283:
destination on networks of roads, but are also stored at warehouses located throughout the transportation infrastructure. This led to a nomenclature in which LN network storage resources are termed "storage depots". The principles that underpin LN have been abstracted into the more general study of scheduling and optimization across the traditional infrastructure silos of
Storage, Networking and Processing which was named Data Logistics.
63:. "The study of solutions to problems in Computer Systems that flexibly span resources and services relating to Data Movement, Data Storage and Data Processing." Systems that support general Data Logistics solutions thus must span the traditionally separate fields of Networking, File/Database Systems and Process Management. Data Logistics is a more general form of the term
168:. The combination of certain IEs leads to an information product (IP), which is any final product in the form of information that a person needs to have. When a higher number of different IEs are required, it often results in more planning problems in capacity and inherently leads to a non-delivery of the IP.
398:
274:
and later at intermediate network locations using shared network caches. This line of development also gave rise to Web server replication and other techniques for offloading and distributing the work of delivering large volume Web services to widely dispersed client communities, ultimately resulting
47:
Firstly, it can be defined as "managing and controlling information handling processes optimally with respect to time (flow time and capacity), storage, distribution and presentation in such a way that it contributes to company results in concurrence with the costs of capturing (creation, searching,
282:
At the same time, research efforts in server replication and content delivery gave rise to a number of related projects and strategies, including
Logistical Networking (LN). The name LN was intended as an analogy to physical supply chain logistics, in which goods are not only carried from source to
151:
and thus reduce ignorance or lack of precision. In a stricter sense, raw data only becomes information to those who can interpret it. Interpreting relevant, related information produces insight that either leads to existing, or eventually builds new, knowledge.
292:
Data
Caching and Replication are classic examples of Data Logistics solutions to problems in Computer Systems and Networking with high data access latencies or data transfer resource limitations. It works mainly across the areas of data transfer and data
75:
The goal of
Information Logistics is to deliver the right product, consisting of the right information element, in the right format, at the right place at the right time for the right people at the right price and all of this is customer
171:
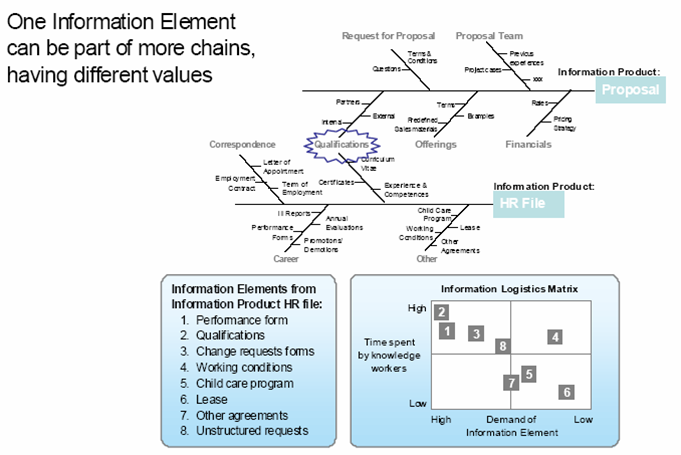
To illustrate the concept of an IP, an example is shown of a bottleneck analysis in HR (by J. Willems 2008). Here, the illustration shows how the information elements (e.g. qualifications) build up the information product (e.g. HR file).
255:
The growth in all
Internet traffic, especially across international telecommunication links, resulted in stress to institutional infrastructure and high costs on networks that billed Internet traffic on a per-use
19:(IL) deals with the flow of information between human and / or machine actors within or between any number of organizations that in turn form a value creating network (see, e.g.). IL is closely related to
270:
These factors led to interest in the use of large scale storage (and to a lesser extent, processing) resources to cache the response to network requests, first at the
Internet endpoint using a
187:
Data logistics is a concept that developed independently of information logistics in the 1990s, in response to the explosion of
Internet content and traffic due to the invention of the
177:
84:
are best equipped with information for the task at hand for improved interaction with its customers and machines are enabled to respond automatically to meaningful information.
223:, combined with the steady increase in the size of Web-delivered objects such as images, audio and video clips resulted in the localized overloading of the
203:
encouraged users to freely dereference those links without regard to, or in many cases without even having any knowledge of, the identity (much less the
296:
Dynamic
Compression in data transfer is another example which uses computational resources to minimize the bandwidth requirements of data transfer.
259:
Much of this traffic was redundant, the results of repeated requests by many independent users to access the same stored files and content.
338:
247:
can cause Web clients to experience poor performance or complete denial of access to servers that host high volume sites (the so-called
333:
132:
run of supply. The contemporary logistics focuses on the organization, planning, control and implementation of the flow of goods,
371:
Beck, M.; Moore, T.; Plank, J.; Swany, M.:"Logistical
Networking", Active Middleware Services, pp. 141-154. Springer US, 2000
328:
334:"Information Logistics Research Report:Framework in the healthcare industry" by Willems, Willems and Hajdasinski 2009
311:
228:
147:. Information (from Latin informare: "shape, shapes, instruct") means in a general sense everything that adds
434:
48:
maintenance etc)." (Petri,2017) Thus IL utilizes logistic principles to optimize information handling.
276:
357:
28:
24:
20:
381:
224:
8:
244:
60:
51:
Secondly, IL can be seen as a concept using information technology to optimize logistics.
429:
266:
was often delayed due to high delays experienced over long and complex
Internet paths.
