42:
1928:
were colonial creations. Categories or groupings such as 'Congo' or 'Angola' had no ethnic content in themselves and often combined peoples drawn from broad areas of
African who before enslavement had shared little sense of relationship or identity." Instead, he characterizes Palmares as a hybrid society combining traditions of various African groups. He traces the etymology of the word quilombo to the ki-lombo, a circumcision camp common among the Mbundu people of Angola that served to forge cultural unity among disparate local ethnic groups, and argues that this practice might have informed the diversity of Palmares. He also notes class stratification within the quilombo; those kidnapped in raids were often enslaved by the people of Palmares. He further highlights an economic interdependence between the inhabitants of Palmares and white Portuguese living nearby, manifested in the regular exchange of goods.
1919:, there is no documentary evidence that the residents of Palmares actually used this method of fighting. Most accounts describe them as armed with spears, bows, arrows and guns. They were able to acquire guns by trading with the Portuguese and by allowing small-holding cattle raisers to use their land. Guerrilla warfare was common; the inhabitants of Palmares, familiar with the terrain, marshaled camouflage and surprise attacks to their advantage. Fortifications of the Palmares encampments themselves included fences, walls, and traps.
308:
283:
1764:, which was a Christianized country at that time. Others had been converted to Christianity while enslaved. According to the Dutch, they used a local person who knew something of the church as a priest, though they did not think he practiced the religion in its usual form. Schwartz notes that African religious practices were also preserved and suggests that the depiction of Palmares as a largely Christian settlement is perhaps reflective of confusion or bias on the part of contemporary commentators.
1752:(published 1682) spoke of two larger consolidated entities, "Great Palmares" and "Little Palmares". In each of these units there was a large central town that was fortified and held 5,000-6,000 people. The surrounding hills and valleys were filled with many more mocambos of 50 to 100 people. A description of the visit of Johan Blaer to one of the larger mocambos in 1645 (which had been abandoned) revealed that there were 220 buildings in the community, a church, four
345:
1807:
1502:
1901:
2031:
1703:, perhaps as many as 90%, and therefore it is no surprise that tradition, reported as early as 1671 related that its first founders were Angolan. This large number was primarily because the Portuguese used the colony of Angola as a major raiding base, and there was a close relationship between the holders of
1644:
sociopolitical models, a reflection of the diverse ethnic origins of its inhabitants, although
Schwartz emphasizes that the residents of Palmares "combined these with aspects of European culture and specifically local adaptations." This government was confederate in nature, and was led by an elected
1829:
in 1676-7 that wounded Zumba and led to the capture of some of his children and grandchildren, Ganga Zumba sent a letter to the
Governor of Pernambuco asking for peace. The governor responded by agreeing to pardon Ganga Zumba and all his followers, on condition that they move to a position closer to
1782:
period (after 1640), the kingdoms of
Palmares grew and became even more consolidated. Two descriptions, one an anonymous account called "Relação das Guerras de Palmares" (1678) (Account of the war of Palmares), the other written by Manuel Injosa (1677), describe a large consolidated entity with nine
1927:
In his article "Rethinking
Palmares: Slave Resistance in Colonial Brazil," Schwartz challenges somewhat the historiographical conception of Palmares as a straightforward transposition of Angolan culture and sociopolitical structures, writing, "Much of what passed for African 'ethnicity' in Brazil
1846:
In a short time, Zumbi had organized a rebellion against Ganga Zumba, who was styled as his uncle, and poisoned him (though this is not proven, and many believe Zumba poisoned himself as a warning not to trust the
Portuguese). It is argued that Zumba was sick of fighting, but even more wary of
41:
1878:, the main settlement, fell; accounts suggest a bitter fight that saw 200 inhabitants of Palmares kill themselves rather than surrender and face re-enslavement. Zumbi was wounded. He eluded the Portuguese, but was betrayed, finally captured, and beheaded on November 20, 1695.
1798:
Although the "Guerra de
Palmares" consistently calls the king Ganga Zumba, and translates his name as "Great Lord" other documents, including a letter addressed to the king written in 1678 refer to him as "Ganazumba" (which is consistent with a Kimbundu term
1834:
refused to accept the terms. According to a deposition made in 1692 by a
Portuguese priest, Zumbi was born in Palmares in 1655, but was captured by Portuguese forces in a raid while still an infant. He was raised by the priest, and taught to read and write
1730:, they were unable (and generally unwilling) to conquer the rest of the province. As a result, there was a constant low-intensity war between Dutch and Portuguese settlers. During this time thousands of enslaved people escaped and went to the Palmares.
1931:
Historian Alida C. Metcalf cites recent archeological discoveries at the site of
Palmares that "reveal extensive Indian influence" to argue for an "image of the community as one formed by both Indians and Africans seeking freedom."
1639:
places the number at roughly 11,000, noting that it was, regardless, "undoubtedly the largest fugitive community to have existed in Brazil". These inhabitants developed a society and government that derived from a range of
1783:
major settlements and many smaller ones. Slightly later accounts tell us that the kingdom was named "Angola Janga" which according to the
Portuguese meant "Little Angola," although this is not a direct translation from a
1885:
in the territory of Angola Janga, which they occupied as a means of keeping the kingdom from being reconstituted. Palmares had been destroyed by a large army of Indians under the command of white and
566:
1741:
decided to send expeditions against Palmares. These expeditions also collected intelligence about them, and it is from these accounts that we learn about the organization of Palmares in their time.
