413:
ongoing symptoms down the track, or if there are other injuries in the knee (e.g. posterolateral corner injury) will ligament reconstruction be required. Ligament reconstruction is used to replace the torn PCL with a new ligament, which is usually a graft taken from the hamstring or
Achilles tendon from a host cadaver. An arthroscope allows a complete evaluation of the entire knee joint, including the knee cap (patella), the cartilage surfaces, the meniscus, the ligaments (ACL & PCL), and the joint lining. Then, the new ligament is attached to the bone of the thigh and lower leg with screws to hold it in place. Surgery to repair the posterior cruciate ligament is controversial due to its placement and technical difficulty.
500:
225:
371:
476:
524:
488:
396:) they can handle higher amounts of stress only when the load is increased slowly. When hyperflexion and hyperextension occur suddenly in combination with this viscoelastic behavior, the PCL deforms or tears. In the third and most common mechanism, the dashboard injury mechanism, the knee experiences impact in a posterior direction during knee flexion toward the space above the tibia. These mechanisms occur in excessive
29:
512:
358:
416:
It is possible for the PCL to heal on its own without surgery when it is a Grade I or Grade II injury. PCL injuries that are diagnosed in these categories can have their recovery times reduced by performing certain rehabilitative exercises. Fernandez and Pugh(2012) found that following a PCL grade
374:
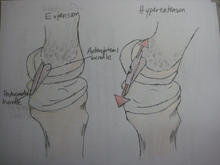
In this medial view of the flexed knee, the lateral femoral condyle has been removed to reveal the structure of the PCL. Because the anterolateral bundle is stretched and the posteromedial bundle relaxed during flexion, excessive flexion in the form of hyperflexion causes tensile stress, shown in
228:
In this medial view of the extended knee, the lateral femoral condyle has been removed to reveal the structure of the PCL. Because the posteromedial bundle is stretched and the anterolateral bundle relaxed during extension, excessive extension in the form of hyperextension causes tensile stress,
412:
It is possible for the PCL to heal on its own. Even if the PCL does not heal normally, it is unusual for surgery to be required. Treatment is usually physiotherapy to strengthen the muscles around the knee; usually they provide adequate stability even without a functional PCL. Only if there are
309:
is one of the tests used by doctors and physiotherapists to detect injury to the PCL. Patients who are suspected to have a posterior cruciate ligament injury should always be evaluated for other knee injuries that often occur in combination with an PCL injuries. These include
181:
The PCL and ACL are intracapsular ligaments because they lie deep within the knee joint. They are both isolated from the fluid-filled synovial cavity, with the synovial membrane wrapped around them. The PCL gets its name by attaching to the posterior portion of the tibia.
238:
Although each PCL is a unified unit, they are described as separate anterolateral and posteromedial sections based on where each section's attachment site and function. During knee joint movement, the PCL rotates such that the anterolateral section stretches in
379:
In this position, the PCL functions to prevent movement of the tibia in the posterior direction and to prevent the tilting or shifting of the patella. However, the respective laxity of the two sections makes the PCL susceptible to injury during
289:, where, in contrast to the drawer test, no active force is applied. Rather, the person lies supine with the leg held by another person so that the hip is flexed to 90 degrees and the knee 90 degrees. The main parameter in this test is
639:
Chandrasekaran, S.; Ma, D.; Scarvell, JM.; Woods, KR.; Smith, PN. (Dec 2012). "A review of the anatomical, biomechanical and kinematic findings of posterior cruciate ligament injury with respect to non-operative management".
2042:
250:
The function of the PCL is to prevent the femur from sliding off the anterior edge of the tibia and to prevent the tibia from displacing posterior to the femur. The posterior cruciate ligament is located within the knee.
2019:
281:
Common causes of injuries are direct blows to the flexed knee, such as the knee hitting the dashboard in a car accident or falling hard on the knee, both instances displacing the tibia posterior to the femur.
499:
437:, 1-leg squats, and trunk stabilization proved to be an effective way to recover from the PCL injury. For Grades III and IV, operative surgery is recommended or is usually needed.
441:
is the method when addressing PCL injuries that are in need of operative surgery. With grafts, there are different methods such as the tibial inlay or tunnel method.