316:
271:
236:
108:
81:
67:, used as the name of a particular network storage architecture and software stack.
412:
Quantifying the Value of RFID and the EPCglobal Architecture Framework in Logistics
339:"From Having to Using" by Willems 2008 Information Logistics Working Paper Nyenrode
306:
208:
191:(WWW). Some motivations for the emergence of interest in Data Logistics included:
55:
A term which is closely related to the first meaning of Information Logistics is
248:
188:
423:
232:
388:
Network Storage Symposium], October 14 & 15, 1999; Seattle, Washington.
329:"IL quadrants for information access technology" by Olthof and Willems 2008
385:
165:
144:
137:
397:
Plank, J.S.; Bassi ,A.; Beck, M.; Moore. T.; Swany, D.M.; Wolski, R.: "
380:
Plank, J.S.; Beck, M.; Elwasif, W.R.; Moore, T.; Swany, M. Wolski, R.:
263:
240:
212:
164:(IE) is an information component that is located in the organizational
129:
176:
204:
196:
148:
125:
121:
115:
107:
The expression was formed by the Indian mathematician and librarian
401:", IEEE Internet Computing, vol. 5, no. 5, pp 50-58, Sept/Oct 2001,
220:
77:
133:
200:
286:
118:. The purpose of this discipline is described as follows:
100:
maintaining both security and organizational flexibility
382:
The Internet Backplane Protocol: Storage in the Network
114:The supply of a product is part of the discipline
421:
262:Large files and content retrieved from distant
103:integrated information and billing solutions
97:the optimization of the flow of information
80:driven. If this goal is to be achieved,
287:Illustrative examples of data logistics
422:
386:http://loci.cs.utk.edu/dsi/netstore99/
155:
124:is the teachings of the plans and the
399:Managing Data Storage in the Network
87:Methods for achieving the goal are:
43:may be used in either of two ways:
13:
143:Information Logistics focusses on
91:the analysis of information demand
14:
446:
182:
312:Information lifecycle management
175:
94:intelligent information storage
404:
391:
374:
365:
350:
243:infrastructure. The resulting
1:
359:What is Information Logistics
344:
195:The incorporation of network
34:
317:Transformational outsourcing
219:The growth in the volume of
7:
300:
10:
451:
322:
275:in the creation of modern
41:Information Logistics (IL)
356:Hafter, D.; Kajtazi, M.:
277:Content delivery networks
414:, Springer, Berlin 2012.
211:location of) the target
199:into content encoded in
70:
29:information technology
25:information operations
21:information management
65:Logistical Networking
17:Information Logistics
59:, a concept used in
435:Information science
245:Internet bottleneck
239:network and/or the
209:network topological
162:information element
156:Information element
61:Computer Networking
272:Web browser cache
231:resources of the
109:S. R. Ranganathan
82:knowledge workers
442:
415:
408:
402:
395:
389:
378:
372:
369:
363:
354:
307:Data warehousing
179:
450:
449:
445:
444:
443:
441:
440:
439:
420:
419:
418:
410:Uckelmann, D.:
409:
405:
396:
392:
379:
375:
370:
366:
355:
351:
347:
325:
303:
289:
249:Slashdot effect
185:
158:
73:
37:
12:
11:
5:
448:
438:
437:
432:
417:
416:
403:
390:
373:
364:
348:
346:
343:
342:
341:
336:
331:
324:
321:
320:
319:
314:
309:
302:
299:
298:
297:
294:
288:
285:
268:
267:
260:
257:
217:
216:
189:World Wide Web
184:
183:Data logistics
181:
157:
154:
105:
104:
101:
98:
95:
92:
72:
69:
57:Data Logistics
53:
52:
49:
36:
33:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
447:
436:
433:
431:
428:
427:
425:
413:
407:
400:
394:
387:
383:
377:
368:
361:
360:
353:
349:
340:
337:
335:
332:
330:
327:
326:
318:
315:
313:
310:
308:
305:
304:
295:
291:
290:
284:
280:
278:
273:
265:
261:
258:
254:
253:
252:
250:
246:
242:
238:
234:
230:
226:
222:
214:
210:
206:
202:
198:
194:
193:
192:
190:
180:
178:
173:
169:
167:
163:
153:
150:
146:
141:
139:
135:
131:
127:
123:
119:
117:
112:
110:
102:
99:
96:
93:
90:
89:
88:
85:
83:
79:
68:
66:
62:
58:
50:
46:
45:
44:
42:
32:
30:
26:
22:
18:
411:
406:
393:
376:
367:
358:
352:
281:
269:
218:
205:geographical
186:
174:
170:
161:
159:
142:
140:and people.
120:
113:
106:
86:
74:
64:
56:
54:
40:
38:
16:
15:
264:Web servers
166:value chain
145:information
138:information
424:Categories
345:References
241:Web server
229:processing
213:Web server
197:hyperlinks
35:Definition
430:Logistics
237:wide area
225:bandwidth
149:knowledge
130:efficient
126:effective
122:Logistics
116:Logistics
39:The term
301:See also
293:storage.
221:Web hits
362:, 2009.
323:Sources
235:and/or
256:basis.
78:demand
233:local
134:money
227:and
201:HTML
128:and
71:Goal
27:and
384:",
251:).
207:or
160:An
426::
279:.
136:,
111:.
31:.
23:,
215:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.