377:. Other means of prevention can include testing all ruminants in a herd and eliminating any individuals who test positive for anaplasmosis, leading to an anaplasmosis-free herd. Vector control measures can also be used. Tick control is widely used in some countries, including Africa, but rarely used in the United States due to the fact that this prevention method is labor-intensive and expensive. In contrast, the control of flies is effective and there are many ways to do this. Chemical agents can be used, sanitation methods (such as cleaning stalls/pens regularly, manure management, and protecting feed), as well as biological control by natural enemies of flies (including bees, mites, parasitoids). Ways to prevent iatrogenic transmission include avoiding re-using of needles and sanitizing medical equipment between uses.
1104:
161:, the parasite multiplies in the blood stream and attaches to red blood cells. The immune system will attempt to kill the infected blood cells but will also kill uninfected red blood cells in the process. The number of red blood cells being destroyed becomes larger than new red blood cells being made, causing the host to become anemic and leading to many other symptoms. Once infected with anaplasmosis, the cattle will always be a carrier of the infectious disease, and calves born from carriers will also carry the disease.
36:
109:, the Sparouine anaplasmosis, detected only in French Guiana, South America. This disease was described from a clandestine gold miner working deep in rainforest. Infection of his red blood cells led to a severe deterioration of his health and required his hospitalization. Molecular typing showed that
128:
for anaplasmosis, there are other means of prevention. Tick and fly control for herds of ruminants can be effective but also labor intensive. Chemical methods can also be used, including sanitizing surgical equipment after each use. Tetracycline drugs are the most common treatment for anaplasmosis,
478:
spp. are found. It is also a seemingly increasing antibody in humans in Europe. Although vaccines have been developed, none are currently available in the United States. Early in the 20th century, this disease was considered one of major economic consequence in the
Western United States. In the
137:
Mechanical and biological vector transmission work in different ways but both lead to infection of the red blood cells. Mechanical transmission happens in two ways, one when red blood cells are inoculated with the blood parasite through surgical equipment including needles, dehorners, ear taggers,
153:
species can transmit this disease through a bite. The blood parasite survives and can multiply in the tick, and can sit dormant for months without being transmitted to an animal. When bitten by a tick carrying a blood parasite, the blood parasite can then enter the new host and cause infection.
81:
bacteria. Anaplasmosis is an infectious but not contagious disease. Anaplasmosis can be transmitted through mechanical and biological vector processes. Anaplasmosis can also be referred to as "yellow bag" or "yellow fever" because the infected animal can develop a jaundiced look. Other signs of
325:. Out of the six MSP found on this species, three of the major surface proteins do not seem to differ between all strains, those including MSP1a, MSP4, and MSP5. The msp1a gene, which codes for MSP1a, is used as a marker for the identification of
670:
Hartelt K, Oehme R, Frank H, Brockmann SO, Hassler D, Kimmig P (April 2004). "Pathogens and symbionts in ticks: prevalence of
Anaplasma phagocytophilum (Ehrlichia sp.), Wolbachia sp., Rickettsia sp., and Babesia sp. in Southern Germany".
502:
populations in
Mongolia. This pathogen and its associated syndrome (characterized by lethargy, fever, and pale mucous membranes) was previously observed in only wild sheep and goats in the region, and is the first observed occurrence of
337:
is a gram-negative bacterium that does not have lipopolysaccharides or peptidoglycan. The outer membrane does not have a capsule, and is coarse with irregular periplasmic spaces. This species was originally included in the genus
129:
and can provide the animal with immunity for a period of time. The disease is more common in the South and West parts of the United States, but is no longer considered a major problem since the use of tetracycline drugs.
435:, but has been identified as a possible carcinogen and is not approved in the United States or Europe. Countries such as South Africa, Australia, Israel, and South America have used live vaccines containing infectious
1182:
319:, all with differing morphology, antigenic properties, protein sequence, and ability to be transmitted by ticks. Major surface proteins (MSP) have been found to play a major role in the infection by
514:, is found in only the northern and eastern parts of Australia where the cattle tick is present. It was probably introduced as early as 1829 by cattle from Indonesia infested with the cattle tick
491:, has led to the point where the disease is no longer considered a major problem. The disease affects immunoglobulin G, therefore G-specific antibody levels can be used to diagnose the disease.
214:, but the severity worsens with age increase. Older cattle tend to exhibit the most severe clinical symptoms; cattle aged 1–3 may also show severe symptoms but are able to recover easier.
1233:
329:
because it has shown to be conserved in the multiplication of rickettsia in cattle and ticks and has been shown to be involved in adhesion to bovine erythrocytes and tick cells.
2785:
101:. Once the host is infected with anaplasmosis, the immune system will try to fight off and kill the infected red blood cells, but will also kill healthy red blood cells. The
371:. Some vaccines that rely on erythrocyte-derived antigen sources provide immunity or prevent clinical disease, although these do not prevent cattle from being infected with
290:– found worldwide. There is a prevalence of 82.9% in sheep, and 74.9% in goats. This species is the most prevalent for causing anaplasmosis in sheep and goats, although
207:, anorexia, and weight loss. Infected animals may develop a jaundiced look which then turns into paleness around the eyes, muzzle, lips, and teats of the cattle.
1117:
552:
911:
1226:
2778:
145:
Biological vector transmission is through ticks that carry a blood parasite able to cause anaplasmosis. The most common
Anaplasmosis-causing tick is
939:
Atif FA (November 2015). "Anaplasma marginale and
Anaplasma phagocytophilum: Rickettsiales pathogens of veterinary and public health significance".
1219:
2771:
169:
Classic signs and symptoms of anaplasmosis will not occur until 3–6 weeks after infection. The most common symptoms of anaplasmosis include
3000:
138:
castrating knives, and tattoo instruments. Another mechanical transmission mode is through the mouthparts of biting flies who carry an
362:
125:
3054:
2399:
453:
pulled from infected bovine erythrocytes, which can provide some immunity but leaves cattle susceptible to other strains of
3285:
2049:
1794:
2970:
1475:
447:. Live vaccines are prohibited in the United States, and there has been production of vaccines consisting of nonliving
2845:
1603:
1246:
994:
715:
912:"Keep a watchful eye out for anaplasmosis in cattle herds — Division of Agricultural Sciences and Natural Resources"
2039:
1150:
560:
85:
Many different tick species can carry the bacteria that cause anaplasmosis. The two major bacterial pathogens are
2841:
2044:
1585:
786:
425:. An injection of tetracycline drugs can give ruminants immunity to Anaplasma species for at least eight months.