305:
is approximately 1 cm, but is decreased (Grade I) or even absent (Grade II) or inverse (Grade III) in injuries to the posterior cruciate ligament. The posterior
1043:
Janousek, Andreas T.; Jones, Deryk G.; Clatworthy, Mark; Higgins, Laurence D.; Fu, Freddie H. (1999). "Posterior
Cruciate Ligament Injuries of the Knee Joint".
985:
von
Eisenhart-Rothe, Ruediger; Lenze, Ulrich; Hinterwimmer, Stefan; Pohlig, Florian; Graichen, Heiko; Stein, Thomas; Welsch, Frederic; Burgkart, Rainer (2012).
2047:
118:
2024:
475:
1376:
1245:
Wind, William M.; Bergfeld, John A.; Parker, Richard D. (2004). "Evaluation and
Treatment of Posterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries: Revisited".
715:
Voos, JE.; Mauro, CS.; Wente, T.; Warren, RF.; Wickiewicz, TL. (Jan 2012). "Posterior cruciate ligament: anatomy, biomechanics, and outcomes".
599:
Girgis, FG.; Marshall, JL.; Monajem, A. (1975). "The cruciate ligaments of the knee joint. Anatomical, functional and experimental analysis".
94:
987:"Tibiofemoral and patellofemoral joint 3D-kinematics in patients with posterior cruciate ligament deficiency compared to healthy volunteers"
675:
Edwards, A.; Bull, AM.; Amis, AA. (Mar 2007). "The attachments of the fiber bundles of the posterior cruciate ligament: an anatomic study".
1621:
1616:
556:
Amis, AA.; Gupte, CM.; Bull, AM.; Edwards, A. (Mar 2006). "Anatomy of the posterior cruciate ligament and the meniscofemoral ligaments".
1713:
763:
Malone, AA.; Dowd, GS.; Saifuddin, A. (Jun 2006). "Injuries of the posterior cruciate ligament and posterolateral corner of the knee".
798:
DeFrate, LE.; Gill, TJ.; Li, G. (Dec 2004). "In vivo function of the posterior cruciate ligament during weightbearing knee flexion".
457:
1929:
1924:
1307:
1120:
1095:
505:
Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation demonstrating normal signal of both anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments (arrows).
487:
1198:"Multimodal and interdisciplinary management of an isolated partial tear of the posterior cruciate ligament: a case report"
1137:
1766:
1476:
1369:
841:
Race, A.; Amis, AA. (Jan 1994). "The mechanical properties of the two bundles of the human posterior cruciate ligament".
1891:
1798:
276:
221:
then stretches, at a posterior and lateral angle, toward the posterior of the tibia just below its articular surface.
1991:
1958:
1896:
1486:
922:
1963:
1914:
1868:
1752:
1481:
1919:
1873:
1831:
1748:
1644:
523:
2034:
2001:
1996:
1821:
1757:
1723:
1639:
1434:
1362:
418:
1793:
1761:
1718:
430:
113:
1981:
1649:
218:
163:
892:
178:. This configuration allows the PCL to resist forces pushing the tibia posteriorly relative to the femur.
1986:
1785:
1631:
1608:
1559:
1517:
190:
2011:
1530:
1512:
1502:
1497:
895:
From The
University of West Alabama, Athletic Training & Sports Medicine Center. Retrieved Feb 2011
256:
186:
159:
404:
of the tibia, which is referred to as varus-extension stress, or that occur while the knee is flexed.
1429:
1728:
321:
There are four different grades of classification in which medical doctors classify a PCL injury:
77:
2099:
1883:
1776:
315:
244:
171:
1973:
1950:
1564:
1423:
914:
354:
With these grades of PCL injuries, there are different treatments available for such injuries.
