31:
563:. The neural crest is responsible for a large part of early development in vertebrates. It is specifically responsible for development of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The neural-crest stem cells split from the neural tube as it closes, and nociceptors grow from the dorsal part of this neural-crest tissue. They form late during neurogenesis. Earlier forming cells from this region can become non-pain sensing receptors, either
547:: a completely non-noxious stimulus like light touch causes extreme pain. Allodynia can also be caused when a nociceptor is damaged in the peripheral nerves. This can result in deafferentation, which means the development of different central processes from the surviving afferent nerve. With this situation, surviving dorsal root axons of the nociceptors can make contact with the spinal cord, thus changing the normal input.
651:
250:(CNS). This leads to the train of events that allows for the conscious awareness of pain. The sensory specificity of nociceptors is established by the high threshold only to particular features of stimuli. Only when the high threshold has been reached by either chemical, thermal, or mechanical environments are the nociceptors triggered.
317:
characteristics. So it is possible that some of the transducers for thermal stimuli are the same for mechanical stimuli. The same is true for chemical stimuli, since TRPA1 appears to detect both mechanical and chemical changes. Some mechanical stimuli can cause release of intermediate chemicals, such as
538:
Nociceptor sensitivity is modulated by a large variety of mediators in the extracellular space, such as toxic and inflammatory molecules. Peripheral sensitization represents a form of functional plasticity of the nociceptor. The nociceptor can change from being simply a noxious stimulus detector to a
135:
contrasts with the more sensitive visual, auditory, olfactory, taste, and somatosensory responses to stimuli. The experience of pain is individualistic and can be suppressed by stress or exacerbated by anticipation. Simple activation of a nociceptor does not always lead to perceived pain, because the
582:
Following sensory neurogenesis, differentiation occurs, and two types of nociceptors are formed. They are classified as either peptidergic or nonpeptidergic nociceptors, each of which express a distinct repertoire of ion channels and receptors. Their specializations allow the receptors to innervate
356:
and a component of cigarette smoke. Apart from these external stimulants, chemical nociceptors have the capacity to detect endogenous ligands, and certain fatty acid amines that arise from changes in internal tissues. Like in thermal nociceptors, TRPV1 can detect chemicals like capsaicin and spider
316:
Mechanical nociceptors respond to excess pressure or mechanical deformation. They also respond to incisions that break the skin surface. The reaction to the stimulus is processed as pain by the cortex, just like chemical and thermal responses. These mechanical nociceptors frequently have polymodal
634:
For example, in fruit flies, specific multidendritic sensory neurons play a role in nociception. In mollusks, nociceptive responses are mediated by pedal sensory neurons. Crustaceans, on the other hand, utilize a variety of sensory cell types, including chordotonal organs and mechanoreceptors, to
307:
channels. Its C-terminal domain differs from the heat sensitive TRPs. Although this channel corresponds to cool stimuli, it is still unknown whether it also contributes in the detection of intense cold. An interesting finding related to cold stimuli is that tactile sensibility and motor function
440:
as the neurotransmitter. Aδ fibers form synapses in laminae I and V, C fibers connect with neurons in lamina II, Aβ fibers connect with lamina I, III, & V. After reaching the specific lamina within the spinal cord, the first order nociceptive project to second order neurons that cross the
369:
Although each nociceptor can have a variety of possible threshold levels, some do not respond at all to chemical, thermal or mechanical stimuli unless injury actually has occurred. These are typically referred to as silent or sleeping nociceptors since their response comes only on the onset of
176:
Studies of nociceptors have been conducted on conscious humans as well as surrogate animal models. The process is difficult due to invasive methods that could change the cellular activity of nociceptors being studied, the inability to record from small neuronal structures, and uncertainties in
623:. Although these neurons may have pathways and relationships to the central nervous system that are different from those of mammalian nociceptors, nociceptive neurons in non-mammals often fire in response to similar stimuli as mammals, such as high temperature (40 degrees C or more), low
269:
of their axon. As a result, pain comes in two phases: an initial extremely sharp pain associated with the Aδ fibers and a second, more prolonged and slightly less intense feeling of pain from the C fibers. Massive or prolonged input to a C fiber results in a progressive build up in the
595:(RUNX1) which is vital in the development of nonpeptidergic nociceptors. On the contrary, the peptidergic nociceptors continue to use TrkA, and they express a completely different type of growth factor. There currently is a lot of research about the differences between nociceptors.
152:
in 1906. In earlier centuries, scientists believed that animals were like mechanical devices that transformed the energy of sensory stimuli into motor responses. Sherrington used many different experiments to demonstrate that different types of stimulation to an
115:
that responds to damaging or potentially damaging stimuli by sending "possible threat" signals to the spinal cord and the brain. The brain creates the sensation of pain to direct attention to the body part, so the threat can be mitigated; this process is called
290:
Thermal nociceptors are activated by noxious heat or cold at various temperatures. There are specific nociceptor transducers that are responsible for how and if the specific nerve ending responds to the thermal stimulus. The first to be discovered was
229:
ganglia. The trigeminal ganglia are specialized nerves for the face, whereas the dorsal root ganglia are associated with the rest of the body. The axons extend into the peripheral nervous system and terminate in branches to form receptive fields.
453:. The former is reserved more for regular non-painful sensation, while the latter is reserved for pain sensation. Upon reaching the thalamus, the information is processed in the ventral posterior nucleus and sent to the
543:. Inflammation is one common cause that results in the sensitization of nociceptors. Normally hyperalgesia ceases when inflammation goes down, however, sometimes genetic defects and/or repeated injury can result in
299:. Each of these channels express a particular C-terminal domain that corresponds to the warm–hot sensitivity. The interactions between all these channels and how the temperature level is determined to be above the
465:
As there is an ascending pathway to the brain that initiates the conscious realization of pain, there also is a descending pathway which modulates pain sensation. The brain can request the release of specific
487:
583:
different central and peripheral targets. This differentiation occurs in both perinatal and postnatal periods. The nonpeptidergic nociceptors switch off the TrkA and begin expressing
742:
470:
or chemicals that can have analgesic effects which can reduce or inhibit pain sensation. The area of the brain that stimulates the release of these hormones is the
3302:
295:, and it has a threshold that coincides with the heat pain temperature of 43 °C. Other temperature in the warm–hot range is mediated by more than one
539:
detector of non-noxious stimuli. The result is that low intensity stimuli from regular activity, initiates a painful sensation. This is commonly known as
1861:
1497:"Multidendritic sensory neurons in the adult Drosophila abdomen: origins, dendritic morphology, and segment- and age-dependent programmed cell death"
3297:
341:
Chemical nociceptors have TRP channels that respond to a wide variety of spices. The one that sees the most response and is very widely tested is
1598:"Cold stress alters Mytilus edulis pedal ganglia expression of mu opiate receptor transcripts determined by real-time RT-PCR and morphine levels"
1661:
588:
1854:
238:
Nociceptors are usually electrically silent when not stimulated. The peripheral terminal of the mature nociceptor is where the
1575:
1495:
Shimono K, Fujimoto A, Tsuyama T, Yamamoto-Kochi M, Sato M, Hattori Y, Sugimura K, Usui T, Kimura Ki, Uemura T (2009-10-02).
