306:
to conduct towards the ventricle (the anterograde limb of the circuit) and the fast AV nodal pathway to conduct to the atria (the retrograde limb). The re-entrant circuit can be reversed such that the fast AV nodal pathway is the anterograde limb and the slow AV nodal pathway is the retrograde limb, referred to as "atypical", "uncommon", or "fast-slow" AVNRT. Atypical AVNRT may also use the slow AV nodal pathway as the anterograde limb and left atrial fibres that approach the AV node from the left side of the inter-atrial septum as the retrograde limb, and is sometimes referred to as "slow-slow" AVNRT.
443:
298:
46:
359:(portable, wearable ECG recorder). Again, this will show the diagnosis if the recorder is attached at the time of the symptoms. In rare cases, disabling but infrequent episodes of palpitations may require the insertion of a small device under the skin that continuously record heart activity (an implantable loop recorder). All these ECG-based technologies also enable the distinction between AVNRT and other abnormal fast heart rhythms such as
284:
Symptoms often occur without any specific trigger, although some find that their palpitations often occur after lifting heavy items or bending forwards. The onset of palpitations is sudden, with the acceleration of the heart rate occurring within a single beat, and may be preceded by a feeling of the
571:
or freeze the slow pathway of the AV node, destroying its ability to conduct electrical impulses, and preventing AVNRT. The risks and benefits are weighed up before this is performed. Catheter ablation of the slow pathway, if successfully carried out, can potentially cure AVNRT with success rates of
547:
While preventative treatment may be very helpful at stopping the unpleasant symptoms associated with AVNRT, as this arrhythmia is a benign condition, preventative treatment is not essential. Some of those who choose not to have further treatment will eventually become asymptomatic. Those who wish to
317:
Because the retrograde conduction is via the fast pathway, stimulation of the atria (which produces the inverted P wave) occurs very soon after stimulation of the ventricles (which causes the QRS complex). As a result, the time from the QRS complex to the P wave (the RP interval) is short, less than
305:
The fundamental mechanism of AVNRT is a presence of a dual atrioventricular node physiology (present in half of the population), which acts as a re-entrant circuit within the atrioventricular node. This can take several forms. "Typical", "common", or "slow-fast" AVNRT uses the slow AV nodal pathway
337:
Multiple slow pathways can exist so that both anterograde and retrograde conduction are over slow pathways. ("slow-slow" AVNRT).Because the retrograde conduction is via the slow pathway, stimulation of the atria will be delayed by the slow conduction tissue and will typically produce an inverted P
252:
The main symptom of AVNRT is the sudden development of rapid regular palpitations. These palpitations may be associated with a fluttering sensation in the neck, caused by near-simultaneous contraction of the atria and ventricles against a closed tricuspid valve leading to the pressure or atrial
228:(AVRT). In AVNRT, the fast and slow pathways are located within the right atrium close to or within the AV node and exhibit electrophysiologic properties similar to AV nodal tissue. Accessory pathways that give rise to WPW syndrome and AVRT are located in the
748:
Shen, Sharon; Knight, Bradley P. (2014), Kibos, Ambrose S.; Knight, Bradley P.; Essebag, Vidal; Fishberger, Steven B. (eds.), "How to
Differentiate Between AVRT, AT, AVNRT, and Junctional Tachycardia Using the Baseline ECG and Intracardiac Tracings",
837:"2015 ACC/AHA/HRS Guideline for the Management of Adult Patients With Supraventricular Tachycardia: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society"
288:
During AVNRT the heart rate is typically between 140 and 280 beats per minute. Close inspection of the neck may reveal pulsation of the jugular vein in the form of "cannon A-waves" as the right atrium contracts against a closed tricuspid valve.
253:
contraction being transmitted backwards into the venous system. The rapid heart rate may lead to feelings of anxiety, and may therefore be mistaken for panic attacks. In some cases, the onset of the fast heart is associated with a brief drop in
637:
Ayala-Paredes, Félix; Roux, Jean-Francois; Verdu, Mariano Badra (2014), Kibos, Ambrose S.; Knight, Bradley P.; Essebag, Vidal; Fishberger, Steven B. (eds.), "AVNRT Ablation: Significance of
Anatomic Findings and Nodal Physiology",
548:
have further treatment can choose to take long term antiarrhythmic medication. The first line drugs are calcium channel antagonists and beta blockers, with second line agents including flecainide, amiodarone, and occasionally
433:
Treatments for AVNRT aim to terminate episodes of tachycardia, and to prevent further episodes from occurring in the future. These treatments include physical manoeuvres, medication, and invasive procedures such as ablation.
