79:
128:. Gross contamination of the material or marring of the optical surface can be remedied by sanding under a stream of running water. This surface refinishing both restores the original topography of the surface and returns the material to its original reflectance. Weathering tests on the material show no damage upon exposure to atmospheric UV flux. The material shows no sign of optical or physical degradation after long-term immersion testing in sea water.
20:
137:
offers the same physical characteristics as optical-grade material, but is a different formulation of resin that gives enhanced performance when used in laser pump cavities. Spectralon is used in a variety of "side pumped" lasers. Space-grade
Spectralon combines high reflectance with an extremely lambertian reflectance profile, and is used for terrestrial
112:
arises from the material's surface and immediate subsurface structure. The porous network of thermoplastic produces multiple reflections in the first few tenths of a millimeter. Spectralon can partially depolarize the light it reflects, but this effect decreases at high incidence angles. Although it
136:
Three grades of
Spectralon reflectance material are available: optical grade, laser grade, and space grade. Optical-grade Spectralon has a high reflectance and Lambertian behavior, and is used primarily as a reference standard or target for calibration of spectrophotometers. Laser-grade Spectralon
96:
at wavelengths from 257 nm to 10,600 nm, although reflectivity decreases at wavelengths beyond the near infrared. Spectralon exhibits absorbances at 2800 nm, then absorbs strongly (<20% reflectance) from 5400 to 8000 nm. Although the high diffuse reflectance allows efficient
91:
powder that has been compressed into solid forms and sintered for stability, with approx. 40% void volume to enhance scattering of light. Surface or subsurface contamination may lower the reflectance at the extreme upper and lower ends of the spectral range. The material is also highly
113:
is extremely hydrophobic, this open structure readily absorbs non-polar solvents, greases and oils. Impurities are difficult to remove from
Spectralon; thus, the material should be kept free from contaminants to maintain its reflectance properties.
86:
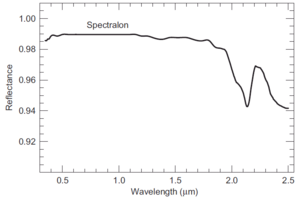
Spectralon's reflectance is generally >99% over a range from 400 to 1500 nm and >95% from 250 to 2500 nm., however grades are available with added carbon to achieve various gray levels. The material consists of
450:
Evain S, Flexas J, Moya I (2004). "A new instrument for passive remote sensing: 2. Measurement of leaf and canopy reflectance changes at 531 nm and their relationship with photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence".
236:
Stiegman, Albert E.; Bruegge, Carol J.; Springsteen, Arthur W. (1 April 1993). "Ultraviolet stability and contamination analysis of
Spectralon diffuse reflectance material".
496:
153:
160:. Spectralon allows removal of contributions in the emitted light that are directly linked not to the surface (leaf) properties but to geometrical factors.
145:
324:
Raymond F. Kokaly; Andrew K. Skidmore (December 2015). "Plant phenolics and absorption features in vegetation reflectance spectra near 1.66 μm".
149:
144:
Spectralon's optical properties make it ideal as a reference surface in remote sensing and spectroscopy. For instance, it is used to obtain
193:
Georgiev, Georgi T.; Butler, James J. (2007). "Long-term calibration monitoring of
Spectralon diffusers BRDF in the air-ultraviolet".
412:
387:
375:
120:
and is thermally stable to > 350 °C. It is chemically inert to all but the most powerful bases such as
281:
Voss, Kenneth J.; Zhang, Hao (2006). "Bidirectional reflectance of dry and submerged
Labsphere Spectralon plaque".
438:
54:
behavior, and can be machined into a wide variety of shapes for the construction of optical components such as
515:
535:
520:
117:
258:
545:
540:
253:
109:
93:
51:
495:. Air Force Research Laboratory, Munitions Directorate. p. 16. AFRL-MN-EG-TR-2003-7013.
460:
290:
245:
202:
413:"Optimization Of Spectralon Through Numerical Modeling And Improved Processes And Designs"
8:
464:
294:
249:
206:
59:
55:
35:
434:
371:
341:
306:
218:
78:
468:
349:
333:
298:
263:
210:
157:
43:
63:
487:
138:
472:
337:
529:
345:
98:
47:
31:
16:
Fluoropolymer which has the highest diffuse reflectance of any known material
310:
222:
121:
353:
302:
214:
168:
Spectralon was developed by
Labsphere and has been available since 1986.
125:
39:
429:
Fischer, Robert Edward; Tadic-Galeb, Biljana and Yoder, Paul R. (2008)
267:
326:
International
Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation
19:
323:
124:
and organo-sodium or lithium compounds. The material is extremely
105:
per square centimeter, limiting its use to lower-powered systems.
102:
380:
67:
368:
152:(BRDF) in the laboratory. It can also be applied to obtain
88:
235:
101:, the material has a fairly low damage threshold of 4
116:
The material has a hardness roughly equal to that of
486:Goldstein, Dennis H.; et al. (February 2003).