1112:
996:
918:
881:
750:
446:
189:
In mammals, nociceptors are found in any area of the body that can sense noxious stimuli. External nociceptors are found in
296:
261:
axons are myelinated and can allow an action potential to travel towards the CNS at speeds from 5 to 30 meters/second. The
2908:
131:
and pain are usually evoked only by pressures and temperatures that are potentially damaging to tissues. This barrier or
1654:
1083:
441:
midline at the anterior white commissure. The second order neurons then send their information via two pathways to the
713:
1847:
937:
Fields HL, Rowbotham M, Baron R (October 1998). "Postherpetic neuralgia: irritable nociceptors and deafferentation".
3292:
3252:
2326:
3413:
1067:
265:
axons conduct more slowly at speeds from 0.4 to 2 meters/second due to their smaller diameters and little or no
3099:
2341:
428:
in the dorsal horn are divided into physiologically distinct layers called laminae. Different fiber types form
3219:
2356:
1647:
572:
518:
to cause inhibition of the post-synaptic neuron, thus inhibiting pain. The periaqueductal grey also contains
421:
330:
242:
are detected and transduced into electrical energy. When the electrical energy reaches a threshold value, an
3185:
2842:
2708:
2619:
221:, the visceral organs, and the digestive tract. The cell bodies of these neurons are located in either the
3041:
743:"Nociception and pain: What is the difference and why does it matter? - Massage St. Louis, St. Louis, MO"
515:
2580:
498:
region of the dorsal horn and mediates the sensation of spinothalamic inputs. This is done first by the
3518:
3482:
2995:
2331:
2804:
2746:
2557:
1913:
254:
149:
3451:
2751:
2585:
849:
Sherrington C. The
Integrative Action of the Nervous System. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1906.
370:
inflammation to the surrounding tissue. They were identified using electrical stimulation of their
358:
166:
50:
1567:
3528:
2731:
2107:
1795:
479:
140:, integration of pre- and postsynaptic signals, and influences from higher or central processes.
2895:
2726:
2336:
2122:
1941:
318:
247:
62:
3497:
3385:
3214:
2933:
1923:
1903:
873:
866:
603:
Nociception has been documented in non-mammalian animals, including fish and a wide range of
495:
271:
1555:
579:(NGF). However, transcription factors that determine the type of nociceptor remain unclear.
3523:
3408:
2794:
2761:
2460:
2175:
2079:
1678:
1339:
499:
491:
483:
450:
198:
154:
30:
1284:
897:
571:. All neurons derived from the neural crest, including embryonic nociceptors, express the
8:
2450:
2435:
2321:
2260:
2196:
1800:
1714:
678:
668:
636:
576:
475:
326:
222:
1343:
386:. They are the most common type of C-fiber nociceptors and express a rich repertoire of
3162:
3092:
2534:
2486:
2440:
2379:
2364:
1918:
1785:
1694:
1531:
1496:
1477:
1415:
1406:
1386:
1260:
1236:"Do fishes have nociceptors? Evidence for the evolution of a vertebrate sensory system"
1235:
1211:
1159:
1048:
962:
827:
802:
584:
1613:
1464:
1439:
3487:
3467:
3360:
2990:
2959:
2736:
2683:
2614:
2455:
2445:
2201:
2191:
2160:
2064:
1966:
1882:
1805:
1744:
1724:
1704:
1625:
1617:
1571:
1536:
1518:
1469:
1420:
1367:
1362:
1323:
1304:
1265:
1216:
1198:
1151:
1108:
1040:
992:
954:
914:
877:
832:
387:
190:
162:
137:
132:
36:
1052:
966:
482:. They both in turn project to other areas involved in pain regulation, such as the
474:. This effect of descending inhibition can be shown by electrically stimulating the
181:
systems as to whether a response should be attributed to pain or some other factor.
3325:
3175:
2776:
2721:
2653:
2470:
2413:
2316:
2311:
2221:
2170:
2165:
2127:
2074:
2069:
1609:
1563:
1526:
1508:
1481:
1459:
1410:
1402:
1357:
1347:
1296:
1255:
1247:
1206:
1190:
1141:
1030:
946:
863:
822:
814:
568:
527:
519:
429:
243:
226:
1163:
3428:
3395:
3380:
2693:
2634:
2606:
2422:
2397:
2392:
2387:
2346:
2155:
2112:
2059:
1686:
1146:
1129:
1035:
1018:
656:
454:
424:. This nociceptive fiber (located in the periphery) is a first order neuron. The
371:
353:
322:
239:
218:
158:
55:
3472:
3375:
3242:
3011:
2862:
2814:
2549:
2529:
2255:
2206:
2142:
2090:
2046:
1908:
1790:
1777:
1767:
1670:
1332:
Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
772:
564:
425:
405:
300:
112:
84:
1300:
1194:
282:
in muscles. Wind-up increases the probability of greater sensitivity to pain.
90:
3512:
3370:
3335:
3287:
3247:
3085:
3031:
3026:
2980:
2918:
2903:
2799:
2521:
2465:
2280:
2247:
2231:
2150:
2094:
2054:
2003:
1994:
1951:
1621:
1522:
1352:
1202:
620:
604:
587:, which is a transmembrane signaling component that allows the expression of
560:
258:
35:
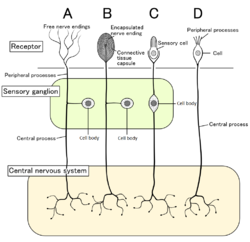
Four types of sensory neurons and their receptor cells. Nociceptors shown as
1597:
1178:
173:. The specific receptors for these intense stimuli were called nociceptors.
3282:
3267:
3262:
2985:
2964:
2949:
2923:
2741:
2562:
2539:
2511:
2506:
2430:
2369:
2132:
2117:
1839:
1828:
1629:
1540:
1513:
1473:
1371:
1269:
1251:
1220:
1155:
1044:
950:
836:
721:
687:
556:
540:
471:
275:
178:
1424:
1308:
1233:
958:
3492:
3418:
3403:
3365:
3320:
3277:
3272:
3170:
3144:
3046:
2954:
2928:
2913:
2875:
2698:
2673:
2668:
2658:
2644:
2270:
2226:
2102:
2031:
1759:
437:
417:
350:
266:
128:
117:
1437:
3441:
3355:
3193:
3129:
3066:
3021:
2885:
2880:
2852:
2832:
2756:
2716:
2663:
2648:
2036:
2026:
1933:
1874:
1285:"Properties of the nociceptive neurons of the leech segmental ganglion"
1130:"Signaling pathways in sensitization: toward a nociceptor cell biology"
674:
511:
507:
457:
in the brain via fibers in the posterior limb of the internal capsule.