125:
101:
89:
1906:
1826:
1587:
1337:
906:
1860:
1813:
1444:
1418:
1413:
511:
8:
1836:
1803:
1175:
1354:
2074:
2069:
2061:
1851:
1542:
1270:
1222:
1197:
1068:
1013:
986:
967:
823:
740:
581:
311:
939:
1439:
1303:
1290:
1262:
1227:
1116:
1091:
1060:
1056:
1018:
959:
955:
918:
907:
858:
854:
815:
780:
732:
692:
657:
616:
612:
573:
397:
298:
1274:
1072:
971:
827:
585:
1703:
1698:
1693:
1688:
1683:
1552:
1449:
1254:
1217:
1209:
1115:. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. p. 30.
1090:. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams and Wilkins. p. 50.
1052:
1008:
998:
951:
850:
807:
772:
744:
724:
684:
649:
608:
565:
434:
224:
881:
481:
Head of right tibia seen from above, showing menisci and attachments of ligaments.
1582:
1547:
776:
688:
214:
82:
1349:
1162:
1740:
653:
385:
370:
1213:
569:
229:
shown in red, on the posteromedial bundle of the PCL that leads to PCL injury.
2093:
1258:
1003:
811:
728:
426:
340:, the PCL is torn completely and the knee can now be categorized as unstable.
106:
293:, which is the shortest distance from the femur to a hypothetical line that
1266:
1231:
1064:
1022:
819:
784:
736:
696:
661:
577:
453:
422:
393:
381:
240:
984:
963:
862:
620:
876:
306:
247:
and the posteromedial bundle stretches in extension rather than flexion.
1332:
940:"Posterior Tibial Subluxation of the Posterior Cruciate-Deficient Knee"
546:
Saladin, K. S. 2010. Anatomy & Physiology: 5th edition. McGraw-Hill
1288:
Blood, Douglas C.; Studdert, Virginia P.; Gay, Clive C., eds. (2007).
158:
of humans and various other animals. It works as a counterpart to the
131:
1393:
450:
401:
389:
375:
red, on the anterolateral bundle of the ACL that leads to ACL injury.
252:
213:, during movement. It originates from the lateral edge of the medial
1389:
1299:
1135:
347:
205:
joint where it stabilizes the articulating bones, particularly the
151:
1344:
294:
1335:
at The
Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (
285:
An additional test of posterior cruciate ligament injury is the
438:
255:
are sturdy bands of tissues that connect bones. Similar to the
28:
1042:
1672:
1385:
638:
264:
260:
210:
206:
175:
167:
65:
421:
treatment that spanned the course of 8 weeks consisting of
400:
and during falls that induce a combination of extension and
357:
1663:
1574:
1468:
1459:
202:
155:
938:
Castle, Thomas H; Noyes, Frank R; Grood, Edward S (1992).
904:
493:
Capsule of right knee-joint (distended). Posterior aspect.
388:, and in a mechanism known as a dashboard injury. Because
361:
The posterior cruciate ligament is located within the knee
1401:
1384:
978:
429:, and implementing an exercise program that emphasized
334:, the PCL ligament is minimally torn and becomes loose.
1173:
634:
632:
630:
598:
193:
are the four main ligaments of the knee in primates.
714:
555:
1176:"Injuries to the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)"
762:
1289:
1244:
627:
2091:
1287:
1038:
1036:
1034:
1032:
937:
674:
47:Antero-lateral aspect of medial femoral condyle
314:injuries, bone bruises, ACL tears, fractures,
1370:
1350:http://www.orthspec.com/pdfs/PCL-injuries.pdf
1195:
1163:http://www.orthspec.com/pdfs/PCL-injuries.pdf
1110:
1085:
1029:
797:
758:
756:
754:
346:, the ligament is damaged along with another
1296:Saunders Comprehensive Veterinary Dictionary
456:(analogous to the human knee), based on its
931:
791:
710:
708:
706:
668:
1377:
1363:
1111:Hamill, Joseph; Knutzen, Kathleen (2009).
1086:Hamill, Joseph; Knutzen, Kathleen (2009).
944:Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research
751:
529:Knee joint. Deep dissection. Anterior view
27:
1221:
1144:. American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons
1136:American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons.
1012:
1002:
1196:Fernandez, Matthew; Pugh, David (2012).
882:Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) injury
840:
834:
703:
549:
369:
356:
270:
223:
1345:Dealing with Torn Ligament in the Knee
55:Posterolateral aspect of proximal tibia
16:One of four major ligaments of the knee
2092:
1281:
1138:"Posterior Cruciate Ligament Injuries"
592:
1358:
1113:Biomechanical basis of human movement
1088:Biomechanical basis of human movement
905:Cole, Brian; Miller, Mark J. (2004).
1174:Jonathan Cluett, M.D. (2003-08-05).
467:
71:ligamentum cruciatum posterius genus
1622:posterior of the head of the fibula
1247:American Journal of Sports Medicine
558:Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc
13:
1684:medial of talocrural joint/deltoid
1617:anterior of the head of the fibula
913:. Philadelphia: Saunders. p.
318:and collateral ligament injuries.
297:the surface of the tibia from the
277:Posterior cruciate ligament injury
14:
2111:
1714:lateral collateral of ankle joint
1487:Posterior meniscofemoral ligament
1326:
1799:plantar calcaneonavicular/spring
1482:Anterior meniscofemoral ligament
1202:Journal of Chiropractic Medicine
1057:10.2165/00007256-199928060-00005
956:10.1097/00003086-199211000-00027
613:10.1097/00003086-197501000-00033
522:
510:
498:
486:
474:
444:
1238:
1189:
1167:
1156:
1129:
1104:
1079:
898:
886:
869:
1804:bifurcated (calcaneonavicular)
540:
350:housed in the knee (i.e. ACL).
201:The PCL is located within the
1:
991:BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders
534:
1930:interosseous cuneometatarsal
1650:Interosseous membrane of leg
855:10.1016/0021-9290(94)90028-0
777:10.1016/j.injury.2005.08.003
689:10.1016/j.arthro.2006.11.005
407:
365:
328:, the PCL has a slight tear.
196:
164:posterior intercondylar area
7:
1925:interosseous intercuneiform
1837:bifurcated (calcaneocuboid)
460:, it is referred to as the
301:and upwards. Normally, the
233:
144:posterior cruciate ligament
22:Posterior cruciate ligament
10:
2116:
1974:Intermetatarsal/metatarsal
654:10.1016/j.knee.2012.09.005
425:lumbopelvic manipulation,
274:
257:anterior cruciate ligament
160:anterior cruciate ligament
2060:
2033:
2010:
1972:
1949:
1942:
1905:
1882:
1859:
1849:
1812:
1784:
1775:
1739:
1671:
1662:
1630:
1607:
1600:
1573:
1467:
1458:
1400:
1214:10.1016/j.jcm.2011.10.005
570:10.1007/s00167-005-0686-x
124:
112:
100:
88:
76:
64:
59:
51:
43:
38:
26:
21:
1951:Tarsometatarsal/Lisfranc
1259:10.1177/0363546504270481
1004:10.1186/1471-2474-13-231
877:MedlinePlus Encyclopedia
812:10.1177/0363546504264896
729:10.1177/0363546511416316
462:caudal cruciate ligament
398:external tibial rotation
909:Textbook of arthroscopy
517:Anterior view of knee.
316:posterolateral injuries
259:, the PCL connects the
162:(ACL). It connects the
1997:superficial transverse
1832:plantar calcaneocuboid
1741:Subtalar/talocalcaneal
1645:Posterior tibiofibular
1338:antkneejointopenflexed
376:
362:
230:
126:Anatomical terminology
1822:dorsal calcaneocuboid
1786:Talocalcaneonavicular
1724:posterior talofibular
1640:Anterior tibiofibular
1632:Inferior tibiofibular
1609:Superior tibiofibular
1588:Infrapatellar fat pad
1435:transverse acetabular
601:Clin Orthop Relat Res
373:
360:
271:Clinical significance
227:
1794:dorsal talonavicular
1719:anterior talofibular
1694:posterior tibiotalar
1673:Talocrural and ankle
433:muscle contraction (
217:and the roof of the
2012:Metatarsophalangeal
1689:anterior tibiotalar
458:anatomical position
33:Diagram of the knee
893:Posterior Sag Test
377:
363:
287:posterior sag test
231:
219:intercondyle notch
2087:
2086:
2083:
2082:
2056:
2055:
1938:
1937:
1884:Cuboideonavicular
1845:
1844:
1777:Transverse tarsal
1658:
1657:
1596:
1595:
1440:acetabular labrum
1309:978-0-7020-2788-8
1122:978-0-7817-9128-1
1097:978-0-7817-9128-1
468:Additional images
299:tibial tuberosity
140:
139:
135:
2107:
1947:
1946:
1857:
1856:
1782:
1781:
1669:
1668:
1605:
1604:
1465:
1464:
1450:zona orbicularis
1379:
1372:
1365:
1356:
1355:
1321:
1320:
1318:
1316:
1298:(3rd ed.).
