386:
320:
455:
424:
358:
190:
235:
122:
25:
137:
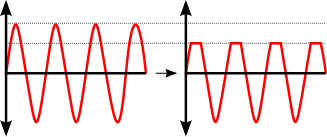
is a circuit designed to prevent a signal from exceeding a predetermined reference voltage level. A clipper does not distort the remaining part of the applied waveform. Clipping circuits are used to select, for purposes of transmission, that part of a signal waveform which lies above or below the
299:
The diode capacitance affects the operation of the clipper at high frequency and influences the choice between the above two types. High frequency signals are attenuated in the shunt clipper as the diode capacitance provides an alternative path to output current. In the series clipper, clipping
206:
diode) but the clipping voltage can be set to any desired value with the addition of a reference voltage. The diagram illustrates a positive reference voltage but the reference can be positive or negative for both positive and negative clipping giving four possible configurations in all.
306:
The clipping action can be made to happen at an arbitrary level by using a biasing element (potential source) in series with the diode. In the following diagrams the green plot is the input voltage, the orange plot is the output voltage, and the blue plot is the clipping level voltage.
197:
A simple diode clipper can be made with a diode and a resistor. This will remove either the positive, or the negative half of the waveform depending on the direction the diode is connected. The simple circuit clips at zero voltage (or to be more precise, at the small
141:
Clipping may be achieved either at one level or two levels. A clipper circuit can remove certain portions of an arbitrary waveform near the positive or negative peaks or both. Clipping changes the shape of the waveform and alters its
266:
of the diode can result in clipping onset that is not very sharp. Precision clippers can be made by placing the clipping device in the feedback circuit of an
541:. The clamper circuit fixes either the positive or negative peaks at a fixed voltage (determined by the biasing voltage) rather than clipping them off.
427:
Negative peak clipping at a positive voltage. In this circuit, a short circuit output will result in a large current being driven through the diode by
361:
Positive peak clipping at a negative voltage. In this circuit, a short circuit output will result in a large current being driven through the diode by
303:
Clippers may be classified based on the orientation of the diode. The orientation decides which half cycle is affected by the clipping action.
537:
is not a clipper, but the simple diode version has a similar topology to a clipper with the exception that the resistor is replaced with a
89:
61:
42:
300:
effectiveness is reduced for the same reason as the high frequency current passes through without being sufficiently blocked.
646:
68:
666:
626:
602:
108:
75:
661:
Robert L. Boylestad, Electronic devices and circuit Theory. 8th
Edition. Eastern Economy Edition, 2002, Page 83,
57:
46:
203:
694:
555:
447:
The signal can be clipped to between two levels by using both types of diode clippers in combination.
214:
connected between the voltage rails. This can be improved by replacing the lower resistor with a
82:
35:
592:
534:
528:
267:
125:
Voltage clipping limits the voltage to a device without affecting the rest of the waveform
8:
423:
385:
357:
319:
271:
454:
143:
662:
642:
622:
598:
223:
219:
211:
282:
Clippers may be classified into two types based on the positioning of the diode.
199:
550:
250:. The voltage in either direction is limited to the reverse breakdown voltage
678:
688:
560:
243:
215:
130:
189:
162:
158:
226:
stabilising the reference voltage against supply and load variations.
571:
538:
263:
24:
262:
For very small values of clipping voltage on low-level signals the
150:
121:
566:
563:
which can function as a mechanical clipper for acoustic signals.
234:
222:
equal to the required reference voltage. The zener acts as a
210:
The simplest circuit for the voltage reference is a resistor
154:
289:, where the diode is in series with the load resistance, and
442:
295:, where the diode is shunted across the load resistance.
161:, but it does not contain energy-storage elements like
389:
Negative peak clipping at a negative voltage. When
323:
Positive peak clipping at a positive voltage. When
149:
A clipping circuit consists of linear elements like
49:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
376:
310:
621:. 2nd Edition. Tata McGraw Hill, 2008, Page 555,
254:the forward voltage drop across one zener diode.
686:
257:
242:In the example circuit on the right, two
109:Learn how and when to remove this message
453:
422:
384:
356:
318:
233:
188:
120:
138:predetermined reference voltage level.
687:
443:Combinational two-level diode clipper
590:
47:adding citations to reliable sources
18:
522:
13:
655:
168:Clipping circuits are also called
14:
706:
672:
277:
679:An overview of Clipping Circuits
594:Modern Dictionary of Electronics
184:
23:
619:Electronic devices and circuits
377:Negatively biased diode clipper
311:Positively biased diode clipper
238:Two shunt diode clipper circuit
34:needs additional citations for
631:
611:
591:Graf, Rudolf F. (1999-08-11).
584:
246:are used to clip the voltage V
229:
1:
577:
193:Positive peak clipper circuit
153:and non-linear elements like
16:Protective electronic circuit
556:Clipping (signal processing)
7:
641:, Pearson, 2010, page 163,
544:
10:
711:
639:Pulse And Digital Circuits
526:
58:"Clipper" electronics
403:,diode is conducting,and
337:,diode is conducting,and
258:Op-amp precision clipper
179:
270:in a manner similar to
515:
500:,D2 is conducting,and
472:,D1 is conducting,and
435:
418:
369:
352:
239:
194:
126:
529:Clamper (electronics)
457:
426:
388:
360:
322:
268:operational amplifier
237:
192:
124:
272:precision rectifiers
43:improve this article
695:Electronic circuits
174:amplitude selectors
144:spectral components
516:
436:
434:and may damage it.
