122:
225:
May and continuing to late
September-early October, and is characterized by warm summers and cold winters with heavy snow. South of the 30th parallel, the growing season is year-round in many areas with hot summers and mild winters. Cool season crops such as peas, lettuce, and spinach are planted in fall or late winter, while warm season crops such as beans and corn are planted in late winter to early spring. In the desert Southwest, the growing season effectively runs in winter, from October to April as the summer months are characterized by extreme heat and arid conditions, making it inhospitable for plants not adapted to this environment.
25:
257:. The growing seasons last six months or more, and the climate is characterized by hot summers and milder winters. Precipitation mainly falls between October and March, while summers are dry. In the extreme south of Europe, the growing season can be year-round. Vegetation on the Mediterranean islands is often evergreen because of the relatively warm winters.
204:. However, even if colder temperatures are mitigated, most crops will stop growing when the days become shorter than 10 hours, and resume after winter as the daylight increases above 10 hours. A hothouse — a greenhouse which is heated and illuminated — creates an environment where plants are fooled into thinking it is their normal growing season. Though this
224:
The continental United States ranges from 49° north at the US-Canadian border to 25° north at the southern tip of the US-Mexican border. Most populated areas of Canada are below the 55th parallel. North of the 45th parallel, the growing season is generally 4–5 months, beginning in late April or early
167:
Geographic conditions have major impacts on the growing season for any given area. Latitude is one of the major factors in the length of the growing season. The further from the equator one goes, the angle of the Sun gets lower in the sky. Consequently, sunlight is less direct and the low angle of
267:
extend north from the 45th parallel past the Arctic Circle. The growing seasons are shorter because of the lower angle of the Sun and generally range from five months to as little as three in the highlands of
Scandinavia and Russia. Climate on the Atlantic coast is considerably moderated by humid
335:
In the tropical regions, the growing season can be interrupted by periods of heavy rainfall, called the rainy season. For example, in
Colombia, where coffee is grown and can be harvested year-round, they don’t see a rainy season. However, in Indonesia, another large coffee-producing area, they
228:
Certain crops such as tomatoes and melons originated in subtropical or tropical regions. Consequently, they require hot weather and a growing season of eight months or more. In colder climate areas where they cannot be directly sowed in the ground, these plants are usually started indoors in a
324:), the growing season is limited by the availability of water, with little growth in the dry season. Unlike in cooler climates where snow or soil freezing is a generally insurmountable obstacle to plant growth, it is often possible to greatly extend the growing season in hot climates by
168:
the Sun means that soil takes longer to warm during the spring months, so the growing season begins later. The other factor is altitude, with high elevations having cooler temperatures which shortens the growing season compared with a low-lying area of the same latitude.
452:
328:
using water from cooler and/or wetter regions. This can in fact go so far as to allow year-round growth in areas that without irrigation could only support
210:
Season extension can apply to other climates, where conditions other than cold and shortened period of sunlight end the growing year (e.g. a rainy season).
268:
ocean air, which makes winters comparatively mild, and freezing weather or snow are rare. Because summers are also mild, many heat-loving plants such as
196:
time frame, or the extra time thus achieved. To extend the growing season into the colder months, one can use unheated techniques such as
121:
428:
400:
89:
61:
460:
498:
68:
488:
360:
108:
421:
The Winter
Harvest Handbook: Year-Round Vegetable Production Using Deep-Organic Techniques and Unheated Greenhouses
42:
75:
46:
284:, the extreme length of daylight during summer (17 hours or more) allows plants to put on significant growth.
137:
is that portion of the year in which local conditions (i.e. rainfall, temperature, daylight) permit normal
57:
293:
276:. Further inland, winters become considerably colder. Despite the short growing season in parts of
133:
is a division of the year marked by changes in weather, ecology, and the amount of daylight. The
35:
392:
493:
317:
301:
82:
246:
192:
is any method that allows a crop to be grown beyond its normal outdoor growing season and
138:
8:
384:
273:
254:
350:
309:
197:
434:
424:
396:
208:
a form of season extension for the grower, it is not the usual meaning of the term.
503:
389:
The Market
Gardener: A Successful Grower's Handbook for Small-Scale Organic Farming
185:
178:
260:
250:
336:
experience this rainy season and the growth of the coffee beans is interrupted.
264:
482:
438:
416:
153:, growing seasons can generally be grouped into macro-environmental classes.
277:
189:
16:
Portion of the year in which local conditions permit normal plant growth
364:
329:
325:
201:
156:
150:
229:
greenhouse and transplanted outside in late spring or early summer.
24:
238:
125:
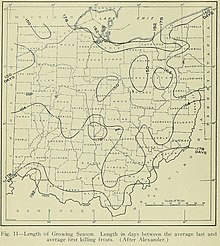
Map of average growing season length from "Geography of Ohio," 1923
193:
159:
of the Earth inherently affect growing seasons across the globe.