1015:
1000:
346:
If the symptoms are present while the person is receiving medical care (e.g., in an emergency department), an ECG may show typical changes that confirm the diagnosis i.e., QRS duration <120 ms, unless a
209:. The fast pathway is usually located just superior and posterior to the AV node. These pathways are formed from tissue that behaves very much like the AV node, and some authors regard them as
170:. AV nodal reentrant tachycardia is the most common regular supraventricular tachycardia. It is more common in women than men (approximately 75% of cases occur in females). The main symptom is
835:
Page, Richard L.; Joglar, José A.; Caldwell, Mary A.; Calkins, Hugh; Conti, Jamie B.; Deal, Barbara J.; Estes, N. A. Mark; Field, Michael E.; Goldberger, Zachary D. (May 2016).
887:
Brubaker, Sarah; Long, Brit; Koyfman, Alex (February 2018). "Alternative
Treatment Options for Atrioventricular-Nodal-Reentry Tachycardia: An Emergency Medicine Review".
205:. The slow pathway (which is usually targeted for ablation) is located inferior and slightly posterior to the AV node, often following the anterior margin of the
1765:
53:
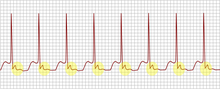
An example of an ECG tracing typical of uncommon AV nodal reentrant tachycardia. Highlighted in yellow is the P wave that falls after the QRS complex.
285:
heart skipping a beat. The heart may continue to race for minutes or hours, but the eventual termination of the arrhythmia is as rapid as its onset.
563:
can be used to confirm the diagnosis and potentially offer a cure. This procedure involves introducing wires or catheters into the heart through a
424:(heart attack) has occurred either as a cause or as a result of the AVNRT; this is usually only the case if the patient has experienced chest pain
334:
In atypical AVNRT, the anterograde conduction is via the fast pathway and the retrograde conduction is via the slow pathway ("fast-slow" AVNRT).
314:
In typical AVNRT, the anterograde conduction is via the slow pathway and the retrograde conduction is via the fast pathway ("slow-fast" AVNRT).
318:
50% of the time between consecutive QRS complexes. The RP interval is often so short that the inverted P waves may not be seen on the surface
1406:
930:
Kumar, Darpan S.; Dewland, Thomas A.; Balaji, Seshadri; Henrikson, Charles A. (May 2017). "How to
Approach Difficult Cases of AVNRT".
707:
1096:
598:
Rosero, Spencer (2015), "A Brief
Overview of Supraventricular Tachycardias", in Huang, MD, David T.; Prinzi, MD, Travis (eds.),
477:(increasing the pressure in the chest by attempting to exhale against a closed airway by bearing down or holding one's breath).
1823:
1140:
99:
17:
766:
655:
615:
1627:
1464:
457:. Some of those with AVNRT may be able to stop their attack by using physical manoeuvres that increase the activity of the
201:. The circuit usually involves two anatomical pathways: the fast pathway and the slow pathway, which are both in the right
1818:
1632:
1622:
1211:
1929:
1760:
1374:
322:(ECG) as they are buried within or immediately after the QRS complexes, appearing as a "pseudo R prime" wave in lead V
1800:
281:; this pain is band- or pressure-like around the chest and often radiates to the left arm and angle of the left jaw.
572:>95%, balanced against a small risk of complications including damaging the AV node and subsequently requiring a
453:
An episode of supraventricular tachycardia due to AVNRT can be terminated by any action that transiently blocks the
1795:
301:
During typical AVNRT, electrical impulses travel down the slow pathway of the AV node and back up the fast pathway.
1664:
1445:
1740:
1659:
480:
Medications that slow or briefly halt electrical conduction through the AV node can terminate AVNRT, including
376:
221:
107:
2086:
1962:
1891:
1723:
1459:
2081:
1874:
1857:
1790:
1710:
1089:
573:
163:
2179:
1924:
1369:
135:
1906:
1394:
1379:
87:
1453:
552:. These drugs are moderately effective at preventing further episodes but need to be taken long term.