1293:
1285:
1279:
1278:
1242:
1236:
1235:
1225:
1193:
1187:
1186:
1184:
1183:
1171:
1165:
1160:
1154:
1153:
1151:
1149:
1133:
1127:
1126:
1108:
1102:
1101:
1083:
1077:
1076:
1040:
1027:
1026:
1016:
1006:
982:
976:
975:
950:(284): 193–202.
935:
929:
928:
912:
902:
896:
890:
884:
873:
867:
866:
838:
832:
831:
795:
789:
788:
760:
749:
748:
712:
701:
700:
672:
666:
665:
636:
625:
624:
596:
590:
589:
553:
547:
544:
526:
514:
502:
490:
478:
417:II diagnosis, a
132:edit on Wikidata
129:
31:
19:
18:
2115:
2114:
2110:
2109:
2108:
2106:
2105:
2104:
2090:
2089:
2088:
2079:
2052:
2035:Interphalangeal
2029:
2006:
2002:deep transverse
1968:
1934:
1901:
1878:
1841:
1808:
1771:
1735:
1729:calcaneofibular
1654:
1626:
1592:
1583:Patellar tendon
1569:
1518:fibular/lateral
1454:
1396:
1383:
1329:
1324:
1314:
1312:
1310:
1286:
1282:
1243:
1239:
1194:
1190:
1181:
1179:
1172:
1168:
1161:
1157:
1147:
1145:
1134:
1130:
1123:
1109:
1105:
1098:
1084:
1080:
1045:Sports Medicine
1041:
1030:
983:
979:
936:
932:
925:
903:
899:
891:
887:
874:
870:
839:
835:
800:Am J Sports Med
796:
792:
761:
752:
717:Am J Sports Med
713:
704:
673:
669:
637:
628:
607:(106): 216–31.
597:
593:
554:
550:
545:
541:
537:
530:
527:
518:
515:
506:
503:
494:
491:
482:
479:
470:
447:
410:
368:
279:
273:
236:
215:femoral condyle
199:
136:
34:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2113:
2103:
2102:
2100:Knee ligaments
2085:
2084:
2081:
2080:
2078:
2077:
2072:
2066:
2064:
2058:
2057:
2054:
2053:
2051:
2050:
2045:
2039:
2037:
2031:
2030:
2028:
2027:
2022:
2016:
2014:
2008:
2007:
2005:
2004:
1999:
1994:
1989:
1984:
1978:
1976:
1970:
1969:
1967:
1966:
1961:
1955:
1953:
1944:
1940:
1939:
1936:
1935:
1933:
1932:
1927:
1922:
1917:
1911:
1909:
1907:Intercuneiform
1903:
1902:
1900:
1899:
1894:
1888:
1886:
1880:
1879:
1877:
1876:
1871:
1865:
1863:
1861:Cuneonavicular
1854:
1847:
1846:
1843:
1842:
1840:
1839:
1834:
1829:
1824:
1818:
1816:
1814:Calcaneocuboid
1810:
1809:
1807:
1806:
1801:
1796:
1790:
1788:
1779:
1773:
1772:
1770:
1769:
1764:
1755:
1745:
1743:
1737:
1736:
1734:
1733:
1732:
1731:
1726:
1721:
1708:
1707:
1706:
1704:tibionavicular
1701:
1699:tibiocalcaneal
1696:
1691:
1677:
1675:
1666:
1660:
1659:
1656:
1655:
1653:
1652:
1647:
1642:
1636:
1634:
1628:
1627:
1625:
1624:
1619:
1613:
1611:
1602:
1598:
1597:
1594:
1593:
1591:
1590:
1585:
1579:
1577:
1575:Patellofemoral
1571:
1570:
1568:
1567:
1562:
1557:
1556:
1555:
1550:
1540:
1539:
1538:
1533:
1525:intracapsular:
1522:
1521:
1520:
1515:
1507:
1506:
1505:
1500:
1492:extracapsular:
1489:
1484:
1479:
1473:
1471:
1462:
1456:
1455:
1453:
1452:
1447:
1442:
1437:
1432:
1427:
1421:
1416:
1406:
1404:
1398:
1397:
1382:
1381:
1374:
1367:
1359:
1353:
1352:
1347:
1342:
1328:
1327:External links
1325:
1323:
1322:
1308:
1280:
1253:(7): 1765–75.