355:
281:
130:
345:
269:
142:
409:
242:
146:
149:
has a specific growing season that depends on its genetic
377:
49:. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.
445:
253:and the Mediterranean are in general south of the
480:
202:low tunnels, caterpillar tunnels, or hoophouses
249:effectively divide Europe into two regions.
109:Learn how and when to remove this message
120:
415:
383:
481:
287:
47:adding citations to reliable sources
18:
292:In some warm climates, such as the
171:
13:
14:
515:
361:Annual growth cycle of grapevines
219:
177:This section is an excerpt from
23:
34:needs additional citations for
1:
370:
214:
162:
7:
339:
10:
520:
176:
499:Meteorological quantities
294:tropical savanna climates
272:do not typically grow in
232:
489:Agricultural terminology
393:New Society Publishers
318:Mediterranean climates
302:hot semi-arid climates
126:
124:
395:. pp. 119–125.
385:Fortier, Jean-Martin
363:- growing season of
247:Southern Carpathians
43:improve this article
457:National Geographic
310:hot desert climates
288:Tropics and deserts
274:Northwestern Europe
198:floating row covers
351:Growing degree day
127:
430:978-1-60358-081-6
402:978-0-86571-765-7
119:
118:
111:
93:
511:
473:
472:
470:
468:
463:on June 23, 2013
459:. Archived from
453:"Growing season"
449:
443:
442:
413:
407:
406:
381:
186:Season extension
179:Season extension
172:Season extension
114:
107:
103:
100:
94:
92:
58:"Growing season"
51:
27:
19:
519:
518:
514:
513:
512:
510:
509:
508:
479:
478:
477:
476:
466:
464:
451:
450:
446:
431:
414:
410:
403:
382:
378:
373:
342:
290:
251:Southern Europe
235:
222:
217:
212:
211:
182:
174:
165:
115:
104:
98:
95:
52:
50:
40:
28:
17:
12:
11:
5:
517:
507:
506:
501:
496:
491:
475:
474:
444:
429:
417:Coleman, Eliot
408:
401:
375:
374:
372:
369:
368:
367:
358:
353:
348:
341:
338:
289:
286:
265:Central Europe
234:
231:
221:
218:
216:
213:
183:
175:
173:
170:
164:
161:
135:growing season
117:
116:
31:
29:
22:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
516:
505:
502:
500:
497:
495:
492:
490:
487:
486:
484:
462:
458:
454:
448:
440:
436:
432:
426:
422:
418:
412:
404:
398:
394:
390:
386:
380:
376:
366:
362:
359:
357:
354:
352:
349:
347:
344:
343:
337:
333:
331:
327:
323:
319:
315:
311:
307:
303:
299:
295:
285:
283:
280:and northern
279:
275:
271:
266:
262:
258:
256:
255:45th parallel
252:
248:
244:
240:
230:
226:
220:North America
209:
207:
203:
199:
195:
191:
187:
180:
169:
160:
158:
154:
152:
148:
144:
141:. While each
140:
136:
132:
123:
113:
110:
102:
91:
88:
84:
81:
77:
74:
70:
67:
63:
60: –
59:
55:
54:Find sources:
48:
44:
38:
37:
32:This article
30:
26:
21:
20:
494:Horticulture
465:. Retrieved
461:the original
456:
447:
420:
411:
388:
379:
334:
321:
313:
305:
297:
291:
259:
236:
227:
223:
205:
184:
166:
155:
139:plant growth
134:
128:
105:
96:
86:
79:
72:
65:
53:
41:Please help
36:verification
33:
278:Scandinavia
190:agriculture
483:Categories
371:References
365:grapevines
330:xerophytic
326:irrigation
194:harvesting
157:Axial tilt
151:adaptation
69:newspapers
439:262883165
316:) or the
215:Locations
163:Geography
99:July 2021
467:2 August
419:(2009).
387:(2014).
340:See also
332:plants.
261:Northern
239:Pyrenees
504:Seasons
308:), the
300:), the
83:scholar
437:
427:
399:
356:Season
282:Russia
245:, and
233:Europe
131:season
85:
78:
71:
64:
56:
346:Frost
270:maize
143:plant
90:JSTOR
76:books
469:2014
435:OCLC
425:ISBN
397:ISBN
263:and
243:Alps
237:The
147:crop
62:news
314:BWh
306:BSh
188:in
145:or
45:by
485::
455:.
433:.
423:.
391:.
322:Cs
298:Aw
241:,
206:is
200:,
129:A
471:.
441:.
405:.
320:(
312:(
304:(
296:(
181:.
112:)
106:(
101:)
97:(
87:·
80:·
73:·
66:·
39:.
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.