1984:
1681:
1649:
1576:
1303:
2108:
1934:
1864:
1654:
1551:
1532:
1362:
1135:
1030:
225:
2141:
2115:
2103:
2091:
2076:
1810:
1752:
1556:
1537:
1189:
1129:
1082:
568:
556:
489:
372:
266:
187:
122:
194:
1730:
1696:
1639:
1617:
1439:
1421:
1357:
1224:
1177:
1105:
389:
229:
94:
1494:
1489:
1384:
1299:
1194:
466:
462:
421:
1990:
1518:
1499:
1399:
1310:
1253:
8:
1995:
1852:
1847:
1770:
1674:
1644:
1603:
1229:
1146:
1059:
1019:
536:
501:
442:
360:
319:
297:
2098:
1896:
1718:
1669:
1294:
1241:
1151:
1024:
963:
407:
262:
103:
68:
799:
782:
2158:
2009:
1967:
1882:
1700:
1598:
1315:
1258:
1156:
955:
947:
912:
904:
866:
858:
804:
762:
684:
651:
611:
560:
474:
368:
237:
233:
217:
83:
78:
58:
967:
2131:
2023:
1916:
1612:
939:
900:
896:
848:
794:
754:
643:
603:
731:
2153:
1545:
1526:
1513:
1320:
1199:
1074:
1035:
758:
647:
508:. Less commonly used drugs for this purpose include antiarrhythmic drugs such as
393:
270:
45:
607:
2146:
2054:
1952:
1944:
1842:
1352:
1345:
1332:
1062:
853:
836:
676:
417:
364:
356:
254:
206:
202:
175:
1009:
943:
2173:
2136:
2047:
1182:
951:
908:
862:
708:"Dual Atrioventricular Nodal Physiology - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics"
528:
520:
470:
183:
167:
166:(SVT), meaning that it originates from a location within the heart above the
139:
2068:
2042:
1886:
1834:
1507:
1483:
1430:
1289:
959:
916:
870:
808:
688:
564:
485:
171:
2003:
1901:
1691:
1608:
1590:
1416:
1389:
1340:
1281:
458:
399:
348:
179:
159:
539:, an electric shock is applied to the heart to restore a normal rhythm.
2031:
1581:
513:
509:
382:
274:
241:
190:, in which the abnormally conducting tissue in the heart is destroyed.
143:
129:
992:
504:, and are therefore used with caution in people who are known to have
1054:
497:
493:
481:
447:
411:
403:
352:
258:
118:
519:
If the fast heart rate is poorly tolerated (e.g. the development of
1957:
1114:
532:
780:
549:
454:
198:
2037:
2017:
1172:
1004:
505:
278:
379:, all of which may have symptoms that are similar to AVNRT.
929:
524:
216:
The fast and slow pathways should not be confused with the
338:
wave that falls after the QRS complex on the surface ECG.
834:
602:, In Clinical Practice, Springer London, pp. 37–53,
232:. They provide a direct connection between the atria and
600:
Clinical
Cardiac Electrophysiology in Clinical Practice
732:"Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia (AVNRT)"
636:
982:
932:
Current
Treatment Options in Cardiovascular Medicine
677:"Atrioventricular Nodal Reentry Tachycardia (AVNRT)"
527:) then AVNRT can be terminated electrically using a
385:
commonly performed in people with palpitations are:
886:
567:. The tip of one of these catheters can be used to
351:is suspected. If the palpitations are recurrent, a
1104:
531:. In this procedure, after administering a strong
273:) who has a very rapid heart rate may experience
2171:
674:
555:Alternatively, an invasive procedure called an
783:"Atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia"
500:). Both adenosine and beta blockers may cause
446:AVNRT termination following administration of
1090:
841:Journal of the American College of Cardiology
781:Demosthenes G Katritsis; A John Camm (2010).
73:Palpitations, chest tightness, neck pulsation
675:Hafeez, Yamama; Armstrong, Tyler J. (2019),
326:or a "pseudo S" wave in the inferior leads.