17:
2980:
2849:
1617:
1211:
1010:
Alessandra T, Santo C (2012-08-01). "Tick-borne diseases in sheep and goats: Clinical and diagnostic aspects".
985:
Boes KM, Durham AC (2017). "Anaplasmosis, Ehrlichiosis, Heartwater and Tick-Borne Fever". In
Zachary JF (ed.).
2707:
2905:
1433:
381:
can also be used, although it is more commonly used in the case of active infection. This includes the drugs
3280:
2884:
2603:
1927:
1363:
2915:
2864:
2264:
2258:
1874:
3275:
2343:
345:
186:
2064:
1899:
1868:
1798:
1579:
1321:
1063:"A novel clinical syndrome and detection of Anaplasma ovis in Mongolian reindeer (Rangifer tarandus)"
333:
298:
292:
248:
230:
93:
1103:
149:, also known as the black-legged tick or the deer tick. Ticks who contain species of many different
82:
infection include weight loss, diarrhea, paleness of the skin, aggressive behavior, and high fever.
3249:
2874:
2869:
2539:
2442:
2321:
2059:
2054:
1938:
1727:
1546:
1469:
1461:
1194:
472:
In the United States, anaplasmosis is notably present in the South and West, where the tick hosts
3010:
2985:
2743:
2623:
2583:
2525:
2244:
2011:
1447:
1405:
3290:
3145:
2990:
2559:
2477:
2436:
2432:
2313:
2307:
2074:
1784:
1719:
1513:
1419:
1391:
1325:
3138:
3116:
2995:
2576:
2565:
2363:
1993:
1819:
1790:
1597:
1357:
1311:
1125:
528:
389:, and is used in healthy ruminants to decrease the clinical effects of an active infection.
3231:
3217:
3109:
3102:
3005:
2975:
2737:
2697:
2650:
2532:
2183:
2141:
2121:
2078:
1934:
1733:
1413:
862:
8:
3224:
3020:
2965:
2810:
2715:
2660:
2329:
2205:
2150:
2098:
2017:
1960:
1913:
1848:
1696:
1688:
1682:
1399:
1385:
1254:
516:
455:
449:
443:
431:
372:
366:
321:
315:
236:
224:
189:
rash may be seen with anaplasmosis as it is co-transmitted in 10% of Lyme disease cases.
87:
56:
2794:
2763:
2703:
2614:
2115:
2104:
2025:
1969:
1757:
1455:
1441:
1371:
1348:
1092:
964:
839:
814:
760:
735:
734:
Duron O, Koual R, Musset L, Buysse M, Lambert Y, Jaulhac B, et al. (August 2022).
437:
266:
16:
This article is about the disease in ruminant animals. For anaplasmosis in humans, see
1023:
684:
3195:
3174:
3049:
2832:
2688:
2654:
2518:
2450:
2213:
2191:
2160:
1611:
1377:
1084:
1027:
990:
956:
844:
765:
711:
688:
649:
644:
627:
601:
402:
146:
120:
While there are no current live or inactivated vaccines effective for all strains of
51:
2132:
2089:
1984:
1096:
968:
113:
is distinct to all known species and more genetically related to recently described
3181:
3167:
3074:
2679:
2594:
2385:
2232:
2219:
2034:
1651:
1633:
1540:
1499:
1427:
1297:
1074:
1019:
948:
834:
826:
755:
747:
680:
639:
410:
182:
178:
46:
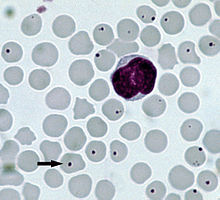
infecting the red blood cells of a cow: The arrow points to typical infected cell.
2947:
2629:
2550:
2504:
2409:
2349:
2284:
2226:
2195:
2187:
1890:
1860:
1854:
1737:
1566:
1490:
1317:
1199:
675:. Proceedings of the VII International Potsdam Symposium on Tick-Borne Diseases.
406:
1241:
397:
The most common source of treatment is the use of tetracycline drugs (including
3188:
3044:
2879:
2729:
2379:
2373:
2236:
1974:
1505:
1272:
1242:
1079:
1062:
461:
286:
98:
952:
605:
203:
may occur due to the lysis of red blood cells. General systemic signs include
3269:
2960:
2925:
2819:
2725:
2641:
2468:
2423:
2164:
2156:
1999:
1766:
1677:
1531:
1337:
1303:
1278:
1263:
1031:
815:"Human granulocytic anaplasmosis acquired from a blacklegged tick in Ontario"
378:
271:
242:
3207:
2955:
2910:
2859:
2837:
2721:
2495:
1702:
1642:
1574:
1519:
1088:
960:
848:
769:
751:
692:
653:
524:
488:
398:
382:
258:
ticks. Other species that cause anaplasmosis in specific species include:
3128:
2897:
2295:
2250:
2201:
1905:
1657:
736:"Novel Chronic Anaplasmosis in Splenectomized Patient, Amazon Rainforest"
532:
484:
418:
414:
275:
196:
1174:
830:
3028:
1669:
480:
200:
174:
595:
3092:
2933:
2483:
2335:
2003:
1944:
1825:
1044:
887:
426:
422:
386:
77:
35:
1919:
499:
222:
The two major species that cause anaplasmosis in ruminants include
204:
106:
72:
2510:
2456:
1810:
1775:
1048:
358:
3157:
1288:
1186:
474:
254:
192:
117:
species causing infections in rainforest wild fauna of Brazil.
195:
may be severe and result in cardiovascular changes such as an
170:
1060:
989:(6th ed.). Elsevier Health Sciences. pp. 749–50.
812:
68:
1061:
Haigh JC, Gerwing V, Erdenebaatar J, Hill JE (July 2008).
706:
Capucille DJ (2011). "Anaplasmosis". In
Haskell SR (ed.).