1237:
1188:
1166:
1155:
1128:
1121:
1103:
1096:
1078:
1028:
977:
930:
923:
897:
885:
868:
833:
790:
771:(6): 485–501.
750:
702:
667:
626:
591:
548:
538:
536:
533:
532:
531:
528:
521:
519:
516:
509:
507:
504:
497:
495:
492:
485:
483:
480:
473:
469:
466:
446:
443:
409:
406:
386:hyperextension
367:
364:
352:
351:
341:
335:
329:
275:Main article:
272:
269:
245:knee extension
235:
232:
198:
195:
185:The PCL, ACL,
172:medial condyle
138:
137:
128:
122:
121:
116:
110:
109:
104:
98:
97:
92:
86:
85:
80:
74:
73:
68:
62:
61:
57:
56:
53:
49:
48:
45:
41:
40:
36:
35:
32:
24:
23:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2112:
2101:
2098:
2097:
2095:
2076:
2073:
2071:
2068:
2067:
2065:
2063:
2059:
2049:
2046:
2044:
2041:
2040:
2038:
2036:
2032:
2026:
2023:
2021:
2018:
2017:
2015:
2013:
2009:
2003:
2000:
1998:
1995:
1993:
1990:
1988:
1985:
1983:
1980:
1979:
1977:
1975:
1971:
1965:
1962:
1960:
1957:
1956:
1954:
1952:
1948:
1945:
1941:
1931:
1928:
1926:
1923:
1921:
1918:
1916:
1913:
1912:
1910:
1908:
1904:
1898:
1895:
1893:
1890:
1889:
1887:
1885:
1881:
1875:
1872:
1870:
1867:
1866:
1864:
1862:
1858:
1855:
1853:
1848:
1838:
1835:
1833:
1830:
1828:
1825:
1823:
1820:
1819:
1817:
1815:
1811:
1805:
1802:
1800:
1797:
1795:
1792:
1791:
1789:
1787:
1783:
1780:
1778:
1774:
1768:
1765:
1763:
1759:
1756:
1754:
1750:
1747:
1746:
1744:
1742:
1738:
1730:
1727:
1725:
1722:
1720:
1717:
1716:
1715:
1712:
1709:
1705:
1702:
1700:
1697:
1695:
1692:
1690:
1687:
1686:
1685:
1682:
1679:
1678:
1676:
1674:
1670:
1667:
1665:
1661:
1651:
1648:
1646:
1643:
1641:
1638:
1637:
1635:
1633:
1629:
1623:
1620:
1618:
1615:
1614:
1612:
1610:
1606:
1603:
1599:
1589:
1586:
1584:
1581:
1580:
1578:
1576:
1572:
1566:
1565:anterolateral
1563:
1561:
1558:
1554:
1551:
1549:
1546:
1545:
1544:
1541:
1537:
1534:
1532:
1529:
1528:
1526:
1523:
1519:
1516:
1514:
1513:medial/tibial
1511:
1510:
1508:
1504:
1501:
1499:
1496:
1495:
1493:
1490:
1488:
1485:
1483:
1480:
1478:
1475:
1474:
1472:
1470:
1466:
1463:
1461:
1457:
1451:
1448:
1446:
1443:
1441:
1438:
1436:
1433:
1431:
1430:head of femur
1428:
1425:
1424:ischiofemoral
1422:
1420:
1417:
1415:
1411:
1408:
1407:
1405:
1403:
1399:
1395:
1391:
1387:
1380:
1375:
1373:
1368:
1366:
1361:
1360:
1357:
1351:
1348:
1346:
1343:
1340:
1339:
1334:
1331:
1330:
1311:
1305:
1301:
1297:
1292:
1284:
1276:
1272:
1268:
1264:
1260:
1256:
1252:
1248:
1241:
1233:
1229:
1224:
1219:
1215:
1211:
1207:
1203:
1199:
1192:
1177:
1170:
1164:
1159:
1143:
1139:
1132:
1124:
1118:
1114:
1107:
1099:
1093:
1089:
1082:
1074:
1070:
1066:
1062:
1058:
1054:
1051:(6): 429–41.