257:. When this happens, someone may experience
38:Atrioventricular-nodal reentrant tachycardia
269:(narrowing of the arteries of the heart by
1407:Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia
1097:
1083:
747:
226:atrioventricular reciprocating tachycardia
44:
852:
798:
437:
197:circuit forms within or just next to the
542:
441:
296:
2172:
1141:Spontaneous coronary artery dissection
597:
100:Atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia
18:Atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia
1078:
753:, Springer London, pp. 199–208,
642:, Springer London, pp. 387–400,
247:
1465:Nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis
882:
880:
830:
828:
826:
824:
822:
820:
818:
774:
743:
741:
670:
668:
666:
632:
630:
628:
626:
593:
591:
589:
13:
1761:Accelerated idioventricular rhythm
461:on the heart, specifically on the
14:
2191:
978:
889:The Journal of Emergency Medicine
877:
815:
800:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.936591
738:
663:
623:
586:
329:
265:(faint). Someone with underlying
523:symptoms, low blood pressure or
375:and tachyarrhythmias related to
309:
1446:Subacute bacterial endocarditis
923:
230:atrioventricular valvular rings
186:. Frequent attacks may require
901:10.1016/j.jemermed.2017.10.003
724:
700:
377:Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
222:Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
152:AV-nodal reentrant tachycardia
108:junctional ectopic tachycardia
29:AV-nodal reentrant tachycardia
1:
1963:Pulseless electrical activity
1892:Multifocal atrial tachycardia
1766:Catecholaminergic polymorphic
579:
420:– if there is a concern that
292:
759:10.1007/978-1-4471-5316-0_15
648:10.1007/978-1-4471-5316-0_30
557:electrophysiology (EP) study
428:
341:
164:supraventricular tachycardia
7:
608:10.1007/978-1-4471-5433-4_3
465:. These manoeuvres include
396:increases the risk of AVNRT
244:of the heart's ventricles.
182:, or, rarely, synchronized
176:specific physical maneuvers
136:calcium channel antagonists
10:
2196:
1907:Wandering atrial pacemaker
1454:non-infective endocarditis
1395:Endocardial fibroelastosis
854:10.1016/j.jacc.2015.08.856
88:electrophysiological study
15:
2124:
2067:
1985:hexaxial reference system
1976:
1943:
1930:Jervell and Lange-Nielsen
1915:
1873:
1832:
1809:
1783:
1751:
1709:
1690:
1589:
1575:
1475:
1460:Libman–Sacks endocarditis
1429:
1415:
1331:
1280:
1273:
1210:
1165:
1122:
1113:
1045:
986:
944:10.1007/s11936-017-0531-9
683:, StatPearls Publishing,
502:tightening of the airways
488:, or non-dihydropyridine
128:
113:
93:
77:
67:
57:
52:
43:
33:
28:
1865:Ventricular fibrillation
1136:Coronary artery aneurysm
490:calcium channel blockers
174:. Treatment may be with
158:) is a type of abnormal
104:focal atrial tachycardia
16:Not to be confused with
2142:Diastolic heart failure
2116:Athletic heart syndrome
2077:Ventricular hypertrophy
1811:Pre-excitation syndrome
1665:Left posterior fascicle
1190:Acute coronary syndrome
1130:Coronary artery disease
414:may predispose to AVNRT
373:ventricular tachycardia
267:coronary artery disease
188:radiofrequency ablation
