249:
interpret the general sea floor topography and sea-floor spreading rates. Additional surveys have been taken during 1988–1991 by multiple cruises of the OGS-Explora. These surveys consist of approximately 6300 km the regions seismicity, gravitational signatures, and additional magnetic and bathymetric surveys, significantly contributing to the understanding of the
Macquarie Triple Junction. From analysis of the data obtained from the OGS-Explora, a major change in the Pacific-Antarctic plate motion has been interpreted, instigating the compressional region of the Macquarie Ridge. High-resolution bathymetric and magnetic data were acquired by R/V Araon and M/V L’Astrolabe cruises along the axis of the two easternmost Southeast Indian Ridge segments which by 2017 had confirmed the recent existence of a Macquire microplate. In 2017 and 2019 R/V Explora and R/V Laura Bassi undertook multibeam and magnetic surveys focused on the three plate boundaries meeting at the Macquarie Triple Junction.
173:
20:
155:. Already on the Indo-Australian Plate independent rotational motion had developed in a small distal portion of what is now the Australian Plate, and this created a Macquire microplate. This resulted in the current state of the Macquarie Triple Junction and is interpreted as a ridge–fault–fault triple junction that now involves a Macquire microplate rather than the Indo-Australian Plate as was the case before 6 million years ago, Pacific Plate and Antarctic Plate.
1154:
181:
312:
is increasing evidence that the last 6.4 million years of this evolution at the triple junction has been associated with the creation of a separate microplate, the
Macquarie Plate. The assumption in models of this microplate's existence not only allows a much better fit to historic data relevant to the triple junction, it fits with more recent data for what was an understudied area at the time this triple junction's evolution was first studied.
319:, which includes the Fjord Trench, is the southern region of the boundary closest to the Macquarie Triple Junction. The Puysegur Trench formed as the Australian Plate subducted beneath the Pacific plate. The Puysegur Trench ranges approximately 800 kilometers in length, from the most southern tip of the New Zealand Islands to the Macquarie Triple Junction. The Puysegur Trench makes contact with the
215:
is the divergent boundary that separates the Indo-Australian and
Antarctic Plates. This boundary has experienced a vast right-lateral transform fault called the Balleny Fault Zone, which is also thought to be caused in response to the formation of the Emerald Fracture Zone. This large offset in the
198:
activity. The alteration of the
Pacific Plate ‘s motion caused a left-lateral strike-slip fault to form at the Pacific-Antarctic Boundary. This strike-slip fault is located near the triple junction along a sharp bend in the westernmost region of the Pacific-Antarctic Boundary. This sharp bend is now
311:
The
Australian Plate (previous to 3 million years ago the Indo-Australian Plate) and Pacific Plate boundary is the most complex boundary of the Macquarie Triple Junction region, due to the unique collision of the two plates creating two convergent boundaries separated by a transform boundary. There
107:
as well as local fractures reconstruction. The origin of the
Macquarie Triple Junction has been interpreted to have occurred 47.91 Mya (million years ago), based on Anomaly 21. Thorough reconstruction of the Macquarie Triple Junction begins at 33.3 Mya, in respect to Anomaly 13o, and can
23:
Figure 1: The present
Macquarie Triple Junction portrays the three most common oceanic tectonic boundaries. The first is Emerald Fracture Zone, a leaky transform fault, which is the region between A and A’. The second is the Southeast Indian Ridge, located just west of the MTJ and is split by the
193:
The
Emerald Fracture Zone is the westernmost portion of the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge and is a young leaky transform fault zone no older than 2.197-2.229 Ma. This zone was formed during a change in the Pacific-Antarctic Plate Boundary between 3.4 and 3.86 Ma during a transformation of the
159:
302:
located in the eastern portion of the East