68:
3477:
3446:
3436:
3330:
3257:
3237:
3229:
3201:
3152:
3139:
2678:
2624:
2491:
2021:
2011:
1956:
1946:
1823:
818:
796:
794:
792:
790:
788:
786:
784:
664:
628:
616:
544:
503:
433:
382:
Nociceptors that respond to more than one type of stimuli are called
342:
209:. Internal nociceptors are found in a variety of organs, such as the
1639:
1494:
1391:
siphon encode noxious stimuli and display nociceptive sensitization"
3134:
2847:
2837:
2827:
2766:
2639:
2496:
2294:
1596:
Cadet P, Zhu W, Mantione KJ, Baggerman G, Stefano GB (2002-02-28).
683:
612:
523:
467:
442:
346:
1438:
Tracey J., Daniel W., Wilson R. I., Laurent G., Benzer S. (2003).
781:
3206:
3016:
2870:
2822:
2784:
2688:
2629:
1961:
1240:
Proceedings of the Royal
Society of London B: Biological Sciences
777:. National Academies Press (US) – via www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
608:
279:
262:
864:
Jessell, Thomas M., Kandel, Eric R., Schwartz, James H. (1991).
161:
led to different responses. Some intense stimuli trigger reflex
2275:
2265:
1971:
210:
206:
202:
522:
which explains one of the mechanisms by which opioids such as
2501:
2303:
2216:
2211:
1985:
1895:
1870:
1556:"Comparative and evolutionary aspects of nociceptor function"
592:
345:. Other chemical stimulants are environmental irritants like
304:
292:
214:
1282:
506:
neurons to neurons in the dorsal cord, that in turn secrete
3108:
3036:
2789:
1736:
908:
692:
194:
170:
1321:
2016:
1595:
1384:
303:
are unknown at this time. The cool stimuli are sensed by
3303:
congenital insensitivity to pain with partial anhidrosis
3077:
1234:
Sneddon L. U., Braithwaite V. A., Gentle M. J. (2003).
1107:(14th ed.). Philadelphia, Pa.: Saunders/Elsevier.
986:
898:
http://cell.uchc.edu/pdf/fein/nociceptors_fein_2012.pdf
624:
936:
646:
865:
987:Yuan J, Brooks HL, Barman SM, Barrett KE (2019).
3510:
3298:congenital insensitivity to pain with anhidrosis
896:Fein, A Nociceptors: the cells that sense pain
800:
510:to the interneurons that carry pain perception.
408:nociceptive fibers (those that send information
486:which also receives similar afferents from the
1105:Guyton and Hall textbook of medical physiology
982:
980:
978:
976:
872:. Norwalk, CT: Appleton & Lange. pp.
803:"Nociceptors: the sensors of the pain pathway"
635:detect potentially damaging stimuli (see also
3093:
1855:
1655:
1869:
1562:, Oxford University Press, pp. 92–114,
308:deteriorate while pain perception persists.
136:latter also depends on the frequency of the
1127:
973:
589:glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor
274:of the spinal cord; this phenomenon called
143:
96:
3100:
3086:
1862:
1848:
1662:
1648:
1328:: an approach to the study of nociception"
1176:
29:
1568:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780198523345.003.0004
1530:
1512:
1463:
1414:
1361:
1351:
1283:Pastor J., Soria B., Belmonte C. (1996).
1259:
1210:
1145:
1034:
859:
857:
855:
826:
801:Dubin AE, Patapoutian A (November 2010).
488:nucleus reticularis paragigantocellularis
1602:Brain Research. Molecular Brain Research
1553:
1102:
1019:"Nociceptors—noxious stimulus detectors"
1012:
1010:
1008:
932:
930:
913:. Sunderland, Mass: Sinauer Associates.
1016:
770:
591:(GDNF). This transition is assisted by
3511:
1096:
1069:Nociceptors: the cells that sense pain
909:Williams, S. J., Purves, Dale (2001).
852:
257:, nociceptors come in two groups. The
233:
3081:
2080:Somatosensory system (sense of touch)
1843:
1669:
1643:
1322:Wittenburg N., Baumeister R. (1999).
1005:
989:Ganong's Review of Medical Physiology
927:
807:The Journal of Clinical Investigation
550:
447:dorsal column medial-lemniscal system
2065:Vestibular system (sense of balance)
1387:"Mechanosensory neurons innervating
1385:Illich P. A., Walters E. T. (1997).
432:in different layers, and use either
331:Tropomyosin receptor kinase A (TrkA)
1183:Journal of Comparative Physiology A
714:"NOI - Neuro Orthopaedic Institute"
598:
593:runt-related transcription factor 1
13:
2060:Auditory system (sense of hearing)
1407:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-01-00459.1997
1179:"Nociceptors: a phylogenetic view"
1128:Hucho T, Levine JD (August 2007).
364:
246:is induced and driven towards the
14:
3540:
2075:Gustatory system (sense of taste)
2070:Olfactory system (sense of smell)
1177:Smith ES, Lewin GR (2009-12-01).
3293:Congenital insensitivity to pain
3253:Paroxysmal extreme pain disorder
2327:Infrared sensing in vampire bats
1065:
649:
420:where they form synapses in its
359:Acid-sensing ion channels (ASIC)
16:Sensory neuron that detects pain
2055:Visual system (sense of vision)
1589:
1547:
1488:
1448:gene essential for nociception"
1431:
1378:
1315:
1276:
1227:
1170:
1121:
1076:
1059:
575:(TrkA), which is a receptor to
148:Nociceptors were discovered by
1017:Woolf CJ, Ma Q (August 2007).
902:
890:
843:
771:Animals NR (8 December 2017).
764:
735:
706:
533:
416:the brain) travel back to the
123:
1:
2197:Auditory perception (hearing)
1614:10.1016/s0169-328x(01)00342-4
1465:10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00272-1
699:
573:tropomyosin receptor kinase A
530:exhibit an analgesic effect.