1660:Left anterior fascicle
1440:infective endocarditis
1225:Hibernating myocardium
1106:Cardiovascular disease
450:
438:Arrhythmia termination
390:thyroid function tests
302:
240:properties similar to
95:Differential diagnosis
1824:Wolff–Parkinson–White
1784:Premature contraction
1682:Adams–Stokes syndrome
1385:Loeffler endocarditis
1195:Myocardial infarction
712:www.sciencedirect.com
543:Arrhythmia prevention
473:in the neck) and the
467:carotid sinus massage
463:atrioventricular node
445:
422:myocardial infarction
300:
242:muscular heart tissue
199:atrioventricular node
1991:Right axis deviation
1953:Sudden cardiac death
1311:Pericardial effusion
1254:Ventricular aneurysm
193:AVNRT occurs when a
1996:Left axis deviation
1853:Atrial fibrillation
1848:Ventricular flutter
1771:Torsades de pointes
1645:Bundle branch block
1604:Sick sinus syndrome
1390:Cardiac amyloidosis
1375:Tachycardia-induced
1230:Myocardial stunning
1178:Prinzmetal's angina
1147:Coronary thrombosis
751:Cardiac Arrhythmias
640:Cardiac Arrhythmias
537:general anaesthetic
361:atrial fibrillation
2180:Cardiac arrhythmia
2099:Atrial enlargement
1897:Pacemaker syndrome
1819:Lown–Ganong–Levine
1741:Junctional ectopic
1736:AV nodal reentrant
1242:Myocardial rupture
1152:Coronary vasospasm
1046:External resources
475:Valsalva manoeuvre
451:
402:– disturbances in
394:overactive thyroid
303:
263:lose consciousness
248:Signs and symptoms
238:electrophysiologic
224:(WPW syndrome) or
220:that give rise to
218:accessory pathways
162:. It is a type of
117:vagal manoeuvres,
2167:
2166:
2159:Obstructive shock
2063:
2062:
2010:Short QT syndrome
1977:Other / ungrouped
1968:Sinoatrial arrest
1883:Ectopic pacemaker
1779:
1778:
1599:Sinus bradycardia
1571:
1570:
1567:
1566:
1316:Cardiac tamponade
1269:
1268:
1259:Dressler syndrome
1157:Myocardial bridge
1072:
1071:
768:978-1-4471-5315-3
657:978-1-4471-5315-3
617:978-1-4471-5432-7
561:catheter ablation
469:(pressure on the
369:sinus tachycardia
320:electrocardiogram
160:fast heart rhythm
149:
148:
84:electrocardiogram
79:Diagnostic method
23:Medical condition
2187:
2132:Cardiac fibrosis
2024:T wave alternans
1917:Long QT syndrome
1711:Supraventricular
1707:
1706:
1640:Intraventricular
1587:
1586:
1427:
1426:
1278:
1277:
1123:Coronary disease
1120:
1119:
1099:
1092:
1085:
1076:
1075:
984:
983:
972:
971:
927:
921:
920:
884:
875:
874:
856:
847:(13): e27–e115.
832:
813:
812:
802:
778:
772:
771:
745:
736:
735:
728:
722:
721:
719:
718:
704:
698:
697:
696:
695:
672:
661:
660:
634:
621:
620:
595:
48:
26:
25:
2195:
2194:
2190:
2189:
2188:
2186:
2185:
2184:
2170:
2169:
2168:
2163:
2154:Rheumatic fever
2120:
2059:
1972:
1939:
1911:
1869:
1828:
1805:
1775:
1747:
1694:
1686:
1580:
1563:
1471:
1420:
1411:
1327:
1321:Hemopericardium
1265:
1206:
1200:Unstable angina
1173:Angina pectoris
1166:Active ischemia
1161:
1109:
1103:
1073:
1068:
1067:
1041:
1040:
995:
981:
976:
975:
928:
924:
885:
878:
833:
816:
779:
775:
769:
746:
739:
730:
729:
725:
716:
714:
706:
705:
701:
693:
691:
673:
664:
658:
635:
624:
618:
596:
587:
582:
565:vein in the leg
545:
440:
431:
418:cardiac markers
