212:
162:
40:
2220:
294:: a PERT activity can be further decomposed into a set of sub-activities. For example, activity A1 can be decomposed into A1.1, A1.2 and A1.3. Sub-activities have all the properties of activities; in particular, a sub-activity has predecessor or successor events just like an activity. A sub-activity can be decomposed again into finer-grained sub-activities.
328:: the best estimate of the time required to accomplish an activity (te) or a path (TE), accounting for the fact that things don't always proceed as normal (the implication being that the expected time is the average time the task would require if the task were repeated on a number of occasions over an extended period of time).
288:: the actual performance of a task which consumes time and requires resources (such as labor, materials, space, machinery). It can be understood as representing the time, effort, and resources required to move from one event to another. A PERT activity cannot be performed until the predecessor event has occurred.
1722:
upon completion of the process, a far simpler mechanism involves computing the total of all activity durations. If an EF of more than the total is found, the computation should be terminated. It is worth saving the identities of the most recently visited dozen or so nodes to help identify the problem link.
1721:
Depending upon the capabilities of the data input phase of the critical path algorithm, it may be possible to create a loop, such as A -> B -> C -> A. This can cause simple algorithms to loop indefinitely. Although it is possible to "mark" nodes that have been visited, then clear the "marks"
1248:
In order to determine this information it is assumed that the activities and normal duration times are given. The first step is to determine the ES and EF. The ES is defined as the maximum EF of all predecessor activities, unless the activity in question is the first activity, for which the ES is
720:
others (there are two areas that need to be graded, but there are only enough bulldozers to do one). Additionally, the time estimates usually reflect the normal, non-rushed time. Many times, the time required to execute the task can be reduced for an additional cost or a reduction in the quality.
1791:
During project execution a real-life project will never execute exactly as it was planned due to uncertainty. This can be due to ambiguity resulting from subjective estimates that are prone to human errors or can be the result of variability arising from unexpected events or risks. The main reason
202:
of time and range of time necessary to complete each activity between two successive events. Such time expectations include estimates of "most likely time", "optimistic time", and "pessimistic time" for each activity. The technique is a management control tool that sizes up the outlook for meeting
93:
PERT is a method of analyzing the tasks involved in completing a project, especially the time needed to complete each task, and to identify the minimum time needed to complete the total project. It incorporates uncertainty by making it possible to schedule a project while not knowing precisely the
719:
The first step for scheduling the project is to determine the tasks that the project requires and the order in which they must be completed. The order may be easy to record for some tasks (e.g., when building a house, the land must be graded before the foundation can be laid) while difficult for
125:
PERT and CPM are complementary tools, because "CPM employs one time estimation and one cost estimation for each activity; PERT may utilize three time estimates (optimistic, expected, and pessimistic) and no costs for each activity. Although these are distinct differences, the term PERT is applied
1040:
is not specifically indicated on task 5 (d), though it can be observed on tasks 3 and 7 (b and f), (3) since weekends are indicated by a thin vertical line, and take up no additional space on the work calendar, bars on the Gantt chart are not longer or shorter when they do or don't carry over a
610:
665:: the longest possible continuous pathway taken from the initial event to the terminal event. It determines the total calendar time required for the project; and, therefore, any time delays along the critical path will delay the reaching of the terminal event by at least the same amount.
98:
of all the activities. It is more event-oriented than start- and completion-oriented, and is used more for projects where time is the major constraint rather than cost. It is applied to very large-scale, one-time, complex, non-routine infrastructure projects, as well as
203:
objectives on time; highlights danger signals requiring management decisions; reveals and defines both methodicalness and slack in the flow plan or the network of sequential activities that must be performed to meet objectives; compares current expectations with
1522:
to complete. To determine the path times, add the task durations for all available paths. Activities that have slack can be delayed without changing the overall time of the project. Slack is computed in one of two ways, slack = LF − EF
1557:
and the critical time is 19.51 work days. It is important to note that there can be more than one critical path (in a project more complex than this example) or that the critical path can change. For example, let's say that activities
480:
261:: a point that marks the start or completion of one or more activities. It consumes no time and uses no resources. When it marks the completion of one or more activities, it is not "reached" (does not occur) until
1017:
is the black lines connected to non-critical activities, (3) since
Saturday and Sunday are not work days and are thus excluded from the schedule, some bars on the Gantt chart are longer if they cut through a
1393:. The LF is defined as the minimum LS of all successor activities, unless the activity is the last activity, for which the LF equals the EF. The LS is the LF minus the task duration (LS = LF − duration).
1389:, the project should take 19.51 work days to complete. The next step is to determine the late start (LS) and late finish (LF) of each activity. This will eventually show if there are activities that have
1701:
485:
198:
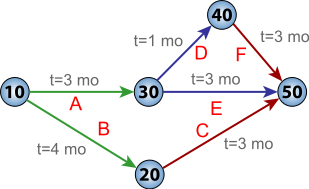
Through an electronic computer, the PERT technique processes data representing the major, finite accomplishments (events) essential to achieve end-objectives; the inter-dependence of those events; and
1219:
By itself, the network diagram pictured above does not give much more information than a Gantt chart; however, it can be expanded to display more information. The most common information shown is:
237:. The Work Breakdown Structure provides "a framework for complete networking, the Work Breakdown Structure was formally introduced as the first item of analysis in carrying out basic PERT/CPM."