1854:
From 1680 to 1694, the Portuguese and Zumbi, now the new king of Angola Janga, waged an almost constant war. The Portuguese government finally brought in the famed Portuguese military commanders
1696:, or small communities. However, the Portuguese were unable to dislodge these communities, which were probably small and scattered, and so expeditions continued periodically into the interior.
1137:
1843:. At the age of 15, however, Zumbi escaped and returned to Palmares. There he quickly won a reputation for military skill and bravery and was promoted to the leader of a large mocambo.
1874:. These men enlisted existing Pernambuco forces and local indigenous allies, who proved instrumental in the campaign. The final assault against Palmares occurred in January 1694.
1847:
signing the deal with the Portuguese, foreseeing their betrayal, and renewed war. By 1679 the Portuguese were again sending military expeditions against Zumbi. Meanwhile, the
1830:
the Portuguese settlements and return all enslaved Africans that had not been born in Palmares. Although Ganga Zumba agreed to the terms, one of his more powerful leaders,
1892:
Although the kingdom was destroyed the Palmares region continued to host many smaller runaway settlements, but there was no longer the centralized state in the mountains.
1635:
One estimate places the population of Palmares in the 1690s at around 20,000 inhabitants, although recent scholarship has questioned whether this figure is exaggerated.
571:
580:
857:
2355:
2015:
1733:
Although initially the Dutch considered making an alliance with Palmares against the Portuguese, peace agreements put them in the position of supporting the
1692:
there. As early as 1602, Portuguese settlers complained to the government that their captives were running away into this inaccessible region and building
1819:
2058:
593:
440:
2489:
2415:
2192:
1416:
169:
1530:
1452:
1442:
561:
551:
536:
411:
1161:
2179:
John Thornton, "Les Etats de l'Angola et la formation de Palmares (Bresil)" Annales Histoire, Science Sociales, 63.4 (2008): 760–797.
1171:
610:
1646:
1387:
1087:
1778:
After 1654 the Dutch were expelled, and the Portuguese began organizing expeditions against the mocambos of Palmares. In the post-
2464:
1645:
chief who allocated landholdings, appointed officials (usually family members), and resided in a type of fortification called
2403:
2365:
2147:
1392:
1142:
847:
677:
2341:
Africans of the Diaspora: The Evolution of African Consciousness and Leadership in the Americas (From Slavery to the 1920s)
1130:
605:
1337:
489:
2459:
1627:, and poor or marginalized Portuguese settlers, especially Portuguese soldiers trying to escape forced military service.
1447:
747:
1881:
Zumbi's brother continued the resistance, but Palmares was ultimately destroyed, and Velho and his followers were given
1606:
came into existence when Africans began arriving in Brazil in the mid-1530s and grew significantly as slavery expanded.
541:
2384:
2304:
2246:
2043:
1402:
1332:
1307:
1102:
710:
2010:
1915:
Although it is often argued that the inhabitants of Palmares defended themselves using the martial art form called
1437:
1047:
371:
1787:
term as one might expect. The two texts agree that it was ruled by a king, which the "Relação das Guerras" named "
1082:
1027:
1005:
1523:
1075:
928:
755:
702:
650:
364:
1744:
By the 1640s, many of the mocambos had consolidated into larger entities ruled by kings. Dutch descriptions by
1377:
1312:
1010:
985:
852:
687:
670:
462:
2055:
1482:
1477:
1457:
1427:
1412:
1382:
1272:
1191:
645:
423:
1851:
reneged on the agreement and re-enslaved many of Ganga Zumba's followers who had moved closer to the coast.
2332:
1863:
1317:
980:
975:
692:
640:
1252:
2302:
R. Anderson, "The Quilombo of Palmares: A New Overview of a Maroon State in Seventeenth-Century Brazil,"
1620:
1196:
1112:
777:
2074:
Orser, Charles E.; Funari, Pedro P.A. (January 2001). "Archaeology and slave resistance and rebellion".
2474:
2295:
1704:
1649:. Six Portuguese expeditions tried to conquer Palmares between 1680 and 1686, but failed. Finally the
1516:
1432:
1397:
1209:
990:
762:
615:
328:
1699:
During this time the vast majority of the enslaved Africans who were brought to Pernambuco were from
1040:
943:
893:
717:
504:
888:
862:
2454:
1715:
1708:
840:
827:
2189:
556:
2484:
1859:
1669:
1599:
1487:
1277:
968:
102:
1756:, and a council house. Churches were common in Palmares partly because Angolans were frequently
1908:
1738:
1422:
1367:
1267:
1149:
1097:
1022:
628:
445:
1871:
1322:
1262:
1247:
1052:
2469:
1688:
beyond the settlements on the coast, especially the mountain ranges, because there were many
1297:
881:
807:
452:
433:
406:
2139:
1824:
1577:
1287:
2127:
1959:
1855:
1719:
1665:
1347:
1017:
998:
1292:
923:
8:
2283:(São Paulo, 1947, only edition with documentary appendix, and three subsequent editions).
