863:
610:
633:
1664:
330:
20:
1676:
410:
in an attempt to make contact with
Greater Yuezhi. Zhang Qian's envoy was intercepted by Xiongnu while travelling through the Hexi Corridor, and he was held a captive for ten years, until he finally escaped and continued his mission further west. He eventually arrived at Yuezhi territory, but was
682:. Hostilities between the Tang and Tibet continued until they signed a formal peace treaty in 821. The terms of this treaty, including fixed borders between the two countries, are recorded in a bilingual inscription on a stone pillar outside the
379:, forcing the westward exodus of majority of the Yuezhi survivors (later known as the Greater Yuezhi) into Central Asia, while the small portion of Yuezhi population that didn't migrate (known as the Lesser Yuezhi) was forced to mixed among the
411:
unable to convince the Yuezhi leaders to ally against
Xiongnu. On his return journey he was once again captured by Xiongnu while traversing the Hexi Corridor, but again managed to escape two years later. He finally returned to
1426:
815:
266:
According to Dodson and coauthors (2013), wheat entered via the Hexi
Corridor into southern Gansu around 3000 BC, although other scholars date this somewhat later.
1471:
898:, serving an effective area of about 215,000 km (83,000 sq mi). It was an area where mountain and desert limited caravan traffic to a narrow
587:. The Han forces, allied with the subjugated Southern Xiongnu, again defeated the Northern Chanyu twice in 90 CE and 91 CE, forcing him to flee west into
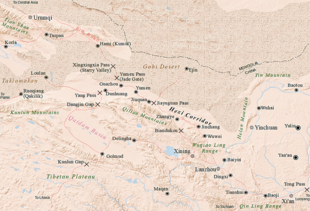
474:. The Han Empire acquired a new territory with trade access to the Western Regions, and also cutting the Xiongnu off from their Qiang allies. Again in
1276:
Youli Li; Jingchun Yang; Lihua Tan; Fengjun Duan (July 1999). "Impact of tectonics on alluvial landforms in the Hexi
Corridor, Northwest China".
791:
536:, Han lost control over the Tarim Basin, which was reconquered by the Xiongnu in 63 CE and used as a base to invade the Hexi Corridor.
1516:
834:
255:, appeared in China around 2800 BC at Donghuishan at the Hexi corridor. Several other crops are also attested at this time period.
1649:
1529:
1403:
1376:
1361:
1343:
862:
1159:
522:
351:
655:
for control of areas in Inner and
Central Asia. There was a long string of conflicts with Tibet over territories in the
1739:
1095:"Between China and South Asia: A Middle Asian corridor of crop dispersal and agricultural innovation in the Bronze Age"
999:
748:
739:
387:. At this point, the Hexi Corridor was under complete Xiongnu control, mainly occupied by the two tribes of Hunye and
57:
712:. Western Xia controlled from 1038 CE up to 1227 CE the areas in what are now the northwestern Chinese provinces of
1539:
1749:
1695:
1264:
790:
The Hexi
Corridor is a long, narrow passage stretching for some 1,000 kilometres (620 mi) from the steep
1544:
580:
572:
478:, Han forces repelled a joint Xiongnu-Qiang invasion, and to consolidate the control of the region, four new
1754:
1744:
1534:
1463:
760:
94:, meaning 'west of the river'), flanked between the much more elevated and inhospitable terrains of the
1396:
972:
at the narrowest point of the Hexi
Corridor, some 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) southwest of the city of
1734:
670:. It was during this rebellion that the Tang withdrew its western garrisons stationed in what is now
380:
298:
768:
277:, having traveled over the northern branch of the Silk Road, including the Hexi Corridor segment.