1792:
that PERT may provide inaccurate information about the project completion time is due to this schedule uncertainty. This inaccuracy may be large enough to render such estimates as not helpful.
1156:
1002:
1025:
637:
is a measure of the excess time and resources available to complete a task. It is the amount of time that a project task can be delayed without causing a delay in any subsequent tasks (
271:: an event that immediately precedes some other event without any other events intervening. An event can have multiple predecessor events and can be the predecessor of multiple events.
448:
387:
277:: an event that immediately follows some other event without any other intervening events. An event can have multiple successor events and can be the successor of multiple events.
1401:
is equal to the EF (19.51 work days) since it is the last activity in the project. Since the duration is zero, the LS is also 19.51 work days. This will be used as the LF for
1753:
PERT provides for potentially reduced project duration due to better understanding of dependencies leading to improved overlapping of activities and tasks where feasible.
1060:). Activity on node diagrams are generally easier to create and interpret. To create an AON diagram, it is recommended (but not required) to start with a node named
671:: An activity that has total float equal to zero. An activity with zero free float is not necessarily on the critical path since its path may not be the longest.
17:
1603:
The activities on the critical path by definition have a slack of zero; however, it is always a good idea to check the math anyway when drawing by hand.
1799:, however, allowing for every possible disruption would be very slow and couldn't be accommodated by the baseline schedule. A second approach, termed
194:, Head of the Program Evaluation Branch, Special Projects Office, U.S. Navy, gave a detailed description of the main concepts of PERT. He explained:
316:: the maximum possible time required to accomplish an activity (p) or a path (P), assuming everything goes wrong (but excluding major catastrophes).
605:{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}&\sigma _{te}={\frac {p-o}{6}}\\&\sigma _{TE}={\sqrt {\sum _{i=1}^{n}{\sigma _{te_{i}}}^{2}}}\end{aligned}}}
1795:
One possible method to maximize solution robustness is to include safety in the baseline schedule in order to absorb disruptions. This is called
1416:
is 19.51 work days. The duration (5.17 work days) is subtracted from the LF to get an LS of 14.34 work days. This will be used as the LF for
310:: the minimum possible time required to accomplish an activity (o) or a path (O), assuming everything proceeds better than is normally expected
1438:
is 14.34 work days. The duration (5.17 work days) is subtracted from the LF to get an LS of 9.17 work days. This will be used as the LF for
1427:
is 19.51 work days. The duration (4.5 work days) is subtracted from the LF to get an LS of 15.01 work days. This will be used as the LF for
207:
completion dates and computes the probability for meeting scheduled dates; and simulates the effects of options for decision— before decision.
684:
must be completed in order to allow sufficient time for the activities that must elapse before a specific PERT event reaches completion.
135:
1052:
A network diagram can be created by hand or by using diagram software. There are two types of network diagrams, activity on arrow (
138:
to support the U.S. Navy's
Polaris nuclear submarine project. It found applications throughout industry. An early example is the
2004:
2260:
2255:
146:
which used PERT from 1965 until the opening of the 1968 Games. This project model was the first of its kind, a revival for the
2158:
2139:
2117:
2098:
322:: the best estimate of the time required to accomplish an activity (m) or a path (M), assuming everything proceeds as normal.
134:
PERT was developed primarily to simplify the planning and scheduling of large and complex projects. It was developed for the
2036:
cited in: Stauber, B. Ralph; Douty, Harry M.; Fazar, Willard; Jordan, Richard H.; Weinfeld, William; and Manvel, Allen D.;
176:
but by 1959 was renamed. It had been made public in 1958 in two publications of the U.S. Department of the Navy, entitled
1257:
is zero since it is the first activity. Since the duration is zero, the EF is also zero. This EF is used as the ES for
1775:
The network charts tend to be large and unwieldy, requiring several pages to print and requiring specially-sized paper.
1064:. This "activity" has a duration of zero (0). Then you draw each activity that does not have a predecessor activity (
2177:
1828:
2285:
2280:
1737:
1332:
is 9.17. The duration (5.17 work days) is added to the ES to get an EF of 14.34. This EF is used as the ES for
1301:
is four. The duration (6.33 work days) is added to the ES to get an EF of 10.33. This EF is used as the ES for
199:
2200:
44:
393:
1272:
is zero. The duration (4 work days) is added to the ES to get an EF of four. This EF is used as the ES for
1132:
as a predecessor activity, so an arrow is drawn connecting the activities. Likewise, an arrow is drawn from
204:
95:
1453:
is 15.01 work days. The duration (6.33 work days) is subtracted from the LF to get an LS of 8.68 work days.
339:
2275:
2270:
2265:
2224:
1778:
The lack of a timeframe on most PERT/CPM charts makes it harder to show status, although colours can help,
1467:
is 9.17 work days. The duration (5.33 work days) is subtracted from the LF to get an LS of 3.84 work days.