669:
813:
Edginton S, Guan TH, Evans G, Srivastava S (March 2018).
2793:
302:
has a prevalence of 11.9% in sheep, and 15.2% in goats.
733:
181:
in the bloodstream, and abnormally elevated levels of
97:. These microorganisms are Gram-negative, and infect
1124:. Department of Agriculture, Fisheries and Forestry,
1164:
593:
708:
Blackwell's Five-Minute
Veterinary Consult Ruminant
531:, conducted important research on anaplasmosis and
710:. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons. pp. 50–51.
3267:
2687:
1009:
594:Whittier WD, Currin N, Currin JF (2005-09-01).
252:is also found worldwide, mainly transmitted by
483:and practical treatment with prolonged-action
479:1980s and 1990s, control of ticks through new
429:has been shown to be highly effective against
2779:
1227:
673:International Journal of Medical Microbiology
510:In Australia, bovine anaplasmosis, caused by
980:
978:
3001:Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome
210:All cattle are susceptible to infection by
2786:
2772:
1234:
1220:
984:
625:
365:that are effective against all strains of
34:
1078:
975:
838:
759:
705:
643:
240:is found worldwide and is transmitted by
1038:
340:Ehrlichia (Ehrlichia phagocytophilium),
3268:
987:Pathologic Basis of Veterinary Disease
3055:Southern tick-associated rash illness
2767:
2400:Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans
1215:
934:
932:
175:decreased number of white blood cells
164:
75:, dogs, and horses, and is caused by
1785:Neisseria meningitidis/meningococcus
1110:
1014:. Supplement: SIPAOC Congress 2010.
938:
808:
806:
781:
779:
729:
727:
665:
663:
621:
619:
617:
615:
589:
587:
585:
583:
581:
579:
577:
1147:A Dictionary of Louisiana Biography
863:"Transmission | Anaplasmosis | CDC"
787:"Anaplasmosis – Circulatory System"
632:Transboundary and Emerging Diseases
626:Aubry P, Geale DW (February 2011).
13:
1247:Gram-negative bacterial infections
929:
904:
600:. Virginia Cooperative Extension.
357:Currently, no live or inactivated
105:species is responsible for a rare
14:
3302:
1604:Human monocytotropic ehrlichiosis
1160:
1024:10.1016/j.smallrumres.2012.04.026
855:
803:
776:
724:
660:
628:"A review of bovine anaplasmosis"
612:
574:
342:but is now included in the genus
1820:Neisseria gonorrhoeae/gonococcus
1795:Waterhouse–Friderichsen syndrome
1151:Louisiana Historical Association
1102:
645:10.1111/j.1865-1682.2010.01173.x
157:Once infected with a species of
2971:Crimean–Congo hemorrhagic fever
1586:Human granulocytic anaplasmosis
1139:
1054:
1003:
880:
467:
132:
18:Human granulocytic anaplasmosis
2981:Kemerovo tickborne viral fever
1618:Ehrlichiosis ewingii infection
699:
545:
1:
1434:Flinders Island spotted fever
685:10.1016/S1433-1128(04)80013-5
538:
464:and fluids may be necessary.
352:
308:
2885:Rocky Mountain spotted fever
2604:Stenotrophomonas maltophilia
1928:Burkholderia cepacia complex
1364:Rocky Mountain spotted fever
1067:Journal of Wildlife Diseases
740:Emerging Infectious Diseases
557:Pennsylvania Game Commission
392:
296:can also cause the disease.
7:
3286:Zoonotic bacterial diseases
2916:Relapsing fever borreliosis
2865:Spotted fever rickettsiosis
2265:Far East scarlet-like fever
2259:Yersinia pseudotuberculosis
1875:Chromobacteriosis infection
1145:"George Patout Broussard",
1051:, accessed 10 October 2011.
597:Anaplasmosis in Beef Cattle
460:Supportive therapy such as
142:species of blood parasite.
10:
3307:
1080:10.7589/0090-3558-44.3.569
1047:reviewed and published by
361:have been approved by the
346:Anaplasma phagocytophilium
313:There are many strains of
299:Anaplasma phagocytophilium
293:Anaplasma phagocytophilium
187:erythema chronicum migrans
15:
3241:
3205:
3155:
3126:
3090:
3083:
3067:
3037:
3019:
2946:
2924:
2906:Baggio–Yoshinari syndrome
2896:
2818:
2809:
2802:
2678:
2640:
2613:
2593:
2549:
2494:
2467:
2422:
2396:
2360:
2292:
2283:
2175:
2140:
2131:
2088:
2065:Hemolytic-uremic syndrome
1983:
1968:
1959:
1900:Burkholderia pseudomallei
1889:
1869:Chromobacterium violaceum
1836:
1809:
1799:Meningococcal septicaemia
1774:
1765:
1756:
1668:
1641:
1632:
1580:Anaplasma phagocytophilum
1565:
1530:
1489:
1347:
1336:
1287:
1271:
1262:
1253:
1168:
953:10.1007/s00436-015-4698-2
334:Anaplasma phagocytophilum
249:Anaplasma phagocytophilum
231:Anaplasma phagocytophilum
217:
94:Anaplasma phagocytophilum
71:-borne disease affecting
50:
42:
33:
28:
3250:Rhipicephalus sanguineus
2875:American tick bite fever
2870:Pacific Coast tick fever
2540:Plesiomonas shigelloides
2322:Brazilian purpuric fever
1939:Bordetella parapertussis
1728:Bartonella bacilliformis
1547:Flea-borne spotted fever
1477:Rickettsia aeschlimannii
1470:Rickettsia aeschlimannii
1462:American tick bite fever
441:to prevent infection of
3011:Tick-borne encephalitis
2986:Kyasanur Forest disease
2708:Guillain–Barré syndrome
2624:Cardiobacterium hominis
2584:Acinetobacter baumannii
2526:Vibrio parahaemolyticus
2245:Yersinia enterocolitica
2012:Klebsiella granulomatis
1448:African tick bite fever
1406:North Asian tick typhus
1012:Small Ruminant Research
791:Merck Veterinary Manual
527:George P. Broussard of
379:Antimicrobial treatment
3146:Dermacentor variabilis
2991:Omsk hemorrhagic fever
2560:Pseudomonas aeruginosa
2478:Francisella tularensis
2437:Legionella longbeachae
2433:Legionella pneumophila
2075:Enterobacter aerogenes
1720:Bacillary angiomatosis
1514:Orientia tsutsugamushi
1420:Queensland tick typhus
1392:Japanese spotted fever
1326:Flying squirrel typhus
752:10.3201/eid2808.212425
197:increase in heart rate
111:Anaplasma sparouinense
103:Anaplasma sparouinense
3139:Dermacentor andersoni
3117:Amblyomma triguttatum
2996:Powassan encephalitis
2577:Moraxella catarrhalis
2443:Legionnaires' disease
2364:Pasteurella multocida
1994:Klebsiella pneumoniae
1791:Meningococcal disease
1598:Ehrlichia chaffeensis
1358:Rickettsia rickettsii
1322:Brill–Zinsser disease
1312:Rickettsia prowazekii
1126:Queensland Government
1118:"Bovine anaplasmosis"
941:Parasitology Research
916:www.dasnr.okstate.edu
888:"Anaplasmosis | ALDF"
529:New Iberia, Louisiana
3232:Ornithodoros moubata
3218:Ornithodoros gurneyi
3110:Amblyomma cajennense
3103:Amblyomma americanum
3021:Protozoan infections
3006:Tete orthobunyavirus
2976:Heartland bandavirus
2846:Human monocytotropic
2811:Bacterial infections
2738:Helicobacter cinaedi
2698:Campylobacter jejuni
2651:Aeromonas hydrophila
2533:Vibrio alginolyticus
2184:Shigella dysenteriae
2122:Citrobacter freundii
2079:Enterobacter cloacae
1935:Bordetella pertussis
1414:Rickettsia australis
1153:publication, p. 114.