1644:
1578:
1311:
1680:
1167:
1389:
1224:
957:. South of Gansu Province, in the middle just over the provincial boundary, lies the city of
1285:
1176:
1106:
310:
8:
1588:
977:
667:
455:
161:
1289:
1180:
1110:
1639:
1524:
1192:
1135:
1094:
946:
479:
364:
344:
314:
177:
106:
1297:
829:
A strikingly inhospitable environment surrounds this chain of oases: the snow-capped
1634:
1629:
1562:
1372:
1357:
1339:
1260:
1140:
1122:
1093:
Stevens, C. J.; Murphy, C.; Roberts, R.; Lucas, L.; Silva, F.; Fuller, D. Q. (2016).
1067:
399:
185:
173:
95:
67:
1209:
1196:
1496:
1293:
1184:
1130:
1114:
1023:
994:
973:
969:
934:
830:
807:
541:
503:
252:
145:
34:
806:. There are many fertile oases along the path, watered by rivers flowing from the
1619:
1476:
1051:
954:
926:
856:
838:
584:
513:
From roughly 115–60 BCE, Han forces fought the
Xiongnu over control of the oasis
440:
407:
368:
197:
157:
153:
133:
122:
99:
1668:
1624:
1435:
1059:
1041:
989:
918:
852:
778:
in 1227, pacifying the Hexi
Corridor region, which was later absorbed into the
756:
652:
618:
228:
217:
71:
752:
176:. At the western end, the route splits into three, going either north of the
1728:
1710:
1697:
1506:
1481:
1188:
1126:
1118:
811:
709:
609:
632:
1486:
1144:
965:
Province. Xining used to be the chief commercial hub of the Hexi
Corridor.
942:
871:
779:
744:
733:
648:
637:
626:
614:
604:
483:
420:
237:
222:
189:
169:
137:
126:
83:
1369:
The Western Regions Xiongnu and Han: From the Shiji, Hanshu and Hou Hanshu
1275:
968:
The Jiayuguan fort guards the western entrance to China. It is located in
953:
in the southeast. In the past, Dunhuang was part of the area known as the
1491:
1160:"Early cultivated wheat and broadening of agriculture in Neolithic China"
867:
823:
775:
764:
705:
699:
663:
656:
641:
622:
549:
529:
518:
412:
355:
334:
318:
306:
286:
184:. At the eastern end, the mountains around Lanzhou grants access to the
181:
165:
118:
236:, and other crops travelled westwards through the Corridor, and reached
1614:
1604:
1257:
Dust in the Wind: Retracing Dharma Master Xuanzang's Western Pilgrimage
914:
902:, where relatively small fortifications could control passing traffic.
895:
819:
514:
459:
403:
256:
149:
109:, running northwest from the western section of the Ordos Loop between
87:
1448:
678:, which the Tibetans then occupied along with the area that is modern
525:
in 60 BCE, which dealt with the region's defense and foreign affairs.
329:
1609:
1554:
1453:
1443:
799:
553:
533:
444:
384:
201:
193:
78:. It refers to a narrow stretch of traversable and relatively arable
833:(the so-called "southern mountains" or "Nanshan") to the south; the
1583:
938:
910:
905:
There are several major cities along the Hexi Corridor. In western
899:
883:
875:
849:
803:
679:
576:
564:
495:
110:
482:
were established in the Hexi Corridor, namely (from east to west)
419:, bringing back invaluable detailed information about the various
1422:
962:
950:
930:
922:
887:
795:
721:
717:
683:
675:
560:
491:
487:
475:
471:
467:
463:
436:
416:
395:
376:
302:
274:
114:
19:
1381:
1031:
958:
891:
592:
545:
537:
432:
424:
372:
290:
241:
156:
further to the south. To the north are the Longshou, Heli and
301:, occupying the western Hexi Corridor. Later, the newly risen
49:
1412:
906:
713:
687:
671:
636:
Map of the Tang dynasty showing the Hexi Corridor connecting
588:
568:
448:
428:
388:
294:
260:
248:
141:
79:
75:
842:
313:, and established a dominant confederacy empire during the
270:
233:
40:
46:
1092:
1354:
Wars With The Xiongnu: A Translation From Zizhi tongjian
1213:, C.Michael Hogan, the Megalithic Portal, ed. A. Burnham
559:
After the new Protector General of the Western Regions
244:
from the fifth millennium to the second millennium BC.