2290:
2250:
1898:
1460:
is 9.17 work days. The duration (5.17 work days) is subtracted from the LF to get an LS of 4 work days.
1833:
1515:
1390:
1242:
1037:
1014:
633:
629:
1756:
The large amount of project data can be organized and presented in diagram for use in decision making.
1988:
1848:
1769:
There can be potentially hundreds or thousands of activities and individual dependency relationships.
1057:
186:
67:
1818:
1741:
1214:
A node like this one can be used to display the activity name, duration, ES, EF, LS, LF, and slack.
1053:
234:
1600:
are milestones and by definition have no duration, therefore they can have no slack (0 work days).
1486:
is 4 work days. The duration (4 work days) is subtracted from the LF to get an LS of 0 work days.
2240:
1868:
1803:, defines a procedure to react to disruptions that cannot be absorbed by the baseline schedule.
752:
is complete). Additionally, each task has three time estimates: the optimistic time estimate (
1582:
is reduced to 15.34 work days, which is slightly less than the time of the new critical path,
2066:
1386:
147:
31:
2170:
Schedule, Cost, and Profit
Control with PERT - A Comprehensive Guide for Program Management
1709:
1589:
Assuming these scenarios do not happen, the slack for each activity can now be determined.
1511:
1164:
1072:
in this example) and connect them with an arrow from start to each node. Next, since both
1047:
1033:
1010:
706:
698:
661:
211:
139:
82:
8:
1750:
PERT facilitates identification of early start, late start, and slack for each activity.
624:
PERT supplies a number of tools for management with determination of concepts, such as:
2189:
1858:
78:
63:
2245:
2196:
2173:
2154:
2135:
2113:
2094:
1823:
1700:
1527:
slack = LS − ES. Activities that are on the critical path have a slack of zero (0).
1160:
1006:
1678:
can be delayed almost 4 work days without delaying the project. Likewise, activity
161:
2191:
The
Polaris System Development: Bureaucratic and Programmatic Success in Government
2151:
Project
Management ToolBox: Tools and Techniques for the Practicing Project Manager
1863:
1813:
2019:
1350:
is 14.34. The duration (5.17 work days) is added to the ES to get an EF of 19.51.
230:
with about 150 publications on PERT and CPM, all published between 1958 and 1968.
1853:
1705:
1343:
is 10.33. The duration (4.5 work days) is added to the ES to get an EF of 14.83.
1975:; "Application of a Technique for Research and Development Program Evaluation",
1294:
is four. The duration (5.17 work days) is added to the ES to get an EF of 9.17.
1287:
is zero. The duration (5.33 work days) is added to the ES to get an EF of 5.33.
2132:
Project
Management: A Systems Approach to Planning, Scheduling, and Controlling
2127:
1505:
1381:
is a milestone (and therefore has a duration of zero), so the EF is also 19.51.
1155:
1148:, it is recommended (but again not required) to connect them to a node labeled
2234:
2033:
1972:
191:
1747:
PERT facilitates identification of the critical path and makes this visible.
1689:
can be delayed 4.68 work days without delaying the project (alternatively,
1024:
1001:
675:
227:
106:
PERT offers a management tool, which relies "on arrow and node diagrams of
1740:(precedence relationships) between the work breakdown structure (commonly
233:
For the subdivision of work units in PERT another tool was developed: the
1838:
1566:
take their pessimistic (b) times to complete instead of their expected (T
1249:
zero (0). The EF is the ES plus the task duration (EF = ES + duration).
1084:
as a predecessor activity, their nodes are drawn with arrows coming from
993:
254:, with connections to its known predecessor events and successor events.
1048:
Next step, creating network diagram by hand or by using diagram software
744:) while others cannot be done until their predecessor task is complete (
2037:
1574:
and the critical time is 22 work days. On the other hand, if activity
1670:
has an LF of 19.51 and an EF of 14.83, so the slack is 4.68 work days.
1663:
has an LF of 15.01 and an EF of 10.33, so the slack is 4.68 work days.
1897:
Kelley, James E.; Walker, Morgan R.; Sayer, John S. (February 1989).
223:
39:
1656:
has an LF of 9.17 and an EF of 5.33, so the slack is 3.84 work days.
461: : the variability of the time for accomplishing an activity (σ
303:
PERT defines four types of time required to accomplish an activity:
1029:
143:
122:
or nodes that indicate each completed phase of the total project."
1873:
1759:
PERT can provide a probability of completing before a given time.
184:
both primarily written by
Charles F. Clark. In a 1959 article in
151:
71:
281:
Besides events, PERT also tracks activities and sub-activities:
2219:
155:
100:
1959:, Council of Planning Librarians, Monticello (IL), 1968, p. 1
2088:
1506:
Next step, determination of critical path and possible slack
265:
of the activities leading to that event have been completed.
1843:
1971:
Malcolm, Donald G.; Roseboom, John H.; Clark, Charles E.;
178:
Program
Evaluation Research Task, Summary Report, Phase 1.