3281:Tick-borne diseases
3225:Ornithodoros hermsi
2966:Colorado tick fever
2795:Tick-borne diseases
2716:Helicobacter pylori
2206:Bacillary dysentery
2151:Salmonella enterica
2099:Serratia marcescens
2018:Granuloma inguinale
1914:Burkholderia mallei
1849:Eikenella corrodens
1697:Bartonella quintana
1689:Cat-scratch disease
1683:Bartonella henselae
1400:Rickettsia sibirica
1386:Rickettsia japonica
831:10.1503/cmaj.171243
679:(Suppl 37): 86–92.
517:Boophilus microplus
456:Anaplasma marginale
450:Anaplasma marginale
444:Anaplasma marginale
432:Anaplasma marginale
327:Anaplasma marginale
322:Anaplasma marginale
316:Anaplasma marginale
237:Anaplasma marginale
225:Anaplasma marginale
212:Anaplasma marginale
88:Anaplasma marginale
57:Veterinary medicine
2842:Human granulocytic
2704:Campylobacteriosis
2615:Cardiobacteriaceae
2116:Citrobacter koseri
2026:Klebsiella oxytoca
1456:Rickettsia parkeri
1442:Rickettsia africae
1372:Rickettsia conorii
438:Anaplasma centrale
270:– found mainly in
267:Anaplasma centrale
201:Blood in the urine
165:Signs and symptoms
44:Anaplasma centrale
3276:Ruminant diseases
3263:
3262:
3259:
3258:
3196:Ixodes scapularis
3175:Ixodes holocyclus
3084:Species and bites
3063:
3062:
3050:Alpha-gal allergy
2942:
2941:
2833:Boutonneuse fever
2761:
2760:
2757:
2756:
2689:Campylobacterales
2674:
2673:
2655:Aeromonas veronii
2519:Vibrio vulnificus
2451:Coxiella burnetii
2418:
2417:
2344:H. parainfluenzae
2279:
2278:
2275:
2274:
2214:Proteus mirabilis
2161:Paratyphoid fever
2050:Enterohemorrhagic
1970:Enterobacteriales
1955:
1954:
1885:
1884:
1752:
1751:
1748:
1747:
1734:Carrion's disease
1628:
1627:
1612:Ehrlichia ewingii
1561:
1560:
1557:
1556:
1378:Boutonneuse fever
1209:
1208:
1149:, Vol. 1 (1988),
947:(11): 3941–3957.
825:(12): E363–E366.
403:chlortetracycline
282:Sheep and goats:
274:, Africa and the
147:Ixodes scapularis
62:
61:
23:Medical condition
3298:
3182:Ixodes pacificus
3168:Ixodes cornuatus
3088:
3087:
3075:Tick infestation
2948:Viral infections
2816:
2815:
2807:
2806:
2797:and infestations
2788:
2781:
2774:
2765:
2764:
2685:
2684:
2595:Xanthomonadaceae
2403:
2386:Actinobacillosis
2367:
2300:
2290:
2289:
2220:Proteus vulgaris
2138:
2137:
2035:Escherichia coli
1981:
1980:
1966:
1965:
1841:
1772:
1771:
1763:
1762:
1652:Brucella abortus
1639:
1638:
1634:Hyphomicrobiales
1541:Rickettsia felis
1500:Rickettsia akari
1428:Rickettsia honei
1345:
1344:
1298:Rickettsia typhi
1285:
1284:
1269:
1268:
1260:
1259:
1236:
1229:
1222:
1213:
1212:
1166:
1165:
1154:
1143:
1137:
1136:
1134:
1132:
1114:
1108:
1107:
1106:
1100:
1082:
1058:
1052:
1042:
1036:
1035:
1007:
1001:
1000:
982:
973:
972:
936:
927:
926:
924:
923:
908:
902:
901:
899:
898:
884:
878:
877:
875:
874:
859:
853:
852:
842:
810:
801:
800:
798:
797:
783:
774:
773:
763:
746:(8): 1673–1676.