1836:
1372:
1232:
722:
521:
516:
418:
91:
2167:
1302:
1257:
1242:
1227:
1181:
2396:
Fighting for Honor: The History of African Martial Art Traditions in the Atlantic World
2099:
1636:
1342:
1327:
1222:
1186:
1092:
933:
903:
600:
499:
479:
1282:
2479:
2399:
2380:
2361:
2252:
2242:
2143:
2103:
2091:
2039:
1848:
1700:
1557:
1107:
1057:
876:
817:
787:
457:
386:
336:
2135:
2083:
1803:
meaning "lord"). One other official, Gana Zona also had this element in his name.
1761:
1734:
1237:
663:
531:
209:
72:
1791:" and that members of his family ruled other settlements, suggesting an incipient
2196:
2062:
2019:
1946:
1875:
1745:
1561:
1217:
802:
767:
472:
399:
301:
288:
196:
87:
2320:
2032:"Leadership and Authority in Maroon Settlements in Spanish America and Brazil."
1964:
1941:
1641:
1619:
was used. Palmares was home to not only escaped enslaved Africans, but also to
1407:
938:
918:
908:
797:
737:
697:
682:
106:
2038:
José C. Curto and Renée Soulodre-LaFrance, eds. 2005. p. 178fn31 (p. 183–184)
1940:
A semi-fictional account of Palmares was made into the 1984 Brazilian film by
1564:
that developed from 1605 until its suppression in 1694. It was located in the
727:
546:
2448:
2430:
2417:
2256:
2095:
1779:
1757:
1749:
1723:
1650:
1506:
1062:
792:
137:
122:
1795:. He also had officials and judges as well as a more or less standing army.
1117:
2087:
1792:
1662:
1156:
871:
772:
509:
484:
353:
222:
1867:
822:
1788:
1672:
and defeated a palmarista force, putting an end to the republic in 1694.
812:
782:
635:
526:
376:
156:
110:
1811:
1680:
Palmares was the general name given by the Portuguese in Pernambuco and
1882:
1753:
1685:
1658:
1569:
1176:
961:
898:
1689:
1654:
1565:
948:
732:
225:
destroy the last fortress (resistance in the region goes until 1790)
46:
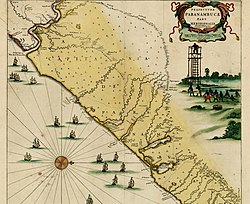
Southern part of the Captaincy of Pernambuco, in modern-day state of
1916:
1806:
1784:
1615:
1594:
1552:
1166:
913:
742:
381:
344:
140:
62:
2036:
Africa and the Americas: Interconnections During the Slave Trade.
1969:
1886:
1681:
1624:
1573:
126:
114:
76:
47:
2348:
Quilombo dos Palmares: Brazil's Lost Nation of Fugitive Slaves,
2313:
1900:
1727:
1661:, Pedro Almeida, organized an army under the leadership of the
1576:. The quilombo was located in what is now the municipality of
1975:
1840:
1831:
1773:
181:
118:
1998:
Slaves, Peasants and Rebels: Reconsidering Brazilian Slavery
1598:
were settlements mainly of survivors and free-born enslaved
2128:"Rethinking Palmares: Slave Resistance in Colonial Brazil"
1718:
sent a fleet to conquer Pernambuco, in the context of the
2343:. Trenton, NJ: Africa World Press, 2000. pp. 39–44.
2206:
1588:
The modern tradition has been to call the community the
1818:
After a particularly devastating attack by the captain
2377:
Capoeira: The Jogo de Angola from Luanda to Cyberspace
2357:
Capoeira: The History of an Afro-Brazilian Martial Art
2311:
Irene Diggs: "Zumbi and the Republic of Os Palmares".
2218:
1737:
economy of Pernambuco. Consequently, the Dutch leader
208:• Runaway African slaves found the settlement on
2317:. 1953. Atlantic Clark University. Vol. 2 p. 62.
2239:
Go-betweens and the colonization of Brazil, 1500–1600
2290:(Rio de Janeiro, 1973 and five subsequent editions).
16:
Community of escaped slaves in Brazil (1605 to 1694)
2241:(1st ed.). Austin: University of Texas Press.
2293:R. Kent, "Palmares: An African State in Brazil,"
2236:
2446:
1767:
1760:, either from the Portuguese colony or from the
2379:. Vol. 1. Berkeley, CA: Blue Snake Books.
2336:, Vol. 3, No. 1 (January 1918), pp. 29–32.
2188:João José Reis & Flávio dos Santos Gomes,
1726:. Although they captured and held the city of
1992:
1990:
1889:(white/Indian mixed-bloods) captains-of-war.
1675:
1524:
2190:"Quilombo: Brazilian Maroons during slavery"
2073:
1609:No contemporary document called Palmares a
2012:Material Didático: O Quilombo dos Palmares
1987:
1572:, in what is today the Brazilian state of
1531:
1517:
562:Transfer of the Portuguese court to Brazil
40:
2393:
2212:
1862:, who had made their reputation fighting
2490:17th-century disestablishments in Brazil
2353:
2224:
2125:
1899:
1805:
2350:Hanover, CT:New London Librarium, 2014.
