38:
305:
54:
313:
46:
407:
In the years 1967 and 1968, following theoretical studies about the location of the monument and after the demolition of the houses placed above it, excavations revealed some foundations and a fragment (now re-erected as a pillar) belonging to the building. These remains could be positively
181:
The mother of all milestones, the Milion, erected by
Septimus Severus, would be considered a kind of ground zero for civilisation and it marks the moment when Byzantium truly becomes a topographical and cultural reference point. Built in the first
105:, it became the zero-mile marker for the empire upon the re-founding of the city as Constantinople in 330 AD. Thereafter, it would serve as the starting-place for the measurement of distances for all the
408:
identified as belonging to the Milion thanks to their vicinity to a part of bent
Byzantine canalization. This seems to indicate the angle of the disappeared Mese, as reported by the literary sources.
145:
in 1453, it disappeared by the start of the 16th century in the
Ottoman era. During excavations in the 1960s, some partial fragments of the Milion were discovered under houses in the area.
388:(1453), the building remained intact up to the end of the fifteenth century. It disappeared possibly at the beginning of the sixteenth century because of the enlargement of the nearby
137:. The domed building of the Milion rested on four large arches and, over the centuries, it was expanded and decorated with several statues and paintings. Though it had survived the
1002:
575:
963:
951:
568:
224:, and on its base were inscribed the distances of all the main cities of the Empire from Constantinople. The monument was just west of the
41:
Reconstruction of
Byzantion's Milion based on historic accounts and remaining fragments. The arched structure is approximately 14.6 m wide.
187:
561:
208:("New Rome"), he consciously emulated many of the features of "Old Rome". Among these was the modification of the Milion: , it was
1007:
532:
253:
From the beginning of the sixth century, the building became an increasingly important station of the imperial ceremonial.
817:
1022:
675:
653:
270:
1027:
725:
792:
786:
782:
553:
345:
183:
822:
274:
266:
525:
Bildlexikon zur
Topographie Istanbuls: Byzantion, Konstantinupolis, Istanbul bis zum Beginn d. 17 Jh
520:
715:
241:
1012:
919:
329:
201:
751:
385:
142:
138:
355:, the Milion, due to its strategic position, witnessed fights in the city, like those between
929:
843:
796:
644:
417:
191:
934:
867:
811:
705:
619:
321:
278:
37:
8:
873:
853:
848:
766:
700:
629:
304:
220:: it was considered as the origin of all the roads leading to the European cities of the
228:, and was much more complex than its Roman counterpart. It can be described as a double
939:
899:
889:
838:
333:
924:
909:
858:
614:
528:
213:
114:
914:
904:
735:
710:
679:
397:
364:
221:
170:
110:
98:
86:
53:
204:
rebuilt the city of
Byzantium to make it his new imperial capital, which he named
761:
730:
689:
634:
389:
212:
surmounted with a dome,. The refurbished building fulfilled the same role as the
1017:
806:
801:
585:
382:
374:, the Milion—together with the Augustaeum—became the property of the church of
356:
229:
162:
66:
996:
978:
965:
863:
694:
649:
624:
506:
341:
290:
198:
894:
583:
756:
548:
375:
371:
166:
158:
94:
599:
401:
325:
254:
130:
659:
604:
337:
225:
209:
194:(Μέση Οδός), which at that point formed a bend. (Bettany Hughes, 2017)
106:
24:
244:
with a cross, looking towards the east, between them. A statue of the
360:
262:
102:
190:
at the very beginning of the main thoroughfare of the new city, the
720:
639:
352:
294:
154:
134:
57:
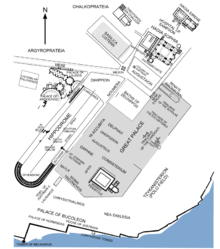
Milion can be seen at the center of the plaza near the
Hippodrome.
286:
258:
31:
312:
684:
298:
282:
240:. It was crowned by the statues of Constantine and his mother
45:
19:
This article is about the
Byzantine zero-mile marker. For the
246:
76:
70:
237:
233:
217:
126:
513:(in French). Paris: Institut Français d'Etudes Byzantines.
367:, who from this position was controlling the Augustaeum.
49:
A fragment of the Milion has been re-erected as a pillar.
1003:
Buildings and structures completed in the 4th century
265:
adorned the lower part with the statues of his wife
93:) was a marker from which all distances across the
370:In the period 1268 to 1271, after the end of the
320:During the first half of the eighth century, the
308:Distances of major modern cities from the Milion.