1050:
1046:
1039:
1037:
1035:
1033:
1024:
1020:
1015:
1010:
1005:
1000:
996:
992:
988:
981:
973:
969:
965:
961:
957:
953:
949:
945:
941:
934:
926:
924:0-7216-0013-1
920:
916:
911:
910:
901:
894:
889:
883:
879:
878:
872:
864:
860:
856:
852:
848:
844:
837:
829:
825:
821:
817:
813:
809:
806:(8): 1923–8.
805:
801:
794:
786:
782:
778:
774:
770:
766:
759:
757:
755:
746:
742:
738:
734:
730:
726:
723:(1): 222–31.
722:
718:
711:
709:
707:
698:
694:
690:
686:
683:(3): 284–90.
682:
678:
671:
663:
659:
655:
651:
648:(6): 738–45.
647:
643:
635:
633:
631:
622:
618:
614:
610:
606:
602:
595:
587:
583:
579:
575:
571:
567:
564:(3): 257–63.
563:
559:
552:
543:
539:
525:
520:
513:
508:
501:
496:
489:
484:
477:
472:
471:
465:
463:
459:
455:
452:
445:Other animals
442:
440:
436:
432:
428:
427:physiotherapy
424:
420:
414:
405:
403:
399:
395:
391:
387:
383:
372:
359:
355:
349:
345:
342:
339:
336:
333:
330:
327:
324:
323:
322:
319:
317:
313:
308:
304:
300:
296:
292:
288:
283:
278:
268:
266:
262:
258:
254:
248:
246:
242:
226:
222:
220:
216:
212:
208:
204:
194:
192:
188:
183:
179:
177:
173:
169:
165:
161:
157:
153:
149:
145:
133:
127:
123:
120:
117:
115:
111:
108:
105:
103:
99:
96:
93:
91:
87:
84:
81:
79:
75:
72:
69:
67:
63:
58:
54:
50:
46:
42:
37:
30:
25:
20:
2070:Longitudinal
1992:interosseous
1827:long plantar
1767:interosseous
1710:
1680:
1601:Tibiofibular
1535:
1524:
1491:
1469:Tibiofemoral
1409:
1336:
1315:September 8,
1313:. Retrieved
1295:
1283:
1250:
1246:
1240:
1208:(2): 84–93.
1205:
1201:
1191:
1180:. Retrieved
1169:
1158:
1146:. Retrieved
1141:
1131:
1112:
1106:
1087:
1081:
1048:
1044:
994:
990:
980:
947:
943:
933:
908:
900:
888:
875:
871:
849:(1): 13–24.