2447:
2398:. University of South Carolina Press.
2374:
1895:
2140:10.1093/acref/9780195301731.013.43121
2121:
2119:
2117:
2115:
2113:
1711:, and the governors of Pernambuco.
748:Declaration of majority of Pedro II
13:
2354:Assunção, Matthias Röhrig (2002).
2308:28, no. 3 (October 1996): 545–566.
1972:, female warrior and wife of Zumbi
552:Spanish–Portuguese War (1776–1777)
537:Spanish–Portuguese War (1735–1737)
14:
2501:
2305:Journal of Latin American Studies
2110:
1922:
1103:March of the One Hundred Thousand
1676:Formative period (1620–53)
1500:
343:
306:
281:
2266:
2230:
2132:African American Studies Center
2126:Schwartz, Stuart (2005-04-07),
2465:1600s establishments in Brazil
2274:História da América Portuguesa
2182:
2173:
2161:
2067:
2049:
2024:
2003:
1810:Bust of Zumbi dos Palmares in
1172:1993 Constitutional referendum
1162:Impeachment of Fernando Collor
611:Conquest of the Banda Oriental
581:Invasion of the Banda Oriental
1:
2394:Desch-Obi, Thomas J. (2008).
2288:Palmares: Guerra dos escravos
1768:From Palmares to Angola Janga
1583:
1192:Impeachment of Dilma Rousseff
424:Letter of Pero Vaz de Caminha
412:Pedro Álvares Cabral's voyage
50:, with representation of the
2333:The Journal of Negro History
1935:
1905:Capoeira or the Dance of War
981:Constitutionalist Revolution
848:Proclamation of the Republic
693:Confederation of the Equator
594:United Kingdom with Portugal
7:
2201:Cultural Survival Quarterly
2134:, Oxford University Press,
2009:Nicolette, Carlos Eduardo.
1953:
1722:, during the period of the
1630:
651:Recognition of Independence
641:Declaration of Independence
10:
2506:
2460:Slave rebellions in Brazil
2339:Vincent Bakpetu Thompson.
2296:Journal of African History
2272:Pita, Sebastião da Rocha,
2237:Metcalf, Alida C. (2005).
1771:
1083:1964 Brazilian coup d'état
1006:1937 Brazilian coup d'état
991:Communist uprising of 1935
763:Liberal rebellions of 1842
616:Constituent Cortes of 1820
2000:(Illinois, 1994), p. 121.
1143:1988 Constituent Assembly
1088:Vacancy in the Presidency
1028:Ousting of Getúlio Vargas
969:Second Brazilian Republic
894:Coffee with milk politics
828:Post–abolition of slavery
678:1823 Constituent Assembly
606:Conquest of French Guiana
260:
256:
246:
242:
237:
233:
219:
206:
202:
192:
188:
175:
163:
150:
146:
133:
98:
83:
68:
58:
39:
34:
21:
2327:Online. 24 October 2007.
1981:
1716:Dutch West India Company
1053:Construction of Brasília
1048:Lott's preventative coup
2375:Taylor, Gerard (2007).
2325:Encyclopædia Britannica
2281:O Quilombo dos Palmares
1860:Bernardo Vieira de Melo
1670:Bernardo Vieira de Melo
557:Minas Gerais Conspiracy
103:Afro-American religions
2088:10.1080/00438240126646
1912:
1909:Johann Moritz Rugendas
1815:
1739:John Maurice of Nassau
1705:the contract of Angola
1187:Car Wash investigation
1098:Araguaia Guerrilla War
778:Eusébio de Queirós Law
94:, Indigenous languages
2276:, Ed. Itatiaia, 1976.
1903:
1809:
1748:(published 1647) and
1548:Quilombo dos Palmares
1076:Military dictatorship
882:Federalist Revolution
858:Republic of the Sword
808:Revolt of the Muckers
703:Abdication of Pedro I
495:Quilombo dos Palmares
407:Treaty of Tordesillas
84:Common languages
52:Quilombo dos Palmares
24:Quilombo dos Palmares
2431:9.17056°S 36.08389°W
2330:Charles E. Chapman,
2199:, January 31, 2002,
2170:, Britannica Online.