Pacific Rise. These deep mantle plumes however, have given the Pacific Plate a left lateral force vector creating a transform boundary in the western Pacific-Antarctic Plate Boundary in the vicinity of the Macquarie Triple Junction, forming the Emerald
248:
The understanding of the
Macquarie Triple Junction is primarily known due to the study of the seismicity, gravitational, magnetic and bathymetric data of the region. Initial studies took place during the early 1970s by the Eltanin Cruises, which took bathymetric and magnetic tracks in order to
162:
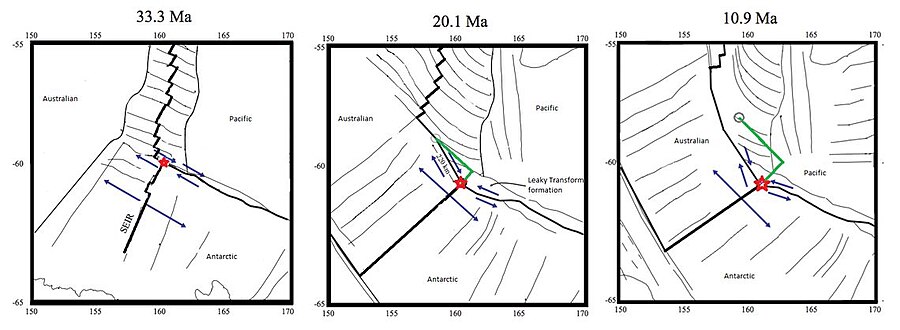
Figure 2: The evolution of the Macquarie Triple Junction has been well studied dating back to 33.3 Mya and has been reconstructed in at 20.1 Mya and 10.9 Mya. The green line shows the migration distance between intervals. The label Australian refers to the Indo-Australian Plate at the times
239:
of the Indo-Australian Plate underneath the Pacific Plate. This region of underthrusting may eventually evolve into a self-sustaining subduction zone, though the Hjort Trench is thought to be an example of an oceanic subduction zone initiated in response to transform fault development.
146:
Between 5.9 and 2.6 Mya, the Macquarie Triple Junction evolved back into a Ridge–Transform Fault–Transform Fault triple junction as the convergence at the Hjort Trench diminished and Antarctic–Pacific spreading boundary changed back into a transform fault. Elsewhere the
82:
collide and interact. The term Triple Junction is given to particular tectonic boundaries at which three separate tectonic plates meet at a specific, singular location. The Macquarie Triple Junction is located on the seafloor of the southern region of the
234:
is found in a region of diagonal convergence produced by the transform fault evolution of the Emerald Fracture Zone. Due to these transpressive plate movements this trench has frequent seismic events generally less than 20 km depth, which suggest
331:. The Alpine Fault runs through the majority of the southern island of New Zealand and is associated with New Zealand's frequent and intense earthquake history. The last major region of the Australian Plate and Pacific Plate Boundary is the
115:–transform fault triple junction. In reference to the Australian Plate, the triple junction moved southeast at an angle of 120° at an approximate rate of 40 km/million years. This trajectory remain relatively constant throughout the
130:
Then 10.9 Mya, the Macquarie Triple Junction evolved into a ridge-trench-fault triple junction due to the alteration of the Australian–Pacific Boundary motion. This oblique convergent boundary instigated a clockwise rotation of the
143:. This rotation also transpired into the Macquarie Triple Junction changing its migration path to an angle of 150° and rate of 34 km/million years in reference to the Australian Plate, making the migration direction southward.
594:
108:
be simply described as a southeastward migration of approximately 1100 km in respect to the Indo-Australian Plate. The total migration was largely driven by the Australian–Pacific transform boundary.
28:
which is represented by C. The Macquarie microplate occupies an illdefined southern region of the area labelled as the Indio-australian Plate which for the last 3 million years has been a separate
335:
at which the Pacific Plate is subducted beneath the Australian Plate, in opposition of the Puysegur Trench. This convergent boundary has a rate of subduction of approximately 5.5-7.4 cm/yr.
536:
Lodolo, E. and F. Coren (1994). "The Westernmost Pacific Antarctic plate boundary in the vicinity of the Macquarie triple junction." (In C.A. Ricci, ed. Terra Antarctica, vol.1). pp. 158–161
772:
Weissel, J. K.; Hayes, D. E.; Herron, E. M. (1977). "Plate tectonics synthesis: the displacements between Australia, New Zealand, and Antarctica since the Late Cretaceous".
216:
Southeast Indian Ridge is thought to have produced a significant difference in crustal thickness within the Australian Plate influencing the Hjort Trench formation.
236:
842:
Roger Hekinian; Peter Stoffer; Dietrich Ackerman (1999). "Ridge-hotspot Interaction: the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge and the Foundation Seamounts".