77:
PERT was originally developed by
Charles E. Clark for the
2021:
Program
Evaluation Research Task, Summary Report, Phase 2
2006:
Program Evaluation Research Task, Summary Report, Phase 1
728:
In the following example there are seven tasks, labeled
222:
Ten years after the introduction of PERT, the American
43:
PERT network chart for a seven-month project with five
1493:
is the minimum LS of its successor activities. Since
1474:
is the minimum LS of its successor activities. Since
158:'s CPM was invented at roughly the same time as PERT.
1934:
1932:
1930:
1928:
1926:
1924:
483:
396:
342:
150:
of Frederick Taylor and later refined by Henry Ford (
81:
in 1958; it is commonly used in conjunction with the
1979:, vol. 7, no. 5, September–October 1959, pp. 646–669
1786:
1772:
PERT is not easy to scale down for smaller projects.
2091:
A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge
2024:, Government Printing Office, Washington (DC), 1958
2009:, Government Printing Office, Washington (DC), 1958
1501:
has an LS of 3.84 work days, the LS is 0 work days.
2188:
1921:
1578:can be reduced to one work day, the path time for
1357:is the greatest EF of its predecessor activities (
1312:is the greatest EF of its predecessor activities (
604:
442:
381:
250:In a PERT diagram, the main building block is the
66:, which was designed to analyze and represent the
1896:
1140:. Since there are no activities that come after
702:: performing more critical activities in parallel
47:(10 through 50) and six activities (A through F).
2232:
1736:PERT chart explicitly defines and makes visible
1518:. The critical path is the path that takes the
126:increasingly to all critical path scheduling."
2093:(5th ed.). Project Management Institute.
1725:
756:), the most likely or normal time estimate (
710:: Shortening duration of critical activities
1967:
1965:
992:Once this step is complete, one can draw a
30:"PERT" redirects here. For other uses, see
27:Statistical tool used in project management
2027:
1704:A completed network diagram created using
85:(CPM), which was also introduced in 1958.
2148:
2107:
1951:
1949:
1947:
1892:
1890:
2186:
2110:Project Management: Tools and Trade-offs
1962:
1899:"The Origins of CPM: a personal history"
1699:
1482:has an LS of 8.68 work days, the LF for
1154:
1023:
1000:
736:. Some tasks can be done concurrently (
443:{\displaystyle TE=\sum _{i=1}^{n}te_{i}}
245:
210:
160:
38:
2126:
2055:Program Evaluation and Review Technique
1938:
18:Program Evaluation and Review Technique
14:
2233:
2167:
1944:
1887:
1782:, specific colour for completed nodes.
1104:is drawn with arrows coming from both
760:), and the pessimistic time estimate (
382:{\displaystyle te={\frac {o+4m+p}{6}}}
2089:Project Management Institute (2013).
1957:PERT and CPM: a selected bibliography
1909:(2). Project Management Institute: 18
1697:can be delayed 2.34 work days each).
226:Maribeth Brennan compiled a selected
2071:Handbook of Business Administration,
2044:, 13(2): 9–12 (April 1959), pp. 9–12
1989:1968 Winter Olympics official report
1991:, p. 49. Accessed 1 November 2010.
1570:) times. The critical path is now
1100:as predecessor activities, so node
619:
24:
2080:
1510:The next step is to determine the
25:
2302:
2212:
1829:Critical chain project management
1787:Uncertainty in project scheduling
1716:
768:) is computed using the formula (
714:
694:can follow a specific PERT event.
645:). Positive slack would indicate
174:Program Evaluation Research Task,
136:U.S. Navy Special Projects Office
2218:
2038:"Federal Statistical Activities"
1763:
1159:A network diagram created using
653:; and zero slack would indicate
649:; negative slack would indicate
62:) is a statistical tool used in
2060:
1124:have been completed. Activity
690:: the earliest time by which a
118:or work necessary to reach the
70:involved in completing a given
56:evaluation and review technique
2047:
2012:
2003:U.S. Department of the Navy,
1997:
1982:
1373:has an EF of 19.51, the ES of
240:
13:
1:
2261:Schedule (project management)
2256:Project management techniques
2149:Milosevic, Dragan Z. (2003).
2018:U.S. Department of the Navy,
1880:
1730:
1497:has an LS of 0 work days and
1478:has an LS of 4 work days and
1328:has an EF of 9.17, the ES of
216:PERT Guide for Management Use
2195:. Harvard University Press.
2187:Sapolsky, Harvey M. (1971).
1028:A Gantt chart created using
1005:A Gantt chart created using
7:
1806:
1514:and if any activities have
166:PERT Summary Report Phase 2
88:
10:
2307:
2168:Miller, Robert W. (1963).
1834:Float (project management)
1726:As project scheduling tool
1232:The early finish time (EF)
1226:The expected duration time
723:
459:standard deviation of time
129:
29:
2042:The American Statistician
1849:Precedence diagram method
1238:The late finish time (LF)
1229:The early start time (ES)
1191:
794:
791:
788:
785:
187:The American Statistician
172:Initially PERT stood for
2134:(10th ed.). Wiley.