344:
332:
325:
312:
295:
271:atherosclerosis
250:
24:
21:
12:
11:
5:
2193:
2183:
2182:
2165:
2164:
2162:
2161:
2156:
2151:
2150:
2149:
2147:Cardiac asthma
2144:
2134:
2128:
2126:
2122:
2121:
2119:
2118:
2113:
2112:
2111:
2106:
2096:
2095:
2094:
2089:
2084:
2073:
2071:
2065:
2064:
2061:
2060:
2058:
2057:
2055:Strain pattern
2052:
2051:
2050:
2045:
2040:
2028:
2027:
2026:
2014:
2013:
2012:
2000:
1999:
1998:
1993:
1980:
1978:
1974:
1973:
1971:
1970:
1965:
1960:
1955:
1949:
1947:
1945:Cardiac arrest
1941:
1940:
1938:
1937:
1932:
1927:
1925:Andersen–Tawil
1921:
1919:
1913:
1912:
1910:
1909:
1904:
1899:
1894:
1889:
1879:
1877:
1871:
1870:
1868:
1867:
1862:
1861:
1860:
1850:
1845:
1843:Atrial flutter
1839:
1837:
1830:
1829:
1827:
1826:
1821:
1815:
1813:
1807:
1806:
1804:
1803:
1798:
1793:
1787:
1785:
1781:
1780:
1777:
1776:
1774:
1773:
1768:
1763:
1757:
1755:
1749:
1748:
1746:
1745:
1744:
1743:
1738:
1728:
1727:
1726:
1715:
1713:
1704:
1688:
1687:
1685:
1684:
1679:
1678:
1677:
1672:
1667:
1662:
1657:
1652:
1642:
1637:
1636:
1635:
1630:
1625:
1615:
1606:
1601:
1595:
1593:
1584:
1573:
1572:
1569:
1568:
1565:
1564:
1562:
1561:
1560:
1559:
1554:
1542:
1541:
1540:
1535:
1523:
1522:
1521:
1516:
1504:
1503:
1502:
1497:
1492:
1479:
1477:
1473:
1472:
1470:
1469:
1468:
1467:
1462:
1450:
1449:
1448:
1435:
1433:
1424:
1413:
1412:
1410:
1409:
1404:
1403:
1402:
1397:
1392:
1387:
1382:
1377:
1372:
1367:
1366:
1365:
1353:Cardiomyopathy
1350:
1349:
1348:
1346:Chagas disease
1337:
1335:
1329:
1328:
1326:
1325:
1324:
1323:
1318:
1308:
1307:
1306:
1297:
1286:
1284:
1275:
1271:
1270:
1267:
1266:
1264:
1263:
1262:
1261:
1256:
1246:
1245:
1244:
1234:
1233:
1232:
1227:
1216:
1214:
1208:
1207:
1205:
1204:
1203:
1202:
1197:
1187:
1186:
1185:
1180:
1169:
1167:
1163:
1162:
1160:
1159:
1154:
1149:
1144:
1138:
1133:
1126:
1124:
1117:
1111:
1110:
1102:
1101:
1094:
1087:
1079:
1070:
1069:
1066:
1065:
1060:article/160215
1050:
1049:
1047:
1043:
1042:
1039:
1038:
1027:
1012:
996:
991:
990:
988:
987:Classification
980:
979:External links
977:
974:
973:
922:
895:(2): 198–206.
876:
814:
773:
767:
737:
723:
699:
662:
656:
622:
616:
584:
583:
581:
578:
544:
541:
439:
436:
430:
427:
426:
425:
415:
397:
365:atrial flutter
357:Holter monitor
355:may request a
343:
340:
331:
330:Atypical AVNRT
328:
323:
311:
308:
294:
291:
255:blood pressure
249:
246:
207:coronary sinus
147:
146:
132:
126:
125:
115:
111:
110:
97:
91:
90:
81:
75:
74:
71:
65:
64:
61:
55:
54:
50:
49:
41:
40:
35:
31:
30:
22:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
2192:
2181:
2178:
2177:
2175:
2160:
2157:
2155:
2152:
2148:
2145:
2143:
2140:
2139:
2138:
2137:Heart failure
2135:
2133:
2130:
2129:
2127:
2123:
2117:
2114:
2110:
2107:
2105:
2102:
2101:
2100:
2097:
2093:
2090:
2088:
2085:
2083:
2080:
2079:
2078:
2075:
2074:
2072:
2070:
2066:
2056:
2053:
2049:
2048:ST depression
2046:
2044:
2041:
2039:
2036:
2035:
2034:
2033:
2029:
2025:
2022:
2021:
2020:
2019:
2015:
2011:
2008:
2007:
2006:
2005:
2001:
1997:
1994:
1992:
1989:
1988:
1987:
1986:
1982:
1981:
1979:
1975:
1969:
1966:
1964:
1961:
1959:
1956:
1954:
1951:
1950:
1948:
1946:
1942:
1936:
1933:
1931:
1928:
1926:
1923:
1922:
1920:
1918:
1914:
1908:
1905:
1903:
1900:
1898:
1895:
1893:
1890:
1888:
1884:
1881:
1880:
1878:
1876:
1872:
1866:
1863:
1859:
1856:
1855:
1854:
1851:
1849:
1846:
1844:
1841:
1840:
1838:
1836:
1831:
1825:
1822:
1820:
1817:
1816:
1814:
1812:
1808:
1802:
1799:
1797:
1794:
1792:
1789:
1788:
1786:
1782:
1772:
1769:
1767:
1764:
1762:
1759:
1758:
1756:
1754:
1750:
1742:
1739:
1737:
1734:
1733:
1732:
1729:
1725:
1722:
1721:
1720:
1717:
1716:
1714:
1712:
1708:
1705:
1702:
1698:
1693:
1689:
1683:
1680:
1676:
1675:Trifascicular
1673:
1671:
1668:
1666:
1663:
1661:
1658:
1656:
1653:
1651:
1648:
1647:
1646:
1643:
1641:
1638:
1634:
1631:
1629:
1626:
1624:
1621:
1620:
1619:
1616:
1614:
1610:
1607:
1605:
1602:
1600:
1597:
1596:
1594:
1592:
1588:
1585:
1583:
1578:
1574:
1558:
1557:regurgitation
1555:
1553:
1550:
1549:
1548:
1547:
1543:
1539:
1538:regurgitation
1536:
1534:
1531:
1530:
1529:
1528:
1524:
1520:
1519:regurgitation
1517:
1515:
1512:
1511:
1510:
1509:
1505:
1501:
1500:regurgitation
1498:
1496:
1493:
1491:
1488:
1487:
1486:
1485:
1481:
1480:
1478:
1474:
1466:
1463:
1461:
1458:
1457:
1456:
1455:
1451:
1447:
1444:
1443:
1442:
1441:
1437:
1436:
1434:
1432:
1428:
1425:
1423:
1418:
1414:
1408:
1405:
1401:
1398:
1396:
1393:
1391:
1388:
1386:
1383:
1381:
1378:
1376:
1373:
1371:
1368:
1364:
1361:
1360:
1359:
1356:
1355:
1354:
1351:
1347:
1344:
1343:
1342:
1339:
1338:
1336:
1334:
1330:
1322:
1319:
1317:
1314:
1313:
1312:
1309:
1305:
1301:
1298:
1296:
1293:
1292:
1291:
1288:
1287:
1285:
1283:
1279:
1276:
1272:
1260:
1257:
1255:
1252:
1251:
1250:
1247:
1243:
1240:
1239:
1238:
1235:
1231:
1228:
1226:
1223:
1222:
1221:
1218:
1217:
1215:
1213:
1209:
1201:
1198:
1196:
1193:
1192:
1191:
1188:
1184:
1183:Stable angina
1181:
1179:
1176:
1175:
1174:
1171:
1170:
1168:
1164:
1158:
1155:
1153:
1150:
1148:
1145:
1142:
1139:
1137:
1134:
1131:
1128:
1127:
1125:
1121:
1118:
1116:
1112:
1107:
1100:
1095:
1093:
1088:
1086:
1081:
1080:
1077:
1064:
1061:
1057:
1056:
1052:
1051:
1048:
1044:
1037:
1033:
1032:
1028:
1026:
1022:
1021:
1017:
1013:
1011:
1007:
1006:
1002:
998:
997:
994:
989:
985:
969:
965:
961:
957:
953:
949:
945:
941:
937:
933:
926:
918:
914:
910:
906:
902:
898:
894:
890:
883:
881:
872:
868:
864:
860:
855:
850:
846:
842:
838:
831:
829:
827:
825:
823:
821:
819:
810:
806:
801:
796:
793:(8): 831–40.
792:
788:
784:
777:
770:
764:
760:
756:
752:
744:
742:
734:. 2009-09-30.
733:
727:
713:
709:
703:
690:
686:
682:
678:
671:
669:
667:
659:
653:
649:
645:
641:
633:
631:
629:
627:
619:
613:
609:
605:
601:
594:
592:
590:
585:
577:
575:
570:
566:
562:
558:
553:
551:
540:
538:
534:
530:
529:cardioversion
526:
522:
521:heart failure
517:
515:
511:
507:
503:
499:
495:
491:
487:
486:beta blockers
483:
478:
476:
472:
471:carotid sinus
468:
464:
460:
456:
449:
444:
435:
423:
419:
416:
413:
409:
405:
401:
398:
395:
391:
388:
387:
386:
384:
380:
378:
374:
370:
366:
362:
358:
354:
350:
339:
335:
327:
321:
315:
310:Typical AVNRT
307:
299:
290:
286:
282:
280:
276:
272:
268:
264:
260:
256:
245:
243:
239:
235:
231:
227:
223:
219:
214:
213:the AV node.