419:
370:
368:and may damage it.
353:
240:
195:
127:
647:978-81-317-2135-3
520:
519:
440:
439:
374:
373:
224:voltage regulator
220:breakdown voltage
212:potential divider
119:
118:
111:
93:
702:
681:, Circuits Today
649:
635:
629:
615:
609:
608:
588:
523:Clamping circuit
450:
449:
381:
380:
315:
314:
114:
107:
103:
100:
94:
92:
51:
27:
19:
710:
709:
705:
704:
703:
701:
700:
699:
685:
684:
675:
658:
656:Further reading
653:
652:
637:Rao K Venkata,
636:
632:
616:
612:
605:
589:
585:
580:
547:
535:clamper circuit
531:
525:
513:
506:
499:
492:
485:
478:
471:
464:
445:
433:
416:
409:
402:
395:
379:
367:
350:
343:
336:
329:
313:
287:Series clippers
280:
260:
249:
232:
202:of the forward
200:forward voltage
187:
182:
115:
104:
98:
95:
52:
50:
40:
28:
17:
12:
11:
5:
708:
698:
697:
683:
682:
674:
673:External links
671:
670:
669:
657:
654:
651:
650:
630:
610:
603:
582:
581:
579:
576:
575:
574:
569:
564:
558:
553:
551:Amplitude gate
546:
543:
527:Main article:
524:
521:
518:
517:
511:
504:
497:
490:
483:
476:
469:
462:
444:
441:
438:
437:
431:
420:
414:
407:
400:
393:
378:
375:
372:
371:
365:
354:
348:
341:
334:
327:
312:
309:
297:
296:
293:Shunt clippers
290:
279:
278:Classification
276:
259:
256:
247:
231:
228:
186:
183:
181:
178:
117:
116:
31:
29:
22:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
707:
696:
693:
692:
690:
680:
677:
676:
668:
667:81-203-2064-6
664:
660:
659:
648:
644:
640:
634:
628:
627:0-07-066049-2
624:
620:
617:Salivahanan,
614:
606:
604:9780080511986
600:
596:
595:
587:
583:
573:
570:
568:
565:
562:
561:Orifice plate
559:
557:
554:
552:
549:
548:
542:
540:
536:
530:
510:
503:
496:
489:
482:
475:
468:
461:
456:
452:
451:
448:
430:
425:
421:
413:
406:
399:
392:
387:
383:
382:
364:
359:
355:
347:
340:
333:
326:
321:
317:
316:
308:
304:
301:
294:
291:
288:
285:
284:
283:
275:
273:
269:
265:
255:
253:
245:
236:
227:
225:
221:
217:
213:
208:
205:
201:
191:
185:Diode clipper
177:
175:
171:
166:
164:
160:
156:
152:
147:
145:
139:
136:
132:
123:
113:
110:
102:
99:December 2009
91:
88:
84:
81:
77:
74:
70:
67:
63:
60: –
59:
55:
54:Find sources:
48:
44:
38:
37:
32:This article
30:
26:
21:
20:
638:
633:
618:
613:
593:
586:
532:
508:
501:
494:
487:
480:
473:
466:
459:
446:
428:
411:
404:
397:
390:
362:
345:
338:
331:
324:
305:
302:
298:
292:
286:
281:
261:
251:
244:zener diodes
241:
209:
196:
173:
169:
167:
148:
140:
134:
128:
105:
96:
86:
79:
72:
65:
53:
41:Please help
36:verification
33:
230:Zener diode
216:zener diode
159:transistors
131:electronics
597:. Newnes.
578:References
163:capacitors
69:newspapers
572:Rectifier
539:capacitor
264:I-V curve
151:resistors
689:Category
545:See also
567:Limiter
486:. When
218:with a
170:slicers
135:clipper
83:scholar
665:
645:
625:
601:
204:biased
155:diodes
85:
78:
71:
64:
56:
493:<
465:>
458:When
396:<
330:>
180:Types
90:JSTOR
76:books
663:ISBN
643:ISBN
623:ISBN
599:ISBN
252:plus
133:, a
62:news
172:or
165:.
157:or
129:In
45:by
691::
533:A
512:B2
507:=
498:B2
484:B1
479:=
470:B1
410:=
344:=
274:.
248:IN
176:.
146:.
607:.
514:.
509:U
505:o
502:u
495:U
491:i
488:u
481:U
477:o
474:u
467:U
463:i
460:u
432:B
429:U
417:.
415:B
412:U
408:o
405:u
401:B
398:U
394:i
391:u
366:B
363:U
351:.
349:B
346:U
342:o
339:u
335:B
332:U
328:i
325:u
112:)
106:(
101:)
97:(
87:·
80:·
73:·
66:·
39:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.