662:
In 763 the Tibetans even captured the Tang capital of
521:. Han was eventually victorious and established the
58:
1237:
1088:
1086:
976:. The Jiayuguan fort is the first fortification of
43:
37:
1726:
1083:
563:was killed in 75 CE by allies of the Xiongnu in
466:from the Hexi Corridor and even drove them from
571:, the garrison at Hami was withdrawn. At the
1397:
848:Geologically, the Hexi Corridor belongs to a
837:("northern mountains") mountainous area, the
470:when King Hunye surrendered to Huo Qubing in
435:, as well as other farther countries such as
708:was established in the 11th century by the
117:, the Hexi Corridor was the most important
1404:
1390:
755:continued it after his death in 1227. The
343:Principalities and centrally-administered
16:Historical region in Gansu Province, China
1134:
136:for traders and military incursions into
861:
785:
631:
608:
328:
18:
1650:Zhangye Danxia National Geological Park
1312:"The Silk Roads and Eurasian Geography"
1046:
613:Mural commemorating victory of General
212:
1727:
1530:Northwest University for Nationalities
1333:
1243:
1066:
855:system on the northeast margin of the
693:
1385:
383:and become the subjects of Xiongnu's
1675:
1158:Li, Xiaoqiang; et al. (2007a).
269:As early as the 1st millennium BCE,
1157:
763:fell in 1234 CE with help from the
523:Protectorate of the Western Regions
352:Protectorate of the Western Regions
13:
1000:Silk Road transmission of Buddhism
740:Mongol conquest of the Jin dynasty
552:before establishing a garrison at
540:defeated the Xiongnu again at the
14:
1766:
794:hillside near the modern city of
1674:
1663:
1662:
1540:Lanzhou University of Technology
1411:
293:overcame previous settlers, the
144:along the northern edges of the
33:
1055:
727:
598:
180:or south on either side of the
1336:Mapping History: World History
1304:
1269:
1249:
1217:
1203:
1151:
1036:
1017:
841:, and the vast expanse of the
324:
280:
70:located in the modern western
1:
1545:Gansu Agricultural University
1298:10.1016/S0169-555X(98)00114-7
1005:
573:Battle of the Altai Mountains
544:in 73 CE, evicting them from
152:, with the high and desolate
1077:
666:for fifteen days during the
498:, collectively known as the
160:separating it from the arid
7:
1535:Northwest Normal University
983:
802:at the border of Gansu and
749:conquest of the Jin dynasty
548:and chasing them as far as
259:is another similar site in
188:, which leads east through
10:
1771:
1327:
774:Ögedei also conquered the
737:
731:
697:
602:
385:Worthy Prince of the Right
207:
1740:Sites along the Silk Road
1658:
1597:
1571:
1553:
1515:
1462:
1434:
1420:
1338:. London: Cartographica.
1027:
583:, who retreated into the
507:
500:Four Commanderies of Hexi
406:as the ambassador to the
273:goods began appearing in
196:valley into the populous
1189:10.1177/0959683607078978
1119:10.1177/0959683616650268
1010:
886:formerly passed through
23:Map of the Hexi Corridor
1645:Gansu Provincial Museum
1579:Chinese Islamic cuisine
1367:Yap, Joseph P. (2019),
1352:Yap, Joseph P. (2009),
1068:[xɤ̌ɕítsòʊlɑ̌ŋ]
1064:Mandarin pronunciation:
1750:Geopolitical corridors
1211:Silk Road, North China
937:) in the center, then
879:
644:
629:
360:
24:
865:
845:desert to the north.
786:Geography and climate
769:Southern Song dynasty
738:Further information:
659:between 670 and 692.
635:
612:
333:A map of the Western
332:
251:, originating at the
140:. It is a string of
62:), also known as the
22:
1334:Barnes, Ian (2007).