1960:Atlantic slave trade
1872:São Francisco valley
1856:Domingos Jorge Velho
1720:Dutch-Portuguese War
1666:Domingos Jorge Velho
1590:Quilombo of Palmares
1197:Coronavirus pandemic
1018:Integralist Uprising
823:Abolition of Slavery
567:Opening of the ports
2436:-9.17056; -36.08389
2427: /
2346:Glenn Alan Cheney,
1896:Fighting techniques
1709:governors of Angola
1613:; instead the term
1313:Rio Grande do Norte
723:1834 Additional Act
646:War of Independence
522:War of the Emboabas
152:• c.1670-1678
2195:2007-09-28 at the
2061:2007-07-02 at the
2056:Africans in Brazil
2018:2022-04-22 at the
1913:
1816:
1686:interior districts
1621:Indigenous peoples
1578:União dos Palmares
1273:Mato Grosso do Sul
1210:By federative unit
1093:Institutional Acts
976:Revolution of 1930
949:Lieutenant revolts
934:Revolt of the Lash
914:Annexation of Acre
904:Amazon rubber boom
500:France Equinoxiale
480:France Antarctique
419:European discovery
372:Indigenous Peoples
2475:Slavery in Brazil
2405:978-1-57003-718-4
2367:978-0-7146-8086-6
2149:978-0-19-530173-1
2076:World Archaeology
1996:Stuart Schwartz,
1701:Portuguese Angola
1556:, a community of
1541:
1540:
1507:Brazil portal
1428:Jewish Brazilians
1318:Rio Grande do Sul
1150:1988 Constitution
1113:Redemocratization
1108:Brazilian Miracle
1058:Legality Campaign
1041:Populist Republic
1011:1937 Constitution
986:1934 Constitution
924:Taubaté Agreement
853:1891 Constitution
818:Military Question
756:Reign of Pedro II
688:1824 Constitution
601:Pernambuco Revolt
387:Marajoara culture
337:History of Brazil
322:
321:
318:
317:
314:
313:
294:
293:
177:• 1678–1694
159:(first confirmed)
2497:
2442:
2441:
2439:
2438:
2437:
2432:
2428:
2425:
2424:
2423:
2420:
2409:
2390:
2371:
2279:Edison Carneiro,
2261:
2260:
2234:
2228:
2222:
2216:
2210:
2204:
2186:
2180:
2177:
2171:
2165:
2159:
2158:
2157:
2156:
2123:
2108:
2107:
2071:
2065:
2053:
2047:
2028:
2022:
2007:
2001:
1994:
1870:and then in the
1828:
1762:Kingdom of Kongo
1735:sugar plantation
1533:
1526:
1519:
1505:
1504:
1503:
1248:Federal District
866:
671:Reign of Pedro I
664:Empire of Brazil
575:
542:Treaty of Madrid
532:Vila Rica Revolt
449:
441:Brazilwood cycle
347:
324:
323:
310:
309:
298:
297:
285:
284:
278:
277:
262:
261:
210:Serra da Barriga
73:Serra da Barriga
44:
19:
18:
2505:
2504:
2500:
2499:
2498:
2496:
2495:
2494:
2455:Colonial Brazil
2445:
2444:
2435:
2433:
2429:
2426:
2421:
2418:
2416:
2414:
2413:
2406:
2387:
2368:
2286:Décio Freitas,
2269:
2264:
2249:
2235:
2231:
2223:
2219:
2215:, pp. 290.
2211:
2207:
2197:Wayback Machine
2187:
2183:
2178:
2174:
2166:
2162:
2154:
2152:
2150:
2124:
2111:
2072:
2068:
2063:Wayback Machine
2054:
2050:
2029:
2025:
2020:Wayback Machine
2008:
2004:
1995:
1988:
1984:
1956:
1938:
1925:
1898:
1876:Cerca do Macaco
1822:
1820:Fernão Carrilho
1776:
1770:
1746:Caspar Barlaeus
1678:
1642:Central African
1637:Stuart Schwartz
1633:
1586:
1562:colonial Brazil
1560:and others, in
1537:
1501:
1499:
1494:
1493:
1492:
1488:Years in Brazil
1472:
1464:
1463:
1462:
1388:Catholic Church
1368:Afro-Brazilians
1362:
1354:
1353:
1352:
1212:
1202:
1201:
1133:
1123:
1122:
1078:
1068:
1067:
1043:
1033:
1032:
995:
964:
954:
953:
929:Naval arms race
860:
843:
833:
832:
803:Religious Issue
788:Christie Affair
768:Praieira revolt
752:
707:
666:
656:
655:
631:
621:
620:
596:
586:
585:
569:
505:Dutch invasions
490:Jesuit missions
473:State of Brazil
469:
443:
430:
402:
400:Colonial Brazil
392:
391:
367:
357:
307:
302:Colonial Brazil
289:Colonial Brazil
282:
249:
226:
212:
197:Colonial Brazil
178:
166:
153:
88:Bantu languages
54:
30:
17:
12:
11:
5:
2503:
2493:
2492:
2487:
2485:1694 in Brazil
2482:
2477:
2472:
2467:
2462:
2457:
2411:
2410:
2404:
2391:
2385:
2372:
2366:
2351:
2344:
2337:
2328:
2318:
2309:
2300:
2291:
2284:
2277:
2268:
2265:
2263:
2262:
2247:
2229:
2227:, pp. 44.
2217:
2213:Desch-Obi 2008
2205:
2181:
2172:
2160:
2148:
2109:
2066:
2048:
2030:Jane Landers.
