may be classified based on morphology in order to identify lesions at increased risk of malignant transformation. For example, adenomatous polyps in the colon may be pedunculated (lobular head with a long slender stalk) or sessile (broad base).
367:
nodules. Investigation is required because a small percentage of these is malignant. Biopsy usually confirms the growth to be an adenoma, but, sometimes, excision at surgery is required, especially when the cells found at biopsy are of the follicular type.
247:
Adenoma is a benign tumor of glandular tissue, such as the mucosa of stomach, small intestine, and colon, in which tumor cells form glands or gland-like structures. In hollow organs (digestive tract), the adenoma grows into the lumen - adenomatous
292:
have a 6% higher risk rate of getting adenomas, and then colon cancer, than do the general population, so it is important that they have regular actual colonoscopies, and specifically none of the less invasive diagnostic methods.
508:
Grade 3 cancers (also called high grade or poorly differentiated) look very different from normal cells and often grow and/or spread quickly. The outlook for these cancers is usually not as good as for lower grade
795:
767:
555:
379:
are seen in 10% of neurological patients. A lot of them remain undiagnosed. Treatment is usually surgical, to which patients generally respond well. The most common subtype,
502:
Grade 1 cancers (also called low grade or well differentiated) look very much like normal salivary gland cells. They tend to grow slowly and have a good outcome (prognosis).
630:
227:. Most adenomas do not transform. However, even though benign, they have the potential to cause serious health complications by compressing other structures (
827:
527:
similarly in most patients. Two common responses are removing the adenoma with surgery and then monitoring the patient according to established guidelines.
505:
Grade 2 cancers (also called intermediate grade or moderately differentiated) have an appearance and outlook that is between grade 1 and grade 3 cancers.
601:
559:
883:
910:
441:. They are often very small and difficult to detect. Often there are no symptoms. Treatments can include a needle biopsy, and/or removal.
1539:
207:, and others. Some adenomas grow from epithelial tissue in nonglandular areas but express glandular tissue structure (as can happen in
644:
626:
301:
This is a tumor that is most often small and asymptomatic, and is derived from renal tubules. It may be a precursor lesion to
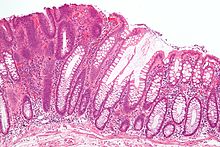
582:
875:
489:
condition characterized by a slow-growing tumour usually presenting as a pink, flesh-coloured, or yellow papule or nodule.
1385:
713:
Rex DK, Petrini JL, Baron TH, Chak A, Cohen J, Deal SE, et al. (April 2006). "Quality indicators for colonoscopy".
954:
903:
648:
1435:
1439:
1272:
1060:
429:
Hepatic adenomas are a rare benign tumour of the liver, which may present with hepatomegaly or other symptoms.
674:"Colorectal cancer screening and surveillance: clinical guidelines and rationale-Update based on new evidence"
1534:
1377:
896:
1166:
1424:
1341:
974:
412:
1481:
1463:
1373:
1324:
534:
1458:
1381:
1218:
1044:
1007:
395:
generally suppresses prolactinomas; progesterone antagonist therapy has not proven to be successful.
1486:
1419:
1354:
1228:
1208:
1175:
1153:
1115:
838:
518:
Prostate adenoma develops from the periurethral glands at the site of the median or lateral lobes.
216:
54:
and a precursor of colorectal cancer. Normal colorectal mucosa is seen on the right of the image.
964:
470:
239:). Some adenomas are too small to be seen macroscopically but can still cause clinical symptoms.
236:
208:
1347:
1171:
1111:
424:
228:
286:. They are removed because of their tendency to become malignant and to lead to colon cancer.
1509:
1233:
1337:
1196:
1133:
969:
949:
531:
383:, is seen more often in women, and is frequently diagnosed during pregnancy as the hormone
302:
8:
1473:
1125:
959:
799:
408:
1306:
1138:
1101:
997:
979:
832:
672:
Winawer S, Fletcher R, Rex D, Bond J, Burt R, Ferrucci J, et al. (February 2003).
466:
279:
820:
812:
808:
804:
450:
challenges, especially if malignant cells have formed and thus spread to the abdomen.