894:and the environs of
363:During the reign of
213:Early crop dispersal
200:, and then into the
1707: /
1598:Visitor attractions
1589:Lanzhou beef lamian
1290:1999Geomo..28..299L
1181:2007Holoc..17..555L
1111:2016Holoc..26.1541S
978:Great Wall of China
870:watchtower made of
776:Western Xia dynasty
706:Western Xia dynasty
694:Western Xia dynasty
668:An Lushan Rebellion
311:expelled the Yuezhi
289:(221–206 BCE), the
162:Badain Jaran Desert
1755:Historical regions
1745:Geography of Gansu
1711:38.700°N 100.783°E
1640:Maijishan Grottoes
1525:Lanzhou University
1225:"Dunhuang History"
880:
645:
630:
625:156, late Chinese
365:Emperor Wen of Han
361:
315:Chu-Han contention
285:At the end of the
178:Tianshan Mountains
107:Northern Silk Road
66:, is an important
25:
1690:
1689:
1635:Labrang Monastery
1630:Silk Route Museum
1563:Tangwang language
1377:978-1-79282-915-4
1362:978-1-4490-0605-1
1345:978-1-84573-323-0
1105:(10): 1541–1555.
961:, the capital of
423:kingdoms such as
223:Panicum miliaceum
174:Mongolian Plateau
68:historical region
1762:
1735:History of Gansu
1722:
1721:
1719:
1718:
1717:
1712:
1708:
1705:
1704:
1703:
1700:
1678:
1677:
1666:
1665:
1497:Qilian Mountains
1406:
1399:
1392:
1383:
1382:
1349:
1322:
1321:
1319:
1318:
1308:
1302:
1301:
1284:(3–4): 299–308.
1273:
1267:
1253:
1247:
1241:
1235:
1234:
1232:
1231:
1221:
1215:
1207:
1201:
1200:
1164:
1155:
1149:
1148:
1138:
1090:
1071:
1070:
1065:
1062:: حْسِ ظِوْلاْ;
1057:
1048:
1047:Ho-hsi Tsou-lang
1038:
1029:
1021:
995:Juyan Lake Basin
913:(Shazhou), then
831:Qilian Mountains
808:Qilian Mountains
751:around 1207 and
542:Battle of Yiwulu
509:
350:
342:
253:Fertile Crescent
158:Mazong Mountains
146:Qilian Mountains
132:to the historic
90:(hence the name
56:
55:
52:
51:
48:
45:
42:
39:
1770:
1769:
1765:
1764:
1763:
1761:
1760:
1759:
1725:
1724:
1716:38.700; 100.783
1715:
1713:
1709:
1706:
1701:
1698:
1696:
1694:
1693:
1691:
1686:
1654:
1620:Bingling Temple
1593:
1567:
1549:
1511:
1477:Tibetan Plateau
1458:
1430:
1416:
1410:
1356:. AuthorHouse,
1346:
1330:
1325:
1316:
1314:
1310:
1309:
1305:
1274:
1270:
1259:, 經典雜誌編著, 2006
1254:
1250:
1242:
1238:
1229:
1227:
1223:
1222:
1218:
1208:
1204:
1162:
1156:
1152:
1091:
1084:
1080:
1075:
1074:
1063:
1022:
1018:
1013:
1008:
986:
955:Western Regions
866:The ruins of a
857:Tibetan Plateau
839:Alashan Plateau
788:
742:
736:
730:
702:
696:
607:
601:
585:Altai Mountains
581:Northern Chanyu
530:turbulent reign
456:Han–Xiongnu War
408:Western Regions
369:Laoshang Chanyu
359:
348:
347:
340:
338:
327:
309:vanquished and
283:
229:Setaria italica
218:Chinese millets
215:
210:
198:Guanzhong Plain
154:Tibetan Plateau
134:Western Regions
123:Northwest China
105:As part of the
36:
32:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1768:
1758:
1757:
1752:
1747:
1742:
1737:
1688:
1687:
1685:
1684:
1672:
1659:
1656:
1655:
1653:
1652:
1647:
1642:
1637:
1632:
1627:
1625:Mogao Grottoes
1622:
1617:
1612:
1607:
1601:
1599:
1595:
1594:
1592:
1591:
1586:
1581:
1575:
1573:
1569:
1568:
1566:
1565:
1559:
1557:
1551:
1550:
1548:
1547:
1542:
1537:
1532:
1527:
1521:
1519:
1513:
1512:
1510:
1509:
1504:
1499:
1494:
1489:
1484:
1479:
1474:
1468:
1466:
1460:
1459:
1457:
1456:
1451:
1446:
1440:
1438:
1432:
1431:
1421:
1418:
1417:
1409:
1408:
1401:
1394:
1386:
1380:
1379:
1365:
1350:
1344:
1329:
1326:
1324:
1323:
1303:
1268:
1255:Zhihong Wang,
1248:
1236:
1216:
1202:
1175:(5): 555–560.