1819:Arrow diagramming method
1235:The late start time (LS)
1116:cannot begin until both
1056:) and activity on node (
1036:is highlighted, (2) the
641:) or the whole project (
235:Work Breakdown Structure
2112:(3rd ed.). Wiley.
2108:Klastorin, Ted (2003).
1993:(in English and French)
1869:Triangular distribution
1369:has an EF of 14.83 and
764:). The expected time (
298:
114:: arrows represent the
2286:Engineering management
2281:Management cybernetics
2067:Maynard, Harold Bright
1713:
1324:has an EF of 5.33 and
1168:
1042:
1019:
996:or a network diagram.
707:crashing critical path
680:: the time by which a
606:
566:
444:
426:
383:
219:
209:
169:
48:
1703:
1553:The critical path is
1545:The duration of path
1538:The duration of path
1531:The duration of path
1158:
1027:
1009:(MSP). Note (1) the
1004:
607:
546:
445:
406:
384:
246:Events and activities
214:
196:
164:
148:scientific management
42:
32:PERT (disambiguation)
2227:at Wikimedia Commons
1797:proactive scheduling
1674:Therefore, activity
481:
394:
340:
140:1968 Winter Olympics
83:Critical Path Method
2276:Operations research
2271:Booz Allen Hamilton
2266:Systems engineering
1977:Operations Research
1955:Brennan, Maribeth;
1801:reactive scheduling
1647:= 19.51 − 19.51 = 0
1636:= 14.34 − 14.34 = 0
1586:(15.67 work days).
1549:is 15.67 work days.
1542:is 19.51 work days.
1535:is 14.83 work days.
1013:is in red, (2) the
748:cannot begin until
2291:Management science
2251:Evaluation methods
2053:Cook, Desmond L.;
1903:Project Management
1859:Project management
1714:
1169:
1112:, signifying that
1043:
1020:
602:
600:
440:
379:
220:
170:
79:United States Navy
64:project management
49:
2223:Media related to
2160:978-0-471-20822-8
2141:978-0-470-27870-3
2119:978-0-471-41384-4
2100:978-1-935589-67-9
1824:PERT distribution
1625:= 9.17 − 9.17 = 0
1387:unforeseen events
1223:The activity name
1211:
1210:
1163:(MSP). Note the
1161:Microsoft Project
1007:Microsoft Project
990:
989:
682:predecessor event
669:critical activity
647:ahead of schedule
596:
521:
377:
292:PERT sub-activity
269:predecessor event
16:(Redirected from
2298:
2222:
2206:
2194:
2183:
2164:
2145:
2123:
2104:
2074:
2064:
2058:
2051:
2045:
2031:
2025:
2016:
2010:
2001:
1995:
1994:
1986:
1980:
1969:
1960:
1953:
1942:
1936:
1919:
1918:
1916:
1914:
1894:
1864:Project planning
1814:Activity diagram
1174:
1173:
1032:. Note (1) the
783:
782:
620:Management tools
611:
609:
608:
603:
601:
597:
595:
594:
589:
588:
587:
586:
585:
565:
560:
545:
540:
539:
526:
522:
517:
506:
501:
500:
487:
449:
447:
446:
441:
439:
438:
425:
420:
388:
386:
385:
380:
378:
373:
353:
320:most likely time
314:pessimistic time
21:
2306:
2305:
2301:
2300:
2299:
2297:
2296:
2295:
2231:
2230:
2215:
2210:
2209:
2203:
2180:
2172:. McGraw-Hill.
2161:
2142:
2128:Kerzner, Harold
2120:
2101:
2083:
2081:Further reading
2078:
2077:
2065:
2061:
2052:
2048:
2032:
2028:
2017:
2013:
2002:
1998:
1992:
1987:
1983:
1970:
1963:
1954:
1945:
1937:
1922:
1912:
1910:
1895:
1888:
1883:
1878:
1854:Project network
1809:
1789:
1766:
1733:
1728:
1719:
1706:Microsoft Visio
1646:
1642:
1635:
1631:
1624:
1620:
1613:
1609:
1569:
1508:
1217:
1216:
1215:
1212:
1206:
1198:
1186:
1178:
1092:is listed with
1050:
792:Time estimates
726:
717:
692:successor event
651:behind schedule
622:
599:
598:
590:
581:
577:
573:
569:
568:
567:
561:
550:
544:
532:
528:
524:
523:
507:
505:
493:
489:
484:
482:
479:
478:
468:
464:
434:
430:
421:
410:
395:
392:
391:
354:
352:
341:
338:
337:
308:optimistic time
301:
275:successor event
248:
243:
132:
91:
35:
28:
23:
22:
15:
12:
11:
5:
2304:
2294:
2293:
2288:
2283:
2278:
2273:
2268:
2263:
2258:
2253:
2248:
2243:
2241:Network theory
2229:
2228:
2214:
2213:External links
2211:
2208:
2207:
2201:
2184:
2178:
2165:
2159:
2146:
2140:
2124:
2118:
2105:
2099:
2085:
2084:
2082:
2079:
2076:
2075:
2059:
2046:
2026:
2011:
1996:
1981:
1973:Fazar, Willard
1961:
1943:
1920:
1885:
1884:
1882:
1879:
1877:
1876:
1871:
1866:
1861:
1856:
1851:
1846:
1841:
1836:
1831:
1826:
1821:
1816:
1810:
1808:
1805:
1788:
1785:
1784:
1783:
1776:
1773:
1770:
1765:
1762:
1761:
1760:
1757:
1754:
1751:
1748:
1745:
1732:
1729:
1727:
1724:
1718:
1717:Avoiding loops
1715:
1672:
1671:
1664:
1657:
1650:
1649:
1648:
1644:
1640:
1637:
1633:
1629:
1626:
1622:
1618:
1615:
1611:
1607:
1601:
1567:
1551:
1550:
1543:
1536:
1507:
1504:
1503:
1502:
1487:
1468:
1461:
1454:
1447:
1432:
1421:
1410:
1383:
1382:
1351:
1344:
1337:
1306:
1295:
1288:
1281:
1266:
1246:
1245:
1239:
1236:
1233:
1230:
1227:
1224:
1213:
1209:
1208:
1203:
1200:
1194:
1193:
1189:
1188:
1183:
1180:
1172:
1171:
1170:
1049:
1046:
1045:
1044:
1021:
988:
987:
984:
981:
978:
975:
970:
964:
963:
960:
957:
954:
951:
946:
940:
939:
936:
933:
930:
927:
918:
912:
911:
908:
905:
902:
899:
894:
888:
887:
884:
881:
878:
875:
870:
864:
863:
860:
857:
854:
851:
848:
842:
841:
838:
835:
832:
829:
826:
820:
819:
812:
805:
797:
796:
795:Expected time
793:
790:
787:
725:
722:
716:
715:Implementation
713:
712:
711:
703:
695:
685:
672:
666:
658:
621:
618:
617:
616:
615:
614:
613:
612:
593:
584:
580:
576:
572:
564:
559:
556:
553:
549:
543:
538:
535:
531:
527:
525:
520:
516:
513:
510:
504:
499:
496:
492:
488:
486:
471:
470:
466:
465:) or a path (σ
462:
455:
454:
453:
452:
451:
450:
437:
433:
429:
424:
419:
416:
413:
409:
405:
402:
399:
389:
376:
372:
369:
366:
363:
360:
357:
351:
348:
345:
330:
329:
323:
317:
311:
300:
297:
296:
295:
289:
279:
278:
272:
266:
247:
244:
242:
239:
131:
128:
90:
87:
26:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2303:
2292:
2289:
2287:
2284:
2282:
2279:
2277:
2274:
2272:
2269:
2267:
2264:
2262:
2259:
2257:
2254:
2252:
2249:
2247:
2244:
2242:
2239:
2238:
2236:
2226:
2221:
2217:
2216:
2204:
2198:
2193:
2192:
2185:
2181:
2179:9780070419940
2175:
2171:
2166:
2162:
2156:
2152:
2147:
2143:
2137:
2133:
2129:
2125:
2121:
2115:
2111:
2106:
2102:
2096:
2092:
2087:
2086:
2072:
2068:
2063:
2057:, 1966, p. 12
2056:
2050:
2043:
2039:
2035:
2034:Willard Fazar
2030:
2023:
2022:
2015:
2008:
2007:
2000:
1990:
1985:
1978:
1974:
1968:
1966:
1958:
1952:
1950:
1948:
1940:
1935:
1933:
1931:
1929:
1927:
1925:
1908:
1904:
1900:
1893:
1891:
1886:
1875:
1872:
1870:
1867:
1865:
1862:
1860:
1857:
1855:
1852:
1850:
1847:
1845:
1842:
1840:
1837:
1835:
1832:
1830:
1827:
1825:
1822:
1820:
1817:
1815:
1812:
1811:
1804:
1802:
1798:
1793:
1781:
1777:
1774:
1771:
1768:
1767:
1764:Disadvantages
1758:
1755:
1752:
1749:
1746:
1743:
1739:
1735:
1734:
1723:
1711:
1710:critical path
1707:
1702:
1698:
1696:
1692:
1688:
1684:
1681:
1677:
1669:
1665:
1662:
1658:
1655:
1651:
1638:
1627:
1616:
1605:
1604:
1602:
1599:
1595:
1592:
1591:
1590:
1587:
1585:
1581:
1577:
1573:
1565:
1561:
1556:
1548:
1544:
1541:
1537:
1534:
1530:
1529:
1528:
1526:
1521:
1517:
1513:
1512:critical path
1500:
1496:
1492:
1488:
1485:
1481:
1477:
1473:
1469:
1466:
1462:
1459:
1455:
1452:
1448:
1445:
1441:
1437:
1433:
1430:
1426:
1422:
1419:
1415:
1411:
1408:
1404:
1400:
1396:
1395:
1394:
1392:
1388:
1380:
1376:
1372:
1368:
1364:
1360:
1356:
1352:
1349:
1345:
1342:
1338:
1335:
1331:
1327:
1323:
1319:
1315:
1311:
1307:
1304:
1300:
1296:
1293:
1289:
1286:
1282:
1279:
1275:
1271:
1267:
1264:
1260:
1256:
1252:
1251:
1250:
1244:
1240:
1237:
1234:
1231:
1228:
1225:
1222:
1221:
1220:
1204:
1201:
1196:
1195:
1190:
1184:
1181:
1176:
1175:
1166:
1165:critical path
1162:
1157:
1153:
1151:
1147:
1143:
1139:
1135:
1131:
1127:
1123:
1119:
1115:
1111:
1107:
1103:
1099:
1095:
1091:
1087:
1083:
1079:
1075:
1071:
1067:
1063:
1059:
1055:
1039:
1035:
1034:critical path
1031:
1026:
1022:
1016:
1012:
1011:critical path
1008:
1003:
999:
998:
997:
995:
985:
982:
979:
976:
974:
971:
969:
966:
965:
961:
958:
955:
952:
950:
947:
945:
942:
941:
937:
934:
931:
928:
926:
922:
919:
917:
914:
913:
909:
906:
903:
900:
898:
895:
893:
890:
889:
885:
882:
879:
876:
874:
871:
869:
866:
865:
861:
858:
855:
852:
849:
847:
844:
843:
839:
836:
833:
830:
827:
825:
822:
821:
817:
813:
810:
806:
803:
799:
798:
784:
781:
779:
775:
771:
767:
763:
759:
755:
751:
747:
743:
739:
735:
731:
721:
709:
708:
704:
701:
700:
699:fast tracking
696:
693:
689:
686:
683:
679:
677:
673:
670:
667:
664:
663:
662:critical path
659:
656:
652:
648:
644:
640:
636:
635:
631:
627:
626:
625:
591:
582:
578:
574:
570:
562:
557:
554:
551:
547:
541:
536:
533:
529:
518:
514:
511:
508:
502:
497:
494:
490:
477:
476:
475:
474:
473:
472:
460:
457:
456:
435:
431:
427:
422:
417:
414:
411:
407:
403:
400:
397:
390:
374:
370:
367:
364:
361:
358:
355:
349:
346:
343:
336:
335:
334:
333:
332:
331:
327:
326:expected time
324:
321:
318:
315:
312:
309:
306:
305:
304:
293:
290:
287:
286:PERT activity
284:
283:
282:
276:
273:
270:
267:
264:
260:
257:
256:
255:
253:
238:
236:
231:
229:
225:
217:
213:
208:
206:
201:
195:
193:
192:Willard Fazar
189:
188:
183:
179:
175:
167:
163:
159:
157:
153:
149:
145:
141:
137:
127:
123:
121:
117:
113:
109:
104:
102:
97:
86:
84:
80:
75:
73:
69:
65:
61:
57:
54:
46:
41:
37:
33:
19:
2190:
2169:
2150:
2131:
2109:
2090:
2070:
2062:
2054:
2049:
2041:
2029:
2020:
2014:
2005:
1999:
1984:
1976:
1956:
1939:Kerzner 2009
1911:. Retrieved
1906:
1902:
1800:
1796:
1794:
1790:
1779:
1738:dependencies
1720:
1708:. Note the
1694:
1690:
1686:
1682:
1679:
1675:
1673:
1667:
1660:
1653:
1597:
1593:
1588:
1583:
1579:
1575:
1571:
1563:
1559:
1554:
1552:
1546:
1539:
1532:
1524:
1519:
1509:
1498:
1494:
1490:
1483:
1479:
1475:
1471:
1464:
1457:
1450:
1443:
1439:
1435:
1428:
1424:
1417:
1413:
1406:
1402:
1398:
1385:Barring any
1384:
1378:
1374:
1370:
1366:
1362:
1358:
1354:
1347:
1340:
1333:
1329:
1325:
1321:
1317:
1313:
1309:
1302:
1298:
1291:
1284:
1277:
1273:
1269:
1262:
1258:
1254:
1247:
1218:
1149:
1145:
1141:
1137:
1133:
1129:
1125:
1121:
1117:
1113:
1109:
1105:
1101:
1097:
1093:
1089:
1088:. Activity
1085:
1081:
1077:
1073:
1069:
1065:
1061:
1051:
991:
972:
967:
948:
943:
924:
920:
915:
896:
891:
872:
867:
845:
823:
815:
808:
801:
789:Predecessor
777:
773:
769:
765:
761:
757:
753:
749:
745:
741:
737:
733:
729:
727:
718:
705:
697:
691:
687:
681:
674:
668:
660:
654:
650:
646:
642:
638:
628:
623:
458:
325:
319:
313:
307:
302:
291:
285:
280:
274:
268:
262:
258:
251:
249:
232:
228:bibliography
221:
215:
197:
185:
181:
177:
173:
171:
165:
133:
124:
119:
115:
111:
107:
105:
94:details and
92:
76:
59:
55:
52:
50:
36:
2225:PERT charts
2073:1967, p. 17
1839:Gantt chart
1744:) elements.
1614:= 4 − 4 = 0
1489:The LF for
1470:The LF for
1463:The LF for
1456:The LF for
1449:The LF for
1434:The LF for
1423:The LF for
1412:The LF for
1397:The LF for
1377:is 19.51.