731:
722:
721:
703:
697:
696:
667:
658:
657:
647:
623:
610:
609:
591:
572:
571:
569:
568:
559:. Archived from
549:
411:rolitetracycline
124:approved by the
38:
26:
25:
3306:
3305:
3301:
3300:
3299:
3297:
3296:
3295:
3266:
3265:
3264:
3255:
3237:
3201:
3151:
3122:
3079:
3059:
3033:
3015:
2938:
2920:
2892:
2798:
2792:
2762:
2753:
2670:
2636:
2609:
2589:
2551:Pseudomonadales
2545:
2505:Vibrio cholerae
2490:
2463:
2414:
2397:
2392:
2361:
2356:
2293:
2271:
2227:Yersinia pestis
2171:
2127:
2084:
2040:Enterotoxigenic
1972:
1951:
1891:Burkholderiales
1881:
1855:Kingella kingae
1837:
1832:
1805:
1744:
1738:Verruga peruana
1664:
1624:
1567:Anaplasmataceae
1553:
1526:
1485:
1339:
1332:
1318:Epidemic typhus
1276:
1249:
1240:
1210:
1205:
1204:
1177:
1163:
1158:
1157:
1144:
1140:
1130:
1128:
1116:
1115:
1111:
1101:
1059:
1055:
1043:
1039:
1008:
1004:
997:
983:
976:
937:
930:
921:
919:
910:
909:
905:
896:
894:
886:
885:
881:
872:
870:
861:
860:
856:
811:
804:
795:
793:
785:
784:
777:
732:
725:
718:
704:
700:
668:
661:
624:
613:
592:
575:
566:
564:
551:
550:
546:
541:
470:
407:oxytetracycline
395:
355:
311:
220:
167:
135:
99:red blood cells
24:
21:
12:
11:
5:
3304:
3294:
3293:
3288:
3283:
3278:
3261:
3260:
3257:
3256:
3254:
3253:
3245:
3243:
3239:
3238:
3236:
3235:
3228:
3221:
3213:
3211:
3203:
3202:
3200:
3199:
3192:
3189:Ixodes ricinus
3185:
3178:
3171:
3163:
3161:
3153:
3152:
3150:
3149:
3142:
3134:
3132:
3124:
3123:
3121:
3120:
3113:
3106:
3098:
3096:
3085:
3081:
3080:
3078:
3077:
3071:
3069:
3065:
3064:
3061:
3060:
3058:
3057:
3052:
3047:
3045:Tick paralysis
3041:
3039:
3038:Other diseases
3035:
3034:
3032:
3031:
3025:
3023:
3017:
3016:
3014:
3013:
3008:
3003:
2998:
2993:
2988:
2983:
2978:
2973:
2968:
2963:
2958:
2952:
2950:
2944:
2943:
2940:
2939:
2937:
2936:
2930:
2928:
2922:
2921:
2919:
2918:
2913:
2908:
2902:
2900:
2894:
2893:
2891:
2890:
2889:
2888:
2882:
2880:rickettsialpox
2877:
2872:
2862:
2857:
2835:
2830:
2824:
2822:
2813:
2804:
2800:
2799:
2791:
2790:
2783:
2776:
2768:
2759:
2758:
2755:
2754:
2752:
2751:
2750:
2749:
2734:
2733:
2732:
2730:Gastric cancer
2712:
2711:
2710:
2693:
2691:
2682:
2676:
2675:
2672:
2671:
2669:
2668:
2667:
2666:
2646:
2644:
2638:
2637:
2635:
2634:
2633:
2632:
2619:
2617:
2611:
2610:
2608:
2607:
2599:
2597:
2591:
2590:
2588:
2587:
2580:
2573:
2572:
2571:
2555:
2553:
2547:
2546:
2544:
2543:
2536:
2529:
2522:
2515:
2514:
2513:
2500:
2498:
2492:
2491:
2489:
2488:
2487:
2486:
2473:
2471:
2465:
2464:
2462:
2461:
2460:
2459:
2447:
2446:
2445:
2428:
2426:
2420:
2419:
2416:
2415:
2413:
2412:
2406:
2404:
2394:
2393:
2391:
2390:
2389:
2388:
2380:Actinobacillus
2376:
2374:Pasteurellosis
2370:
2368:
2358:
2357:
2355:
2354:
2353:
2352:
2340:
2339:
2338:
2326:
2325:
2324:
2319:
2303:
2301:
2287:
2285:Pasteurellales
2281:
2280:
2277:
2276:
2273:
2272:
2270:
2269:
2268:
2267:
2255:
2254:
2253:
2241:
2240:
2239:
2237:Bubonic plague
2223:
2210:
2209:
2208:
2179:
2177:
2173:
2172:
2170:
2169:
2168:
2167:
2146:
2144:
2135:
2129:
2128:
2126:
2125:
2112:
2111:
2110:
2094:
2092:
2086:
2085:
2083:
2082:
2070:
2069:
2068:
2067:
2057:
2052:
2047:
2045:Enteroinvasive
2042:
2030:
2029:
2022:
2021:
2020:
2008:
2007:
2006:
1989:
1987:
1978:
1963:
1957:
1956:
1953:
1952:
1950:
1949:
1948:
1947:
1931:
1924:
1923:
1922:
1910:
1909:
1908:
1895:
1893:
1887:
1886:
1883:
1882:
1880:
1879:
1878:
1877:
1865:
1864:
1863:
1844:
1842:
1834:
1833:
1831:
1830:
1829:
1828:
1815:
1813:
1807:
1806:
1804:
1803:
1802:
1801:
1780:
1778:
1769:
1760:
1754:
1753:
1750:
1749:
1746:
1745:
1743:
1742:
1741:
1740:
1724:
1723:
1722:
1707:
1706:
1705:
1693:
1692:
1691:
1674:
1672:
1670:Bartonellaceae
1666:
1665:
1663:
1662:
1661:
1660:
1647:
1645:
1636:
1630:
1629:
1626:
1625:
1623:
1622:
1621:
1620:
1608:
1607:
1606:
1594:
1593:
1592:
1571:
1569:
1563:
1562:
1559:
1558:
1555:
1554:
1552:
1551:
1550:
1549:
1536:
1534:
1528:
1527:
1525:
1524:
1523:
1522:
1510:
1509:
1508:
1506:Rickettsialpox
1495:
1493:
1487:
1486:
1484:
1483:
1482:
1481:
1466:
1465:
1464:
1452:
1451:
1450:
1438:
1437:
1436:
1424:
1423:
1422:
1410:
1409:
1408:
1396:
1395:
1394:
1382:
1381:
1380:
1368:
1367:
1366:
1353:
1351:
1342:
1334:
1333:
1331:
1330:
1329:
1328:
1308:
1307:
1306:
1293:
1291:
1282:
1273:Rickettsiaceae
1266:
1257:
1251:
1250:
1243:Pseudomonadota
1239:
1238:
1231:
1224:
1216:
1207:
1206:
1203:
1202:
1191:
1178:
1173:
1172:
1170:
1169:Classification
1162:
1161:External links
1159:
1156:
1155:
1138:
1109:
1073:(3): 569–577.