1150:
1081:
1079:
1076:
1073:
1072:
1015:
1014:
1012:
1009:
1007:
1004:
1003:
1002:
997:
992:
990:Liang Province
985:
982:
970:Jiayuguan pass
949:) and finally
853:foreland basin
810:, such as the
787:
784:
732:Main article:
729:
726:
698:Main article:
695:
692:
653:Tibetan Empire
619:Tibetan Empire
603:Main article:
600:
597:
458:, Han general
339:
326:
323:
317:and the early
282:
279:
214:
211:
209:
206:
72:Gansu province
64:Gansu Corridor
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1767:
1756:
1753:
1751:
1748:
1746:
1743:
1741:
1738:
1736:
1733:
1732:
1730:
1723:
1720:
1683:
1682:
1673:
1671:
1670:
1661:
1660:
1657:
1651:
1648:
1646:
1643:
1641:
1638:
1636:
1633:
1631:
1628:
1626:
1623:
1621:
1618:
1616:
1613:
1611:
1608:
1606:
1603:
1602:
1600:
1596:
1590:
1587:
1585:
1582:
1580:
1577:
1576:
1574:
1570:
1564:
1561:
1560:
1558:
1556:
1552:
1546:
1543:
1541:
1538:
1536:
1533:
1531:
1528:
1526:
1523:
1522:
1520:
1518:
1514:
1508:
1507:Liujiaxia Dam
1505:
1503:
1502:Hexi Corridor
1500:
1498:
1495:
1493:
1490:
1488:
1485:
1483:
1482:Loess Plateau
1480:
1478:
1475:
1473:
1470:
1469:
1467:
1465:
1461:
1455:
1452:
1450:
1447:
1445:
1442:
1441:
1439:
1437:
1433:
1428:
1424:
1419:
1414:
1407:
1402:
1400:
1395:
1393:
1388:
1387:
1384:
1378:
1374:
1370:
1366:
1363:
1359:
1355:
1351:
1347:
1341:
1337:
1332:
1331:
1313:
1307:
1299:
1295:
1291:
1287:
1283:
1279:
1278:Geomorphology
1272:
1266:
1262:
1258:
1252:
1246:, p. 63.
1245:
1244:Barnes (2007)
1240:
1226:
1220:
1214:
1212:
1206:
1198:
1194:
1190:
1186:
1182:
1178:
1174:
1170:
1169:
1161:
1154:
1146:
1142:
1137:
1132:
1128:
1124:
1120:
1116:
1112:
1108:
1104:
1100:
1096:
1089:
1087:
1082:
1069:
1061:
1053:
1049:
1043:
1039:
1033:
1025:
1020:
1016:
1001:
998:
996:
993:
991:
988:
987:
981:
980:in the west.
979:
975:
971:
966:
964:
960:
956:
952:
948:
944:
940:
936:
932:
928:
924:
920:
916:
912:
908:
903:
901:
897:
893:
889:
885:
877:
873:
869:
864:
860:
858:
854:
851:
846:
844:
840:
836:
832:
827:
825:
822:(Heihe), and
821:
817:
813:
809:
805:
801:
797:
793:
783:
781:
777:
772:
770:
766:
762:
758:
754:
750:
746:
741:
735:
725:
723:
719:
715:
711:
710:Tangut people
707:
701:
691:
689:
685:
681:
677:
673:
669:
665:
660:
658:
654:
650:
643:
639:
634:
628:
624:
620:
616:
611:
606:
596:
595:territories.