1450:
730:
695:
578:
482:
404:
376:
158:
816:
1411:
1329:
1143:
1055:
722:
685:
346:
330:
249:
109:
71:
888:
187:
origin, glandular characteristics, or both. Adenomas can grow from many glandular
1429:
1092:
843:
639:
358:
196:
188:
39:
1180:
1106:
1035:
325:
While some adrenal adenomas do not secrete hormones at all, often some secrete
289:
224:
192:
788:
780:
1528:
392:
338:
51:
784:
776:
690:
673:
256:
The adenomatous proliferation is characterized by different degrees of cell
1364:
1316:
1260:
1161:
870:
734:
699:
438:
384:
380:
176:
55:
1302:
1077:
989:
388:
334:
283:
556:"What is the relationship between Ashkenazi Jews and colorectal cancer?"
313:
1213:
1082:
1072:
928:
726:
322:
images in three to six months can confirm the stability of the growth.
220:
180:
47:
759:
1265:
1201:
941:
937:
849:
486:
342:
257:
625:
462:
326:
232:
204:
163:
215:, they should be treated as pre-cancerous. Over time adenomas may
1223:
1002:
854:
364:
200:
1500:
1293:
1087:
920:
771:
530:
One common example of treatment is the response recommended by
261:
212:
1021:
184:
142:
130:
98:
92:
235:
in an unregulated, non-feedback-dependent manner (causing
136:
121:
115:
83:
77:
572:
1029:
16:
Benign tumor of glandular origin and/or characteristics
671:
631:"Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question"
127:
112:
89:
74:
749:
139:
118:
80:
918:
712:
133:
124:
95:
86:
282:, are quite prevalent. They are found commonly at
573:Mitchell RS, Kumar V, Abbas AK, Fausto N (2007).
363:About one in 10 people is found to have solitary
317:MRI scan T1 with fat saturation - adrenal adenoma
1526:
50:of a tubular adenoma (left of image), a type of
904:
706:
538:frequently than the standard recommendation.
407:may secrete inappropriately high amounts of
387:increases its growth. Medical therapy with
911:
897:
38:
689:
665:
715:The American Journal of Gastroenterology
645:American Gastroenterological Association
627:American Gastroenterological Association
577:(8th ed.). Philadelphia: Saunders.
312:
566:
1527:
638:Choosing Wisely: an initiative of the
619:
892:
231:) and by producing large amounts of
1386:Papillary serous cystadenocarcinoma
278:Adenomas of the colon, also called
13:
1540:Glandular and epithelial neoplasia
955:Combined small-cell lung carcinoma
492:
14:
1551:
745:
242:
223:, at which point they are called
602:"What Is Salivary Gland Cancer?"
108:
70:
1273:Syringocystadenoma papilliferum
868:Adrenal adenoma description at
1061:Familial adenomatous polyposis
594:
548:
398:
1:
1436:Paget's disease of the breast
1378:Pancreatic serous cystadenoma
541:
1440:Extramammary Paget's disease
1167:Multiple endocrine neoplasia
521:
476:
453:
371:
268:
7:
1425:Pancreatic ductal carcinoma
1342:Mucinous cystadenocarcinoma
975:Transitional cell carcinoma
558:. WebMD LLC. Archived from
513:
444:
437:Breast adenomas are called
413:primary hyperparathyroidism
10:
1556:
1482:Medullary breast carcinoma
1464:Invasive lobular carcinoma
1374:Ovarian serous cystadenoma
1325:Signet ring cell carcinoma
882:Photos (colon adenoma) at
535:professional organizations
422:
356:
352:
308:
1499:
1472:
1459:Lobular carcinoma in situ
1449:
1410:
1399:
1382:Serous cystadenocarcinoma
1363:
1315:
1292:
1281:
1246:
1219:Clear-cell adenocarcinoma
1189:
1152:
1124:
1043:
1020:
1008:Bartholin gland carcinoma
988:
936:
927:
919:Glandular and epithelial
753:
432:
211:). Although adenomas are
157:
62:
46:
37:
29:
24:
1487:Medullary thyroid cancer
1420:Mammary ductal carcinoma
1355:Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
1209:Adenoid cystic carcinoma
1176:Adrenocortical carcinoma
1116:Hepatocellular carcinoma
418:
296:
273:
237:paraneoplastic syndromes
965:Squamous-cell carcinoma
691:10.1053/gast.2003.50044
575:Robbins Basic Pathology
471:paraneoplastic syndrome
209:familial polyposis coli
1348:Pseudomyxoma peritonei
1172:Adrenocortical adenoma
1112:Hepatocellular adenoma
425:Hepatocellular adenoma
318:
1510:Acinic cell carcinoma
1234:Papillary hidradenoma
423:Further information:
357:Further information:
316:
1535:Anatomical pathology
1338:Mucinous cystadenoma
1197:Neuroendocrine tumor
1134:Renal cell carcinoma
970:Basal-cell carcinoma
950:Small-cell carcinoma
461:are adenomas in the
1474:Medullary carcinoma
960:Verrucous carcinoma
562:on 16 October 2019.