460:
311:
2843:Olfactory reference syndrome
2620:Alice in Wonderland syndrome
1147:10.1016/j.neuron.2007.07.008
1036:10.1016/j.neuron.2007.07.016
868:Principles of neural science
478:area of the midbrain or the
400:
377:
7:
3042:Sensory processing disorder
2212:Gustation (taste or flavor)
2202:Equilibrioception (balance)
1560:Neurobiology of Nociceptors
1395:The Journal of Neuroscience
642:
336:
329:, which can be detected by
321:, which can be detected by
184:
10:
3545:
2996:Supernumerary phantom limb
2332:Infrared sensing in snakes
2192:Visual perception (vision)
1289:Journal of Neurophysiology
393:
285:
3460:
3427:
3394:
3348:
3313:
3228:
3184:
3161:
3122:
3115:
3059:
3004:
2973:
2942:
2894:
2861:
2813:
2775:
2747:Microwave auditory effect
2707:
2605:
2598:
2571:
2548:
2520:
2479:
2421:
2410:
2378:
2355:
2302:
2293:
2246:
2184:
2141:
2088:
2045:
2002:
1993:
1984:
1932:
1914:Transduction (physiology)
1894:
1881:
1816:
1776:
1758:
1735:
1677:
1301:10.1152/jn.1996.75.6.2268
1195:10.1007/s00359-009-0482-z
1103:Hall ME, Hall JE (2021).
991:. McGraw-Hill Education.
555:Nociceptors develop from
150:Charles Scott Sherrington
95: 'to harm or hurt';
61:
49:
44:
28:
23:
3107:
2752:Music-specific disorders
2108:Vestibulocochlear (VIII)
1554:Edgar T W (1996-08-01),
1353:10.1073/pnas.96.18.10477
144:Scientific investigation
3414:Posteromarginal nucleus
3349:Measurement and testing
2732:Auditory verbal agnosia
2586:Juxtacapillary receptor
1796:Intrafusal muscle fiber
747:www.massage-stlouis.com
480:periventricular nucleus
323:P2 purinergic receptors
2727:Auditory hallucination
2337:Surface wave detection
1942:Multimodal integration
1514:10.1186/1749-8104-4-37
1326:Caenorhabditis elegans
1324:"Thermal avoidance in
1252:10.1098/rspb.2003.2349
951:10.1006/nbdi.1998.0204
248:central nervous system
89:
63:Anatomical terminology
3498:Drug-seeking behavior
3386:Visual analogue scale
2986:Phantom limb syndrome
2934:Tactile hallucination
2123:Glossopharyngeal (IX)
1924:Active sensory system
631:, and tissue damage.
514:functions by binding
496:substantia gelatinosa
361:also detect acidity.
199:cutaneous nociceptors
3409:Anterolateral system
2795:Labyrinthine fistula
2762:Spatial hearing loss
2461:Campaniform sensilla
2176:Somatosensory cortex
500:nucleus raphe magnus
492:nucleus raphe magnus
484:nucleus raphe magnus
451:anterolateral system
155:afferent nerve fiber
2581:Nociceptin receptor
2451:Merkel nerve ending
2436:Mechanotransduction
1801:Nuclear chain fiber
1715:Merkel nerve ending
1344:1999PNAS...9610477W
1338:(18): 10477–10482.
1246:(1520): 1115–1121.
679:nociceptin receptor
669:mechanism of action
637:Pain in crustaceans
577:nerve growth factor
490:(NPG). In turn the
476:periaqueductal grey
327:nerve growth factor
255:conduction velocity
234:Types and functions
223:dorsal root ganglia
167:autonomic responses
3488:Philosophy of pain
3163:Respiratory system
2943:Nociception (pain)
2535:Olfactory receptor
2487:Photoreceptor cell
2441:Lamellar corpuscle
2365:Photomorphogenesis
2227:nociception (pain)
1919:Sensory processing
1695:Lamellar corpuscle
1501:Neural Development
774:Mechanisms of Pain
585:RET proto-oncogene
559:stem cells during
551:Neural development
357:toxins and acids.
253:In terms of their
37:free nerve endings
3519:Sensory receptors
3506:
3505:
3361:Cold pressor test
3344:
3343:
3075:
3074:
3060:Biases and errors
3055:
3054:
2991:Somatoparaphrenia
2960:Pain dissociation
2805:Ménière's disease
2737:Cortical deafness
2615:Visual impairment
2594:
2593:
2456:Bulbous corpuscle
2446:Tactile corpuscle
2414:sensory receptors
2406:
2405:
2289:
2288:
2242:
2241:
2207:Olfaction (smell)
2161:Vestibular cortex
2143:Cerebral cortices
1980:
1979:
1967:Motion perception
1837:
1836:
1806:Nuclear bag fiber
1745:Free nerve ending
1725:Bulbous corpuscle
1705:Tactile corpuscle
1671:Sensory receptors
1577:978-0-19-852334-5
1189:(12): 1089–1106.
1114:978-0-323-59712-8
998:978-1-260-12240-4
920:978-0-87893-742-4
883:978-0-8385-8034-9
567:or low-threshold
388:neurotransmitters
138:action potentials
77:
76:
72:
3536:
3461:Related concepts
3452:Pain eradication
3210:
3197:
3148:
3120:
3119:
3116:By region/system
3102:
3095:
3088:
3079:
3078:
2722:Auditory agnosia
2654:Optic neuropathy
2603:
2602:
2471:Stretch receptor
2419:
2418:
2317:Magnetoreception
2312:Electroreception
2300:
2299:
2222:mechanoreception
2171:Gustatory cortex
2166:Olfactory cortex
2000:
1999:
1991:
1990:
1909:Sensory receptor
1892:
1891:
1864:
1857:
1850:
1841:
1840:
1664:
1657:
1650:
1641:
1640:
1634:
1633:
1593:
1587:
1586:
1585:
1584:
1551:
1545:
1544:
1534:
1516:
1492:
1486:
1485:
1467:
1435:
1429:
1428:
1418:
1382:
1376:
1375:
1365:
1355:
1319:
1313:
1312:
1295:(6): 2268–2279.