594:
590:
586:
582:
579:defeated the
578:
574:
570:
566:
562:
557:
555:
551:
547:
543:
539:
535:
531:
526:
524:
520:
516:
511:
505:
501:
497:
493:
489:
485:
481:
477:
473:
469:
465:
462:expelled the
461:
457:
452:
450:
446:
442:
438:
434:
430:
426:
422:
421:Central Asian
418:
414:
409:
405:
401:
397:
392:
390:
386:
382:
378:
374:
370:
367:, Modu's son
366:
357:
353:
346:
336:
331:
322:
320:
316:
312:
308:
305:armies under
304:
300:
296:
292:
288:
278:
276:
272:
267:
264:
262:
258:
254:
250:
245:
243:
239:
235:
231:
230:
225:
224:
219:
205:
203:
202:Central Plain
199:
195:
191:
187:
183:
179:
175:
171:
167:
163:
159:
155:
151:
147:
143:
139:
135:
131:
130:
124:
120:
116:
112:
108:
103:
101:
97:
93:
89:
85:
81:
77:
73:
69:
65:
61:
60:
54:
30:
29:Hexi Corridor
21:
1692:
1679:
1667:
1501:
1487:Yellow River
1368:
1353:
1335:
1315:. Retrieved
1306:
1281:
1277:
1271:
1256:
1251:
1239:
1228:. Retrieved
1219:
1210:
1205:
1172:
1168:The Holocene
1166:
1153:
1102:
1099:The Holocene
1098:
1045:
1037:Héxī Zǒuláng
1035:
1019:
967:
909:Province is
904:
882:The ancient
881:
872:rammed earth
847:
828:
789:
780:Yuan dynasty
773:
745:Genghis Khan
743:
734:Yuan dynasty
728:Yuan dynasty
703:
661:
649:Tang dynasty
646:
638:China proper
627:Tang dynasty
615:Zhang Yichao
605:Tang dynasty
599:Tang dynasty
558:
527:
512:
499:
480:commanderies
453:
393:
381:Qiang people
362:
345:commanderies
337:in 2 AD
284:
268:
265:
246:
238:Western Asia
227:
221:
216:
186:Longxi Basin
170:cold steppes
138:Central Asia
128:
125:. It linked
104:
91:
84:Yellow River
82:west of the
63:
28:
26:
1714: /
1492:Gobi Desert
1060:Xiao'erjing
868:Han dynasty
761:Jin dynasty
753:Ögedei Khan
700:Western Xia
657:Tarim Basin
651:fought the
642:Tarim Basin
550:Lake Barkol
528:During the
519:Tarim Basin
515:city-states
454:During the
356:Tarim Basin
335:Han dynasty
325:Han dynasty
319:Han dynasty
307:Modu Chanyu
287:Qin dynasty
281:Qin dynasty
247:Cultivated
182:Tarim Basin
166:Gobi Desert
119:trade route
1729:Categories
1615:Yumen Pass
1605:Jiayu Pass
1317:2007-08-06
1265:9868141982
1230:2009-06-12
1056:Хәщи зулон
1042:Wade–Giles
1006:References
896:Juyan Lake
747:began the
623:Mogao cave
575:in 89 CE,
460:Huo Qubing
404:Zhang Qian
400:Emperor Wu
257:Xishanping
192:along the
190:Mount Long
150:Altyn-Tagh
102:Plateaus.
88:Ordos Loop
1610:Yang Pass
1517:Education
1464:Geography
1127:0959-6836
1078:Citations
974:Jiayuguan
947:Liangzhou
919:Jiayuguan
800:Jade Gate
792:Wushaolin
617:over the
534:Wang Mang
375:again in
371:defeated
194:Wei River
96:Mongolian
1702:100°47′E
1669:Category
1584:Liangfen
1449:Politics
1197:55810068
1145:27942165
984:See also
939:Jinchang
929:), then
911:Dunhuang
900:trackway
884:trackway
876:Dunhuang
850:Cenozoic
826:Rivers.