2023:
2002:
1985:
1983:
1980:
1979:
1978:
1973:
1967:
1962:
1955:
1952:
1942:Carlos Diegues
1937:
1934:
1924:
1923:Historiography
1921:
1897:
1894:
1849:sugar planters
1769:
1766:
1677:
1674:
1632:
1629:
1600:African people
1585:
1582:
1558:escaped slaves
1539:
1538:
1536:
1535:
1528:
1521:
1513:
1510:
1509:
1496:
1495:
1491:
1490:
1485:
1480:
1474:
1473:
1470:
1469:
1466:
1465:
1461:
1460:
1455:
1450:
1448:Rail transport
1445:
1440:
1435:
1430:
1425:
1420:
1410:
1405:
1400:
1395:
1390:
1385:
1380:
1375:
1370:
1364:
1363:
1360:
1359:
1356:
1355:
1351:
1350:
1345:
1340:
1335:
1333:Santa Catarina
1330:
1325:
1320:
1315:
1310:
1308:Rio de Janeiro
1305:
1300:
1295:
1290:
1285:
1280:
1275:
1270:
1265:
1260:
1255:
1253:Espírito Santo
1250:
1245:
1240:
1235:
1230:
1225:
1220:
1214:
1213:
1208:
1207:
1204:
1203:
1200:
1199:
1194:
1189:
1184:
1179:
1174:
1169:
1164:
1159:
1153:
1152:
1146:
1145:
1140:
1134:
1129:
1128:
1125:
1124:
1121:
1120:
1115:
1110:
1105:
1100:
1095:
1090:
1085:
1079:
1074:
1073:
1070:
1069:
1066:
1065:
1060:
1055:
1050:
1044:
1039:
1038:
1035:
1034:
1031:
1030:
1025:
1020:
1015:
1014:
1013:
1002:
1001:
994:
993:
988:
983:
978:
972:
971:
965:
960:
959:
956:
955:
952:
951:
946:
941:
939:Contestado War
936:
931:
926:
921:
919:Vaccine Revolt
916:
911:
909:War of Canudos
906:
901:
896:
891:
885:
884:
879:
874:
868:
867:
855:
850:
844:
839:
838:
835:
834:
831:
830:
825:
820:
815:
810:
805:
800:
798:Paraguayan War
795:
790:
785:
780:
775:
770:
765:
759:
758:
751:
750:
745:
740:
738:Ragamuffin War
735:
730:
725:
720:
714:
713:
711:Regency Period
706:
705:
700:
698:Cisplatine War
695:
690:
685:
683:Night of Agony
680:
674:
673:
667:
662:
661:
658:
657:
654:
653:
648:
643:
638:
632:
627:
626:
623:
622:
619:
618:
613:
608:
603:
597:
592:
591:
588:
587:
584:
583:
578:
577:
576:
559:
554:
549:
544:
539:
534:
529:
524:
519:
514:
513:
512:
502:
497:
492:
487:
482:
476:
475:
468:
467:
466:
465:
455:
450:
437:
436:
429:
428:
427:
426:
415:
414:
409:
403:
398:
397:
394:
393:
390:
389:
384:
379:
374:
368:
363:
362:
359:
358:
350:Terra Brasilis
348:
340:
339:
333:
332:
320:
319:
316:
315:
312:
311:
304:
295:
292:
291:
286:
274:
273:
268:
258:
257:
254:
253:
250:
247:
244:
243:
240:
239:
235:
234:
231:
230:
227:
220:
217:
216:
213:
207:
204:
203:
200:
199:
194:
193:Historical era
190:
189:
186:
185:
179:
176:
173:
172:
167:
164:
161:
160:
154:
151:
148:
147:
144:
143:
135:
131:
130:
107:Kongo religion
100:
96:
95:
85:
81:
80:
70:
66:
65:
60:
56:
55:
45:
37:
36:
32:
31:
22:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2502:
2491:
2488:
2486:
2483:
2481:
2478:
2476:
2473:
2471:
2468:
2466:
2463:
2461:
2458:
2456:
2453:
2452:
2450:
2443:
2440:
2407:
2401:
2397:
2392:
2388:
2386:9781583941836
2382:
2378:
2373:
2369:
2363:
2360:. Routledge.
2359:
2358:
2352:
2349:
2345:
2342:
2338:
2335:
2334:
2329:
2326:
2322:
2319:
2316:
2315:
2310:
2307:
2306:
2301:
2298:
2297:
2292:
2289:
2285:
2282:
2278:
2275:
2271:
2270:
2258:
2254:
2250:
2248:0-292-79622-6
2244:
2240:
2233:
2226:
2225:Assunção 2002
2221:
2214:
2209:
2203:, Issue 25.4.