1280:
1274:
1273:
1263:
1231:
1225:
1224:
1214:
1174:
1168:
1167:
1149:
1125:
1119:
1118:
1100:
1094:
1093:
1091:
1090:
1080:
1074:
1073:
1063:
1057:
1056:
1038:
1014:
1003:
1002:
984:
971:
970:
934:
925:
924:
906:
900:
894:
888:
887:
871:
861:
850:
847:
841:
840:
830:
819:10.1172/JCI42843
798:
779:
778:
768:
762:
761:
759:
758:
749:. Archived from
739:
733:
732:
730:
729:
720:. Archived from
718:www.noigroup.com
710:
659:
654:
653:
652:
599:In other animals
569:mechanoreceptors
528:diacetylmorphine
520:opioid receptors
516:opioid receptors
494:projects to the
244:action potential
110:
107:
104:
101:
98:
69:edit on Wikidata
66:
33:
21:
20:
3544:
3543:
3539:
3538:
3537:
3535:
3534:
3533:
3509:
3508:
3507:
3502:
3456:
3423:
3396:Pathophysiology
3390:
3381:Tail flick test
3340:
3309:
3224:
3208:
3195:
3186:Musculoskeletal
3180:
3157:
3146:
3111:
3106:
3076:
3071:
3051:
3000:
2969:
2938:
2890:
2857:
2809:
2771:
2703:
2694:Stereoblindness
2635:Color blindness
2590:
2567:
2544:
2516:
2475:
2423:Mechanoreceptor
2412:
2402:
2398:Machine hearing
2393:Computer vision
2388:Robotic sensing
2374:
2351:
2285:
2238:
2180:
2156:Auditory cortex
2137:
2084:
2047:Sensory systems
2041:
1976:
1928:
1886:
1884:
1877:
1868:
1838:
1833:
1812:
1772:
1768:Thermoreceptors
1754:
1731:
1687:Mechanoreceptor
1673:
1668:
1638:
1637:
1594:
1590:
1582:
1580:
1578:
1552:
1548:
1493:
1489:
1436:
1432:
1383:
1379:
1320:
1316:
1281:
1277:
1232:
1228:
1175:
1171:
1126:
1122:
1115:
1101:
1097:
1088:
1086:
1082:
1081:
1077:
1064:
1060:
1015:
1006:
999:
985:
974:
935:
928:
921:
907:
903:
895:
891:
884:
862:
853:
848:
844:
813:(11): 3760–72.
799:
782:
769:
765:
756:
754:
741:
740:
736:
727:
725:
712:
711:
707:
702:
657:Medicine portal
655:
650:
648:
645:
601:
553:
536:
463:
455:cerebral cortex
403:
396:
380:
372:receptive field
367:
365:Sleeping/silent
354:chemical weapon
339:
314:
288:
240:noxious stimuli
236:
187:
159:receptive field
146:
126:
108:
105:
102:
99:
73:
40:
17:
12:
11:
5:
3542:
3532:
3531:
3529:Receptor cells
3526:
3521:
3504:
3503:
3501:
3500:
3495:
3490:
3485:
3480:
3475:
3473:Pain tolerance
3470:
3468:Pain threshold
3464:
3462:
3458:
3457:
3455:
3454:
3449:
3444:
3439:
3433:
3431:
3425:
3424:
3422:
3421:
3416:
3411:
3406:
3400:
3398:
3392:
3391:
3389:
3388:
3383:
3378:
3376:Hot plate test
3373:
3368:
3363:
3358:
3352:
3350:
3346:
3345:
3342:
3341:
3339:
3338:
3333:
3328:
3323:
3317:
3315:
3311:
3310:
3308:
3307:
3306:
3305:
3300:
3290:
3285:
3280:
3275:
3270:
3265:
3260:
3255:
3250:
3245:
3243:Pain asymbolia
3240:
3234:
3232:
3226:
3225:
3223:
3222:
3217:
3212:
3204:
3199:
3190:
3188:
3182:
3181:
3179:
3178:
3173:
3167:
3165:
3159:
3158:
3156:
3155:
3150:
3142:
3137:
3132:
3126:
3124:
3117:
3113:
3112:
3105:
3104:
3097:
3090:
3082:
3073:
3072:
3070:
3069:
3063:
3061:
3057:
3056:
3053:
3052:
3050:
3049:
3044:
3039:
3034:
3029:
3024:
3019:
3014:
3008:
3006:
3002:
3001:
2999:
2998:
2993:
2988:
2983:
2977:
2975:
2974:Proprioception
2971:
2970:
2968:
2967:
2962:
2957:
2952:
2946:
2944:
2940:
2939:
2937:
2936:
2931:
2926:
2921:
2916:
2911:
2906:
2900:
2898:
2892:
2891:
2889:
2888:
2883:
2878:
2873:
2867:
2865:
2859:
2858:
2856:
2855:
2850:
2845:
2840:
2835:
2830:
2825:
2819:
2817:
2811:
2810:
2808:
2807:
2802:
2797:
2792:
2787:
2781:
2779:
2773:
2772:
2770:
2769:
2764:
2759:
2754:
2749:
2744:
2739:
2734:
2729:
2724:
2719:
2713:
2711:
2705:
2704:
2702:
2701:
2696:
2691:
2686:
2681:
2676:
2671:
2666:
2661:
2656:
2651:
2642:
2637:
2632:
2627:
2622:
2617:
2611:
2609:
2600:
2596:
2595:
2592:
2591:
2589:
2588:
2583:
2577:
2575:
2569:
2568:
2566:
2565:
2560:
2554:
2552:
2550:Thermoreceptor
2546:
2545:
2543:
2542:
2537:
2532:
2530:Taste receptor
2526:
2524:
2518:
2517:
2515:
2514:
2509:
2504:
2499:
2494:
2489:
2483:
2481:
2477:
2476:
2474:
2473:
2468:
2463:
2458:
2453:
2448:
2443:
2438:
2433:
2427:
2425:
2416:
2408:
2407:
2404:
2403:
2401:
2400:
2395:
2390:
2384:
2382:
2376:
2375:
2373:
2372:
2367:
2361:
2359:
2353:
2352:
2350:
2349:
2344:
2339:
2334:
2329:
2324:
2319:
2314:
2308:
2306:
2297:
2291:
2290:
2287:
2286:
2284:
2283:
2278:
2273:
2268:
2263:
2258:
2256:Proprioception
2252:
2250:
2244:
2243:
2240:
2239:
2237:
2236:
2235:
2234:
2229:
2224:
2214:
2209:
2204:
2199:
2194:
2188:
2186:
2182:
2181:
2179:
2178:
2173:
2168:
2163:
2158:
2153:
2147:
2145:
2139:
2138:
2136:
2135:
2130:
2128:Trigeminal (V)
2125:
2120:
2115:
2110:
2105:
2099:
2097:
2086:
2085:
2083:
2082:
2077:
2072:
2067:
2062:
2057:
2051:
2049:
2043:
2042:
2040:
2039:
2034:
2029:
2024:
2019:
2014:
2008:
2006:
2004:Sensory organs
1997:
1988:
1982:
1981:
1978:
1977:
1975:
1974:
1969:
1964:
1959:
1954:
1949:
1944:
1938:
1936:
1930:
1929:
1927:
1926:
1921:
1916:
1911:
1906:
1900:
1898:
1889:
1879:
1878:
1867:
1866:
1859:
1852:
1844:
1835:
1834:
1832:
1831:
1826:
1820:
1818:
1814:
1813:
1811:
1810:
1809:
1808:
1803:
1798:
1791:Muscle spindle
1788:
1782:
1780:
1778:Proprioception
1774:
1773:
1771:
1770:
1764:
1762:
1756:
1755:
1753:
1752:
1747:
1741:
1739:
1733:
1732:
1730:
1729:
1728:
1727:
1719:
1718:
1717:
1709:
1708:
1707:
1699:
1698:
1697:
1689:
1683:
1681:
1675:
1674:
1667:
1666:
1659:
1652:
1644:
1636:
1635:
1588:
1576:
1546:
1487:
1458:(2): 261–273.