816:Jinchuan
804:Xinjiang
680:Xinjiang
664:Chang'an
621:in 848.
577:Dou Xian
565:Karasahr
496:Dunhuang
413:Chang'an
168:and the
111:Yinchuan
1699:38°42′N
1681:Commons
1572:Cuisine
1555:Culture
1454:Economy
1444:History
1436:General
1427:capital
1423:Lanzhou
1328:Sources
1286:Bibcode
1177:Bibcode
1136:5125436
1107:Bibcode
1024:Chinese
963:Qinghai
951:Lanzhou
941:, then
935:Ganzhou
931:Zhangye
923:Jiuquan
921:, then
917:, then
888:Haidong
835:Beishan
812:Shiyang
798:to the
796:Lanzhou
767:-ruled
757:Jurchen
722:Ningxia
718:Shaanxi
684:Jokhang
676:Qinghai
640:to the
561:Chen Mu
517:in the
504:Chinese
492:Jiuquan
488:Zhangye
476:111 BCE
472:121 BCE
468:Lop Nur
464:Xiongnu
441:Tiaozhi
417:125 BCE
396:138 BCE
377:162 BCE
303:Xiongnu
275:Siberia
208:History
172:of the
115:Lanzhou
100:Tibetan
59:hə-SHEE
1472:Cities
1415:topics
1375:
1360:
1342:
1263:
1195:
1143:
1133:
1125:
1052:Dungan
1044::
1034::
1032:pinyin
1026::
959:Xining
927:Suzhou
892:Xining
720:, and
593:Kangju
546:Turpan
538:Dou Gu
506::
445:Shendu
433:Kangju
425:Dayuan
373:Yuezhi
349:
341:
291:Yuezhi
242:Europe
226:, and
129:proper
127:China
1413:Gansu
1193:S2CID
1163:(PDF)
1011:Notes
943:Wuwei
915:Yumen
907:Gansu
824:Shule
759:-led
714:Gansu
688:Lhasa
672:Gansu
589:Wusun
569:Kucha
484:Wuwei
449:Wusun
429:Daxia
402:sent
389:Xiutu
299:Qiang
295:Wusun
261:Gansu
249:wheat
142:oases
80:plain
76:China
1373:ISBN
1358:ISBN
1340:ISBN
1261:ISBN
1141:PMID
1123:ISSN
1028:河西走廊
843:Gobi
820:Ejin
704:The
674:and
647:The
591:and
567:and
554:Hami
508:河西四郡
494:and
447:and
437:Anxi
431:and
297:and
271:silk
240:and
234:rice
148:and
113:and
98:and
92:Hexi
27:The
1294:doi
1185:doi
1131:PMC
1115:doi
874:at
765:Han
686:in
532:of
510:).
415:in
394:In
358:)
232:),
121:in
86:'s
74:of
1731::
1371:.
1292:.
1282:28
1280:.
1191:.
1183:.
1173:17
1171:.
1165:.
1139:.
1129:.
1121:.
1113:.
1103:26
1101:.
1097:.
1085:^
1058:;
1054::
1050:;
1040:;
1030:;
890:,
859:.
818:,
814:,
782:.
771:.
724:.
716:,
690:.
556:.
490:,
486:,
451:.
443:,
439:,
427:,
398:,
391:.
321:.
263:.
204:.
164:,
50:iː
1429:)
1425:(
1405:e
1398:t
1391:v
1364:.
1348:.
1320:.
1300:.
1296::
1288::
1233:.
1199:.
1187::
1179::
1147:.
1117::
1109::
945:(
933:(
925:(
878:.
502:(
354:(
220:(
53:/
47:ʃ
44:ˈ
41:ə
38:h
35:/
31:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.