230:
The Hjort Trench is the southernmost portion of the Macquarie Ridge Complex and has been identified as an oceanic-oceanic subduction zone. This
409:
Gasperini, L; Ligi, M; Accettella, D; Bosman, A; Cuffaro, M; Lodolo, E; Martorelli, E; Muccini, F; Palmiotto, C; Polonia, A (1 February 2023).
298:, the mid-oceanic ridge located at the base of the Pacific Ocean. The PAR is divergent boundary driven by the interaction of a MOR and deep
511:
Tectonics of the Hjort region of the Macquarie Ridge Complex, southernmost Australian-Pacific Plate Boundary, southwest Pacific Ocean (PhD)
42:
270:. The Southeast Indian Ridge has a complex driving force which is due to the interaction of the Amsterdam-St. Paul Plateau, a developed
194:
Pacific-Antarctic Plate Boundary. This transformation was due to the change in the absolute motion of the Pacific Plate in response to
103:
Our understanding of the evolution of the Macquarie Triple Junction was made possible due to extensive research of the regions tectonic
938:
184:
Figure 4: New crust forms at ridges, such as Mid-Ocean-Ridges, while older crust is destroyed at subduction zones, where trenches form.
807:
Georgen, J.E., Jennifer E. (2014). "Interaction of a mantle plume and a segmented mid-ocean ridge; results from numerical modeling".
882:"Contemporary horizontal velocity and strain rate fields of the Pacific-Australian plate boundary zone through New Zealand"
262:
The Australian Plate (or Indo-Australian Plate) and Antarctic Plate Boundary is an active divergent boundary known as the
986:
1081:
119:
from 33.3 to 20.1 Mya. During this period of time the Australian-Pacific boundary underwent a transformation from
1195:
570:
1123:
1026:
327:. The Alpine Fault is the right-lateral transform fault boundary separating the Puysegur Trench and the northern
931:
332:
282:
further separating the Indo-Australian and Antarctic plates at an intermediate tectonic rate of 65 mm/yr.
1001:
360:"The kinematic evolution of the Macquarie Plate: A case study for the fragmentation of oceanic lithosphere"
176:
Figure 3: Leaky Transform Faults, such as the Emerald Fracture Zone, form at bends in transform boundaries.
1049:
1190:
1180:
1158:
1091:
1031:
1021:
1006:
968:
924:
359:
266:. The Southeast Indian Ridge ranges approximately 2000 kilometers across the southern region of the
1185:
291:
132:
733:"Anomalous Seafloor Spreading of the Southeast Indian Ridge near the Amsterdam-St. Paul Plateau"
547:
1086:
1016:
1011:
996:
263:
212:
199:
the locality of the Emerald Fracture Zone formed from a release bend configuration as seen in
1065:
641:"Underthrusting at the Hjort Trench, Australian-Pacific plate boundary: Incipient subduction"
71:
820:
463:
378:
991:
963:
893:
851:
816:
781:
744:
693:
652:
609:
548:"The January 26, 2001 Bhuj Earthquake and the Diffuse Western Boundary of the Indian Plate"
514:
459:
422:
374:
320:
8:
278:(MOR). The Amsterdam-St. Paul Plateau along with the Southeast Indian Ridge produce new
897:
855:
785:
748:
697:
656:
613:
518:
426:
485:
Marks (1997). "Early Tertiary gravity field reconstructions of the Southwest pacific".
290:
The Pacific-Antarctic Plate Boundary is another active divergent boundary known as the
195:
104:
863:
793:
706:
681:
566:
471:
295:
275:
271:
901:
859:
824:
789:
752:
711:
701:
660:
617:
558:
467:
430:
382:
172:
148:
92:
29:
730:
947:
328:
316:
140:
120:
112:
79:
1139:
828:
682:"Slab pull effects from a flexural analysis of the Tonga and Kermadec Trenches"
386:
16:
Place where the Indo-Australian Plate, Pacific Plate, and Antarctic Plate meet
1174:
636:
299:
279:
124:
84:
75:
57:
44:
841:
621:
411:"Late Miocene to recent tectonic evolution of the Macquarie Triple Junction"
19:
450:
Falconer, R. K. H. (1972). "The Indian-Antarctic-Pacific triple junction".
324:
267:
225:
200:
152:
136:
25:
850:(University of Kiel, Geologist–Paleontologist Institution, Germany): 199.
906:
881:
757:
732:
665:
640:
88:
716:
562:
435:
410:
116:
557:. Geodynamics Series. American Geophysical Union. pp. 243–254.