2202:
2198:
2194:
2191:
2185:
2176:
2169:
2164:
2151:
2145:
2141:
2137:
2133:
2129:
2122:
2120:
2118:
2116:
2114:
2105:
2101:
2097:
2093:
2089:
2085:
2081:
2077:
2070:
2064:
2060:
2057:
2052:
2045:
2044:9781592212729
2041:
2037:
2033:
2027:
2021:
2017:
2014:
2013:
2006:
1999:
1993:
1991:
1986:
1977:
1974:
1971:
1968:
1966:
1963:
1961:
1958:
1957:
1951:
1949:
1948:
1943:
1933:
1929:
1920:
1918:
1910:
1906:
1902:
1893:
1890:
1888:
1884:
1879:
1877:
1873:
1869:
1865:
1861:
1857:
1852:
1850:
1844:
1842:
1838:
1833:
1826:
1821:
1813:
1808:
1804:
1802:
1796:
1794:
1790:
1786:
1781:
1780:Iberian Union
1775:
1765:
1763:
1759:
1758:Christianized
1755:
1751:
1750:Johan Nieuhof
1747:
1742:
1740:
1736:
1731:
1729:
1725:
1724:Iberian Union
1721:
1717:
1712:
1710:
1706:
1702:
1697:
1695:
1691:
1687:
1683:
1673:
1671:
1667:
1664:
1660:
1656:
1652:
1648:
1643:
1638:
1628:
1626:
1622:
1618:
1617:
1612:
1607:
1605:
1601:
1597:
1596:
1591:
1581:
1579:
1575:
1571:
1567:
1563:
1559:
1555:
1554:
1549:
1545:
1534:
1529:
1527:
1522:
1520:
1515:
1514:
1512:
1511:
1508:
1498:
1497:
1489:
1486:
1484:
1481:
1479:
1476:
1475:
1468:
1467:
1459:
1456:
1454:
1451:
1449:
1446:
1444:
1441:
1439:
1436:
1434:
1431:
1429:
1426:
1424:
1421:
1418:
1417:Football Team
1414:
1411:
1409:
1406:
1404:
1401:
1399:
1396:
1394:
1391:
1389:
1386:
1384:
1381:
1379:
1376:
1374:
1371:
1369:
1366:
1365:
1358:
1357:
1349:
1346:
1344:
1341:
1339:
1336:
1334:
1331:
1329:
1326:
1324:
1321:
1319:
1316:
1314:
1311:
1309:
1306:
1304:
1301:
1299:
1296:
1294:
1291:
1289:
1286:
1284:
1281:
1279:
1276:
1274:
1271:
1269:
1266:
1264:
1261:
1259:
1256:
1254:
1251:
1249:
1246:
1244:
1241:
1239:
1236:
1234:
1231:
1229:
1226:
1224:
1221:
1219:
1216:
1215:
1211:
1206:
1205:
1198:
1195:
1193:
1190:
1188:
1185:
1183:
1180:
1178:
1175:
1173:
1170:
1168:
1165:
1163:
1160:
1158:
1155:
1154:
1151:
1148:
1147:
1144:
1141:
1139:
1136:
1135:
1132:
1127:
1126:
1119:
1116:
1114:
1111:
1109:
1106:
1104:
1101:
1099:
1096:
1094:
1091:
1089:
1086:
1084:
1081:
1080:
1077:
1072:
1071:
1064:
1063:Plano Trienal
1061:
1059:
1056:
1054:
1051:
1049:
1046:
1045:
1042:
1037:
1036:
1029:
1026:
1024:
1021:
1019:
1016:
1012:
1009:
1008:
1007:
1004:
1003:
1000:
997:
996:
992:
989:
987:
984:
982:
979:
977:
974:
973:
970:
967:
966:
963:
958:
957:
950:
947:
945:
942:
940:
937:
935:
932:
930:
927:
925:
922:
920:
917:
915:
912:
910:
907:
905:
902:
900:
897:
895:
892:
890:
887:
886:
883:
880:
878:
875:
873:
870:
869:
864:
859:
856:
854:
851:
849:
846:
845:
842:
837:
836:
829:
826:
824:
821:
819:
816:
814:
811:
809:
806:
804:
801:
799:
796:
794:
793:Uruguayan War
791:
789:
786:
784:
781:
779:
776:
774:
771:
769:
766:
764:
761:
760:
757:
754:
753:
749:
746:
744:
741:
739:
736:
734:
731:
729:
726:
724:
721:
719:
716:
715:
712:
709:
708:
704:
701:
699:
696:
694:
691:
689:
686:
684:
681:
679:
676:
675:
672:
669:
668:
665:
660:
659:
652:
649:
647:
644:
642:
639:
637:
634:
633:
630:
625:
624:
617:
614:
612:
609:
607:
604:
602:
599:
598:
595:
590:
589:
582:
579:
573:
568:
565:
564:
563:
560:
558:
555:
553:
550:
548:
545:
543:
540:
538:
535:
533:
530:
528:
525:
523:
520:
518:
515:
511:
508:
507:
506:
503:
501:
498:
496:
493:
491:
488:
486:
483:
481:
478:
477:
474:
471:
470:
464:
461:
460:
459:
456:
454:
451:
447:
442:
439:
438:
435:
432:
431:
425:
422:
421:
420:
417:
416:
413:
410:
408:
405:
404:
401:
396:
395:
388:
385:
383:
380:
378:
375:
373:
370:
369:
366:
365:Pre-Cabraline
361:
360:
355:
351:
346:
342:
341:
338:
335:
334:
330:
326:
325:
305:
303:
300:
299:
296:
290:
287:
280:
279:
276:
275:
272:
269:
267:
264:
263:
259:
255:
251:
245:
241:
236:
232:
228:
224:
218:
214:
211:
205:
201:
198:
195:
191:
187:
183:
180:
174:
171:
168:
162:
158:
155:
149:
145:
142:
139:
136:
132:
128:
124:
123:Protestantism
120:
116:
112:
108:
104:
101:
97:
93:
89:
86:
82:
78:
74:
71:
67:
64:
61:
57:
53:
49:
43:
38:
33:
29:
25:
20:
2470:Dutch Brazil
2412:
2395:
2376:
2356:
2347:
2340:
2331:
2324:
2312:
2303:
2294:
2287:
2280:
2273:
2267:Bibliography
2238:
2232:
2220:
2208:
2200:
2184:
2175:
2163:
2153:, retrieved
2131:
2082:(1): 61–72.