846:
842:
836:
803:
799:
793:
768:
764:
720:
716:
680:
676:
670:
645:
641:
604:
600:
594:
561:
557:
551:
542:
461:
448:
423:chiropractic
415:
411:
394:viscoelastic
382:hyperflexion
378:
353:
343:
337:
331:
325:
320:
302:
290:
286:
284:
280:
249:
241:knee flexion
237:
200:
184:
180:
147:
143:
141:
95:A03.6.08.008
70:
1852:intertarsal
1509:collateral
1419:pubofemoral
1414:iliofemoral
1178:. about.com
677:Arthroscopy
307:drawer test
243:but not in
60:Identifiers
2075:Transverse
2048:collateral
2025:collateral
1560:transverse
1494:popliteal
1291:"Cruciate"
1182:2006-11-11
535:References
419:multimodal
310:cartilage/
1753:posterior
1536:posterior
1527:cruciate
1394:human leg
1390:ligaments
1142:OrthoInfo
843:J Biomech
451:quadruped
431:eccentric
408:Treatment
402:adduction
390:ligaments
366:Mechanism
338:Grade III
253:Ligaments
197:Structure
2094:Category
1749:anterior
1711:lateral:
1531:anterior
1333:lljoints
1300:Elsevier
1275:22150465
1267:15494347
1232:23204951
1073:23746497
1065:10623985
1023:23181354
972:24386922
828:42810072
820:15572322
785:16360655
737:21803977
697:17349472
662:23022245
586:15246937
578:16228178
348:ligament
344:Grade IV
332:Grade II
312:meniscus
303:step-off
295:tangents
291:step-off
234:Function
209:and the
154:in each
152:ligament
2043:plantar
2020:plantar
1982:plantar
1959:plantar
1915:plantar
1892:plantar
1869:plantar
1850:Distal
1758:lateral
1681:medial:
1553:lateral
1543:menisci
1503:arcuate
1498:oblique
1477:Capsule
1445:capsule
1410:femoral
1392:of the
1223:3368977
1014:3517747
997:: 231.
964:1395293
863:8106532
745:3524402
621:1126079
449:In the
326:Grade I
263:to the
174:of the
170:to the
166:of the
150:) is a
83:D016119
39:Details
2062:Arches
1987:dorsal
1964:dorsal
1920:dorsal
1897:dorsal
1874:dorsal
1762:medial
1548:medial
1386:Joints
1306:
1273:
1265:
1230:
1220:
1119:
1094:
1071:
1063:
1021:
1011:
970:
962:
921:
861:
826:
818:
783:
765:Injury
743:
735:
695:
660:
619:
584:
576:
454:stifle
439:Grafts
435:lunges
189:, and
1943:Other
1271:S2CID
1148:7 May
1069:S2CID
968:S2CID
824:S2CID
741:S2CID
582:S2CID
265:tibia
261:femur
211:tibia
207:femur
176:femur
168:tibia
130:[
119:44617
66:Latin
1664:Foot
1460:Knee
1388:and
1317:2009
1304:ISBN
1263:PMID
1228:PMID
1150:2019
1117:ISBN
1092:ISBN
1061:PMID
1019:PMID
960:PMID
919:ISBN
859:PMID
816:PMID
781:PMID
733:PMID
693:PMID
658:PMID
642:Knee
617:PMID
574:PMID
392:are
203:knee
156:knee
142:The
107:1891
90:TA98
78:MeSH
44:From
1402:Hip
1255:doi
1218:PMC
1210:doi
1053:doi
1009:PMC
999:doi
952:doi
948:284
915:719
851:doi
808:doi
773:doi
725:doi
685:doi
650:doi
609:doi
605:106
566:doi
191:LCL
187:MCL
148:PCL
114:FMA
102:TA2
2096::
1302:.
1294:.
1269:.
1261:.
1251:32
1249:.
1226:.
1216:.
1206:11
1204:.
1200:.
1140:.
1067:.
1059:.
1049:28
1047:.
1031:^
1017:.
1007:.
995:13
993:.
989:.
966:.
958:.
946:.
942:.
917:.
880::
857:.
847:27
845:.
822:.
814:.
804:32
802:.
779:.
769:37
767:.
753:^
739:.
731:.
721:40
719:.
705:^
691:.
681:23
679:.
656:.
646:19
644:.
629:^
615:.
603:.
580:.
572:.
562:14
560:.
464:.
384:,
267:.
52:To
1760:/
1751:/
1426:)
1412:(
1378:e
1371:t
1364:v
1341:)
1319:.
1277:.
1257::
1234:.
1212::
1185:.
1152:.
1125:.
1100:.
1075:.
1055::
1025:.
1001::
974:.
954::
927:.
865:.
853::
830:.
810::
787:.
775::
747:.
727::
699:.
687::
664:.
652::
623:.
611::
588:.
568::
146:(
134:]
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.