358:
Choi, H; Kim, SS; Dyment, J.; Granot, R; Park, SH; Hong, JK (2017).
180:
916:
158:
111:
At 33.3 Mya, the Macquarie Triple Junction was a stable ridge–
294:(PAR). The Pacific-Antarctic Ridge is the southwest region of the
679:
257:
731:
Daniel S. Scheirer; Donald W. Forsyth; James A. Conder (2000).
231:
24:
Balleny Fault Zone, identified by the letter B. And lastly the
306:
274:
in the western portion of the Southeast Indian Ridge, and the
408:
285:
91:. This tectonic boundary was named in respect to the nearby
243:
680:
Garcia-Castellanos, D.; Torné, M.; Fernàndez, M. (2000).
634:
252:
123:
to a strike-slip fault and lastly at 20.1 Mya to a
98:
39:
is a geologically active tectonic boundary located at
546:
Stein, Seth; Sella, Giovanni; Okai, Emile A. (2002).
151:
before 3 million years ago separated again from the
357:
771:
1172:
592:
639:; Symonds, P.; Bernardel, G.; Mann, P. (2003).
404:
402:
400:
398:
396:
545:
932:
806:
258:Australian Plate and Antarctic Plate boundary
95:, which is located southeast of New Zealand.
886:Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth
879:
737:Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth
393:
307:Australian Plate and Pacific Plate boundary
939:
925:
595:"Late Neogene motion of the Pacific Plate"
353:
351:
349:
347:
286:Pacific Plate and Antarctic Plate boundary
905:
875:
873:
756:
715:
705:
664:
434:
206:
724:
539:
532:
530:
528:
504:
502:
500:
498:
496:
449:
244:Studies of the Macquarie Triple Junction
188:
179:
171:
157:
18:
800:
765:
344:
139:and numerous fracture zones around the
1173:
870:
586:
508:
920:
835:
525:
493:
484:
253:Overview of relevant plate boundaries
946:
645:Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems
809:Earth and Planetary Science Letters
487:Earth and Planetary Science Letters
452:Earth and Planetary Science Letters
367:Earth and Planetary Science Letters
99:Evolution, stability, and migration
13:
167:
14:
1207:
880:Beavan, J.; Haines, John (2001).
1153:
1152:
707:10.1046/j.1365-246x.2000.00096.x
673:
602:Journal of Geophysical Research
323:, which is associated with the
219:
635:Meckel, T. A.; Coffin, M. F.;
628:
478:
443:
333:Kermadec-Tonga subduction zone
1:
864:10.1016/S0025-3227(99)00027-4
338:
1002:Fifteen-Twenty Fracture Zone
794:10.1016/0025-3227(77)90054-8
472:10.1016/0012-821X(72)90270-1
7:
593:Harbert W.; Cox A. (1989).
10:
1212:
829:10.1016/j.epsl.2014.01.035
387:10.1016/j.epsl.2017.08.035
223:
1148:
1132:
1116:
1100:
1074:
1058:
1040:
977:
954:
37:Macquarie Triple Junction
1196:Seismic zones of Oceania
821:2014E&PSL.392..113G
622:10.1029/JB094iB03p03052
513:(Thesis). p. 206.
464:1972E&PSL..17..151F
379:2017E&PSL.478..132C
292:Pacific-Antarctic Ridge
133:Macquarie Ridge Complex
264:Southeast Indian Ridge
213:Southeast Indian Ridge
207:Southeast Indian Ridge
185:
177:
164:
70:at which the historic
32:
189:Emerald Fracture Zone
183:
175:
161:
127:convergent boundary.
72:Indo-Australian Plate
22:
907:10.1029/2000JB900302
758:10.1029/1999jb900407
666:10.1029/2002GC000498
555:Plate Boundary Zones
321:Macquarie Fault Zone
1059:Trench Trench Ridge
987:Aden-Owen-Carlsberg
898:2001JGR...106..741B
856:1999MGeol.160..199H
786:1977MGeol..25..231W
749:2000JGR...105.8243S
698:2000GeoJI.141..479G
657:2003GGG.....4.1099M
614:1989JGR....94.3052H
519:2003PhDT.......206M
427:2023Geo....51..146G
54: /
1117:Ridge Trench Fault
1082:Kamchatka-Aleutian
1075:Fault Fault Trench
563:10.1029/GD030p0243
196:Louisville hotspot
186:
178:
165:
105:magnetic anomalies
58:61.500°S 161.000°E
33:
1168:
1167:
1101:Ridge Fault Fault
743:(B4): 8243–8262.