2079:
2075:
2069:
2051:
2035:
2026:
2011:
2005:
1997:
1945:
1939:
1930:
1926:
1914:
1904:
1891:
1880:
1853:
1845:
1817:
1800:
1797:
1793:royal family
1777:
1743:
1732:
1714:In 1630 the
1713:
1698:
1693:
1679:
1663:Bandeirantes
1634:
1614:
1610:
1608:
1603:
1593:
1589:
1587:
1551:
1547:
1543:
1542:
1393:Constitution
1278:Minas Gerais
1157:Plano Collor
1131:New Republic
1023:World War II
889:Belle Époque
877:Navy Revolts
872:Encilhamento
841:Old Republic
773:Coffee cycle
718:April Revolt
629:Independence
510:Dutch Brazil
494:
485:Bandeirantes
354:Miller Atlas
349:
271:Succeeded by
270:
265:
248:• 1690
223:Bandeirantes
165:• 1678
138:Confederated
51:
28:Angola Janga
27:
23:
2434: /
1883:land grants
1866:peoples in
1823: [
1789:Ganga Zumba
1458:Transgender
1438:Nationality
1268:Mato Grosso
1138:Lost Decade
999:Estado Novo
944:World War I
861: [
813:Grande Seca
783:Platine War
728:Malê Revolt
636:Dia do Fico
570: [
547:Guaraní War
527:Mascate War
463:Slave trade
453:Sugar cycle
444: [
434:Captaincies
266:Preceded by
157:Ganga Zumba
111:Catholicism
75:, today in
2449:Categories
2422:36°05′02″W
2321:"Palmares"
2168:"Palmares"
2155:2020-12-08
1864:indigenous
1837:Portuguese
1772:See also:
1690:palm trees
1659:Pernambuco
1584:Background
1570:Pernambuco
1298:Pernambuco
1177:Plano Real
1118:Diretas Já
962:Vargas Era
899:Coronelism
517:Gold cycle
238:Population
170:Ganga Zona
134:Government
129:minorities
92:Portuguese
2419:9°10′14″S
2257:605091664
2104:162409042
2096:0043-8243
1936:In movies
1868:São Paulo
1655:captaincy
1604:quilombos
1595:Quilombos
1566:captaincy
1483:Conflicts
1453:Socialism
1408:Etymology
1378:Animation
1373:Anarchism
1348:Tocantins
1338:São Paulo
733:Cabanagem
99:Religion
35:1605–1694
2480:Quilombo
2193:Archived
2059:Archived
2016:Archived
1954:See also
1947:Quilombo
1917:capoeira
1812:Brasília
1785:Kimbundu
1754:smithies
1694:mocambos
1651:governor
1631:Overview
1625:caboclos
1611:quilombo
1553:quilombo
1550:, was a
1544:Palmares
1478:Timeline
1471:Research
1433:Military
1413:Football
1323:Rondônia
1263:Maranhão
1233:Amazonas
1182:Mensalão
1167:Mercosul
743:Balaiada
382:Kuhikugu
329:a series
327:Part of
141:monarchy
117:, maybe
79:, Brazil
63:Quilombo
1970:Dandara
1911:(1825).
1887:caboclo
1684:to the
1682:Alagoas
1653:of the
1616:mocambo
1574:Alagoas
1403:Ethanol
1398:Economy
1343:Sergipe
1328:Roraima
1288:Paraíba
1223:Alagoas
458:Slavery
221:•
127:Judaism
115:Animism
77:Alagoas
69:Capital
48:Alagoas
2402:
2383:
2364:
2314:Phylon
2255:
2245:
2146:
2102:
2094:
2042:
1965:Creole
1728:Recife
1707:, the
1647:Macoco
1602:. The
1443:Postal
1361:Topics
1293:Paraná
356:, 1519
331:on the
252:11,000
184:(last)
59:Status
2100:S2CID
1982:Notes
1976:Zumbi
1841:Latin
1832:Zumbi
1827:]
1801:ngana
1774:Zumbi
1546:, or
1303:Piauí
1258:Goiás
1243:Ceará
1238:Bahia
1228:Amapá
865:]
574:]
448:]
377:Luzia
182:Zumbi
119:Islam
2400:ISBN
2381:ISBN
2362:ISBN
2253:OCLC
2243:ISBN
2144:ISBN
2092:ISSN
2040:ISBN
1858:and
1839:and
1668:and
1423:LGBT
1383:Book
1283:Pará
1218:Acre
229:1694
215:1605
125:and
113:and
2136:doi
2084:doi
2034:in
1907:by
1657:of
1568:of
26:or
2451::
2323:,
2251:.
2142:,
2130:,
2112:^
2098:.
2090:.
2080:33
2078:.
1989:^
1950:.
1944:,
1825:pt
1623:,
1592:.
1580:.
863:pt
572:pt
446:pt
352:,
121:,
109:,
105:,
90:,
2408:.
2389:.
2370:.
2299:.
2259:.
2138::
2106:.
2086::
2046:.
1814:.
1532:e
1525:t
1518:v
1419:)
1415:(
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.