1430:
1401:(1): 459–469.
1377:
1314:
1275:
1226:
1169:
1120:
1113:
1095:
1084:"Pain Pathway"
1075:
1058:
1004:
997:
972:
939:Neurobiol. Dis
926:
919:
901:
889:
882:
851:
842:
780:
763:
734:
704:
703:
701:
698:
697:
696:
690:
681:
672:
671:in nociceptors
661:
660:
644:
641:
600:
597:
565:proprioceptors
552:
549:
535:
532:
504:serotoninergic
462:
459:
412:, rather than
402:
399:
395:
392:
379:
376:
366:
363:
338:
335:
313:
310:
301:pain threshold
287:
284:
278:is similar to
235:
232:
186:
183:
145:
142:
125:
122:
113:sensory neuron
75:
74:
65:
59:
58:
53:
47:
46:
42:
41:
34:
26:
25:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3541:
3530:
3527:
3525:
3522:
3520:
3517:
3516:
3514:
3499:
3496:
3494:
3491:
3489:
3486:
3484:
3481:
3479:
3476:
3474:
3471:
3469:
3466:
3465:
3463:
3459:
3453:
3450:
3448:
3445:
3443:
3440:
3438:
3435:
3434:
3432:
3430:
3426:
3420:
3417:
3415:
3412:
3410:
3407:
3405:
3402:
3401:
3399:
3397:
3393:
3387:
3384:
3382:
3379:
3377:
3374:
3372:
3371:Grimace scale
3369:
3367:
3364:
3362:
3359:
3357:
3354:
3353:
3351:
3347:
3337:
3336:Low back pain
3334:
3332:
3329:
3327:
3324:
3322:
3319:
3318:
3316:
3312:
3304:
3301:
3299:
3296:
3295:
3294:
3291:
3289:
3288:Referred pain
3286:
3284:
3281:
3279:
3276:
3274:
3271:
3269:
3266:
3264:
3261:
3259:
3256:
3254:
3251:
3249:
3248:Pain disorder
3246:
3244:
3241:
3239:
3236:
3235:
3233:
3231:
3227:
3221:
3220:Delayed-onset
3218:
3216:
3213:
3211:
3205:
3203:
3200:
3198:
3192:
3191:
3189:
3187:
3183:
3177:
3174:
3172:
3169:
3168:
3166:
3164:
3160:
3154:
3151:
3149:
3143:
3141:
3138:
3136:
3133:
3131:
3128:
3127:
3125:
3123:Head and neck
3121:
3118:
3114:
3110:
3103:
3098:
3096:
3091:
3089:
3084:
3083:
3080:
3068:
3065:
3064:
3062:
3058:
3048:
3045:
3043:
3040:
3038:
3035:
3033:
3032:Hallucination
3030:
3028:
3027:Derealization
3025:
3023:
3020:
3018:
3015:
3013:
3010:
3009:
3007:
3003:
2997:
2994:
2992:
2989:
2987:
2984:
2982:
2981:Asomatognosia
2979:
2978:
2976:
2972:
2966:
2963:
2961:
2958:
2956:
2953:
2951:
2948:
2947:
2945:
2941:
2935:
2932:
2930:
2927:
2925:
2922:
2920:
2919:Hyperesthesia
2917:
2915:
2912:
2910:
2907:
2905:
2904:Astereognosis
2902:
2901:
2899:
2897:
2893:
2887:
2884:
2882:
2879:
2877:
2874:
2872:
2869:
2868:
2866:
2864:
2860:
2854:
2851:
2849:
2846:
2844:
2841:
2839:
2836:
2834:
2831:
2829:
2826:
2824:
2821:
2820:
2818:
2816:
2812:
2806:
2803:
2801:
2800:Labyrinthitis
2798:
2796:
2793:
2791:
2788:
2786:
2783:
2782:
2780:
2778:
2774:
2768:
2765:
2763:
2760:
2758:
2755:
2753:
2750:
2748:
2745:
2743:
2740:
2738:
2735:
2733:
2730:
2728:
2725:
2723:
2720:
2718:
2715:
2714:
2712:
2710:
2706:
2700:
2697:
2695:
2692:
2690:
2687:
2685:
2682:
2680:
2677:
2675:
2672:
2670:
2667:
2665:
2662:
2660:
2657:
2655:
2652:
2650:
2646:
2643:
2641:
2638:
2636:
2633:
2631:
2628:
2626:
2623:
2621:
2618:
2616:
2613:
2612:
2610:
2608:
2604:
2601:
2597:
2587:
2584:
2582:
2579:
2578:
2576:
2574:
2570:
2564:
2561:
2559:
2556:
2555:
2553:
2551:
2547:
2541:
2538:
2536:
2533:
2531:
2528:
2527:
2525:
2523:
2522:Chemoreceptor
2519:
2513:
2510:
2508:
2505:
2503:
2500:
2498:
2495:
2493:
2490:
2488:
2485:
2484:
2482:
2480:Photoreceptor
2478:
2472:
2469:
2467:
2466:Slit sensilla
2464:
2462:
2459:
2457:
2454:
2452:
2449:
2447:
2444:
2442:
2439:
2437:
2434:
2432:
2429:
2428:
2426:
2424:
2420:
2417:
2415:
2409:
2399:
2396:
2394:
2391:
2389:
2386:
2385:
2383:
2381:
2377:
2371:
2368:
2366:
2363:
2362:
2360:
2358:
2354:
2348:
2345:
2343:
2340:
2338:
2335:
2333:
2330:
2328:
2325:
2323:
2320:
2318:
2315:
2313:
2310:
2309:
2307:
2305:
2301:
2298:
2296:
2292:
2282:
2281:Visceral pain
2279:
2277:
2274:
2272:
2269:
2267:
2264:
2262:
2259:
2257:
2254:
2253:
2251:
2249:
2245:
2233:
2232:thermoception
2230:
2228:
2225:
2223:
2220:
2219:
2218:
2215:
2213:
2210:
2208:
2205:
2203:
2200:
2198:
2195:
2193:
2190:
2189:
2187:
2183:
2177:
2174:
2172:
2169:
2167:
2164:
2162:
2159:
2157:
2154:
2152:
2151:Visual cortex
2149:
2148:
2146:
2144:
2140:
2134:
2131:
2129:
2126:
2124:
2121:
2119:
2116:
2114:
2113:Olfactory (I)
2111:
2109:
2106:
2104:
2101:
2100:
2098:
2096:
2095:spinal nerves
2092:
2087:
2081:
2078:
2076:
2073:
2071:
2068:
2066:
2063:
2061:
2058:
2056:
2053:
2052:
2050:
2048:
2044:
2038:
2035:
2033:
2030:
2028:
2025:
2023:
2020:
2018:
2015:
2013:
2010:
2009:
2007:
2005:
2001:
1998:
1996:
1992:
1989:
1987:
1983:
1973:
1970:
1968:
1965:
1963:
1960:
1958:
1955:
1953:
1952:Consciousness
1950:
1948:
1945:
1943:
1940:
1939:
1937:
1935:
1931:
1925:
1922:
1920:
1917:
1915:
1912:
1910:
1907:
1905:
1902:
1901:
1899:
1897:
1893:
1890:
1888:
1880:
1876:
1872:
1865:
1860:
1858:
1853:
1851:
1846:
1845:
1842:
1830:
1827:
1825:
1822:
1821:
1819:
1815:
1807:
1804:
1802:
1799:
1797:
1794:
1793:
1792:
1789:
1787:
1784:
1783:
1781:
1779:
1775:
1769:
1766:
1765:
1763:
1761:
1757:
1751:
1748:
1746:
1743:
1742:
1740:
1738:
1734:
1726:
1723:
1722:
1720:
1716:
1713:
1712:
1710:
1706:
1703:
1702:
1700:
1696:
1693:
1692:
1690:
1688:
1685:
1684:
1682:
1680:
1676:
1672:
1665:
1660:
1658:
1653:
1651:
1646:
1645:
1642:
1631:
1627:
1623:
1619:
1615:
1611:
1607:
1603:
1599:
1592:
1579:
1573:
1569:
1565:
1561:
1557:
1550:
1542:
1538:
1533:
1528:
1524:
1520:
1515:
1510:
1506:
1502:
1498:
1491:
1483:
1479:
1475:
1471:
1466:
1461:
1457:
1453:
1449:
1447:
1443:
1434:
1426:
1422:
1417:
1412:
1408:
1404:
1400:
1396:
1392:
1390:
1381:
1373:
1369:
1364:
1359:
1354:
1349:
1345:
1341:
1337:
1333:
1329:
1327:
1318:
1310:
1306:
1302:
1298:
1294:
1290:
1286:
1279:
1271:
1267:
1262:
1257:
1253:
1249:
1245:
1241:
1237:
1230:
1222:
1218:
1213:
1208:
1204:
1200:
1196:
1192:
1188:
1184:
1180:
1173:
1165:
1161:
1157:
1153:
1148:
1143:
1140:(3): 365–76.
1139:
1135:
1131:
1124:
1116:
1110:
1106:
1099:
1085:
1079:
1071:
1070:
1062:
1054:
1050:
1046:
1042:
1037:
1032:
1029:(3): 353–64.
1028:
1024:
1020:
1013:
1011:
1009:
1000:
994:
990:
983:
981:
979:
977:
968:
964:
960:
956:
952:
948:
945:(4): 209–27.
944:
940:
933:
931:
922:
916:
912:
905:
899:
893:
885:
879:
875:
870:
869:
860:
858:
856:
846:
838:
834:
829:
824:
820:
816:
812:
808:
804:
797:
795:
793:
791:
789:
787:
785:
776:
775:
767:
753:on 2018-11-01
752:
748:
744:
738:
724:on 2018-10-17
723:
719:
715:
709:
705:
694:
691:
689:
685:
682:
680:
676:
673:
670:
666:
663:
662:
658:
647:
640:
638:
632:
630:
626:
622:
619:, and larval
618:
614:
610:
606:
605:invertebrates
596:
594:
590:
586:
580:
578:
574:
570:
566:
562:
561:embryogenesis
558:
548:
546:
542:
531:
529:
525:
521:
517:
513:
509:
505:
501:
497:
493:
489:
485:
481:
477:
473:
469:
458:
456:
452:
448:
444:
439:
435:
431:
427:
423:
419:
415:
411:
407:
398:
391:
389:
385:
375:
373:
362:
360:
355:
352:
348:
344:
334:
332:
328:
324:
320:
309:
306:
302:
298:
294:
283:
281:
277:
273:
268:
264:
260:
256:
251:
249:
245:
241:
231:
228:
224:
220:
216:
212:
208:
204:
200:
196:
192:
182:
180:
174:
172:
168:
164:
160:
156:
151:
141:
139:
134:
130:
121:
119:
114:
106:pain receptor
94:
93:
92:
86:
82:
70:
64:
60:
57:
54:
52:
48:
43:
38:
32:
27:
22:
19:
3283:Phantom pain
3268:Hyperalgesia
3263:Chronic pain
3147:(swallowing)
3145:Odynophagia
2965:Phantom pain
2950:Hyperalgesia
2924:Hypoesthesia
2742:Hearing loss
2572:
2563:TRP channels
2540:Osmoreceptor
2507:Photopigment
2431:Baroreceptor
2370:Gravitropism
2342:Frog hearing
2322:Echolocation
2118:Facial (VII)
1829:Baroreceptor
1749:
1701:Light touch
1608:(1): 26–33.
1605:
1601:
1591:
1581:, retrieved
1559:
1549:
1504:
1500:
1490:
1455:
1451:
1445:
1441:
1433:
1398:
1394:
1388:
1380:
1335:
1331:
1325:
1317:
1292:
1288:
1278:
1243:
1239:
1229:
1186:
1182:
1172:
1137:
1133:
1123:
1104:
1098:
1087:. Retrieved
1078:
1068:
1061:
1026:
1022:
988:
942:
938:
911:Neuroscience
910:
904:
892:
867:
845:
810:
806:
773:
766:
755:. Retrieved
751:the original
746:
737:
726:. Retrieved
722:the original
717:
708:
688:black pepper
633:
607:, including
602:
581:
557:neural-crest
554:
541:hyperalgesia
537:
472:hypothalamus
464:
413:
409:
404:
397:
383:
381:
368:
340:
315:
289:
252:
237:
193:such as the
188:
179:animal model
175:
147:
127:
88:
80:
78:
18:
3524:Nociception
3493:Cancer pain
3419:Substance P
3404:Nociception
3366:Dolorimeter
3321:Pelvic pain
3278:Hyperpathia
3273:Hypoalgesia
3194:Arthralgia
3176:Pleurodynia
3171:Sore throat
3047:Synesthesia
2955:Hypoalgesia
2929:Paresthesia
2914:Formication
2909:CMT disease
2876:Hypergeusia
2699:Visual snow
2674:Photophobia
2669:Papilledema
2659:Oscillopsia
2645:Hemeralopia
2512:Aureochrome
2347:Toad vision
2271:Suffocation
2185:Perceptions
1786:Golgi organ
1760:Temperature
1750:Nociceptors
695:ion channel
621:fruit flies
534:Sensitivity
438:substance P
422:dorsal horn
418:spinal cord
351:World War I
297:TRP channel
272:dorsal horn
267:myelination
129:Nociception
124:Terminology
118:nociception
45:Identifiers
3513:Categories
3442:Anesthesia
3429:Management
3356:Pain scale
3326:Proctalgia
3230:Neurologic
3130:Eye strain
3067:Pareidolia
3022:Allochiria
3005:Multimodal
2886:Parageusia
2881:Hypogeusia
2853:Phantosmia
2833:Hyperosmia
2777:Vestibular
2757:Palinopsia
2717:Amblyaudia
2664:Palinopsia
2649:Nyctalopia
2573:Nociceptor
2380:Artificial
2103:Optic (II)
1934:Perception
1883:Processes
1875:perception
1824:Hair cells
1691:Vibration
1583:2024-03-21
1446:Drosophila
1089:2008-06-02
757:2017-10-13
728:2017-10-13
700:References
675:Nociceptin
512:Enkephalin
508:enkephalin
461:Descending
312:Mechanical
227:trigeminal
205:, and the
165:, certain
163:withdrawal
83:(from
81:nociceptor
24:Nociceptor
3478:Suffering
3447:Cordotomy
3437:Analgesia
3258:Allodynia
3238:Neuralgia
3202:Bone pain
3153:Toothache
2863:Gustatory
2815:Olfactory
2679:Photopsia
2625:Amaurosis
2599:Disorders
2492:Cone cell
2411:Types of
2022:Inner ear
1957:Cognition
1947:Awareness
1896:Sensation
1871:Sensation
1711:Pressure
1622:0169-328X
1523:1749-8104
1507:(1): 37.