409:parathyroid hormone
33:Adenomas, adenomata
1307:Cystadenocarcinoma
1139:Endometrioid tumor
1102:Cholangiocarcinoma
990:Complex epithelial
980:Inverted papilloma
884:Atlas of Pathology
727:10.1038/ajg2006227
467:carcinoid syndrome
459:Bronchial adenomas
411:and thereby cause
377:Pituitary adenomas
331:Cushing's syndrome
319:
280:adenomatous polyps
1522:
1521:
1518:
1517:
1495:
1494:
1451:Lobular carcinoma
1395:
1394:
1242:
1241:
1016:
1015:
864:
863:
654:on August 9, 2012
584:978-1-4160-2973-1
483:sebaceous adenoma
465:. They may cause
405:parathyroid gland
169:
168:
19:Medical condition
1547:
1442:
1412:Ductal carcinoma
1408:
1407:
1388:
1344:
1330:Krukenberg tumor
1290:
1289:
1144:Renal oncocytoma
1056:Linitis plastica
1045:Gastrointestinal
1041:
1040:
1027:
1026:
934:
933:
913:
906:
899:
890:
889:
751:
750:
739:
738:
710:
704:
703:
693:
678:Gastroenterology
669:
663:
662:
661:
659:
653:
647:, archived from
635:
623:
617:
616:
614:
612:
598:
592:
591:
570:
564:
563:
552:
403:An adenoma of a
347:hyperandrogenism
191:, including the
149:
148:
145:
144:
141:
138:
135:
132:
129:
126:
123:
120:
117:
114:
105:
104:
101:
100:
97:
94:
91:
88:
85:
82:
79:
76:
42:
22:
21:
1555:
1554:
1550:
1549:
1548:
1546:
1545:
1544:
1525:
1524:
1523:
1514:
1491:
1468:
1445:
1434:
1430:Comedocarcinoma
1403:
1401:
1391:
1372:
1359:
1336:
1311:
1285:
1283:
1277:
1248:
1238:
1185:
1148:
1120:
1093:Somatostatinoma
1036:adenocarcinomas
1034:
1012:
998:Warthin's tumor
984:
923:
917:
865:
860:
859:
762:
748:
743:
742:
711:
707:
670:
666:
657:
655:
651:
640:ABIM Foundation
633:
624:
620:
610:
608:
600:
599:
595:
585:
571:
567:
554:
553:
549:
544:
524:
516:
495:
493:Salivary glands
479:
456:
447:
435:
427:
421:
401:
374:
361:
359:Thyroid adenoma
355:
339:Conn's syndrome
311:
303:renal carcinoma
299:
276:
271:
245:
225:adenocarcinomas
197:pituitary gland
153:
111:
107:
73:
69:
20:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1553:
1543:
1542:
1537:
1520:
1519:
1516:
1515:
1513:
1512:
1506:
1504:
1497:
1496:
1493:
1492:
1490:
1489:
1484:
1478:
1476:
1470:
1469:
1467:
1466:
1461:
1455:
1453:
1447:
1446:
1444:
1443:
1432:
1427:
1422:
1416:
1414:
1405:
1397:
1396:
1393:
1392:
1390:
1389:
1369:
1367:
1361:
1360:
1358:
1357:
1352:
1351:
1350:
1334:
1333:
1332:
1321:
1319:
1313:
1312:
1310:
1309:
1299:
1297:
1287:
1279:
1278:
1276:
1275:
1270:
1269:
1268:
1263:
1252:
1250:
1249:skin appendage
1244:
1243:
1240:
1239:
1237:
1236:
1231:
1226:
1221:
1216:
1211:
1206:
1205:
1204:
1193:
1191:
1190:Other/multiple
1187:
1186:
1184:
1183:
1178:
1169:
1164:
1158:
1156:
1150:
1149:
1147:
1146:
1141:
1136:
1130:
1128:
1122:
1121:
1119:
1118:
1109:
1107:Klatskin tumor
1104:
1098:
1097:
1096:
1095:
1090:
1085:
1080:
1075:
1064:
1063:
1058:
1049:
1047:
1038:
1024:
1018:
1017:
1014:
1013:
1011:
1010:
1005:
1000:
994:
992:
986:
985:
983:
982:
977:
972:
967:
962:
957:
952:
946:
944:
931:
925:
924:
916:
915:
908:
901:
893:
887:
886:
879:
878:
862:
861:
858:
857:
846:
835:
824:
792:
763:
758:
757:
755:
754:Classification
747:
746:External links
744:
741:
740:
721:(4): 873–885.