608:(B3): 3052–3064.
296:East Pacific Rise
276:mid-oceanic ridge
1203:
1191:Macquarie Island
1181:Triple junctions
1156:
1155:
948:Triple junctions
941:
934:
927:
918:
917:
912:
911:
909:
877:
868:
867:
839:
833:
832:
804:
798:
797:
780:(1–3): 231–277.
769:
763:
762:
760:
728:
722:
721:
719:
709:
677:
671:
670:
668:
632:
626:
625:
599:
590:
584:
583:
581:
579:
552:
543:
537:
534:
523:
522:
506:
491:
490:
482:
476:
475:
447:
441:
440:
438:
436:10.1130/G50556.1
406:
391:
390:
364:
355:
149:Australian Plate
93:Macquarie Island
87:, just south of
69:
68:
66:
65:
64:
63:-61.500; 161.000
59:
55:
52:
51:
50:
47:
30:Australian Plate
1211:
1210:
1206:
1205:
1204:
1202:
1201:
1200:
1186:Plate tectonics
1171:
1170:
1169:
1164:
1144:
1128:
1124:Queen Charlotte
1112:
1096:
1070:
1054:
1036:
1027:South Greenland
973:
950:
945:
915:
892:(B1): 741–770.
878:
871:
840:
836:
805:
801:
770:
766:
729:
725:
686:Geophys. J. Int
678:
674:
633:
629:
597:
591:
587:
577:
575:
573:
550:
544:
540:
535:
526:
509:Meckel (2003).
507:
494:
489:: 152: 267–274.
483:
479:
448:
444:
407:
394:
362:
356:
345:
341:
329:Kermadec Trench
317:Puysegur Trench
309:
303:Fracture Zone.
288:
260:
255:
246:
228:
222:
209:
191:
170:
168:Local tectonics
141:Macquarie Ridge
121:mid-ocean ridge
113:transform fault
101:
80:Antarctic Plate
62:
60:
56:
53:
48:
45:
43:
41:
40:
17:
12:
11:
5:
1209:
1199:
1198:
1193:
1188:
1183:
1166:
1165:
1163:
1162:
1149:
1146:
1145:
1143:
1142:
1136:
1134:
1130:
1129:
1127:
1126:
1120:
1118:
1114:
1113:
1111:
1110:
1104:
1102:
1098:
1097:
1095:
1094:
1089:
1084:
1078:
1076:
1072:
1071:
1069:
1068:
1062:
1060:
1056:
1055:
1053:
1052:
1046:
1044:
1038:
1037:
1035:
1034:
1029:
1024:
1019:
1014:
1009:
1004:
999:
994:
989:
983:
981:
975:
974:
972:
971:
966:
960:
958:
952:
951:
944:
943:
936:
929:
921:
914:
913:
869:
844:Marine Geology
834:
799:
774:Marine Geology
764:
723:
692:(2): 479–485.
672:
627:
585:
571:
538:
524:
492:
477:
458:(1): 151–158.
442:
392:
342:
340:
337:
308:
305:
287:
284:
259:
256:
254:
251:
245:
242:
237:underthrusting
224:Main article:
221:
218:
208:
205:
190:
187:
169:
166:
100:
97:
15:
9:
6:
4:
3:
2:
1208:
1197:
1194:
1192:
1189:
1187:
1184:
1182:
1179:
1178:
1176:
1161:
1160:
1151:
1150:
1147:
1141:
1138:
1137:
1135:
1131:
1125:
1122:
1121:
1119:
1115:
1109:
1106:
1105:
1103:
1099:
1093:
1090:
1088:
1085:
1083:
1080:
1079:
1077:
1073:
1067:
1064:
1063:
1061:
1057:
1051:
1048:
1047:
1045:
1043:
1039:
1033:
1030:
1028:
1025:
1023:
1020:
1018:
1015:
1013:
1010:
1008:
1005:
1003:
1000:
998:
995:
993:
990:
988:
985:
984:
982:
980:
976:
970:
967:
965:
962:
961:
959:
957:
956:Triple Trench
953:
949:
942:
937:
935:
930:
928:
923:
922:
919:
908:
903:
899:
895:
891:
887:
883:
876:
874:
865:
861:
857:
853:
849:
845:
838:
830:
826:
822:
818:
814:
810:
803:
795:
791:
787:
783:
779:
775:
768:
759:
754:
750:
746:
742:
738:
734:
727:
718:
713:
708:
703:
699:
695:
691:
687:
683:
676:
667:
662:
658:
654:
650:
646:
642:
638:
631:
623:
619:
615:
611:
607:
603:
596:
589:
574:
572:9781118670446
568:
564:
560:
556:
549:
542:
533:
531:
529:
520:
516:
512:
505:
503:
501:
499:
497:
488:
481:
473:
469:
465:
461:
457:
453:
446:
437:
432:
428:
424:
421:(2): 146–50.