1203:1432-1351
665:Capsaicin
629:capsaicin
617:sea slugs
545:allodynia
434:glutamate
401:Ascending
384:polymodal
378:Polymodal
343:capsaicin
133:threshold
3483:SOCRATES
3209:(muscle)
3207:Myalgia
3135:Headache
2848:Parosmia
2838:Hyposmia
2828:Dysosmia
2767:Tinnitus
2709:Auditory
2684:Polyopia
2640:Diplopia
2497:Rod cell
2295:Nonhuman
2248:Internal
2089:Sensory
1995:External
1904:Stimulus
1887:concepts
1721:Stretch
1630:11869805
1541:19799768
1474:12705873
1442:painless
1372:10468634
1270:12816648
1221:19830434
1156:17678851
1066:Fein A.
1053:13576368
1045:17678850
967:13217293
837:21041958
684:Piperine
667:and its
643:See also
613:nematode
524:morphine
502:sending
468:hormones
449:and the
443:thalamus
430:synapses
406:Afferent
347:acrolein
337:Chemical
259:Aδ fiber
185:Location
3196:(joint)
3017:Agnosia
2896:Tactile
2871:Ageusia
2823:Anosmia
2785:Vertigo
2689:Scotoma
2630:Anopsia
2091:cranial
1962:Feeling
1532:2762467
1482:1424315
1425:8987770
1416:6793714
1389:Aplysia
1340:Bibcode
1309:8793740
1261:1691351
1212:2780683
959:9848092
828:2964977
615:worms,
609:leeches
394:Pathway
286:Thermal
280:tetanus
276:wind-up
263:C fiber
225:or the
219:bladder
211:muscles
203:corneas
201:), the
111:) is a
100:
56:D009619
2607:Visual
2558:Cilium
2304:Animal
2276:Nausea
2266:Thirst
2261:Hunger
2133:Spinal
1972:Qualia
1628:
1620:
1574:
1539:
1529:
1521:
1480:
1472:
1423:
1413:
1370:
1360:
1307:
1268:
1258:
1219:
1209:
1201:
1164:815135
1162:
1154:
1134:Neuron
1111:
1051:
1043:
1023:Neuron
995:
965:
957:
917:
880:
874:472–79
835:
825:
445:: the
217:, the
215:joints
213:, the
207:mucosa
191:tissue
169:, and
91:nocere
39:type A
3314:Other
3215:Acute
2502:ipRGC
2357:Plant
2217:Touch
2032:Mouth
1986:Human
1817:Other
1679:Touch
1478:S2CID
1363:17914
1160:S2CID
1049:S2CID
963:S2CID
686:from
426:cells
325:, or
305:TRPM8
293:TRPV1
87:
85:Latin
67:[
3331:Back
3140:Neck
3109:Pain
3037:HSAN
3012:Aura
2790:BPPV
2647:and
2093:and
2037:Skin
2027:Nose
2017:Ears
2012:Eyes
1885:and
1873:and
1737:Pain
1626:PMID
1618:ISSN
1572:ISBN
1537:PMID
1519:ISSN
1470:PMID
1452:Cell
1444:, a
1421:PMID
1368:PMID
1305:PMID
1266:PMID
1217:PMID
1199:ISSN
1152:PMID
1109:ISBN
1041:PMID
993:ISBN
955:PMID
915:ISBN
878:ISBN
833:PMID
693:TRPC
677:and
526:and
414:from
349:, a
195:skin
171:pain
97:lit.
51:MeSH
1610:doi
1564:doi
1527:PMC
1509:doi
1460:doi
1456:113
1411:PMC
1403:doi
1358:PMC
1348:doi
1297:doi
1256:PMC
1248:doi
1244:270
1207:PMC
1191:doi
1187:195
1142:doi
1031:doi
947:doi
823:PMC
815:doi
811:120
639:).
436:or
319:ATP
157:'s
3515::
1624:.
1616:.
1606:99
1604:.
1600:.
1570:,
1558:,
1535:.
1525:.
1517:.
1503:.
1499:.
1476:.
1468:.
1454:.
1450:.
1419:.
1409:.
1399:17
1397:.
1393:.
1366:.
1356:.
1346:.
1336:96
1334:.
1330:.
1303:.
1293:75
1291:.
1287:.
1264:.
1254:.
1242:.
1238:.
1215:.
1205:.
1197:.
1185:.
1181:.
1158:.
1150:.
1138:55
1136:.
1132:.
1047:.
1039:.
1027:55
1025:.
1021:.
1007:^
975:^
961:.
953:.
941:.
929:^
876:.
854:^
831:.
821:.
809:.
805:.
783:^
745:.
716:.
627:,
625:pH
611:,
410:to
390:.
374:.
333:.
120:.
79:A
3101:e
3094:t
3087:v
1863:e
1856:t
1849:v
1663:e
1656:t
1649:v
1632:.
1612::
1566::
1543:.
1511::
1505:4
1484:.
1462::
1440:"
1427:.
1405::
1374:.
1350::
1342::
1311:.
1299::
1272:.
1250::
1223:.
1193::
1166:.
1144::
1117:.
1092:.
1072:.
1055:.
1033::
1001:.
969:.
949::
943:5
923:.
886:.
839:.
817::
760:.
731:.
197:(
109:'
103:'
71:]
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.