705:
684:(2): 544–560.
664:
618:
606:www.cancer.org
593:
583:
565:
546:
545:
543:
540:
523:
520:
515:
512:
511:
510:
506:
503:
494:
491:
478:
475:
455:
452:
446:
443:
434:
431:
420:
417:
400:
397:
373:
370:
354:
351:
310:
307:
298:
295:
290:Ashkenazi Jews
275:
272:
270:
267:
244:
243:Histopathology
241:
193:adrenal glands
167:
166:
161:
155:
154:
152:
151:
66:
64:
60:
59:
44:
43:
35:
34:
31:
27:
26:
18:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1552:
1541:
1538:
1536:
1533:
1532:
1530:
1511:
1508:
1507:
1505:
1502:
1498:
1488:
1485:
1483:
1480:
1479:
1477:
1475:
1471:
1465:
1462:
1460:
1457:
1456:
1454:
1452:
1448:
1441:
1437:
1433:
1431:
1428:
1426:
1423:
1421:
1418:
1417:
1415:
1413:
1409:
1406:
1404:and medullary
1398:
1387:
1383:
1379:
1375:
1371:
1370:
1368:
1366:
1362:
1356:
1353:
1349:
1346:
1345:
1343:
1339:
1335:
1331:
1328:
1327:
1326:
1323:
1322:
1320:
1318:
1314:
1308:
1304:
1301:
1300:
1298:
1295:
1291:
1288:
1280:
1274:
1271:
1267:
1264:
1262:
1259:
1258:
1257:
1254:
1253:
1251:
1245:
1235:
1232:
1230:
1227:
1225:
1222:
1220:
1217:
1215:
1212:
1210:
1207:
1203:
1200:
1199:
1198:
1195:
1194:
1192:
1188:
1182:
1179:
1177:
1173:
1170:
1168:
1165:
1163:
1160:
1159:
1157:
1155:
1151:
1145:
1142:
1140:
1137:
1135:
1132:
1131:
1129:
1127:
1123:
1117:
1113:
1110:
1108:
1105:
1103:
1100:
1099:
1094:
1091:
1089:
1086:
1084:
1081:
1079:
1076:
1074:
1071:
1070:
1069:
1066:
1065:
1062:
1059:
1057:
1054:
1051:
1050:
1048:
1046:
1042:
1039:
1037:
1032:
1028:
1025:
1023:
1019:
1009:
1006:
1004:
1001:
999:
996:
995:
993:
991:
987:
981:
978:
976:
973:
971:
968:
966:
963:
961:
958:
956:
953:
951:
948:
947:
945:
943:
939:
935:
932:
930:
926:
922:
914:
909:
907:
902:
900:
895:
894:
891:
885:
881:
880:
877:
873:
872:
867:
866:
856:
852:
851:
847:
845:
841:
840:
836:
834:
830:
829:
825:
822:
818:
814:
810:
806:
802:
801:
797:
793:
790:
786:
782:
778:
774:
773:
769:
765:
764:
761:
756:
752:
736:
732:
728:
724:
720:
716:
709:
701:
697:
692:
687:
683:
679:
675:
668:
650:
646:
642:
641:
632:
628:
622:
607:
603:
597:
590:
586:
580:
576:
569:
561:
557:
551:
547:
539:
536:
533:
528:
519:
507:
504:
501:
500:
499:
490:
488:
484:
474:
472:
468:
464:
460:
451:
442:
440:
439:fibroadenomas
430:
426:
416:
414:
410:
406:
396:
394:
393:bromocriptine
390:
386:
382:
378:
369:
366:
360:
350:
348:
344:
340:
336:
332:
328:
323:
315:
306:
304:
294:
291:
287:
285:
281:
266:
263:
259:
254:
251:
240:
238:
234:
230:
226:
222:
218:
214:
210:
206:
202:
198:
194:
190:
186:
182:
178:
174:
165:
162:
160:
156:
147:
103:
68:
67:
65:
63:Pronunciation
61:
57:
56:H&E stain
53:
52:colonic polyp