420:
416:
412:
405:
403:
401:
399:
397:
388:
384:
380:
376:
372:
368:
361:
354:
352:
350:
348:
343:
336:
334:
330:
326:
322:
318:
313:
304:
301:
300:mantle plumes
297:
293:
283:
281:
280:oceanic crust
277:
273:
269:
265:
250:
241:
238:
233:
227:
217:
214:
204:
202:
197:
182:
174:
160:
156:
154:
150:
144:
142:
138:
134:
128:
126:
125:transpression
122:
118:
114:
109:
106:
96:
94:
90:
86:
85:Pacific Ocean
81:
77:
76:Pacific Plate
73:
67:
38:
31:
27:
21:
1157:
1107:
1042:Triple Fault
1041:
979:Triple Ridge
978:
955:
889:
885:
847:
843:
837:
812:
808:
802:
777:
773:
767:
740:
736:
726:
717:10261/237992
689:
685:
675:
651:(12): 1099.
648:
644:
630:
605:
601:
588:
576:. Retrieved
554:
541:
510:
486:
480:
455:
451:
445:
418:
414:
370:
366:
325:Alpine Fault
314:
310:
289:
268:Indian Ocean
261:
247:
229:
226:Hjort Trench
220:Hjort Trench
210:
201:transtension
192:
163:illustrated.
153:Indian Plate
145:
137:Hjort Trench
135:forming the
129:
110:
102:
36:
34:
26:Hjort Trench
815:: 113–120.
89:New Zealand
61: /
1175:Categories
1140:Mount Fuji
637:Mosher, S.
373:: 132–42.
339:References
1108:Macquarie
1092:Mendocino
1032:Tongareva
1022:Rodrigues
1007:Galapagos
969:Banda Sea
578:6 October
117:Oligocene
1159:Category
1133:See also
1050:Karlıova
272:hot spot
894:Bibcode
852:Bibcode
817:Bibcode
782:Bibcode
745:Bibcode
694:Bibcode
653:Bibcode
610:Bibcode
515:Bibcode
460:Bibcode
423:Bibcode
415:Geology
375:Bibcode
49:161°0′E
46:61°30′S
1017:Rivera
1012:Bouvet
997:Azores
569:
232:trench
78:, and
1087:Maraş
1066:Chile
598:(PDF)
551:(PDF)
363:(PDF)
992:Afar
964:Boso
890:106b
580:2023
567:ISBN
315:The
211:The
35:The
902:doi
860:doi
848:160
825:doi
813:392
790:doi
753:doi
741:105
712:hdl
702:doi
690:141
661:doi
618:doi
559:doi
468:doi
431:doi
383:doi
371:478
1177::
900:.
888:.
884:.
872:^
858:.
846:.
823:.
811:.
788:.
778:25
776:.
751:.
739:.
735:.
710:.
700:.
688:.
684:.
659:.
647:.
643:.
616:.
606:94
604:.
600:.
565:.
553:.
527:^
495:^
466:.
456:17
454:.
429:.
419:51
417:.
413:.
395:^
381:.
369:.
365:.
346:^
203:.
74:,
940:e
933:t
926:v
910:.
904::
896::
866:.
862::
854::
831:.
827::
819::
796:.
792::
784::
761:.
755::
747::
720:.
714::
704::
696::
669:.
663::
655::
649:4
624:.
620::
612::
582:.
561::
521:.
517::
474:.
470::
462::
439:.
433::
425::
389:.
385::
377::
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.