212:
208:
204:
200:
196:
191:
189:
185:
184:cardioversion
181:
177:
173:
169:
168:bundle of His
165:
161:
157:
153:
145:
141:
140:beta blockers
137:
133:
131:
127:
124:
120:
116:
112:
109:
105:
101:
98:
96:
92:
89:
85:
82:
80:
76:
72:
70:
66:
62:
60:
56:
51:
47:
42:
39:
36:
32:
27:
19:
2069:Cardiomegaly
2043:ST elevation
2030:
2016:
2002:
1983:
1887:Ectopic beat
1835:fibrillation
1735:
1670:Bifascicular
1544:
1525:
1506:
1482:
1452:
1438:
1431:Endocarditis
1370:Hypertrophic
1304:Constrictive
1290:Pericarditis
1248:
1236:
1219:
1053:
1029:
1014:
999:
935:
931:
925:
892:
888:
844:
840:
790:
786:
776:
750:
726:
715:. Retrieved
711:
702:
692:, retrieved
680:
639:
599:
554:
546:
518:
479:
452:
432:
400:electrolytes
392:(TFTs) – an
381:
345:
336:
333:
316:
313:
304:
287:
283:
251:
215:
210:
192:
172:palpitations
155:
151:
150:
37:
1935:Romano–Ward
1902:Parasystole
1801:Ventricular
1753:Ventricular
1692:Tachycardia
1609:Heart block
1591:Bradycardia
1417:Endocardium
1380:Restrictive
1341:Myocarditis
1282:Pericardium
787:Circulation
459:vagus nerve
383:Blood tests
349:heart block
277:similar to
236:, and have
180:medications
134:adenosine,
34:Other names
1833:Flutter /
1796:Junctional
1731:Junctional
1724:Multifocal
1697:paroxysmal
1613:Sinoatrial
1582:arrhythmia
1577:Conduction
1333:Myocardium
717:2022-11-14
694:2019-08-15
681:StatPearls
580:References
514:amiodarone
510:flecainide
293:Mechanisms
275:chest pain
261:or rarely
234:ventricles
144:flecainide
130:Medication
63:Cardiology
2092:Pulmonary
1875:Pacemaker
1546:pulmonary
1527:tricuspid
1363:Alcoholic
1055:eMedicine
952:1092-8464
938:(5): 34.
909:0736-4679
863:1558-3597
574:pacemaker
498:diltiazem
494:verapamil
492:(such as
482:adenosine
448:adenosine
429:Treatment
412:magnesium
404:potassium
342:Diagnosis
259:dizziness
195:reentrant
119:adenosine
114:Treatment
59:Specialty
2174:Category
1958:Asystole
1858:Familial
1552:stenosis
1533:stenosis
1514:stenosis
1495:stenosis
1490:prolapse
1212:Sequelae
1115:Ischemia
1063:ped/2535
968:21354961
960:28374333
917:29239759
871:26409259
809:20733110
689:29763111
533:sedative
123:ablation
69:Symptoms
1358:Dilated
1300:Chronic
1108:(heart)
1036:D013611
550:digoxin
455:AV node
408:calcium
211:part of
2038:J wave
1791:Atrial
1719:Atrial
1508:aortic
1484:mitral
1476:Valves
1422:valves
1274:Layers
1143:(SCAD)
1025:427.89
966:
958:
950:
915:
907:
869:
861:
807:
765:
687:
654:
614:
506:asthma
353:doctor
279:angina
203:atrium
2125:Other
2109:Right
2087:Right
1701:sinus
1650:Right
1400:Viral
1295:Acute
1249:weeks
1220:hours
1132:(CAD)
1010:I47.1
964:S2CID
156:AVNRT
2104:Left
2082:Left
1699:and
1655:Left
1237:days
1031:MeSH
1020:9-CM
956:PMID
948:ISSN
913:PMID
905:ISSN
867:PMID
859:ISSN
805:PMID
763:ISBN
685:PMID
652:ISBN
612:ISBN
569:heat
559:and
525:coma
410:and
1016:ICD
1001:ICD
940:doi
897:doi
849:doi
795:doi
791:122
755:doi
644:doi
604:doi
535:or
512:or
496:or
2176::
2032:ST
2004:QT
1885:/
1633:3°
1628:2°
1623:1°
1618:AV
1611::
1302:/
1058::
1034::
1023::
1008::
1005:10
962:.
954:.
946:.
936:19
934:.
911:.
903:.
893:54
891:.
879:^
865:.
857:.
845:67
843:.
839:.
817:^
803:.
789:.
785:.
761:,
740:^
710:.
679:,
665:^
650:,
625:^
610:,
588:^
576:.
516:.
484:,
406:,
371:,
367:,
363:,
178:,
142:,
138:,
121:,
106:,
102:,
86:,
2018:T
1703:)
1695:(
1579:/
1419:/
1098:e
1091:t
1084:v
1018:-
1003:-
993:D
970:.
942::
919:.
899::
873:.
851::
811:.
797::
757::
720:.
646::
606::
324:1
154:(
20:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.