994:
16:Byzantine mile-marker monument in Constantinople
363:, or those between imperial troops and Empress
23:, the Greek mile of 5000 feet or 8 stadia, see
549:3D reconstruction at the Byzantium1200 project
569:
519:
153:The remains of the monument are located in
119:
952:Churches and Monasteries of Constantinople
584:Public spaces and structures of Byzantine
576:
562:
392:and the subsequent erection of the nearby
176:
165:, at the northern corner of the square of
113:. It thus served the same function as the
324:of the building were adorned by Emperors
311:
303:
52:
44:
36:
479:
477:
475:
473:
471:
469:
459:
457:
455:
453:
451:
449:
439:
437:
435:
433:
995:
316:The label on the remains of the Milion
557:
505:
277:. The monument was also adorned with
101:in the 3rd century AD in the city of
486:
466:
446:
430:
344:replaced them with scenes from the
13:
950:For churches and monasteries, see
818:Imperial Library of Constantinople
143:Ottoman conquest of Constantinople
14:
1039:
542:
250:of the City stood behind them.
1008:Byzantine secular architecture
757:Harbour of Julian/Kontoskalion
676:Great Palace of Constantinople
654:Portrait of the Four Tetrarchs
1:
726:Palace of the Porphyrogenitus
423:
109:leading to the cities of the
793:Hippodrome of Constantinople
787:University of Constantinople
783:Capitolium of Constantinople
236:, which was carried by four
7:
823:Praetoria of Constantinople
411:
148:
10:
1044:
499:
386:conquest of Constantinople
186:of the city, near the old
97:were measured. Erected by
77:
71:
29:
18:
979:41.0080417°N 28.9780667°E
948:
882:
831:
775:
744:
668:
592:
161:, in the neighborhood of
511:Constantinople Byzantine
404:", lit. "water scale").
30:Not to be confused with
920:Cistern of the Hebdomon
521:Müller-Wiener, Wolfgang
332:with paintings of past
202:Constantine I the Great
177:History and description
1023:Kilometre-zero markers
984:41.0080417; 28.9780667
752:Harbour of Eleutherios
317:
309:
139:sack of Constantinople
120:
90:
58:
50:
42:
930:Cistern of Philoxenos
844:Column of Constantine
797:Obelisk of Theodosius
527:. Tübingen: Wasmuth.
418:Umbilicus urbis Romae
315:
307:
279:equestrian sculptures
157:, in the district of
56:
48:
40:
1028:Obelisks in Istanbul
935:Cistern of Pulcheria
874:Column of Theodosius
868:Colossus of Barletta
812:Horses of Saint Mark
706:Palace of Blachernae
669:Palaces and mansions
620:Forum of Constantine
111:Eastern Roman Empire
975: /
854:Column of Justinian
849:Column of the Goths
767:Prosphorion Harbour
701:Palace of Antiochos
630:Forum of Theodosius
334:ecumenical councils
169:, and close to the
940:Theodosius Cistern
900:Baths of Zeuxippus
890:Aqueduct of Valens
839:Column of Arcadius
483:Müller-Wiener, 216
463:Müller-Wiener, 218
318:
310:
188:Walls of Byzantium
59:
51:
43:
958:
957:
925:Cistern of Mocius
910:Cistern of Aetius
859:Column of Marcian
716:Palace of Mangana
615:Forum of Arcadius
593:Roads and squares
534:978-3-8030-1022-3
336:, but during the
214:Milliarium Aureum
121:Milliarium Aureum
1035:
990:
989:
987:
986:
985:
980:
976:
973:
972:
971:
968:
915:Cistern of Aspar
905:Basilica Cistern
832:Column monuments
776:Public buildings
736:Prison of Anemas
711:Palace of Lausus
680:Boukoleon Palace
578:
571:
564:
555:
554:
538:
514:
493:
490:
484:
481:
464:
461:
444:
441:
365:Maria of Antioch
338:Iconoclastic Age
232:surmounted by a
222:Byzantine Empire
171:Basilica Cistern
141:in 1204 and the
123:
115:Golden Milestone
99:Septimus Severus
80:
79:
74:
73:
1043:
1042:
1038:
1037:
1036:
1034:
1033:
1032:
993:
992:
983:
981:
977:
974:
969:
966:
964:
962:
961:
959:
954:
944:
878:
827:
771:
762:Neorion Harbour
740:
731:Placidia Palace
690:Chrysotriklinos
664:
635:Forum of the Ox
588:
582:
545:
535:
502:
497:
496:
491:
487:
482:
467:
462:
447:
442:
431:
426:
414:
269:, his daughter
179:
151:
35:
28:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1041:
1031:
1030:
1025:
1020:
1015:
1013:Constantinople
1010:
1005:
956:
955:
949:
946:
945:
943:
942:
937:
932:
927:
922:
917:
912:
907:
902:
897:
892:
886:
884:
880:
879:
877:
876:
871:
861:
856:
851:
846:
841:
835:
833:
829:
828:
826:
825:
820:
815:
809:
807:Walled Obelisk
804:
802:Serpent Column
799:
790:
779:
777:
773:
772:
770:
769:
764:
759:
754:
748:
746:
742:
741:
739:
738:
733:
728:
723:
718:
713:
708:
703:
698:
692:
687:
682:
672:
670:
666:
665:
663:
662:
657:
647:
642:
637:
632:
627:
622:
617:
612:
602:
596:
594:
590:
589:
586:Constantinople
581:
580:
573:
566:
558:
552:
551:
544:
543:External links
541:
540:
539:
533:
516:
515:
507:Janin, Raymond
501:
498:
495:
494:
485:
465:
445:
428:
427:
425:
422:
421:
420:
413:
410:
357:Nikephoros III
273:and his niece
257:added to it a
230:triumphal arch
178:
175:
150:
147:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1040:
1029:
1026:
1024:
1021:
1019:
1016:
1014:
1011:
1009:
1006:
1004:
1001:
1000:
998:
991:
988:
970:28°58′41.04″E
967:41°00′28.95″N
953:
947:
941:
938:
936:
933:
931:
928:
926:
923:
921:
918:
916:
913:
911:
908:
906:
903:
901:
898:
896:
893:
891:
888:
887:
885:
881:
875:
872:
869:
865:
864:Column of Leo
862:
860:
857:
855:
852:
850:
847:
845:
842:
840:
837:
836:
834:
830:
824:
821:
819:
816:
813:
810:
808:
805:
803:
800:
798:
794:
791:
788:
784:
781:
780:
778:
774:
768:
765:
763:
760:
758:
755:
753:
750:
749:
747:
743:
737:
734:
732:
729:
727:
724:
722:
719:
717:
714:
712:
709:
707:
704:
702:
699:
696:
695:Daphne Palace
693:
691:
688:
686:
683:
681:
677:
674:
673:
671:
667:
661:
658:
655:
651:
650:Philadelphion
648:
646:
643:
641:
638:
636:
633:
631:
628:
626:
623:
621:
618:
616:
613:
610:
606:
603:
601:
598:
597:
595:
591:
587:
579:
574:
572:
567:
565:
560:
559:
556:
550:
547:
546:
536:
530:
526:
522:
518:
517:
512:
508:
504:
503:
489:
480:
478:
476:
474:
472:
470:
460:
458:
456:
454:
452:
450:
440:
438:
436:
434:
429:
419:
416:
415:
409:
405:
403:
399:
395:
391:
387:
384:
379:
377:
373:
368:
366:
362:
358:
354:
353:Comnenian Age
349:
347:
343:
342:Constantine V
339:
335:
331:
330:Anastasios II
327:
323:
314:
306:
302:
300:
296:
293:and a bronze
292:
291:Theodosius II
288:
284:
280:
276:
272:
268:
264:
260:
256:
251:
249:
248:
243:
239:
235:
231:
227:
223:
219:
215:
211:
207:
203:
200:
195:
193:
189:
185:
174:
172:
168:
164:
160:
156:
146:
144:
140:
136:
133:, erected by
132:
128:
124:
122:
116:
112:
108:
104:
100:
96:
92:
88:
84:
68:
64:
55:
47:
39:
33:
26:
22:
960:
883:Water supply
625:Forum of Leo
608:
524:
510:
488:
406:
393:
380:
376:Hagia Sophia
372:Latin Empire
369:
350:
319:
252:
245:
205:
196:
180:
167:Hagia Sophia
152:
118:
95:Roman Empire
82:
62:
60:
20:
982: /
600:Amastrianum
402:water tower
351:During the
326:Philippikos
255:Justinian I
91:Milyon taşı
997:Categories
895:Ballıgerme
660:Strategion
605:Augustaion
492:Janin, 105
443:Janin, 104
424:References
381:After the
346:Hippodrome
340:, Emperor
226:Augustaeum
210:tetrapylon
25:Roman mile
645:Mese Odos
361:Alexios I
263:Justin II
206:Nova Roma
163:Cağaloğlu
103:Byzantium
745:Harbours
721:Magnaura
640:Hebdomon
523:(1977).
509:(1950).
412:See also
394:suterazi
390:aqueduct
295:Quadriga
261:, while
155:Istanbul
149:Location
135:Augustus
500:Sources
398:Turkish
383:Ottoman
287:Hadrian
259:Sundial
199:Emperor
159:Eminönü
87:Turkish
78:Μίλλιον
32:Million
685:Chalke
609:Milion
531:
322:vaults
299:Helios
283:Trajan
275:Helena
271:Arabia
267:Sophia
242:Helena
238:arches
184:Region
83:Mílion
72:Μίλιον
63:Milion
21:milion
1018:Fatih
247:Tyche
197:When
131:forum
125:) in
107:roads
67:Greek
529:ISBN
359:and
328:and
234:dome
218:Rome
192:Mese
127:Rome
61:The
400:: "
297:of
281:of
216:in
129:'s
75:or
999::
468:^
448:^
432:^
378:.
348:.
289:,
285:,
173:.
89::
85:;
81:,
69::
870:)
866:(
814:)
795:(
789:)
785:(
697:)
678:(
656:)
652:(
611:)
607:(
577:e
570:t
563:v
537:.
396:(
301:.
117:(
65:(
34:.
27:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.