49:
45:
41:
36:
32:
28:
23:
1261:Hidrocystoma
1255:
1181:Hürthle cell
1162:Prolactinoma
1067:
1052:
1030:
869:
848:
837:
826:
794:
791:, and others
766:
718:
714:
708:
681:
677:
667:
656:, retrieved
649:the original
637:
621:
609:. Retrieved
605:
596:
588:
574:
568:
560:the original
550:
529:
525:
517:
496:
480:
469:, a type of
458:
457:
448:
436:
428:
402:
385:progesterone
381:prolactinoma
375:
362:
324:
320:
300:
288:
277:
255:
246:
183:tissue with
177:benign tumor
172:
170:
1303:Cystadenoma
1256:sweat gland
1247:Adnexal and
1078:Glucagonoma
399:Parathyroid
389:cabergoline
335:aldosterone
284:colonoscopy
229:mass effect
30:Other names
1529:Categories
1286:and serous
1229:Cylindroma
1214:Oncocytoma
1126:Urogenital
1083:Gastrinoma
1073:Insulinoma
929:Epithelium
658:August 17,
542:References
329:, causing
219:to become
181:epithelial
48:Micrograph
1284:mucinous,
1266:Syringoma
1202:Carcinoid
1154:Endocrine
942:carcinoma
938:Papilloma
850:SNOMED CT
589:Table 6-5
532:specialty
522:Treatment
487:cutaneous
477:Sebaceous
454:Bronchial
372:Pituitary
343:androgens
269:Locations
258:dysplasia
221:malignant
217:transform
185:glandular
159:Specialty
1402:lobular,
1317:Mucinous
1068:pancreas
1031:Adenomas
855:32048006
735:16635231
700:12557158
514:Prostate
509:cancers.
445:Appendix
345:causing
337:causing
327:cortisol
233:hormones
205:prostate
164:Oncology
1400:Ductal,
1296:general
1282:Cystic,
1224:Apudoma
1003:Thymoma
844:D000236
833:M8140/0
611:3 April
463:bronchi
365:thyroid
353:Thyroid
309:Adrenal
201:thyroid
173:adenoma
25:Adenoma
1501:Acinar
1365:Serous
1294:Cystic
1088:VIPoma
1053:tract:
1022:Glands
921:cancer
876:CHORUS
733:
698:
581:
433:Breast
262:atypia
213:benign
189:organs
150:
871:00007
828:ICD-O
821:227.0
813:223.0
809:211.5
805:211.3
789:D35.2
781:D35.0
652:(PDF)
634:(PDF)
485:is a
419:Liver
341:, or
297:Renal
274:Colon
250:polyp
175:is a
1503:cell
839:MeSH
800:9-CM
731:PMID
696:PMID
660:2012
613:2018
579:ISBN
874:at
817:226
796:ICD
785:D34
777:D12
768:ICD
723:doi
719:101
686:doi
682:124
391:or
179:of
171:An
1531::
1438:/
1384:/
1380:/
1376:/
1340:/
853::
842::
831::
819:,
815:,
807:,
803::
787:,
783:,
779:,
775::
772:10
729:.
717:.
694:.
680:.
676:.
643:,
636:,
629:,
604:.
587:.
481:A
473:.
415:.
349:.
333:,
305:.
203:,
199:,
195:,
131:oʊ
106:,
93:oʊ
1305:/
1174:/
1114:/
1033:/
940:/
912:e
905:t
898:v
823:,
811:,
798:-
770:-
760:D
737:.
725::
702:.
688::
615:.
260:(
146:/
143:ə
140:t
137:ɪ
134:m
128:n
125:ˈ
122:ɪ
119:d
116:æ
113:ˌ
110:/
102:/
99:ə
96:m
90:n
87:ˈ
84:ɪ
81:d
78:æ
75:ˌ
72:/
58:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.