407:
405:
527:
449:
150:bidirectional reflectance distribution function
402:
192:
50:regions of the spectrum. It exhibits highly
489:Polarimetric characterization of Spectralon
188:
186:
184:
182:
180:
38:of any known material or coating over the
485:
317:
280:
257:
77:
18:
177:
528:
274:
13:
502:from the original on June 4, 2011.
82:Reflectance spectrum of Spectralon
73:
14:
557:
509:
370:. John Wiley & Sons. p. 133.
479:
131:
443:
423:
360:
229:
1:
453:Remote Sensing of Environment
171:
7:
10:
562:
516:Spectralon Product Details
163:
473:10.1016/j.rse.2004.03.012
338:10.1016/J.JAG.2015.01.010
118:high-density polyethylene
388:"Space Grade Spectralon"
433:. McGraw-Hill. p. 534.
154:vegetation fluorescence
110:Lambertian reflectance
83:
24:
521:Spectralon Tech Guide
431:Optical system design
81:
64:optical pump cavities
34:that has the highest
22:
366:Geladi, Paul (2007)
303:10.1364/AO.45.007924
215:10.1364/AO.46.007892
465:2004RSEnv..91..175E
295:2006ApOpt..45.7924V
250:1993OptEn..32..799S
238:Optical Engineering
207:2007ApOpt..46.7892G
60:integrating spheres
56:calibration targets
36:diffuse reflectance
84:
25:
23:A Spectralon panel
536:Optical materials
289:(30): 7924–7927.
268:10.1117/12.132374
553:
504:
503:
501:
494:
483:
477:
476:
447:
441:
427:
421:
420:
417:Photonics Online
409:
400:
399:
397:
395:
390:. Labsphere, Inc
384:
378:
364:
358:
357:
321:
315:
314:
278:
272:
271:
261:
233:
227:
226:
190:
158:Fraunhofer lines
146:leaf reflectance
561:
560:
556:
555:
554:
552:
551:
550:
526:
525:
512:
507:
499:
492:
484:
480:
448:
444:
428:
424:
411:
410:
403:
393:
391:
386:
385:
381:
365:
361:
322:
318:
279:
275:
259:10.1.1.362.2910
234:
230:
191:
178:
174:
166:
134:
76:
74:Characteristics
17:
12:
11:
5:
559:
549:
548:
546:Thermoplastics
543:
541:Fluoropolymers
538:
524:
523:
518:
511:
510:External links
508:
506:
505:
478:
459:(2): 175–185.
442:
422:
401:
379:
359:
316:
283:Applied Optics
273:
228:
195:Applied Optics
175:
173:
170:
165:
162:
141:applications.
139:remote sensing
133:
130:
75:
72:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
558:
547:
544:
542:
539:
537:
534:
533:
531:
522:
519:
517:
514:
513:
498:
491:
490:
482:
474:
470:
466:
462:
458:
454:
446:
440:
436:
432:
426:
418:
414:
408:
406:
389:
383:
377:
376:9780470010884
373:
369:
363:
355:
351:
347:
343:
339:
335:
331:
327:
320:
312:
308:
304:
300:
296:
292:
288:
284:
277:
269:
265:
260:
255:
251:
247:
243:
239:
232:
224:
220:
216:
212:
208:
204:
200:
196:
189:
187:
185:
183:
181:
176:
169:
161:
159:
155:
151:
147:
142:
140:
129:
127:
123:
119:
114:
111:
106:
104:
100:
99:laser pumping
95:
90:
80:
71:
69:
65:
61:
57:
53:
49:
48:near-infrared
45:
41:
37:
33:
32:fluoropolymer
29:
21:
488:
481:
456:
452:
445:
430:
425:
419:. Labsphere.
416:
392:. Retrieved
382:
367:
362:
329:
325:
319:
286:
282:
276:
241:
237:
231:
201:(32): 7893.
198:
194:
167:
143:
135:
132:Applications
122:sodium amide
115:
107:
85:
27:
26:
126:hydrophobic
40:ultraviolet
530:Categories
439:0071472487
244:(4): 799.
172:References
156:using the
94:lambertian
52:Lambertian
28:Spectralon
354:Q58321875
346:1569-8432
332:: 55–83.
254:CiteSeerX
497:Archived
394:29 March
350:Wikidata
311:17068529
223:17994141
461:Bibcode
291:Bibcode
246:Bibcode
203:Bibcode
164:History
44:visible
437:
374:
352:
344:
309:
256:
221:
103:joules
68:lasers
62:, and
46:, and
500:(PDF)
493:(PDF)
30:is a
435:ISBN
396:2019
372:ISBN
342:ISSN
307:PMID
219:PMID
148:and
108:The
89:PTFE
66:for
469:doi
334:doi
299:doi
264:doi
211:doi
532::
467:.
457:91
455:.
415:.
404:^
348:.
340:.
330:43
328:.
305:.
297:.
287:45
285:.
262:.
252:.
242:32
240:.
217:.
209:.
199:46
197:.
179:^
70:.
58:,
42:,
475:.
471::
463::
398:.
356:.
336::
313:.
301::
293::
270:.
266::
248::
225:.
213::
205::
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.