1353:The ES for
1346:The ES for
1339:The ES for
1308:The ES for
1297:The ES for
1290:The ES for
1283:The ES for
1268:The ES for
1253:The ES for
994:Gantt chart
655:on schedule
643:total float
241:Terminology
218:, June 1963
2235:Categories
2202:0674682254
1881:References
1731:Advantages
1712:is in red.
1365:). Since
1320:). Since
1192:Task Name
1167:is in red.
639:free float
259:PERT event
116:activities
108:activities
103:projects.
45:milestones
2153:. Wiley.
1685:activity
1666:Activity
1659:Activity
1652:Activity
1182:Duration
786:Activity
571:σ
548:∑
530:σ
512:−
491:σ
408:∑
224:librarian
205:scheduled
200:estimates
96:durations
2246:Diagrams
2130:(2009).
1913:20 March
1807:See also
1041:weekend.
1030:OmniPlan
1018:weekend.
807:Normal (
732:through
688:lag time
182:Phase 2.
144:Grenoble
89:Overview
53:program
1874:PRINCE2
1520:longest
1207:finish
1187:finish
814:Pess. (
780:) ÷ 6.
724:Example
152:Fordism
130:History
101:R&D
72:project
2199:
2176:
2157:
2138:
2116:
2097:
1598:finish
1399:finish
1379:Finish
1375:finish
1355:finish
1202:Slack
1199:Start
1179:Start
1150:finish
800:Opt. (
168:, 1958
156:DuPont
120:events
112:events
1594:Start
1516:slack
1491:start
1391:slack
1255:start
1243:slack
1185:Early
1177:Early
1080:list
1062:start
1038:slack
1015:slack
986:5.17
962:4.50
938:5.17
910:6.33
886:5.17
862:5.33
840:4.00
634:slack
630:float
252:event
68:tasks
2197:ISBN
2174:ISBN
2155:ISBN
2136:ISBN
2114:ISBN
2095:ISBN
1915:2024
1844:GERT
1780:e.g.
1693:and
1643:– EF
1632:– EF
1621:– EF
1610:– EF
1596:and
1580:aceg
1562:and
1555:aceg
1540:aceg
1442:and
1405:and
1361:and
1316:and
1276:and
1261:and
1241:The
1205:Late
1197:Late
1128:has
1120:and
1108:and
1096:and
1076:and
1068:and
740:and
678:time
676:lead
299:Time
180:and
110:and
60:PERT
51:The
1742:WBS
1584:beg
1572:adf
1547:beg
1533:adf
1144:or
1136:to
1058:AON
1054:AOA
907:10
772:+ 4
632:or
263:all
154:).
142:in
2237::
2069:,
2040:,
1964:^
1946:^
1923:^
1905:.
1901:.
1889:^
1683:or
1639:LF
1628:LF
1617:LF
1606:LF
1525:or
1152:.
983:8
980:5
977:3
959:8
956:4
953:3
935:7
932:5
929:4
923:,
904:6
901:4
883:7
880:5
877:4
859:9
856:5
853:3
850:—
837:6
834:4
831:2
828:—
818:)
811:)
804:)
776:+
766:te
467:TE
463:te
190:,
74:.
2205:.
2182:.
2163:.
2144:.
2122:.
2103:.
1941:.
1917:.
1907:3
1695:f
1691:d
1687:f
1680:d
1676:b
1668:f
1661:d
1654:b
1645:g
1641:g
1634:e
1630:e
1623:c
1619:c
1612:a
1608:a
1576:c
1568:E
1564:f
1560:d
1499:b
1495:a
1484:a
1480:d
1476:c
1472:a
1465:b
1458:c
1451:d
1446:.
1444:c
1440:b
1436:e
1431:.
1429:d
1425:f
1420:.
1418:e
1414:g
1409:.
1407:g
1403:f
1371:g
1367:f
1363:g
1359:f
1348:g
1341:f
1336:.
1334:g
1330:e
1326:c
1322:b
1318:c
1314:b
1310:e
1305:.
1303:f
1299:d
1292:c
1285:b
1280:.
1278:d
1274:c
1270:a
1265:.
1263:b
1259:a
1146:g
1142:f
1138:g
1134:e
1130:d
1126:f
1122:c
1118:b
1114:e
1110:c
1106:b
1102:e
1098:c
1094:b
1090:e
1086:a
1082:a
1078:d
1074:c
1070:b
1066:a
973:E
968:G
949:D
944:F
925:C
921:B
916:E
897:A
892:D
873:A
868:C
846:B
824:A
816:p
809:m
802:o
778:p
774:m
770:o
762:p
758:m
754:o
750:A
746:C
742:B
738:A
734:G
730:A
657:.
592:2
583:i
579:e
575:t
563:n
558:1
555:=
552:i
542:=
537:E
534:T
519:6
515:o
509:p
503:=
498:e
495:t
469:)
436:i
432:e
428:t
423:n
418:1
415:=
412:i
404:=
401:E
398:T
375:6
371:p
368:+
365:m
362:4
359:+
356:o
350:=
347:e
344:t
58:(
34:.
20:)
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.