1053:
1037:
1002:
995:
974:
928:
903:
879:
854:
802:
775:
723:
716:
698:
659:
611:
573:
553:"Anaplasmosis"
543:
542:
540:
537:
469:
466:
462:blood products
394:
391:
354:
351:
310:
307:
306:
305:
304:
303:
287:Anaplasma ovis
280:
279:
278:
219:
216:
166:
163:
134:
131:
60:
59:
54:
48:
47:
40:
39:
31:
30:
22:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
3303:
3292:
3291:Rickettsioses
3289:
3287:
3284:
3282:
3279:
3277:
3274:
3273:
3271:
3252:
3251:
3247:
3246:
3244:
3240:
3234:
3233:
3229:
3227:
3226:
3222:
3220:
3219:
3215:
3214:
3212:
3210:
3209:
3204:
3198:
3197:
3193:
3191:
3190:
3186:
3184:
3183:
3179:
3177:
3176:
3172:
3170:
3169:
3165:
3164:
3162:
3160:
3159:
3154:
3148:
3147:
3143:
3141:
3140:
3136:
3135:
3133:
3131:
3130:
3125:
3119:
3118:
3114:
3112:
3111:
3107:
3105:
3104:
3100:
3099:
3097:
3095:
3094:
3089:
3086:
3082:
3076:
3073:
3072:
3070:
3066:
3056:
3053:
3051:
3048:
3046:
3043:
3042:
3040:
3036:
3030:
3027:
3026:
3024:
3022:
3018:
3012:
3009:
3007:
3004:
3002:
2999:
2997:
2994:
2992:
2989:
2987:
2984:
2982:
2979:
2977:
2974:
2972:
2969:
2967:
2964:
2962:
2961:Bourbon virus
2959:
2957:
2954:
2953:
2951:
2949:
2945:
2935:
2932:
2931:
2929:
2927:
2926:Thiotrichales
2923:
2917:
2914:
2912:
2909:
2907:
2904:
2903:
2901:
2899:
2895:
2886:
2883:
2881:
2878:
2876:
2873:
2871:
2868:
2867:
2866:
2863:
2861:
2858:
2855:
2853:
2847:
2843:
2839:
2836:
2834:
2831:
2829:
2826:
2825:
2823:
2821:
2820:Rickettsiales
2817:
2814:
2812:
2808:
2805:
2801:
2796:
2789:
2784:
2782:
2777:
2775:
2770:
2769:
2766:
2748:
2746:
2742:
2741:
2740:
2739:
2735:
2731:
2727:
2726:MALT lymphoma
2723:
2720:
2719:
2718:
2717:
2713:
2709:
2705:
2702:
2701:
2700:
2699:
2695:
2694:
2692:
2690:
2686:
2683:
2681:
2677:
2665:
2663:
2659:
2658:
2657:
2656:
2652:
2648:
2647:
2645:
2643:
2642:Aeromonadales
2639:
2631:
2628:
2627:
2626:
2625:
2621:
2620:
2618:
2616:
2612:
2606:
2605:
2601:
2600:
2598:
2596:
2592:
2586:
2585:
2581:
2579:
2578:
2574:
2570:
2568:
2564:
2563:
2562:
2561:
2557:
2556:
2554:
2552:
2548:
2542:
2541:
2537:
2535:
2534:
2530:
2528:
2527:
2523:
2521:
2520:
2516:
2512:
2509:
2508:
2507:
2506:
2502:
2501:
2499:
2497:
2493:
2485:
2482:
2481:
2480:
2479:
2475:
2474:
2472:
2470:
2469:Thiotrichales
2466:
2458:
2455:
2454:
2453:
2452:
2448:
2444:
2441:
2440:
2439:
2438:
2434:
2430:
2429:
2427:
2425:
2424:Legionellales
2421:
2411:
2408:
2407:
2405:
2402:
2401:
2395:
2387:
2384:
2383:
2382:
2381:
2377:
2375:
2372:
2371:
2369:
2366:
2365:
2359:
2351:
2348:
2347:
2346:
2345:
2341:
2337:
2334:
2333:
2332:
2331:
2327:
2323:
2320:
2318:
2316:
2312:
2311:
2310:
2309:
2308:H. influenzae
2305:
2304:
2302:
2299:
2297:
2291:
2288:
2286:
2282:
2266:
2263:
2262:
2261:
2260:
2256:
2252:
2249:
2248:
2247:
2246:
2242:
2238:
2234:
2231:
2230:
2229:
2228:
2224:
2222:
2221:
2216:
2215:
2211:
2207:
2203:
2200:
2199:
2198:
2197:
2193:
2189:
2185:
2181:
2180:
2178:
2174:
2166:
2165:Salmonellosis
2162:
2158:
2157:Typhoid fever
2155:
2154:
2153:
2152:
2148:
2147:
2145:
2143:
2139:
2136:
2134:
2130:
2124:
2123:
2118:
2117:
2113:
2109:
2107:
2103:
2102:
2101:
2100:
2096:
2095:
2093:
2091:
2087:
2081:
2080:
2076:
2072:
2071:
2066:
2063:
2062:
2061:
2058:
2056:
2053:
2051:
2048:
2046:
2043:
2041:
2037:
2036:
2032:
2031:
2028:
2027:
2023:
2019:
2016:
2015:
2014:
2013:
2009:
2005:
2001:
2000:Rhinoscleroma
1998:
1997:
1996:
1995:
1991:
1990:
1988:
1986:
1982:
1979:
1976:
1971:
1967:
1964:
1962:
1958:
1946:
1943:
1942:
1941:
1940:
1936:
1932:
1930:
1929:
1925:
1921:
1918:
1917:
1916:
1915:
1911:
1907:
1904:
1903:
1902:
1901:
1897:
1896:
1894:
1892:
1888:
1876:
1873:
1872:
1871:
1870:
1866:
1862:
1859:
1858:
1857:
1856:
1851:
1850:
1846:
1845:
1843:
1840:
1835:
1827:
1824:
1823:
1822:
1821:
1817:
1816:
1814:
1812:
1808:
1800:
1796:
1792:
1789:
1788:
1787:
1786:
1782:
1781:
1779:
1777:
1773:
1770:
1768:
1764:
1761:
1759:
1755:
1739:
1735:
1732:
1731:
1730:
1729:
1725:
1721:
1718:
1717:
1716:
1712:
1708:
1704:
1701:
1700:
1699:
1698:
1694:
1690:
1687:
1686:
1685:
1684:
1679:
1678:Bartonellosis
1676:
1675:
1673:
1671:
1667:
1659:
1656:
1655:
1654:
1653:
1649:
1648:
1646:
1644:
1640:
1637:
1635:
1631:
1619:
1616:
1615:
1614:
1613:
1609:
1605:
1602:
1601:
1600:
1599:
1595:
1591:
1587:
1584:
1583:
1582:
1581:
1576:
1573:
1572:
1570:
1568:
1564:
1548:
1545:
1544:
1543:
1542:
1538:
1537:
1535:
1533:
1529:
1521:
1518:
1517:
1516:
1515:
1511:
1507:
1504:
1503:
1502:
1501:
1497:
1496:
1494:
1492:
1488:
1480:
1478:
1474:
1473:
1472:
1471:
1467:
1463:
1460:
1459:
1458:
1457:
1453:
1449:
1446:
1445:
1444:
1443:
1439:
1435:
1432:
1431:
1430:
1429:
1425:
1421:
1418:
1417:
1416:
1415:
1411:
1407:
1404:
1403:
1402:
1401:
1397:
1393:
1390:
1389:
1388:
1387:
1383:
1379:
1376:
1375:
1374:
1373:
1369:
1365:
1362:
1361:
1360:
1359:
1355:
1354:
1352:
1350:
1346:
1343:
1341:
1335:
1327:
1323:
1319:
1316:
1315:
1314:
1313:
1309:
1305:
1304:Murine typhus
1302:
1301:
1300:
1299:
1295:
1294:
1292:
1290:
1286:
1283:
1280:
1279:Rickettsioses
1274:
1270:
1267:
1265:
1264:Rickettsiales
1261:
1258:
1256:
1252:
1248:
1244:
1237:
1232:
1230:
1225:
1223:
1218:
1217:
1214:
1201:
1197:
1196:
1192:
1189:
1188:
1184:
1180:
1179:
1176:
1171:
1167:
1152:
1148:
1142:
1127:
1123:
1119:
1113:
1105:
1098:
1094:
1090:
1086:
1081:
1076:
1072:
1068:
1064:
1057:
1050:
1046:
1041:
1033:
1029:
1025:
1021:
1017:
1013:
1006:
998:
996:9780323357975
992:
988:
981:
979:
970:
966:
962:
958:
954:
950:
946:
942:
935:
933:
918:. 6 July 2016
917:
913:
907:
893:
889:
883:
868:
864:
858:
850:
846:
841:
836:
832:
828:
824:
820:
816:
809:
807:
792:
788:
782:
780:
771:
767:
762:
757:
753:
749:
745:
741:
737:
730:
728:
719:
717:9780470961186
713:
709:
702:
694:
690:
686:
682:
678:
674:
666:
664:
655:
651:
646:
641:
637:
633:
629:
622:
620:
618:
616:
607:
603:
599:
598:
590:
588:
586:
584:
582:
580:
578:
563:on 2022-05-24
562:
558:
554:
548:
544:
536:
534:
530:
526:
521:
519:
518:
513:
508:
507:in reindeer.
506:
501:
498:was found in
497:
492:
490:
486:
482:
477:
476:
465:
463:
459:
457:
452:
451:
446:
445:
440:
439:
434:
433:
428:
424:
420:
416:
412:
408:
404:
400:
390:
388:
384:
380:
376:
375:
370:
369:
364:
360:
350:
349:
347:
341:
336:
335:
330:
328:
324:
323:
318:
317:
301:
300:
295:
294:
289:
288:
284:
283:
281:
277:
273:
272:South America
269:
268:
264:
263:
261:
260:
259:
257:
256:
251:
250:
245:
244:
243:Rhipicephalus
239:
238:
233:
232:
227:
226:
215:
213:
208:
206:
202:
198:
194:
190:
188:
184:
183:liver enzymes
180:
176:
172:
162:
160:
155:
152:
148:
143:
141:
130:
127:
123:
118:
116:
112:
108:
104:
100:
96:
95:
90:
89:
83:
80:
79:
74:
70:
66:
58:
55:
53:
49:
45:
41:
37:
32:
27:
19:
3248:
3230:
3223:
3216:
3208:Ornithodoros
3206:
3194:
3187:
3180:
3173:
3166:
3156:
3144:
3137:
3127:
3115:
3108:
3101:
3091:
3068:Infestations
2956:Bhanja virus
2911:Lyme disease
2860:Scrub typhus
2851:
2838:Ehrlichiosis
2828:Anaplasmosis
2827:
2745:Helicobacter
2744:
2736:
2722:Peptic ulcer
2714:
2696:
2661:
2649:
2622:
2602:
2582:
2575:
2566:
2558:
2538:
2531:
2524:
2517:
2503:
2496:Vibrionaceae
2476:
2449:
2431:
2398:
2378:
2362:
2342:
2328:
2314:
2306:
2294:
2257:
2243:
2225:
2218:
2212:
2182:
2149:
2120:
2114:
2105:
2097:
2073:
2033:
2024:
2010:
1992:
1933:
1926:
1912:
1898:
1867:
1853:
1847:
1838:
1818:
1783:
1767:Neisseriales
1726:
1714:
1710:
1703:Trench fever
1695:
1681:
1650:
1643:Brucellaceae
1610:
1596:
1590:Anaplasmosis
1589:
1578:
1575:Ehrlichiosis
1539:
1520:Scrub typhus
1512:
1498:
1476:
1468:
1454:
1440:
1426:
1412:
1398:
1384:
1370:
1356:
1310:
1296:
1245:-associated
1193:
1181:
1146:
1141:
1129:. Retrieved
1121:
1112:
1070:
1066:
1056:
1045:Anaplasmosis
1040:
1015:
1011:
1005:
986:
944:
940:
920:. Retrieved
915:
906:
895:. Retrieved
892:www.aldf.com
891:
882:
871:. Retrieved
869:. 2019-01-11
866:
857:
822:
818:
794:. Retrieved
790:
743:
739:
707:
701:
676:
672:
635:
631:
596:
565:. Retrieved
561:the original
556:
547:
525:veterinarian
522:
515:
512:A. marginale
511:
509:
504:
495:
493:
489:tetracycline
473:
471:
468:Epidemiology
454:
448:
442:
436:
430:
399:tetracycline
396:
383:tetracycline
374:A. marginale
373:
368:A. marginale
367:
356:
343:
339:
332:
331:
326:
320:
314:
312:
297:
291:
285:
265:
253:
247:
241:
235:
229:
223:
221:
211:
209:
191:
168:
158:
156:
150:
144:
139:
136:
133:Transmission
122:A. marginale
121:
119:
114:
110:
102:
92:
86:
84:
76:
65:Anaplasmosis
64:
63:
43:
29:Anaplasmosis
3129:Dermacentor
2898:Spirochaete
2567:Pseudomonas
2315:Haemophilus
2296:Haemophilus
2251:Yersiniosis
2202:Shigellosis
1906:Melioidosis
1715:B. quintana
1711:B. henselae
1658:Brucellosis
867:www.cdc.gov
638:(1): 1–30.
533:brucellosis
485:antibiotics
419:minocycline
415:doxycycline
344:Anaplasma (
276:Middle East
3270:Categories
3029:Babesiosis
2852:E. ewingii
2747:cellulitis
2330:H. ducreyi
2317:meningitis
1839:ungrouped:
1532:Flea-borne
1491:Mite-borne
1349:Tick-borne
1122:Tick fever
1018:: S6–S11.
922:2021-11-16
897:2019-04-02
873:2019-04-02
796:2021-11-14
606:1200163698
567:2021-11-29
539:References
487:, notably
481:acaricides
353:Prevention
309:Morphology
3093:Amblyomma
2934:Tularemia
2854:infection
2664:infection
2662:Aeromonas
2569:infection
2484:Tularemia
2336:Chancroid
2108:infection
2090:Slow/weak
2004:Pneumonia
1945:Pertussis
1826:Gonorrhea
1479:infection
1032:0921-4488
494:In 2005,
427:Imidocarb
423:imidocarb
393:Treatment
387:imidocarb
179:platelets
159:Anaplasma
151:Anaplasma
140:Anaplasma
115:Anaplasma
78:Anaplasma
73:ruminants
52:Specialty
2803:Diseases
2192:flexneri
2106:Serratia
1920:Glanders
1190:: A79.82
1097:26942337
1089:18689641
969:14218282
961:26346451
849:29581163
770:35876693
693:15146989
654:21040509
500:reindeer
359:vaccines
262:Cattle:
205:diarrhea
107:zoonosis
2511:Cholera
2457:Q fever
2060:O104:H4
2055:O157:H7
1709:Either
1338:Spotted
1200:D000712
1131:14 June
1049:WikiVet
840:5871440
761:9328922
505:A. ovis
496:A. ovis
246:ticks.
3158:Ixodes
2850:Human
2233:Plague
2196:boydii
2188:sonnei
1289:Typhus
1095:
1087:
1030:
993:
967:
959:
847:
837:
768:
758:
714:
691:
652:
604:
475:Ixodes
421:) and
417:, and
255:Ixodes
218:Causes
193:Anemia
185:. The
3242:Other
2630:HACEK
2410:HACEK
2350:HACEK
1861:HACEK
1340:fever
1093:S2CID
965:S2CID
171:fever
67:is a
2176:H2S−
2142:H2S+
2133:Lac−
1985:Lac+
1195:MeSH
1133:2012
1085:PMID
1028:ISSN
991:ISBN
957:PMID
845:PMID
819:CMAJ
766:PMID
712:ISBN
689:PMID
650:PMID
602:OCLC
523:The
385:and
363:USDA
228:and
173:, a
126:USDA
91:and
69:tick
1975:OX−
1713:or
1183:ICD
1075:doi
1020:doi
1016:106
949:doi
945:114
835:PMC
827:doi
823:190
756:PMC
748:doi
681:doi
677:293
640:doi
3272::
2848:,
2844:,
2728:,
2724:,
2706:,
2204:,
2163:,
2159:,
2038::
2002:,
1811:M−
1797:,
1793:,
1776:M+
1736:,
1680::
1588:,
1577::
1324:,
1320:,
1198::
1187:10
1120:.
1091:.
1083:.
1071:44
1069:.
1065:.
1026:.
977:^
963:.
955:.
943:.
931:^
914:.
890:.
865:.
843:.
833:.
821:.
817:.
805:^
789:.
778:^
764:.
754:.
744:28
742:.
738:.
726:^
687:.
662:^
648:.
636:58
634:.
630:.
614:^
576:^
555:.
535:.
520:.
413:,
409:,
405:,
401:,
348:).
234:.
199:.
177:,
2887:)
2856:)
2840:(
2787:e
2780:t
2773:v
2680:ε
2653:/
2435:/
2298::
2235:/
2217:/
2194:/
2190:/
2186:/
2119:/
2077:/
1977:)
1973:(
1961:γ
1937:/
1852:/
1758:β
1281:)
1277:(
1275:/
1255:α
1235:e
1228:t
1221:v
1185:-
1175:D
1135:.
1099:.
1077::
1034:.
1022::
999:.
971:.
951::
925:.
900:.
876:.
851:.
829::
799:.
772:.
750::
720:.
695:.
683::
656:.
642::
608:.
570:.
458:.
20:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.